Deep Eutectic Solvents Extraction of Polyphenols from Tieguanyin Tea Optimized by Response Surface Method
-
摘要:
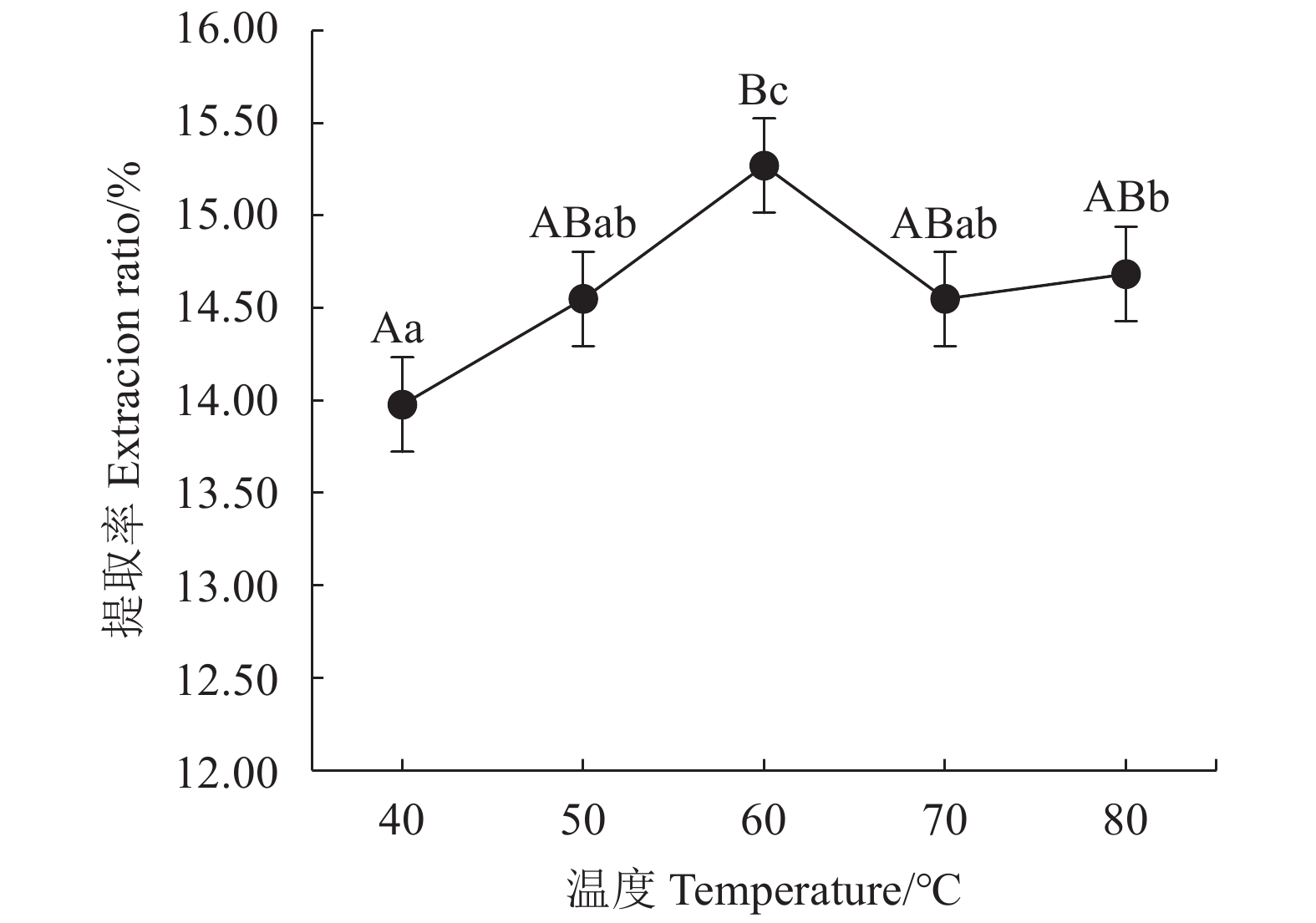
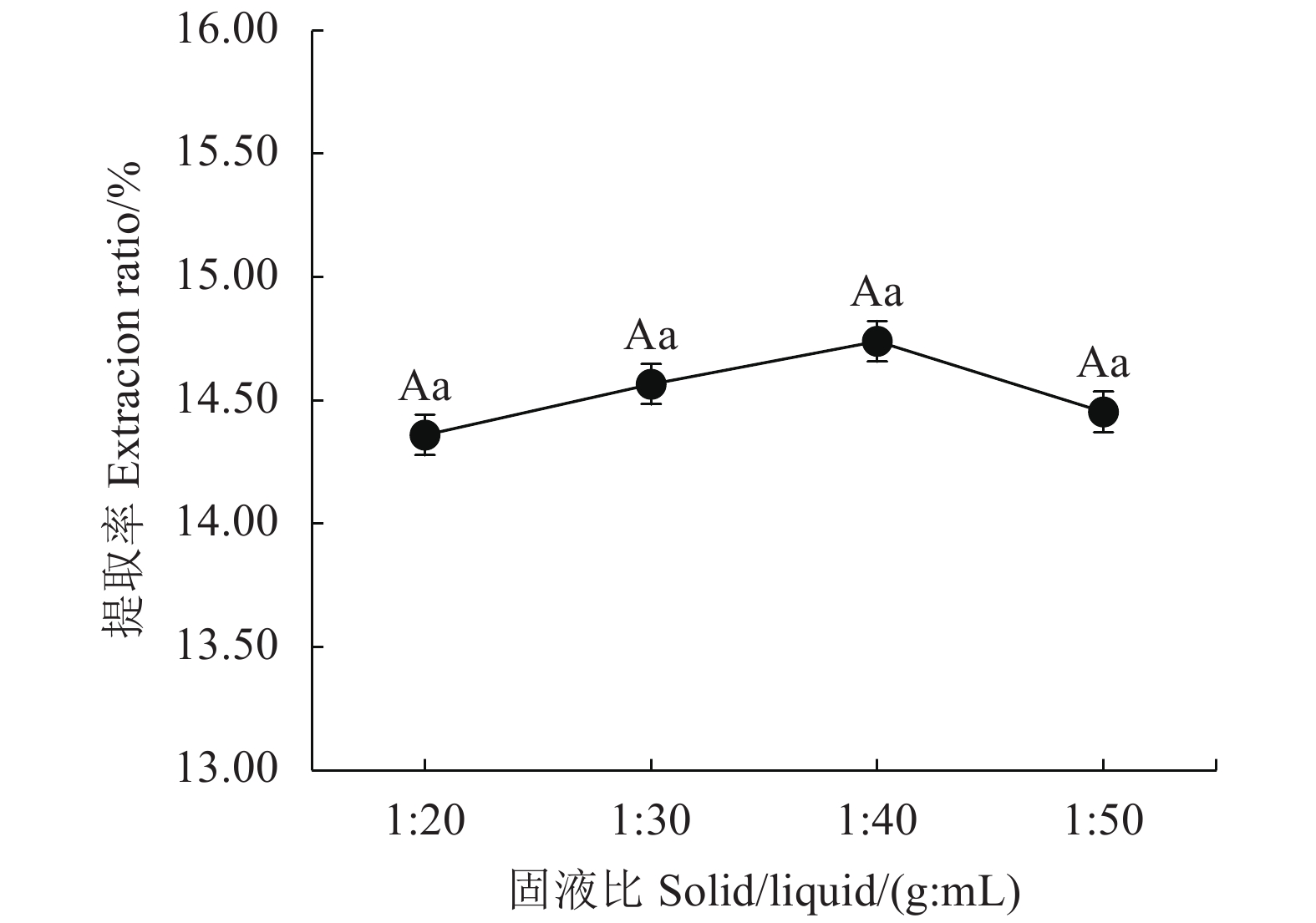
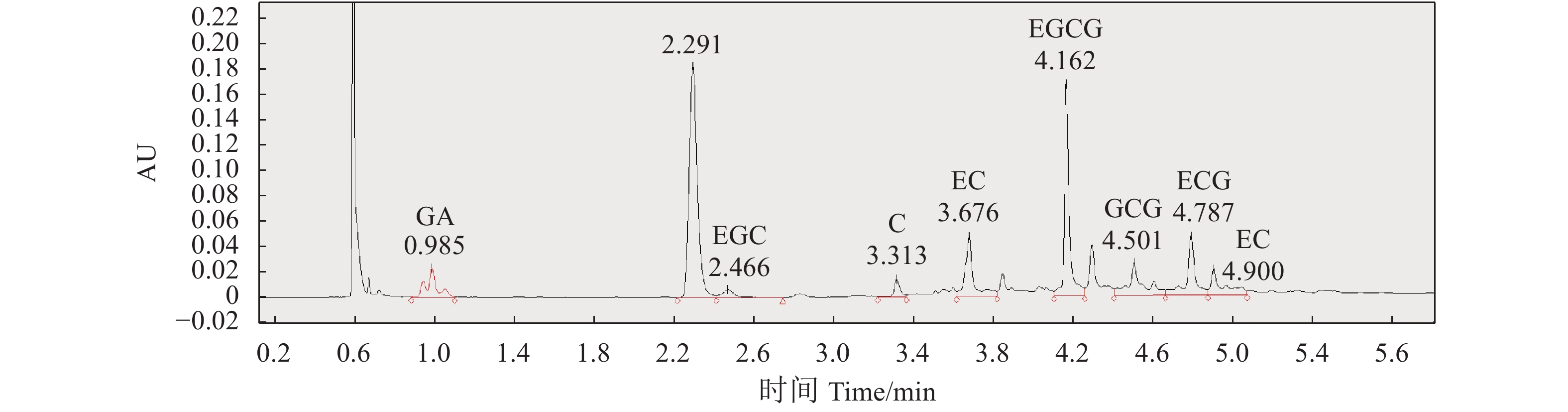
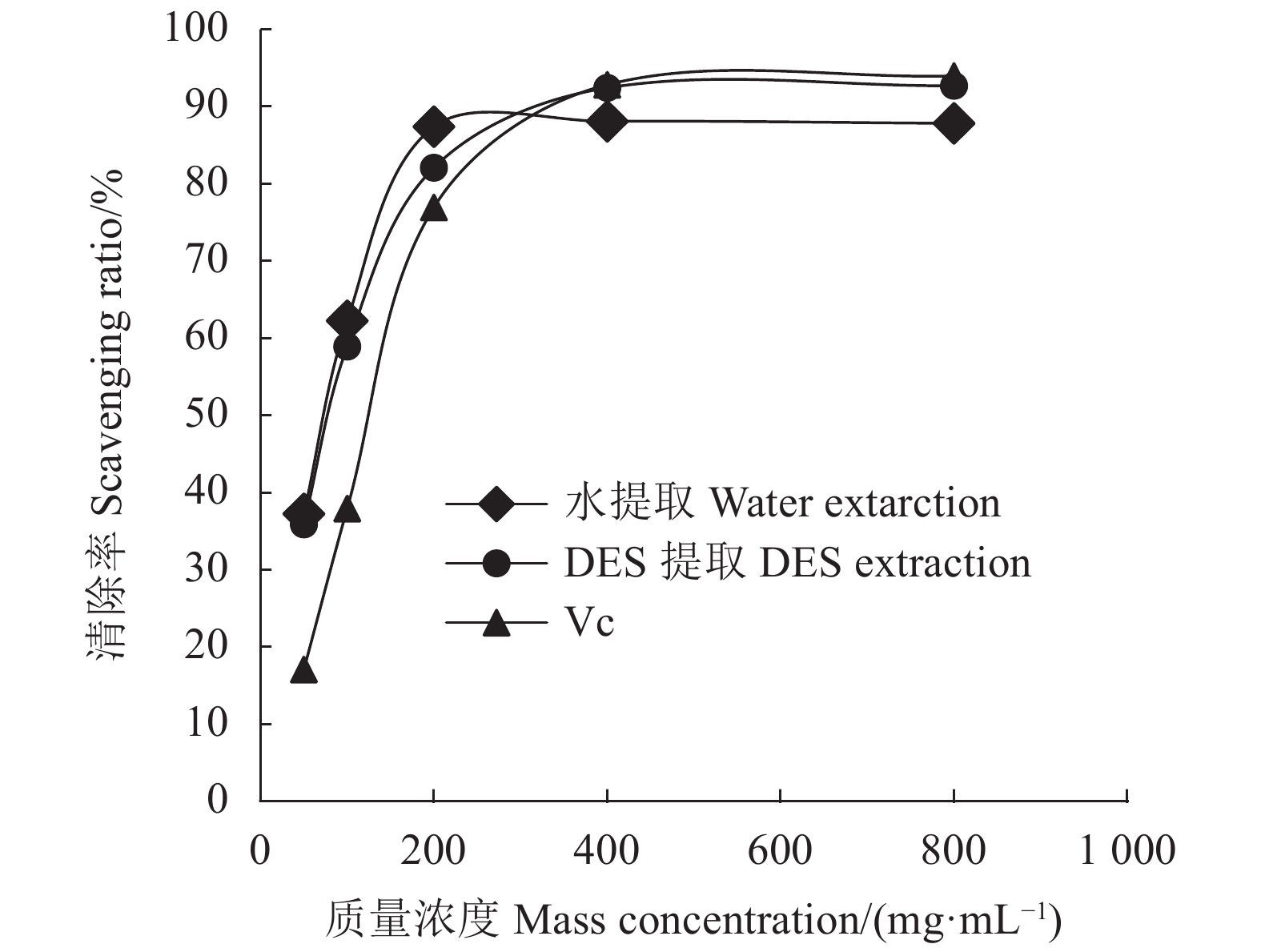
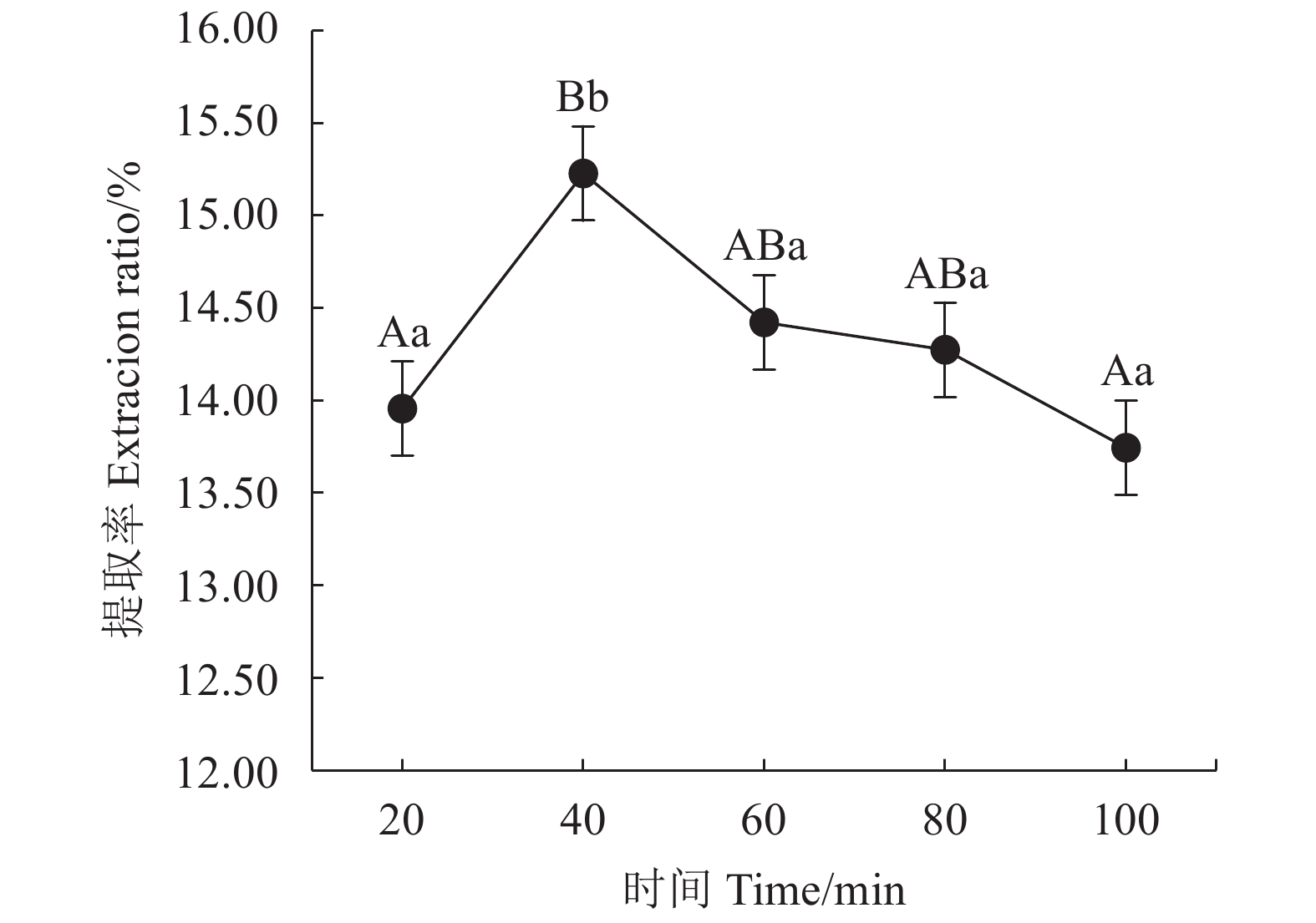
目的 探索一种绿色、环保、安全、高效的铁观音茶多酚提取新方法,为茶多酚绿色提取提供新的技术参考。 方法 以铁观音成品茶为原料,采用新型绿色溶剂——低共熔溶液提取茶多酚;首先筛选出最优的低共熔溶液提取体系,然后在单因素试验的基础上,通过响应面法优化,研究时间、温度、溶液含水率对提取率的影响,得出最佳提取条件并分析其主要成分;最后通过测定DPPH自由基清除率分析茶多酚的抗氧化能力。 结果 筛选出最适的茶多酚低共熔溶液提取体系为:乳酸-甜菜碱,其次得到最佳单因素提取条件为提取时间40 min、提取温度60℃、含水率30%、摩尔比2 ∶ 1、固液比1 ∶ 40(g : mL);响应面优化分析得到最佳提取条件为:时间46.79 min、温度62.48℃、溶液含水率32.15%,在此条件下茶多酚提取率为15.42%。通过高效液相色谱分析茶多酚组分,其中没食子酸含量占1.40%,儿茶素类物质占84.99%,其他组分占13.61%。低共熔溶液法提取的茶多酚DPPH自由基半清除浓度(IC50)值73.89 μg·mL−1,比抗坏血酸提高了37.80%。 结论 采用响应面法优化得出的低共熔溶液提取茶多酚最佳工艺条件,可有效提高铁观音茶多酚提取率。 Abstract:Objective A green, environmentally friendly, safe and efficient process to extract polyphenols from tea was explored and optimized using the response surface method. Methods Tieguanyin tea was used for the extraction with deep eutectic solvents (DESs). After the DES was selected and a single factor experiment conducted, the time, temperature and water content in solvent were optimized for the process with respect of polyphenol extraction rate by a response surface experimentation. Antioxidant capacity of the extract was determined according to the DPPH radical scavenging rate. Results Lactic acid and betaine of a molar ratio of 2:1 with a water content of 30% and a substrate-to-solvent ratio of 1:40 (g:mL) were chosen for the extraction at 60oC for 40 min. The response surface method optimized the process to apply a moisture content of 32.15% of DESs for a 46.79 min-extraction at 62.48℃ with a yield of polyphenols at 15.42%. The polyphenol extract was analyzed by HPLC to show a gallic acid content of 1.40%, catechins of 84.99%, and the remainders of 13.61%. The semi-scavenging concentration (IC50) of the extract was 73.89 μg·mL-1, which was 37.80% higher than that of ascorbic acid. Conclusion The newly developed DESs extraction significantly improved the polyphenol extraction rate from Tieguanyin tea over the conventional process. -
Key words:
- deep eutectic solvents /
- Tieguanyin /
- tea polyphenol /
- antioxidant activity /
- chemical analysis
-
表 1 Box-Behnken试验因素水平及编码
Table 1. Factors and coding levels in Box-Behnken experiment
水平
Levels因素 Factors A时间
Time/minB温度
Temperature/℃C溶液含水率
Water raito of solvent/%−1 20 50 20 0 40 60 30 1 60 70 40 表 2 不同低共熔溶液体系提取茶多酚
Table 2. DESs for polyphenol extraction
名称
Name提取率
Extraction ratio/%相对水提取提高
Aqueous extraction ratio exceeded by DES/%水 Water 8.61±0.27Aa 果糖/氯化胆碱
Fructose/Choline chloride12.47±0.74Bb 44.90 乳酸/氯化胆碱
Lacticacid/Choline chloride12.69±0.81Bb 47.36 苹果酸/甜菜碱
Malicacid/Choline chloride12.68±0.68 Bb 47.24 柠檬酸/甜菜碱
Citricacid/Betaine12.79±0.54Bb 48.59 乳酸/甜菜碱
Lacticacid/Betaine14.40±0.53 Cc 67.29 注:同列数据后不同大、小写字母表示差异极显著(P<0.01)或差异显著(P<0.05)。
Note: Different uppercase and lowercase letters in the same column indicate extremely significant differences (P<0.01) and significant differences (P<0.05).表 3 响应面优化结果
Table 3. Response surface experiment and results
序号
NumberA时间
TimeB温度
TemperatureC含水率
Water ratioY提取率
Extraction ratio/%1 0 0 0 15.46 2 −1 0 1 14.68 3 0 0 0 15.33 4 0 0 0 15.40 5 −1 0 −1 13.93 6 0 −1 −1 13.62 7 −1 −1 0 14.37 8 1 0 −1 14.63 9 0 0 0 15.27 10 1 1 0 15.07 11 1 −1 0 14.74 12 0 1 1 14.88 13 0 1 −1 14.57 14 −1 1 0 14.86 15 0 −1 1 14.76 16 0 0 0 15.39 17 1 0 1 15.01 表 4 方差分析
Table 4. Regression statistical analysis
来源
Source平方和
Sum of square自由度
Degree of freedom均方
Mean squareF值
F valueP值
P value显著性
Significance模型 Model 4.13 9 0.46 48.03 <0.000 1 ** A时间 Time 0.32 1 0.32 33.89 0.000 6 ** B温度 Temperature 0.45 1 0.45 46.7 0.000 2 ** C含水率 Water raito 0.83 1 0.83 87.03 <0.000 1 ** AB 6.40×10−3 1 6.40×10−3 0.67 0.440 2 AC 0.034 1 0.034 3.58 0.100 4 BC 0.17 1 0.17 18.01 0.003 8 ** A2 0.27 1 0.27 28.08 0.001 1 ** B2 0.54 1 0.54 56.29 0.000 1 ** C2 1.3 1 1.3 135.65 <0.000 1 ** 残差 Resdual 0.067 7 9.561×10−3 失拟项 Lack of fit 0.046 3 0.015 2.92 0.164 纯误差 Pure error 0.021 4 5.250×10−3 总和 Cor total 4.2 16 注:*,P<0.05,表示显著差异;**,P<0.01,表示极显著差异。
Note: *, P<0.05, indicating significant difference; **, P<0.01, indicating extremely significant difference. -
[1] 黄欢, 赵展恒, 王玉娇, 等. 铁观音加工过程中咖啡碱、茶多酚、游离氨基酸含量变化研究 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2014, 29(3):282−285. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2014.03.017HUANG H, ZHAO Z H, WANG Y J, et al. Study on the content change of caffeine, tea polyphenols and free amino acids in the Tie-Guanyin oolong tea machining process [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 29(3): 282−285.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2014.03.017 [2] 冯欢欢, 陈识文, 高梦祥. β-环糊精结合响应面法优化茶多酚的提取工艺 [J]. 食品科技, 2014, 39(11):212−216.FENG H H, CHEN S W, GAO M X. Optimization of the extraction process of tea polyphenols from tea dust by response surface methodology and β-CD [J]. Food Science and Technology, 2014, 39(11): 212−216.(in Chinese) [3] 陆爱霞, 姚开, 吕远平, 等. 茶多酚提取和应用研究进展 [J]. 食品科技, 2003, 28(2):53−55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2003.02.020LU A X, YAO K, Lü Y P, et al. Extraction and application of tea polyphenols [J]. Food Science and Technology, 2003, 28(2): 53−55.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2003.02.020 [4] 赵晶晶, 刘宝友, 魏福祥. 低共熔离子液体的性质及应用研究进展 [J]. 河北工业科技, 2012, 29(3):184−189. doi: 10.7535/hbgykj.2012yx0316ZHAO J J, LIU B Y, WEI F X. Property and application of eutectic ionic liquid [J]. Hebei Journal of Industrial Science and Technology, 2012, 29(3): 184−189.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7535/hbgykj.2012yx0316 [5] 杨申明, 王振吉, 王波. 白竹山云雾茶中茶多酚提取工艺研究 [J]. 食品工业, 2014, 35(8):4−8.YANG S M, WANG Z J, WANG B. Study on extraction technology of tea polyphenol from baizhu mountain tea [J]. The Food Industry, 2014, 35(8): 4−8.(in Chinese) [6] 李思睿, 董慧茹. 溶剂浮选法分离富集茶叶中茶多酚的研究 [J]. 分析科学学报, 2007, 23(5):571−574. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6144.2007.05.019LI S R, DONG H R. Study on the separation and concentration of tea polyphenols in tea by solvent sublation [J]. Journal of Analytical Science, 2007, 23(5): 571−574.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6144.2007.05.019 [7] 韦星船, 陈小宏, 王琪莹. 微波-离子沉淀法提取茶叶中茶多酚的工艺研究 [J]. 食品科技, 2007, 32(8):132−138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2007.08.037WEI X C, CHEN X H, WANG Q Y. Study on the extract technology of tea polyphenol by microwave radiation and Ion co-precipitation [J]. Food Science and Technology, 2007, 32(8): 132−138.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2007.08.037 [8] 张效林, 薛伟明, 李平, 等. 树脂吸附法分离茶多酚及咖啡碱 [J]. 化学工程, 2001, 29(3):15−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9954.2001.03.003ZHANG X L, XUE W M, LI P, et al. Adsorptive separation based on resins for tea-polyphenols and caffeine [J]. Chemical Engineering(China), 2001, 29(3): 15−19.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9954.2001.03.003 [9] PAN X J, NIU G G, LIU H Z. Microwave-assisted extraction of tea polyphenols and tea caffeine from green tea leaves [J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 2003, 42(2): 129−133. doi: 10.1016/S0255-2701(02)00037-5 [10] 张素霞. 茶多酚提取工艺的研究 [J]. 食品科技, 2010, 35(8):267−270.ZHANG S X. Study on extraction process of the tea polyphenols [J]. Food Science and Technology, 2010, 35(8): 267−270.(in Chinese) [11] 于基成, 金莉, 薄尔琳, 等. 超临界CO2萃取技术在茶多酚提取中的应用 [J]. 食品科技, 2007, 32(1):85−87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2007.01.024YU J C, JIN L, BO E L, et al. Application of supercritical fluid extraction technique on tea polyhenols [J]. Food Science and Technology, 2007, 32(1): 85−87.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2007.01.024 [12] 代忠波. 茶饮料萃取技术研究现状 [J]. 饮料工业, 2013, 16(9):39−45.DAI Z B. An overview of tea leaf extraction technologies for RTD tea beverages [J]. Beverage Industry, 2013, 16(9): 39−45.(in Chinese) [13] 张咪, 汤小芳. 乙醇/硫酸铵双水相体系萃取茶叶中茶多酚的研究 [J]. 广东化工, 2013, 40(14):26−28, 32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2013.14.013ZHANG M, TANG X F. The study of ethanol/ammonium sulfate aqueous two-phase extraction of tea polyphenols in tea [J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2013, 40(14): 26−28, 32.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2013.14.013 [14] 韦露, 樊友军. 低共熔溶剂及其应用研究进展 [J]. 化学通报, 2011, 74(4):333−339.WEI L, FAN Y J. Progress of deep eutectic solvents and their applications [J]. Chemistry, 2011, 74(4): 333−339.(in Chinese) [15] 崔琦. 沙棘叶中主要黄酮类成分的提取富集工艺研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2016.CUI Q. Study on extraction and enrichment of main flavonoids from Sea buckthorn leaves[D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2016. (in Chinese) [16] OZTURK B, PARKINSON C, GONZALEZ-MIQUEL M. Extraction of polyphenolic antioxidants from orange peel waste using deep eutectic solvents [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2018, 206: 1−13. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2018.05.052 [17] 李婷婷. 微波辅助低共熔溶剂提取黄芩中主要黄酮成分研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2014.LI T T. Study on extraction of main flavonoids from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi by microwave-assisted eutectic solvent. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2014. (in Chinese) [18] XU B J, CHANG S K C. A comparative study on phenolic profiles and antioxidant activities of legumes as affected by extraction solvents [J]. Journal of Food Science, 2007, 72(2): S159−S166. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2006.00260.x [19] 李堆淑. 复合酶提取绿茶茶多酚工艺及其抑菌性 [J]. 广西林业科学, 2019, 48(2):229−234. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1126.2019.02.017LI D S. Compound enzyme extraction of green tea polyphenols and its bacteriostasis [J]. Guangxi Forestry Science, 2019, 48(2): 229−234.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1126.2019.02.017 [20] 李加兴, 陈选, 邓佳琴, 等. 黄秋葵黄酮的提取工艺和体外抗氧化活性研究 [J]. 食品科学, 2014, 35(10):121−125. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201410022LI J X, CHEN X, DENG J Q, et al. Extraction and antioxidant activity in vitro of okra flavonoids [J]. Food Science, 2014, 35(10): 121−125.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201410022 [21] BI W T, TIAN M L, ROW K H. Evaluation of alcohol-based deep eutectic solvent in extraction and determination of flavonoids with response surface methodology optimization [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2013, 1285: 22−30. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2013.02.041 [22] 洪姗. 儿茶素分子定向修饰及其抗氧化构效关系研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2015.HONG S. Development of specific modification methods for catechins and structure and antioxidant activity relationship investigation[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2015. (in Chinese) [23] 韦献雅, 殷丽琴, 钟成, 等. DPPH法评价抗氧化活性研究进展 [J]. 食品科学, 2014, 35(9):317−322. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201409062WEI X Y, YIN L Q, ZHONG C, et al. Advances in the DPPH radical scavenging assay for antioxidant activity evaluation [J]. Food Science, 2014, 35(9): 317−322.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201409062 -







 下载:
下载: