Seasonal Changes on and Environmental Factors Affecting Bacterial Community at Zuohai Lake in Fuzhou
-
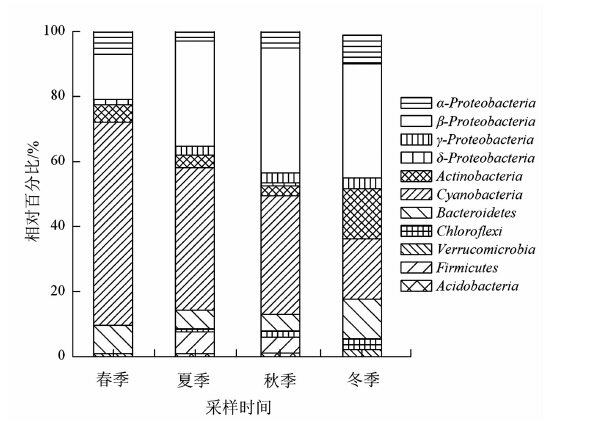
摘要: 为揭示福州左海湖细菌群落的季节变化及其与环境因子的关系,通过构建16S rRNA基因克隆文库对全湖水体细菌群落进行了调查,应用典范对应分析(Canonical correspondence analysis,CCA)探讨影响细菌群落季节性变化的环境因素。结果表明:左海湖细菌群落组成中β-变形菌门β-Proteobacteria和蓝细菌门Cyanobacteria为优势类群,α-变形菌门α-Proteobacteria、拟杆菌门Bacteroidetes和放线菌门Actinobacteria为亚优势类群。细菌群落结构具有明显的季节性变化特征,春、夏季Cyanobacteria为优势类群,秋、冬季β-Proteobacteria为优势类群。春季水体细菌群落结构主要受pH、叶绿素a(Chla)、透明度(SD)和总氮(TN)的影响,夏季水体受pH、Chla、SD、总磷(TP)影响较大,秋季水体受TP、Chla、TN影响较大,冬季水体则受水温(WT)、pH、SD影响较大。本研究发现,左海湖细菌群落结构的季节动态与水温及营养状况密切相关。
-
关键词:
- 左海湖 /
- 细菌群落 /
- 16S rRNA基因克隆文库 /
- 季节变化 /
- 典范对应分析
Abstract: To determine the seasonal changes on and the environmental factors that affected the bacterial community at Zuohai Lake in Fuzhou, a survey was conducted at 4 sampling sites on the lake from February to August in 2012. A genetic library of their 16S rRNA gene clones was established. Canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) was used to examine the correlation between the bacterial diversity and the environmental factors. The results indicated that β-Proteobacteria and Cyanobacteria were the predominate lineages in the water, followed by α-Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes, and Actinobacteria. A significant seasonal variation in composition of the bacterial community was detected. Among various categories of bacteria,Cyanobacteria appeared most dominant in the spring and summer; while β-Proteobacteria, in the autumn and winter. The results of CCA showed that the bacterial community in the water was mainly affected by pH, chlorophyll a (Chla), transparency (SD), and total nitrogen (TN) in the spring; pH, Chla, SD, and total phosphate(TP), in the summer; TP, Chla, and TN in the fall; and, water temperature, pH, and SD, in the winter. Thus, in general, the bacterial growth in the lake closely related to the temperature as well as the nutrients available in the water. -
表 1 左海湖水体理化指标
Table 1. Physio-chemical properties of water at Zuohai Lake
春季 夏季 秋季 冬季 S1 S2 S3 S4 S1 S2 S3 S4 S1 S2 S3 S4 S1 S2 S3 S4 经度(E) 26°5.91′N 26°5.89′N 26°5.83′N 26°5.88′N 26°5.91′N 26°5.89′N 26°5.83′N 26°5.88′N 26°5.91′N 26°5.89′N 26°5.83′N 26°5.88′N 26°5.91′N 26°5.89′N 26°5.83′N 26°5.88′N 纬度(N) 119°17.18′E 119°17.01′E 119°16.95′E 119°16.91′E 119°17.18′E 119°17.01′E 119°16.95′E 119°16.91′E 119°17.18′E 119°17.01′E 119°16.95′E 119°16.91′E 119°17.18′E 119°17.01′E 119°16.95′E 119°16.91′E pH 7.6±0.0 7.5±0.1 7.7±0.0 7.6±0.0 7.4±0.0 7.2±0.0 7.1±0.1 7.1±0.1 7.2±0.1 7.2±0.1 7.1±0.1 7.2±0.1 7.9±0.0 7.6±0.0 7.7±0.0 7.6±0.0 WT/℃ 25.0±0.3 25.1±0.1 25.0±0.2 25.1±0.1 32.1±0.5 32.2±0.5 31.9±0.1 32.0±0.5 23.1±0.1 24.0±0.1 23.7±0.1 23.9±0.1 12.8±0.2 13.0±0.2 13.0±0.1 13.1±0.2 SD/cm 40±2 36±1 40±2 32±1 48±1 33±1 33±1 37±1 20±3 25±1 24±2 25±1 34±1 39±2 42±1 39±1 COD/(mg·L-1) 8.81±0.17 10.51±0.44 8.67±0.15 8.14±0.15 8.75±0.17 10.44±0.14 8.75±0.11 8.08±0.13 8.10±0.15 9.55±0.01 8.09±0.13 7.63±0.09 8.69±0.16 10.37±0.23 8.56±0.42 8.02±0.32 TN/(mg·L-1) 0.41±0.03 0.45±0.02 0.55±0.02 0.39±0.06 1.00±0.03 0.91±0.04 1.28±0.07 0.98±0.04 0.87±0.07 1.06±0.07 0.92±0.03 0.55±0.08 0.42±0.04 0.54±0.05 0.42±0.08 0.63±0.02 TP/(mg·L-1) 0.037±0.004 0.036±0.001 0.043±0.005 0.034±0.001 0.052±0.001 0.039±0.000 0.049±0.005 0.036±0.004 0.036±0.004 0.031±0.007 0.027±0.002 0.036±0.003 0.023±0.001 0.028±0.005 0.024±0.002 0.038±0.002 Chla/(mg·L-1) 0.041±0.002 0.041±0.008 0.037±0.002 0.028±0.000 0.031±0.008 0.030±0.002 0.035±0.003 0.012±0.001 0.037±0.005 0.042±0.008 0.048±0.000 0.017±0.004 0.029±0.001 0.024±0.006 0.031±0.008 0.012±0.000 注:①S1~S4代表左海湖4个不同的采样站位;②表格中的数值代表平均值±标准差(3组平行试验的标准差)。 表 2 左海湖细菌16S rRNA基因克隆文库分析结果
Table 2. 16S rRNA gene clone library on bacteria from Zuohai Lake
样品 克隆子/个 OTUs /个 Coverage/% H′ 1/D Evenness (E) 春季 115 34 79.1 2.85±0.08 11.4±0.01 0.56±0.02 夏季 105 46 69.5 3.30±0.06 15.6±0.00 0.60±0.01 秋季 101 43 74.3 3.29±0.06 16.7±0.00 0.61±0.01 冬季 91 46 71.4 3.52±0.05 23.2±0.00 0.64±0.01 -
[1] SUN J G, JIANG R B, REN T Z, et al. Prospect for farm land and water pollution and microorganism repair in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2008, 29(1):41-47. [2] LIU H X, SONG X Y, HUANG L M, et al. Progress in the mechanism of modulation on marine bacterial production[J]. Ecological Science, 2008, 27(1):61-64. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2371132172&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [3] YANNARELL A C, KENT A D, LAUSTER G H, et al. Temporal patterns in bacterial communities in three temperate lakes of different trophic status[J]. Microb Ecol, 2003, 46:391-405. doi: 10.1007/s00248-003-1008-9 [4] WU L, GE G, ZHU G F, et al. Diversity and composition of the bacterial community of Poyang Lake (China) as determined by 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis[J]. World J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2012, 28:233-244. doi: 10.1007/s11274-011-0812-5 [5] LIU Z, HUANG S, SUN G, et al. Phylogenetic diversity, composition and distribution of bacterioplankton community in the Dongjiang River, China[J]. FEMS Microbiol Ecol, 2012, 80(1):30-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2011.01268.x [6] CHEN Z B, ZHOU Z Y, PENG X, et al. Effects of wet and dry seasons on the aquatic bacterial community structure of the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. World J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2013, 29(5):841-853. doi: 10.1007/s11274-012-1239-3 [7] ZHANG R, WU Q, PICENO Y M, et al. Diversity of bacterioplankton in contrasting Tibetan lakes revealed by high-density microarray and clone library analysis[J]. FEMS Microbiol Ecol, 2013, 86(2):277-287. doi: 10.1111/fem.2013.86.issue-2 [8] ADAMS H E, CRUMP B C, KLING G W. Temperature controls on aquatic bacterial production and community dynamics in arctic lakes and streams[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2010, 12(5):1319-1333. doi: 10.1111/emi.2010.12.issue-5 [9] TAMAKI H, SEKIGUCHI Y, HANADA S, et al. Comparative analysis of bacteria diversity in freshwater sediment of a shallow eutrophic lake by molecular and improved cultivation-based techniques[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2005, 71:2162-2169. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.4.2162-2169.2005 [10] 杨彩根, 宋学宏, 孙丙耀. 浮游植物叶绿素a含量简易测定方法的比较[J]. 海洋科学, 2007, 31(1):6-9. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYKX200701001.htm [11] 王心芳, 魏复盛, 齐文启. 水和废水监测分析方法.[M]. 第4版. 北京:中国环境科学出版社, 2002:216-219. [12] WU Q L, ZWART G, SCHAUER M, et al. Bacterioplankton community composition along a salinity gradient of sixteen high-mountain lakes located on the Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2006, 72(8):5478-5485. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00767-06 [13] MWIRICHIA R, COUSIN S, MUIGAI A W, et al. Bacterial Diversity in the Haloalkaline Lake Elmenteita, Kenya[J]. Curr Microbiol, 2011, 62:209-221. doi: 10.1007/s00284-010-9692-4 [14] 白蓝, 赵明文, 贾军伟, 等. 16S rDNA克隆文库法探索转基因香石竹对土壤细菌群落的影响[J]. 微生物学通报, 2012, 39(4):435-447. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSWT201204000.htm [15] 张继强, 陈文业, 康建军,等. 敦煌西湖盐化草甸芦苇群落特征及多样性沿水分梯度的分布格局[J]. 水土保持通报, 2013, 33(2):173-176. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STTB201302039.htm [16] 邱小琮, 赵红雪. 宁夏沙湖浮游植物群落结构及多样性研究[J]. 水生态学杂志, 2011, 32(1):20-26. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCAN201101005.htm [17] LIU X, LU X, CHEN Y. The effects of temperature and nutrient ratios on Microcystis blooms in Lake Taihu, China:An 11-year investigation[J]. Harmful Algae, 2011, 10(3):337-343. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2010.12.002 [18] MARIA J, MORA R, SCRANTON M I, et al. Bacterial community composition in a large marine anoxic basin:a Cariaco Basin time-series survey[J]. FEMS Microbiol Ecol, 2013, 84:625-639. doi: 10.1111/femsec.2013.84.issue-3 [19] 张胜男, 赵吉睿, 张晓军, 等. 乌梁素海浮游细菌群落结构及其对富营养化因子的响应[J]. 微生物学通报,2014, 41(6):1082-1093. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSWT201406008.htm [20] 钟晶晶, 刘茂松, 王玉, 等. 太湖流域河流与湖泊间主要水质指标的空间关联特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 2014, 33(8):2176-2182. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201408028.htm [21] TER BRAAK C J F. Canonical correspondence analysis:A new eigenvector technique for multivariate direct gradient analysis[J]. Ecology, 1986, 67(5):1167-1179. doi: 10.2307/1938672 [22] 李玉华, 许其功, 赵越, 等. 松花湖水体中不同空间分布的细菌群落结构分析[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2013, 32(4):764-770. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201304017.htm [23] 王晓丹, 翟振华, 赵爽, 等. 北京翠湖表流和潜流湿地对细菌多样性的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2009, 30(1):280-288. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ200901050.htm [24] POLLET T, TADONLÉKÉ R D, HUMBERT J F. Spatiotemporal changes in the structure and composition of a less-abundant bacterial phylum (Planctomycetes) in two perialpine lakes[J]. Applied and environmental microbiology, 2011, 77(14):4811-4821. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02697-10 [25] DU J, XIAO K, LI L, et al. Temporal and Spatial Diversity of Bacterial Communities in Coastal Waters of the South China Sea[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(6):e66968. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066968 [26] WANG J J, ZHANG Y, LI Z G, et al. Higher seasonal variation of actinobacterial communities than spatial heterogeneity in the surface sediments of Taihu Lake, China[J]. Can J Microbiol, 2013, 59(5):353-358. doi: 10.1139/cjm-2012-0663 [27] 孙寓姣, 程陈, 丁爱中, 等. 官厅水库水质特征及水体微生物多样性的响应[J]. 中国环境科学, 2015, 35(5):1547-1553. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ201505049.htm [28] 朱文昌, 陆敏, 石浚哲. 梅梁湖水体浮游植物与环境因子的关系[J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 2010, 22(3):27-30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJS201003009.htm [29] 杨丽标, 韩小勇, 孙璞, 等. 巢湖藻类组成与环境因子典范对应分析[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2011, 30(5):952-958. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201105025.htm [30] 冯胜, 李定龙, 秦伯强. 太湖水华过程中微生物群落的动态变化[J]. 宁波大学学报:理工版, 2010, 23(1):7-12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NBDZ201001003.htm -







 下载:
下载:


