Vertical Nutrient Distribution and Texture of Sandy Soil Added with Soft Rocks
-
摘要:
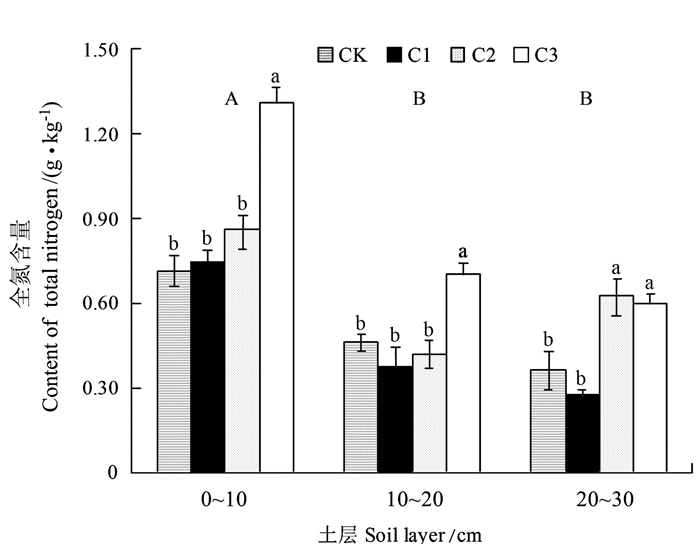
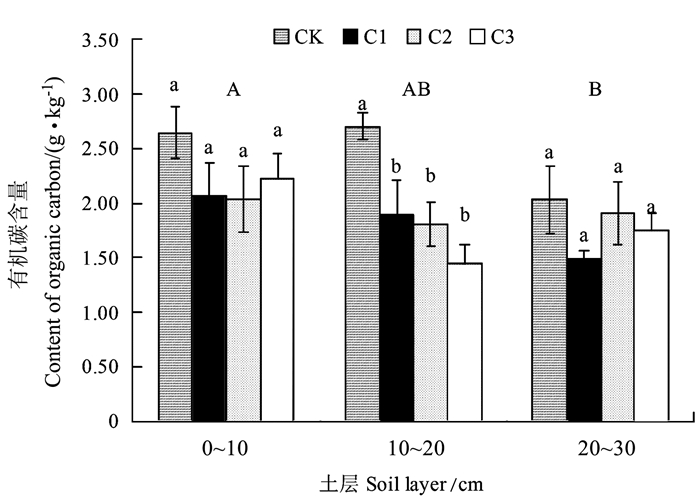
目的 研究不同比例砒砂岩添加对风沙土(沙)中碳氮比垂直分布规律的影响,为沙荒地改良以及复配土体地力的提升提供科学依据。 方法 以位于陕西富平的砒砂岩与沙复配比小区为研究对象,选择砒砂岩与沙体积比分别为0:1(CK)、1:5(C1)、1:2(C2)和1:1(C3)的4个处理,分析复配土碳氮比(C/N)及其与土壤养分和质地的关系。 结果 不同处理下土壤有机碳和全氮含量随着土层深度的增加而降低,有机碳平均值为1.45~2.70 g·kg-1且0~10 cm土层有机碳含量显著高于20~30 cm土层(P < 0.05);复配比单因素对有机碳产生显著影响,随着砒砂岩体积分数的增加,0~10 cm土层有机碳含量以C3处理最高。全氮平均值为0.28~1.31 g·kg-1,且0~10 cm土层全氮含量显著高于10~20 cm和20~30 cm土层,在0~10 cm土层中,C3处理的全氮含量显著高于其他处理,复配比和土层双因素对全氮均产生显著影响。C/N平均值为1.72~5.92,以0~10 cm最低,其值随着砒砂岩体积分数的增加而依次减小,以C3处理最为显著。硝态氮和铵态氮含量在各处理间的变化规律较为一致,平均值分别为33.56~197.00、5.51~70.02 mg·kg-1,以0~10 cm土层含量最高。砂粒含量随着土层的加深而逐渐增加,粉粒和黏粒则随着土层的加深而减少,随着砒砂岩体积分数的增加,土壤质地由砂土变为壤砂土再变为砂壤土。C/N与硝态氮和铵态氮均呈显著负相关关系,与土壤质地的颗粒组成也有一定的相关性,10~20 cm土层最为显著。 结论 砒砂岩与沙复配比为1:1时可以促进0~10 cm表层土壤碳氮的积累,增强微生物的分解作用。 Abstract:Objective Effect of adding soft rocks to aeolian sandy soil in varied ratios on the vertical distributions of carbon (C), nitrogen (N), and texture of the soil was studied for improving fertility of the wasteland. Method At Fuping, Shaanxi, soft rocks were blended to the local sandy soil in different ratios, i.e., 0:1 (CK), 1:5 (C1), 1:2 (C2), and 1:1 (C3) by volume to determine the C/N ratio and texture of soil in different depths. Result The organic C and total N contents decreased with depth upon the additions. The average C content ranged from 1.45 g·kg-1 to 2.70 g·kg-1, and it was significantly higher in the 0-10 cm layer than 20-30 cm layer (P < 0.05). The mixing ratio had a significant effect on C, as the soft rocks increased (i.e., C3) so was C content in the top layer. The total N ranged 0.28-1.31 g·kg-1, and that in the 0-10 cm layer significantly higher than in the deeper soils. In the top layer, C3 rendered significantly more N than other treatments. The average C/N ranged 1.72-5.92 with the lowest in the 0-10 cm layer and a decline upon increased addition of soft rocks. The varied mixing ratios did not affect the nitrate N and ammonium N contents, which ranged 33.56-197.00 mg·kg-1 and 5.51-70.02 mg·kg-1, respectively, with the top layer being the highest. Sand content in the soil gradually increased with depth, while silt and clay particles decreased. Along with the addition of soft rocks the soil texture changed from sand to loamy sand, and to sandy loam. There was a significant inversed correlation between C/N and nitrate N and ammonium N, and a correlation with the particle size distribution in soil. The correlations were most significant in the 10-20 cm soil layer. Conclusion The blending ratio of soft rocks and sand at 1:1 seemed to promote the C and N accumulation in the 0-10 cm layer of soil. It also enhanced the microbial degradation in the soil. -
Key words:
- mixed soil /
- carbon to nitrogen ratio /
- soil nutrient /
- texture /
- soft rocks
-
图 1 砒砂岩与沙不同复配比处理下土壤有机碳的垂直分布特征
注:图中不同小写字母表示同一土层下不同复配比例间有显著差异(5%),大写字母表示所有处理的平均值在3个土层间存在显著差异(5%),图 2、3同。
Figure 1. Vertical distribution of organic C in soil of varied mixing ratios of soft rocks and sand
Note:Different lowercase letters in the figure indicate the significant difference (5%) between different compounding ratios in the same soil layer, while uppercase letters indicate the significant difference (5%) between the average values of all treatments in three soil layers, The same as Fig. 2, 3.
表 1 各测定指标在双因素影响下的方差分析
Table 1. Variance analysis on specific indicator under two factors
指标
Index影响因素
Influencing factor平方和
Quadratic sum自由度
Free degree均方
Mean squareF值
F valueP值
P value有机碳Organic carbon 复配比 2.5994 3 0.8665 3.919 0.0207 土层 1.2635 2 0.6317 2.857 0.077 复配比×土层 1.1151 6 0.1859 0.841 0.5511 全氮Total nitrogen 复配比 0.9265 3 0.3088 34.221 0.0001 土层 1.3922 2 0.6961 77.128 0.0001 复配比×土层 0.2679 6 0.0446 4.947 0.002 碳氮比C/N 复配比 43.0899 3 14.3633 14.006 0.0001 土层 19.8871 2 9.9435 9.696 0.0008 复配比×土层 7.1677 6 1.1946 1.165 0.3573 表 2 砒砂岩与沙不同复配比处理下土壤有效磷、速效钾、硝态氮和铵态氮的垂直分布特征
Table 2. Vertical distribution of available phosphorus, available potassium, nitrate N and ammonium N in soil of varied mixing ratios of soft rocks and sand
土层
Soil layer/cm处理
Treatment有效磷
Available phosphorus(AP)
/(mg·kg-1)速效钾
Available potassium(AK)
/(mg·kg-1)硝态氮
Nitrate nitrogen (NO3--N)
/(mg·kg-1)铵态氮
Ammonium nitrogen(NH4+-N)
/(mg·kg-1)0~10 CK 20.76±1.94b 40.95±1.27c 48.61±1.19c 10.98±2.04c C1 29.29±2.50a 63.93±1.88ab 57.54±2.35c 16.00±1.86bc C2 10.77±1.01c 50.85±0.89c 83.59±4.34b 20.81±1.65b C3 19.48±2.15b 72.95±1.72a 197.00±6.66a 70.02±2.31a 10~20 CK 11.01±1.67b 45.01±1.11c 33.56±1.76c 5.51±1.05c C1 22.54±2.29a 73.30±1.79b 53.58±3.03bc 10.52±1.86c C2 8.15±1.82b 95.05±2.15a 70.07±3.72b 17.51±2.04b C3 9.57±2.17b 74.89±2.38b 130.45±7.59a 31.15±1.85a 20~30 CK 14.57±1.94a 41.65±1.86c 32.53±1.72c 5.80±0.66c C1 9.08±1.79b 51.38±1.32ab 42.86±3.14c 12.13±1.51c C2 15.92±2.81a 64.64±2.44a 63.55±3.85ab 18.13±2.17b C3 5.41±1.26c 40.24±1.01c 81.81±4.87a 31.87±2.31a 注:数据后同列不同小写字母表示同一土层不同处理之间差异显著(P<0.05)。表 3-4同。
Note:The different lowercase letters in the same column under each soil layer indicate significant differences (P<0.05).The same as Table 3-4.表 3 砒砂岩与沙不同复配比处理下土壤质地的垂直分布特征
Table 3. Vertical distribution on texture of soil in varied mixing ratios of soft rocks and sand
土层
Soil layer/cm处理
Treatment砂粒
Sand /%粉粒
Silt/%黏粒
Clay /%质地
Texture0~10 CK 89.87±3.96a 7.68±1.48c 2.45±0.65c 砂土 C1 76.59±4.05b 18.44±1.39b 4.97±0.85b 壤砂土 C2 58.85±3.28c 33.13±2.05a 8.02±0.78a 壤砂土 C3 64.2±4.81c 28.62±2.48a 7.18±1.12ab 砂壤土 10~20 CK 93.14±4.01a 6.06±1.61b 0.80±0.04c 砂土 C1 82.56±2.85ab 14.24±1.54ab 3.20±0.69bc 壤砂土 C2 65.33±5.89ab 27.39±2.81ab 7.27±1.56ab 砂壤土 C3 53.31±3.96b 37.01±2.24a 9.68±1.55a 砂壤土 20~30 CK 99.07±4.16a 0.83±0.09b 0.10±0.02b 砂土 C1 81.08±4.12ab 15.48±1.01a 3.43±0.25ab 壤砂土 C2 74.19±3.11b 20.07±1.58a 5.75±1.55a 壤砂土 C3 77.46±4.18ab 16.97±1.25a 5.57±1.15a 砂壤土 表 4 砒砂岩与沙不同复配比处理下土壤碳氮比与养分元素及质地的相关性
Table 4. Correlations among C/N, nutrients, and texture of soil in varied mixing ratios of soft rocks and sand
土层
Soil layer./cm有效磷
AP/
(mg·kg-1)速效钾
AK/
(mg·kg-1)硝态氮
NO3--N/
(mg·kg-1)铵态氮
NH4+-N /
(mg·kg-1)有机碳
SOC/
(g·kg-1)全氮
TN/
(g·kg-1)砂粒
Sand
/%粉粒
Silt
/%黏粒
Clay
/%0~10 0.2625 -0.8456 -0.9045 * -0.8820 0.6176 -0.8849 * 0.8565 -0.8441 -0.8654 10~20 0.1393 -0.4412 -0.9999 ** -0.9997 ** 0.8653 -0.8513 0.9488 * -0.9498 * -0.9269 * 20~30 0.2007 -0.2883 -0.9438 * -0.8652 -0.1182 -0.9687 ** 0.7639 -0.7211 -0.8726 注:*表示P<0.05水平差异显著,**表示P<0.01水平差异极显著。
Note:* indicates significant at P<0.05 level, and ** indicates extremely significant at P<0.01 level. -
[1] 陈涛, 常庆瑞, 刘钊, 等.耕地土壤有机质与全氮空间变异性对粒度的响应研究[J].农业机械学报, 2013, 44(10):122-129. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2013.10.020CHEN T, CHANG Q R, LIU Z, et al. Response of soil organic matter and total nitrogen spatial variability to grain size in cultivated land[J]. Journal of Agricultural Machinery, 2013, 44(10):122-129.(in Chinese) doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2013.10.020 [2] 郭振, 李娟.砒砂岩与沙复配土体的固碳机制研究进展[J].农技服务, 2019, 36(1):109-110. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/njfw201901046GUO Z, LI J. Advances in carbon sequestration mechanism of soft rock and sand complex soils[J]. Agricultural Technology Services, 2019, 36(1):109-110.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/njfw201901046 [3] 刘骞, 曾文津, 赵宇, 等.城市不同功能分区草坪绿地土壤有机碳与碱解氮垂直分布特征[J].四川林业科技, 2019, 40(1):25-29. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sclykj201901005LIU Q, ZENG W J, ZHAO Y, et al. Vertical distribution characteristics of soil organic carbon and alkali nitrogen in turf greenland with different functional areas in cities[J]. Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology, 2019, 40(1):25-29.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sclykj201901005 [4] 高焕平, 刘世亮, 赵颖, 等.秸秆与氮肥调节C/N比对潮土CH4、CO2和N2O排放/吸收的影响[J].土壤通报, 2019(1):157-164. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-TRTB201901024.htmGAO H P, LIU S L, ZHAO Y, et al. Effects of C/N ratio of straw and nitrogen fertilizer on CH4, CO2 and N2O emission/absorption in fluvo-aquic soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2019(1):157-164.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-TRTB201901024.htm [5] 王小利, 周志刚, 郭振, 等.长期施肥下黄壤稻田土壤有机碳和全氮的演变特征[J].江苏农业科学, 2017, 45(14):195-199. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsnykx201714053WANG X L, ZHOU Z G, GUO Z, et al. Evolution characteristics of soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in yellow paddy soil under long-term fertilization[J]. Journal of Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(14):195-199.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsnykx201714053 [6] HYVONEN R, PERSSON T, ANDERSSON S, et al. Impact of long-term nitrogen addition on carbon stocks in trees and soils in northern Europe[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2008, 89(1):121-137. doi: 10.1007/s10533-007-9121-3 [7] 张乐, 孙向阳, 李素艳, 等.辽宁仙人洞典型林分森林土壤碳氮分布特征[J].吉林农业大学学报, 2017, 39(2):183-188. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jlnydxxb201702009ZHANG L, SUN X Y, LI S Y, et al. Characteristics of Carbon and Nitrogen Distribution across Typical Forest Types in Xianrendong Nature reserve of Liaoning Province[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2017, 39(2):183-188.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jlnydxxb201702009 [8] 赵业婷, 常庆瑞, 李志鹏, 等. 1983-2009年西安市郊区耕地土壤有机质空间特征与变化[J].农业工程学报, 2013, 29(2):132-140. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nygcxb201302019ZHAO Y T, CHANG Q R, LI Z P, et al. Spatial characteristics and changes of soil organic matter in cultivated land in the suburbs of Xi'an from 1983 to 2009[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering, 2013, 29(2):132-140.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nygcxb201302019 [9] WANG Y Q, ZHANG X C, HUANG C Q. Spatial variability of soil total nitrogen and soil total phosphorus under different land uses in a small watershed on the loess plateau, China[J]. Geoderma, 2009, 150(1-2):141-149. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.01.021 [10] ZHANG X Y, SUI Y Y, ZHANG X D, et al. Spatial variability of nutrient properties in black soil of Northeast China[J]. Pedosphere, 2007, 17(1):19-29. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0160(07)60003-4 [11] 韩霁昌, 刘彦随, 罗林涛.毛乌素沙地砒砂岩与沙快速复配成土核心技术研究[J].中国土地科学, 2012, 26(8):87-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8158.2012.08.014HAN J C, LIU Y S, LUO L T. Study on the core technology of rapidly compounding soft rock and sand in Wusu Sandy Land[J]. China Land Science, 2012, 26(8):87-94.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8158.2012.08.014 [12] 李娟, 吴林川, 李玲.砒砂岩与沙复配土的水土保持效应研究[J].西部大开发(土地开发工程研究), 2018, 3(6):35-40. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=0120181106322177LI J, WU L C, LI L. Study on soil and water conservation effect of soft rock and sand compound soil[J]. Western Development (Land Development Engineering Research), 2018, 3(6):35-40.(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=0120181106322177 [13] 张露, 韩霁昌.砒砂岩与沙不同重构比例对表层土体储水量的影响[J].西部大开发(土地开发工程研究), 2016(4):50-53, 74. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBTG201604009.htmZHANG L, HAN J C. Influence of different remodeling ratios of soft rock and sand on water storage in surface soil[J]. Western Development (Land Development Engineering Research), 2016(4):50-53, 74.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBTG201604009.htm [14] 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].北京:中国农业出版社, 2008.BAO S D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis[M]. Beijing:China Agriculture Press, 2008.(in Chinese) [15] HOOK P B, Burke I C. Biogeochemistry in a shortgrass landscape:control by topography, soil texture, and microclimate[J]. Ecology, 2000, 81(10):2686-2703. doi: 10.1890/0012-9658(2000)081[2686:BIASLC]2.0.CO;2 [16] 郭航, 韩霁昌, 张扬, 等.基于拉曼光谱研究砒砂岩与沙复配土的胶结作用力[J].激光与光电子学进展, 2017, 54(11):436-442. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jgygdzxjz201711056GUO H, HAN J C, ZHANG Y, et al. Study on the bonding force of soft rock and sand compound soil based on Raman spectroscopy[J]. Advances in Laser and Optoelectronics, 2017, 54(11):436-442.(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jgygdzxjz201711056 [17] 肖焊, 黄志刚, 武海涛, 等.三江平原4种典型湿地土壤碳氮分布差异和微生物特征[J].应用生态学报, 2014, 25(10):2847-2854. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yystxb201410012XIAO H, HUANG Z G, WU H T, et al. Distribution of carbon and nitrogen in soils and microbial characteristics of four typical wetlands in Sanjiang Plain[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2014, 25(10):2847-2854.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yystxb201410012 -







 下载:
下载: