Physiological Response of Chinese Fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) Seedlings Under Acid and/or Aluminum Stresses
-
摘要:
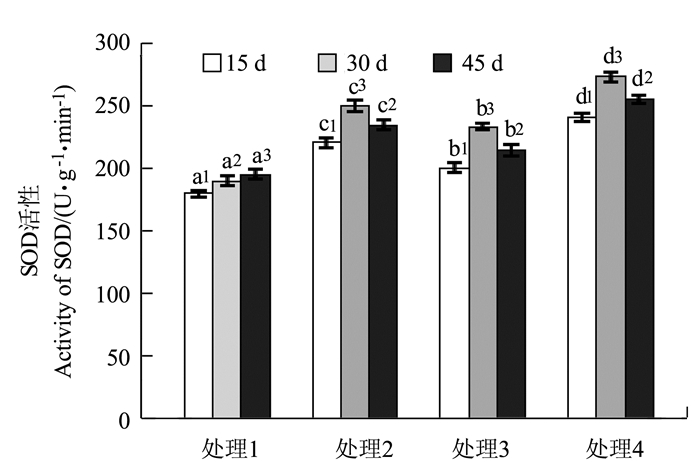
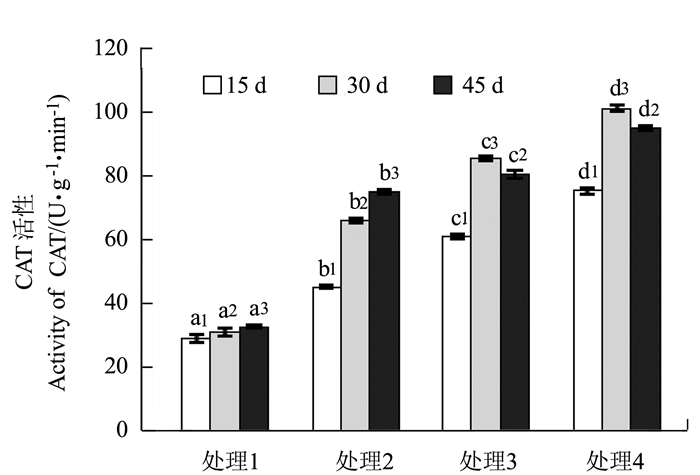
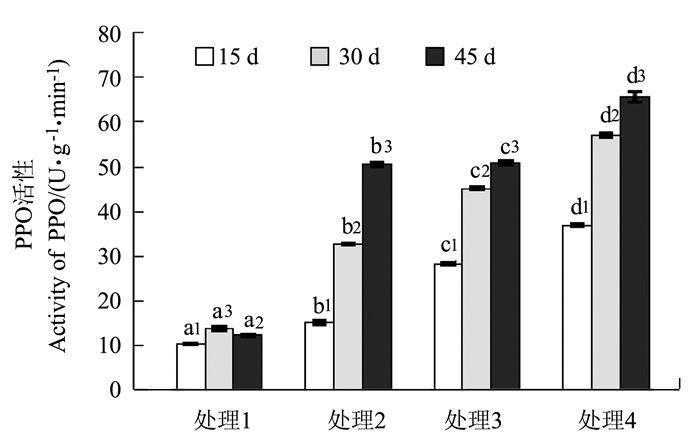
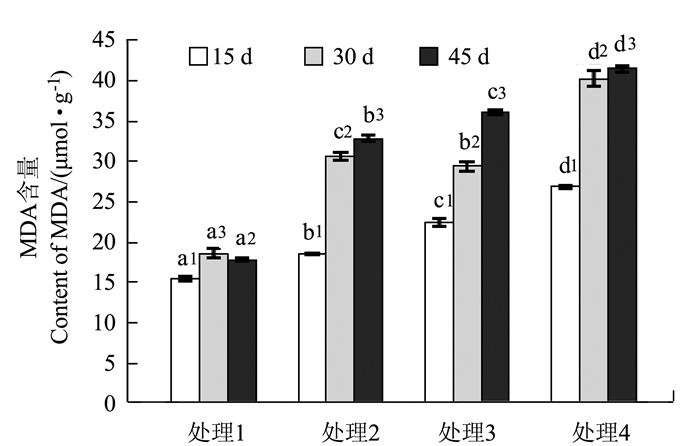
目的 为了探究杉木在酸铝胁迫下抗氧化酶活性的变化规律及其作用机理,以此为基础探索逆境胁迫下杉木的抗性机制。 方法 通过土培盆栽试验,以1年生杉木实生苗为试验对象,采用0.24 g·kg-1的AlCl3·6H2O模拟铝胁迫、pH 4.0的酸液模拟酸胁迫以及两者共施模拟酸铝复合胁迫,测定幼苗叶片不同胁迫时间(15、30和45 d)的MDA含量和SOD、POD、CAT、PPO等酶活性。 结果 无酸无铝状态下,MDA含量均处于低水平状态,单酸、单铝和酸铝处理皆引发MDA的过量积累,且影响程度是酸铝复合胁迫>铝胁迫>酸胁迫。在单酸、单铝和酸铝处理下,发现POD和SOD酶活性的增长幅度是酸铝复合胁迫>酸胁迫>铝胁迫;CAT和PPO酶活性的增长幅度则是酸铝复合胁迫>铝胁迫>酸胁迫。随着胁迫时间延长,POD、SOD活性均先增后减;CAT活性在铝胁迫和酸铝复合胁迫下先增后减,酸胁迫下逐渐增加;PPO活性则均逐渐增加。 结论 单酸、单铝和酸铝处理对POD、SOD、CAT和PPO活性均产生不同程度的诱导,但同时引发MDA的积累。酸铝复合胁迫对抗氧化酶活性具有一定的协同效应,酸胁迫对POD和SOD活性的促进作用大于铝胁迫,对于CAT和PPO活性,铝胁迫的促进作用则大于酸胁迫。 Abstract:Objective The antioxidant enzyme activities and respond mechanism of Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) under acid and/or aluminum stresses were investigated. Method A pot experiment was conducted to determine the MDA content and SOD, POD, CAT, and PPO activities in one-year-old leaves of Chinese fir seedlings under the stress for 15, 30 or 45 d. At the rate of 0.24 g·kg-1, AlCl3 6H2O was applied to the pots to simulate an aluminum stress, a pH 4.0 acid solution added to simulate an acid stress, and the combination of the two incorporated to simulate an acid-aluminum stress. Result Without the presence of acid or aluminum, the potted seedlings had a low content of MDA in the leaves. However, the addition of acid, aluminum or acid-aluminum combination induced excessive accumulation of MDA with the severities ranking as acid-aluminum stress > aluminum stress > acid stress. The addition also raised the POD and SOD activities in leaves with a rank of acid-aluminum stress > acid stress > aluminum stress, and the CAT and PPO activities in the order of acid-aluminum stress > aluminum stress > acid stress. A prolonged treatment caused an initial increase on the POD and SOD activities followed by a decline; and on the CAT activity similarly under the aluminum or acid-aluminum stress but a steady increase under the acid stress; whereas, a gradual increase on the PPO activity under any of the 3 treatments. Conclusion The acid, aluminum or acid-aluminum stress affected the POD, SOD, CAT and PPO activities in the leaves to varying extents and raised MDA accumulation in the leaves of Chinese fir seedlings. There appeared to be a synergistic effect on the activities between acid and aluminum. But alone, the acid stress exerted a greater effect on POD and SOD than did aluminum, whereas, aluminum seemed to be a more formidable adversary than acid for the seedlings on CAT and PPO. -
Key words:
- Chinese fir /
- acid-aluminum stress /
- oxidase activity /
- MDA
-
图 1 酸铝胁迫下幼苗MDA含量的变化
注:小写字母表示同一时间不同处理间的差异显著性,数字表示同一处理不同时间间的差异显著性(P < 0.05),图 2~5同。
Figure 1. Changes on MDA content in seedlings under acid-aluminum stress
Note:Lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in the same period, the numbers indicate the significant difference between different periods of the same treatment (P < 0.05).The same as Fig. 2-5.
表 1 试验处理
Table 1. Experimental design
编号
NumbersAl含量
Al content/(g·kg-1)pH值
pH value处理1Treatment 1 0.00 6.8(dH2O) 处理3Treatment 3 0.24 6.8(dH2O) 处理2Treatment 2 0.00 4.00 处理4Treatment 4 0.24 4.00 注:表中的Al表示的是AlCl3·6H2O的重量;dH2O为蒸馏水。
Note:Al in the table indicates the weight of AlCl3·6H2O; dH2O is distilled water.表 2 不同土层土壤的物理性质
Table 2. Physical properties of soil in different ground layers
土层
Soil layer/cm土壤容重
Bulk density/(g·cm-1)毛管孔隙
Capillary pore/%最大持水量
Maximum water-holding capacity/(g·kg-1)最小持水量
Minimum water-holding capacity/(g·kg-1)毛管持水量
Capillary moisture capacity/(g·kg-1)0~20 0.913 42.07 586.07 372.32 503.17 20~40 0.944 39.78 567.47 381.23 532.36 40~60 0.952 38.96 558.72 383.46 556.07 表 3 不同土层土壤的养分含量
Table 3. Nutrient contents of soil in different ground layers
土层
Soil layer/cm有机质
Organic matter/(g·kg-1)全氮
Total N/(g·kg-1)全磷
Total P /(g·kg-1)水解氮
Hydrolytic N /(g·kg-1)速效磷
Available P /(g·kg-1)0~20 4.12 0.284 0.257 21.87 26.73 20~40 2.28 0.207 0.197 18.72 19.79 40~60 1.76 0.167 0.169 13.16 14.37 -
[1] KOCHIAN L V, HOEKENGA O A, PIÑEROS M A. How do crop plants tolerate acid soils? Mechanisms of aluminum tolerance and phosphorous efficiency[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2004, 55(1):459-493. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.55.031903.141655 [2] GUPTA N, GAURAV S S, KUMAR A. Molecular Basis of Aluminium Toxicity in Plants:A Review[J]. American Journal of Plant Sciences, 2013, 4(12C):21-37. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=0aca10f7aab37092e5645d1108de9585&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [3] WRIGHT R J, BALIGAR V C, RITCHEY K D, et al. Influence of soil solution aluminum on root elongation of wheat seedlings[J]. Plant & Soil, 1989, 113(2):294-298. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=58488a1714414324171d2b61bf150b6d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [4] 曹林, 马丽, 吴玉环, 等.菊芋对酸铝复合胁迫的生理响应[J].生态环境学报, 2016, 25(2):233-240. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tryhj201602008CAO L, MA L, WU Y H, et al. Physiological Responses of Helianthus tuberosus to Acid-aluminum Stress[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2016, 25(2):233-240.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tryhj201602008 [5] BOSE J, BABOURINA O, MA Y, et al. Specificity of Ion Uptake and Homeostasis Maintenance During Acid and Aluminium Stresses[M]//Aluminum Stress Adaptation in Plants. Springer International Publishing, 2015: 269-77. [6] 李朝苏, 刘鹏, 蔡妙珍, 等.荞麦对酸铝胁迫生理响应的研究[J].水土保持学报, 2005, 19(3):105-109. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2005.03.026LI C S, LIU P, CAI M Z, et al. Physiological Response of Buckwheat to Acid-Aluminum Stress in Growth[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2005, 19(3):105-109.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2005.03.026 [7] 王维君, 陈家坊, 何群.酸性土壤交换性铝形态的研究[J].科学通报, 1991, 36(6):460-463. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/281709WANG W J, CHEN J F, HE Q. Study on Exchangeable Aluminum Species in Acidic Soils[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1991, 36(6):460-463.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/281709 [8] 阮少宁, 林婷, 王成伟, 等.铝胁迫对不同杉木无性系质膜透性的影响[J].安徽农学通报, 2008, 14(19):145-146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7731.2008.19.069RUAN S N, LIN T, WANG C W, et al. Effects of Aluminum Stress on Plasma Membrane Permeability of Different Chinese Fir Clones[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2008, 14(19):145-146.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7731.2008.19.069 [9] 许小丽, 崔朋辉, 林思祖, 等.铝胁迫下杉木幼苗体内几种矿质元素含量变化及其相关性[J].福建农业学报, 2015, 30(12):1178-1183. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2015.12.009XU X L, CUI P H, LIN S Z, et al. Changes and Correlations of Minerals in Seedlings of Chinese Fir Under Aluminum Stress[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 30(12):1178-1183.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2015.12.009 [10] 许小丽, 崔朋辉, 林思祖, 等.不同供铝水平对杉木幼苗生长的影响[J].广东农业科学, 2016, 43(7):45-50. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gdnykx201607008XU X L, CUI P H, LIN S Z, et al. Effects of different levels of aluminum on growth of Chinese fir seedlings[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 43(7):45-50.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gdnykx201607008 [11] 李树斌, 翁闲, 王士亚, 等.铝胁迫及营养复合作用对杉木幼苗抗氧化酶活性的影响[J].福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 44(3):264-269. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fjnydxxb201503008LI S B, WENG X, WANG S Y, et al. Combined effects of aluminum and nutrient on the antioxidant enzymes of Chinese fir seedlings[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University(Natural Science Edition), 2015, 44(3):264-269.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fjnydxxb201503008 [12] MA Z, HUANG B, XU S, et al. Ion Flux in Roots of Chinese Fir[Cunninghamia lanceolata (Lamb.) Hook] under Aluminum Stress[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(6):1-14. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2ee9fdb38f8f3524254f4fd099da7da3&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [13] 谢寅峰, 杨万红, 杨阳, 等.外源一氧化氮对模拟酸雨胁迫下箬竹(Indocalamus barbatus)光合特性的影响[J].生态学报, 2007, 27(12):5193-5201. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.12.029XIE Y F, YANG W H, YANG Y, et al. Effects of exogenous nitric oxide on photosynthetic characteristic of Indocalamus barbatus under a simulated acid rain stress condition[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2007, 27(12):5193-5201.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.12.029 [14] 李会云, 郭修武.盐胁迫对葡萄砧木叶片保护酶活性和丙二醛含量的影响[J].果树学报, 2008, 25(2):240-243. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gskx200802019LI H Y, GUO X W. Influence of NaCl on activities of protective enzymes and MDA content in grape rootstock leaves[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2008, 25(2):240-243.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gskx200802019 [15] 苏涛, 司美茹, 王仁君, 等.酸雨与重金属复合胁迫对绞股蓝抗性生理指标的影响[J].山东农业科学, 2014(8):61-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4942.2014.08.016SU T, SI M R, WANG R J, et al. Effects of Combined Stress of Acid Rain and Heavy Metals on Resistant Physiological Indexes of Gynostemma pentaphyllum[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2014(8):61-65.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4942.2014.08.016 [16] 张宇婷, 高建民, 张琼琳, 等.植物超氧化物歧化酶的研究进展[J].畜牧与饲料科学, 2016, 37(9):28-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5190.2016.09.009ZHANG Y T, GAO J M, ZHANG Q L, et al. Research Progress on Plant Superoxide Dismutase[J]. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2016, 37(9):28-31.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5190.2016.09.009 [17] 于姣妲, 李莹, 殷丹阳, 等.杉木对低磷胁迫的响应和生理适应机制[J].林业科学研究, 2017, 30(4):566-575. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykxyj201704005YU J D, LI Y, YIN D Y, et al. Response and Physiological Mechanism of Chinese Fir to Low Phosphorus Stress[J]. Forest Research, 2017, 30(4):566-575.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykxyj201704005 [18] 陈佳华, 李霞, 郑剑英, 等.低温下不同处理对甘薯生理指标和酚类代谢的影响[J].食品科技, 2018, 43(10):50-54. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=spkj201810008CHEN J H, LI X, ZHENG J Y, et al. Effects of different treatments on the physiological indexes and phenolic metabolism of sweet potato under low temperature[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2018, 43(10):50-54.(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=spkj201810008 [19] 刘强, 柳正葳, 龙婉婉, 等.芒萁、玉米对酸铝胁迫生理响应的比较[J].江苏农业科学, 2017, 45(2):65-69. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsnykx201702017LIU Q, LIU Z W, LONG W W, et al. Comparative effects of low pH value and aluminum toxicity on physiological responses between Dicranopteris dichotoma and Zea mays[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(2):65-69.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsnykx201702017 [20] 吴若菁, 庄捷, 黄婧, 等.马尾松幼苗对模拟酸雨与铝胁迫的响应及其抗性机制[J].林业科学, 2009, 45(12):22-29. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykx200912004WU R J, ZHUANG J, HUANG J, et al. Responses and Resistance Mechanism of Pinus massoniana under the Stresses of Simulated Acid Rain and Aluminum[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2009, 45(12):22-29.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykx200912004 [21] 魏国余, 刘云.酸铝对不同速生桉无性系叶片抗氧化酶活性的影响[J].北华大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 16(3):379-384. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bhdxxb201503024WEI G Y, LIU Y. Effects of Acid-Aluminum on the Activities of Antioxidant Enzymes in the Leaves of Different Fast-growing Eucalyptus Clone[J]. Journal of Beihua University(Natural Science), 2015, 16(3):379-384.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bhdxxb201503024 -







 下载:
下载: