Extraction and Composition of Polyphenols from Purple Cowpeas
-
摘要:
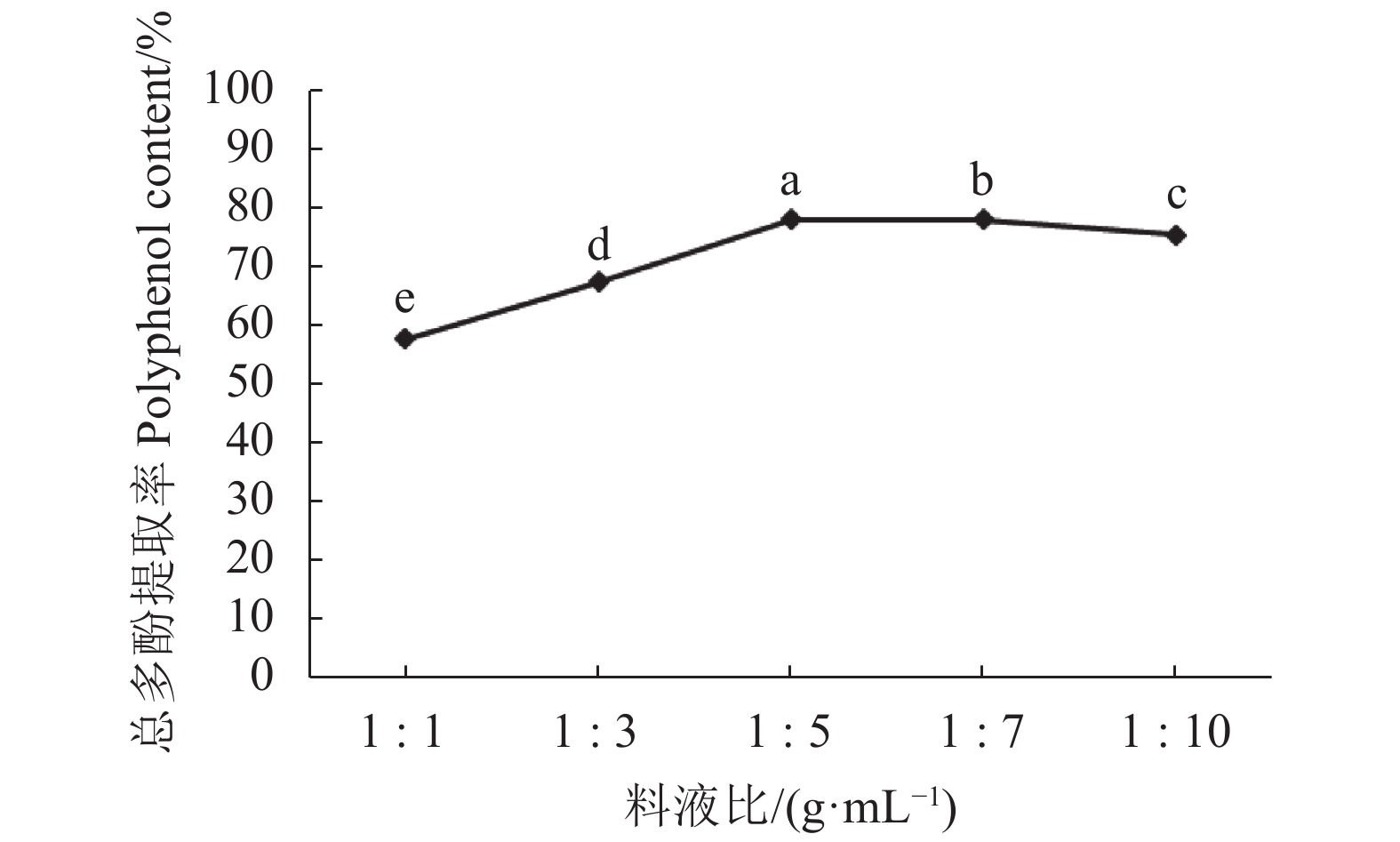
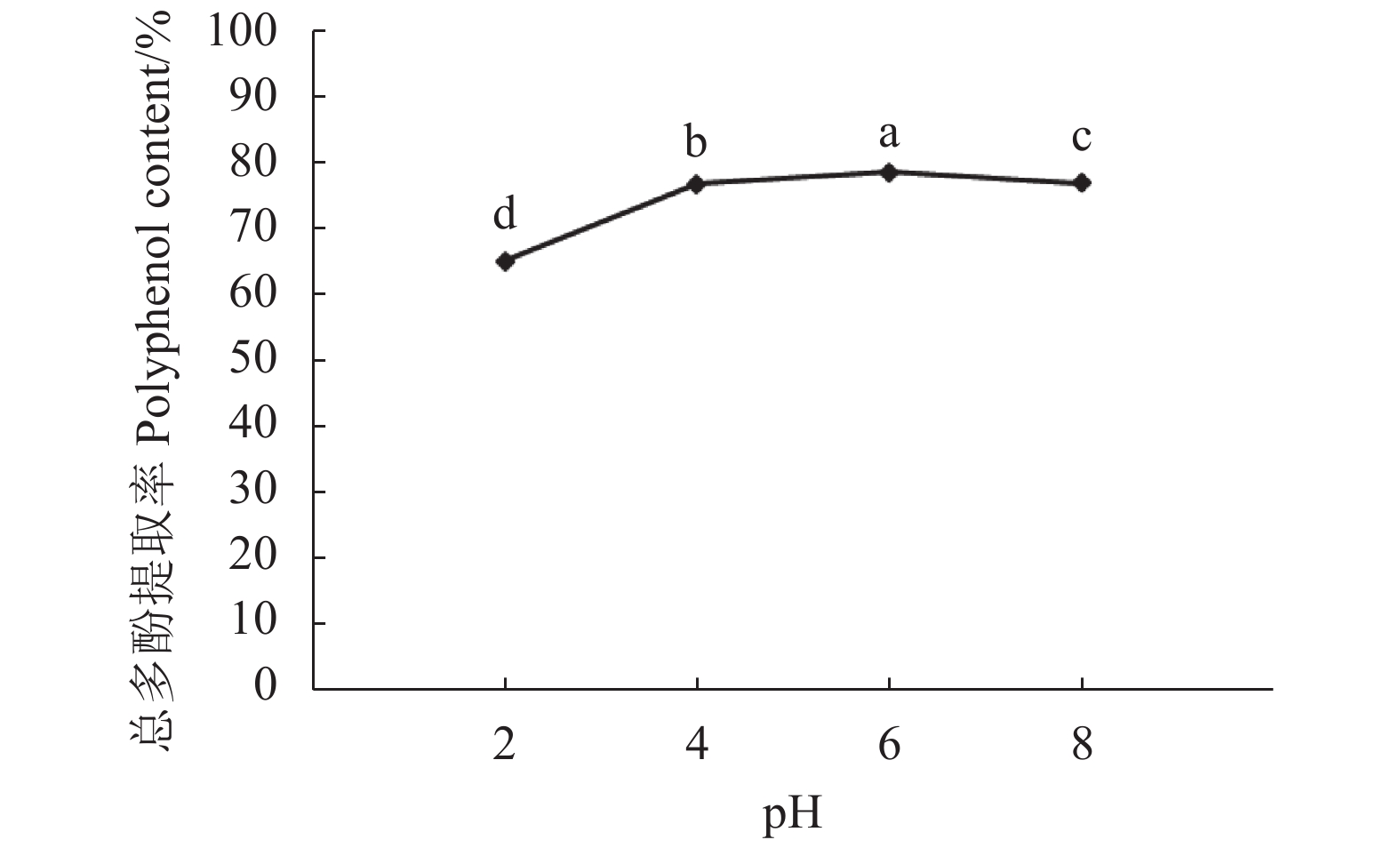
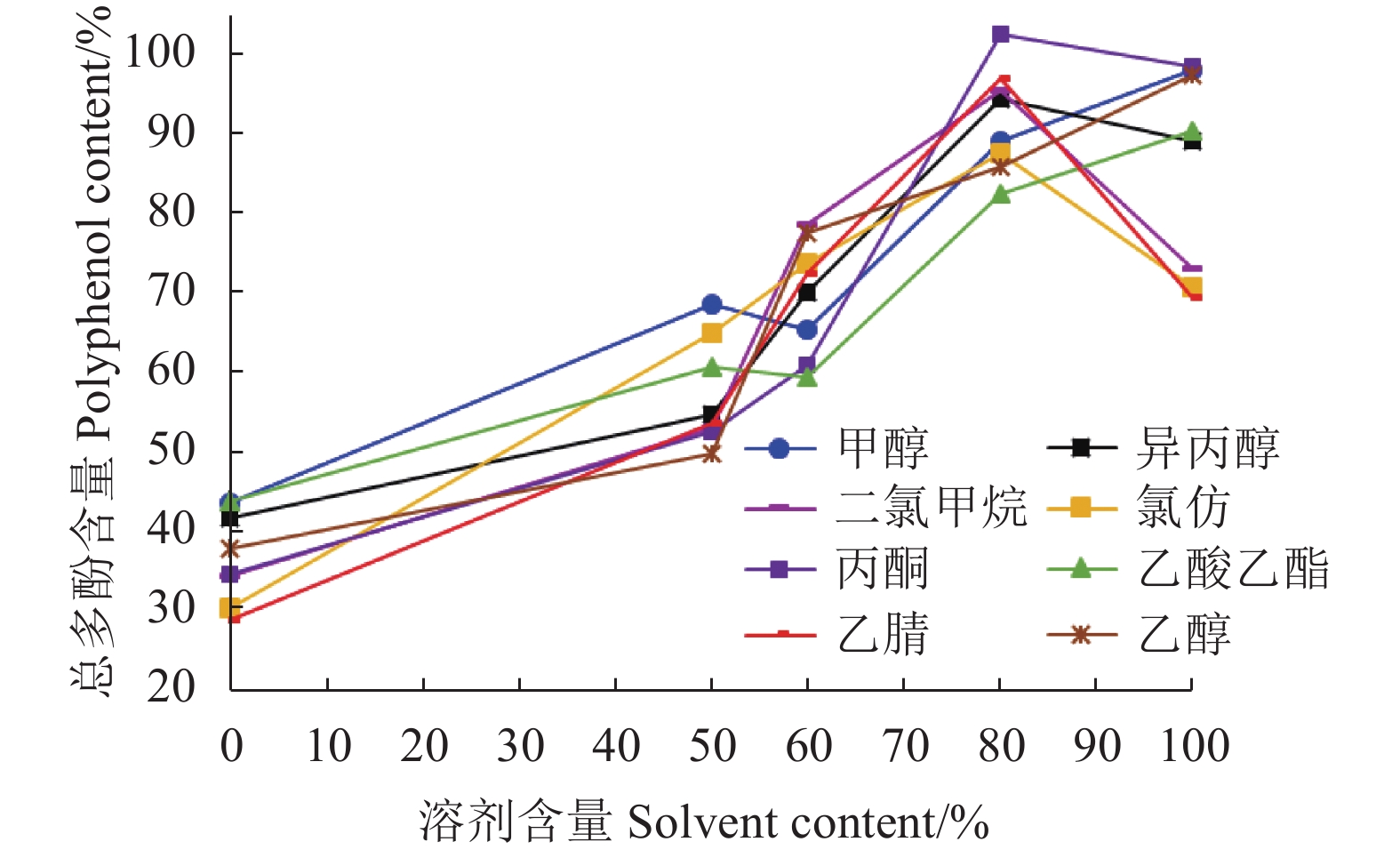
目的 采用溶剂萃取法提取紫皮豇豆中的总多酚,多酚提取物经大孔树脂分离纯化,再利用高效液相色谱(HPLC)分析其多酚类化合物的组成及含量,为紫皮豇豆中多酚类物质的提取、分析提供理论依据。 方法 以总多酚提取量为考察指标,采用单因素和正交试验,分析提取溶剂、料液比、温度和pH对紫皮豇豆总多酚提取量的影响,再通过Sephadex LH-20大孔树脂对粗提物进行分离纯化,并建立紫皮豇豆中6种多酚类组分的HPLC分析方法,采用外标法定量。 结果 紫皮豇豆中总多酚的最佳提取工艺为:经料液比1 ∶ 5(m ∶ V)的80%丙酮水溶液,在4℃、pH 6条件下,提取3次,每次提取5 h时,所得的总酚含量最高为614 mg(GAE)·100 g−1。在优化的试验条件下,没食子酸、没食子儿茶素、绿原酸、芦丁、p-香豆酸和阿魏酸等6种多酚单体在相应的浓度范围内具有良好的线性关系,相关系数(r)为0.995 9~0.999 9,方法检出限和定量限分别为0.1~1 mg·100 g−1和0.2~2.5 mg·100 g−1;加标试验平均回收率74.3~107%,相对标准偏差0.4~8.6%。经HPLC分析,紫皮豇豆中6种多酚单体均有检出,含量在0.46~6.5 mg·100 g−1,其中含量最高的是芦丁。 结论 采用80%丙酮水溶液提取紫皮豇豆总多酚,并利用HPLC法测定紫皮豇豆中几种单体酚的方法提取率高、准确性好,适用于紫皮豇豆中多酚类化合物的提取及定性定量分析。 Abstract:Objective Polyphenol compounds in purple cowpeas were solvent-extracted, purified, and then chemically analyzed by HPLC. Method Single factor and orthogonal experiments were conducted to optimize the polyphenol extraction from purple cowpeas. Using polyphenol yield as the criterion, effects of solvent, solid-liquid ratio, temperature, and pH applied for the process were evaluated for optimization. The crude extract was purified using a Sephadex LH-20 macroporous resin. HPLC with external standards was employed for the chemical determination on the purified product. Result The optimized process applied a peas-to-solvent ratio of 1 ∶ 5 (m ∶ V) with an 80% acetone solution to extract 3 times at 4oC and pH 6 for 5 h per cycle to reach a maximum total polyphenols content of the gallic acid equivalent of 614 mg·100 g−1. The correlation coefficients on the linear functions of the 6 polyphenols against their respective standards ranged from 0.995 9 to 0.999 9 with a limit of detection (LOD) of 0.1~1.0 mg·100 g−1 and that of quantitation 0.2~2.5 mg·100 g−1 on the HPLC test. The average recoveries on these compounds ranged from 74.3% to 107% with a relative standard deviation (RSDs) of 0.4~8.6%. The 6 polyphenols in the purple cowpeas thus determined averaged between 0.46 mg·100 g−1 and 6.5 mg·100 g−1, with rutin being the most abundant.ing the most abundant. Conclusion The polyphenol extraction from purple cowpeas was optimized to deliver high yields on 6 monomer phenols, which could be accurately determined quantitatively by HPLC. -
Key words:
- Purple cowpea /
- total polyphenols /
- extraction and purification /
- composition analysis
-
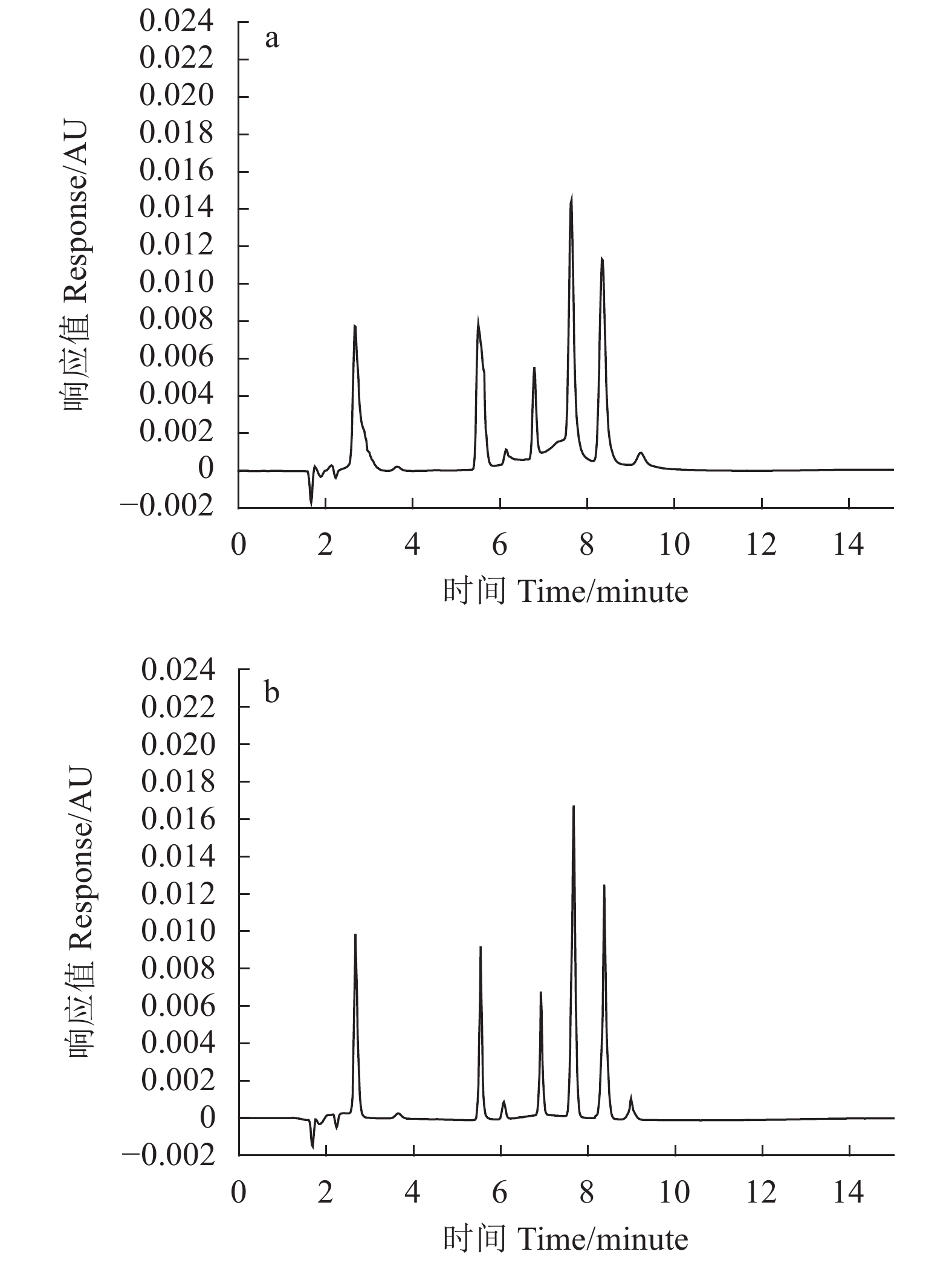
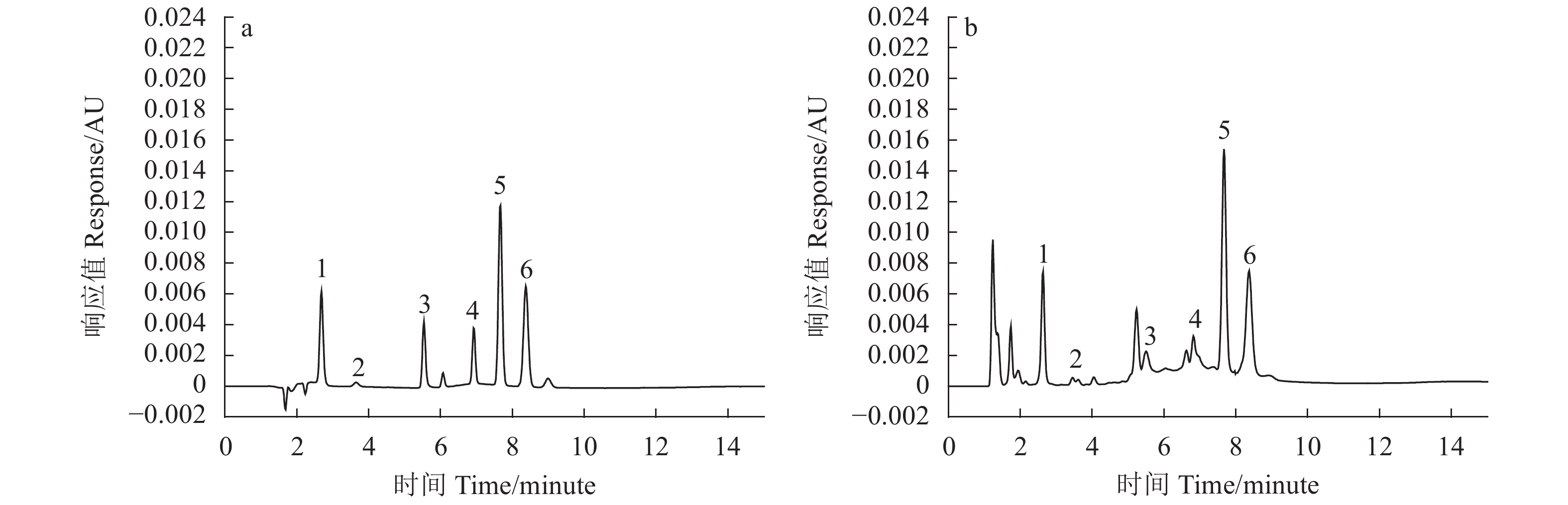
图 6 纯化后紫皮豇豆中单体酚标准品与样品的HPLC色谱
注:1:没食子酸;2:没食子儿茶素;3:绿原酸;4:芦丁;5:p-香豆酸;6:阿魏酸;a:单体酚混合标准溶液(10 μg·mL−1)HPLC 色谱图;b:紫皮豇豆样品 HPLC 色谱图。
Figure 6. HPLC chromatograms of 6 standards and polyphenols in purified purple cowpea extract
Note: 1: Gallic acid; 2: Gallocatechin; 3: Chlorogenic acid; 4: Rutin; 5: p-Coumalic acid; 6: Ferulic acid; a: HPLC chromatogram of polyphenols stanfards (10 μg·mL−1); b: HPLC chromatogram of purple cowpea polyphenols.
表 1 正交试验的因素及水平的选取
Table 1. Factors and levels of orthogonal test
水平
LevelA 溶剂
SolventB 温度
Temperature(℃)C 料液比
Solid-liquid ratio[m (g)∶v (mL)]D pH 1 80%丙酮 80% Acetone 4 1∶3 4 2 乙醇 Alcohol 25(室温RT) 1∶5 6 3 甲醇 Methanol 60 1∶7 8 表 2 多酚的最佳吸收波长
Table 2. Analysis on orthogonal test results
多酚
Polrphenols没食子酸
Gallic acid没食子儿茶素
GC绿原酸
Chlorogenicacid芦丁
Rutinp-香豆酸
p-Coumalicacid阿魏酸
Ferulicacid最佳吸收波长
Optimum absorption wavelength(nm)273 278 327 254,355 308 323 表 3 正交试验的结果及数据分析
Table 3. Optimal UV absorption wavelength for polyphenol detection
序号
Serial NumbersA B C D 总多酚含量(GAE)
Total polyphenol
(GAE)/
(mg·100 g−1)1 1 1 1 1 473 2 1 2 2 2 535 3 1 3 3 3 482 4 2 1 2 3 346 5 2 2 1 1 269 6 2 3 3 2 342 7 3 1 3 3 160 8 3 2 1 2 104 9 3 3 2 1 98 K1 1 490 979 840 840 K2 957 908 979 981 K3 362 922 984 988 k1 497 326 280 280 k2 319 303 326 327 k3 121 307 328 329 极差 R 376 24 48 49 因素主次顺序
Major factorsA>D>C>B 优水平
Best levelA1 B1 C2≈C3 D2 优组合
Best groupA1B1C2D2 注:Ki:表示任一列上水平号为i时所对应的收率试验结果之和;ki=Ki·n−1(n为该因素取第i个水平时所进行的试验次数)n=3;R= kimax- kimin(收率的正交分析结果的极差)
Note: Ki: the sum of yield test results corresponding to the horizontal number i above any column; Ki =Ki·n−1 (n is the number of tests performed when taking the i level of this factor) n =3; R= Kimax - Kimin (range of yield results from orthogonal analysis)表 4 紫皮豇豆中6种多酚组分检测的方法学验证
Table 4. Methodology validation for detecting 6 polyphenols in purple cowpeas
组分
Compound回归方程
Regress equation相关系数
Coefficient(r)线性范围
Linear range/(μg·mL−1)检出限
LOD/(mg·100 g−1)定量限
LOQ/(mg·100 g−1)没食子酸
GalslicacidY=9.13e+003X−3.04e+002 0.997 6 0.025~1 0.2 0.50 没食子儿茶素
GCY=1.86e+004X−1.06e+001 0.999 9 0.150~1 1.0 2.50 绿原酸
Chlorogenic acidY=8.76e+003X+ 1.81e+002 0.995 9 0.025~1 0.1 0.25 芦丁
RutinY=3.28e+004X+2.54e+002 0.999 2 0.100~1 0.5 1.00 p-香豆酸
p-Coumalic acidacidY=9.50e+003X+ 7.33e+001 0.999 8 0.025~1 0.1 0.20 阿魏酸
Ferulic acidY=8.50e+003X−1.74e+002 0.999 8 0.025~1 0.5 0.40 表 5 紫皮豇豆中6种多酚组分的加标回收试验(n=6)
Table 5. Recovery rates of 6 polyphenols of purple cowpeas (n=6)
组分名称
Compound本底值
Background (mg·100 −1)加标浓度
Addition(mg·100 g−1)测量值
MeasuredValue (mg·100g−1)回收率
Recovery/%相对标准偏差
RSD/%没食子酸
Gallic acid0.98±0.01 0.5 1.40±0.01 80.5±5.9 2.2 10 12.40±0.19 85.1±6.3 6.0 20 21.90±0.24 95.1±1.6 3.2 没食子儿茶素
GCND 2.5 1.90±0.05 76.8±4.3 5.6 10 8.96±0.04 89.6±0.4 0.4 20 18.50±0.03 92.7±0.7 0.8 绿原酸
Chlorogenic acid0.51±0.04 0.5 0.96±0.02 89.7±3.1 3.4 10 11.20±0.01 107.0±0.6 0.6 20 21.20±0.13 104.0±2.3 2.2 芦丁
Rutin1.00±0.06 1.0 1.80±0.04 78.3±5.8 7.4 10 8.40±0.06 74.3±2.6 3.5 20 16.40±0.29 76.8±4.3 5.6 p-香豆酸
p-Coumalic acid1.54±0.07 0.5 1.97±0.02 85.7±3.8 4.4 10 9.60±0.14 80.9±6.6 8.1 20 18.89±0.34 86.8±5.8 6.7 阿魏酸
Ferulic acidND 0.5 0.39±0.06 77.3±2.5 3.1 10 9.26±0.04 92.6±1.4 1.5 20 20.00±0.34 100.0±8.6 8.6 注:ND是未检出。
Note:ND means not detected.表 6 纯化后紫皮豇豆多酚的单体酚种类及含量(n=10)
Table 6. Composition and contents of individual polyphenols in purified purple cowpea extract (n=10)
紫皮豇豆多酚类物质单体
Individual phenolic compounds in purple cowpea polyphenols平均含量
Average Content/(mg·100 g−1)没食子酸 Gallic acid 0.462±0.019 没食子儿茶素 Gallocatechin 3.861±0.083 绿原酸 Chlorogenic acid 1.791±0.067 芦丁 Rutin 6.479±0.130 p-香豆酸 p-Coumalic acid 4.725±0.049 阿魏酸 Ferulic acid 2.627±0.025 -
[1] 祖艳侠, 郭军, 梅燚, 等. 2个不同荚色豇豆品种的营养比较 [J]. 浙江农业科学, 2016, 57(2):292−293.ZU Y X, GUO J, MEI Y, et al. Nutritional comparison of two varieties of pod - colored cowpea [J]. <italic>Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences</italic>, 2016, 57(2): 292−293.(in Chinese) [2] 张红梅, 许文静, 陈华涛, 等. 不同荚色豇豆品种花青素和营养成分含量变化分析 [J]. 南方农业学报, 2017, 48(6):1080−1085. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2017.06.23ZHANG H M, XU W J, CHEN H T, et al. Variation of anthocyanin contents and nutrient component contents in yardlong bean varieties with different pod colors [J]. <italic>Journal of Southern Agriculture</italic>, 2017, 48(6): 1080−1085.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2017.06.23 [3] 刘佳伟, 徐康, 杨效登, 等. 豇豆种子及豆芽多酚类物质的含量及抗氧化性比较分析研究 [J]. 齐鲁工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 31(2):41−46.LIU J W, XU K, YANG X D, et al. Comparison research on the contents and antioxidant property of the phenolic compounds in seeds and sprouts of cowpea [J]. <italic>Journal of Qilu University of Technology(Natural Science Edition)</italic>, 2017, 31(2): 41−46.(in Chinese) [4] OJWANG L O, DYKES L, AWIKA J M. Ultra performance liquid chromatography–tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry profiling of anthocyanins and flavonols in cowpea (<italic>Vigna unguiculata</italic>) of varying genotypes [J]. <italic>Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry</italic>, 2012, 60(14): 3735−3744. doi: 10.1021/jf2052948 [5] 刘素娟, 杨蒙蒙, 黄浩, 等. 高效液相色谱-二极管阵列联用同时测定果酒和果醋中10种酚类物质 [J]. 中国调味品, 2018, 43(12):151−153, 163. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2018.12.029LIU S J, YANG M M, HUANG H, et al. Simultaneous determination of 10 phenolics in fruit wine and fruit vinegar by HPLC-PDA [J]. <italic>China Condiment</italic>, 2018, 43(12): 151−153, 163.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2018.12.029 [6] 邓雅妮, 郭时印, 肖航, 等. 果蔬中不可萃取多酚的研究进展 [J]. 农产品加工, 2018(20):62−65.DENG Y N, GUO S Y, XIAO H, et al. Research progress in non-extractable polyphenols in fruits and vegetables [J]. <italic>Farm Products Processing</italic>, 2018(20): 62−65.(in Chinese) [7] 夏婷, 赵超亚, 杜鹏, 等. 食品中多酚类化合物种类、提取方法和检测技术研究进展 [J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2019, 45(5):231−238.XIA T, ZHAO C Y, DU P, et al. Research progress on classification, extraction, and detection of polyphenols in foods [J]. <italic>Food and Fermentation Industries</italic>, 2019, 45(5): 231−238.(in Chinese) [8] 薛宏坤, 谭佳琪, 赵月明, 等. 树莓果渣总花色苷和总多酚微波萃取工艺及组分分析 [J]. 精细化工, 2018, 43(12):151−153, 163.XUE H K, TAN J Q, ZHAO Y M, et al. Optimization of Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Total Anthocyanins and Polyphenols from Raspberry Pomace and Its Composition Analysis [J]. <italic>Fine Chemicals</italic>, 2018, 43(12): 151−153, 163.(in Chinese) [9] 董科, 冷云, 何方婷, 等. 植物多酚及其提取方法的研究进展 [J]. 食品工业科技, 2019, 40(2):326−330.DONG K, LENG Y, HE F T, et al. Research progress of polyphenol and extraction methods in plants [J]. <italic>Science and Technology of Food Industry</italic>, 2019, 40(2): 326−330.(in Chinese) [10] 赖瑞联, 陈瑾, 冯新, 等. 橄榄多酚类物质研究进展 [J]. 热带作物学报, 2018, 39(12):2532−2541. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2018.12.029LAI R L, CHEN J, FENG X, et al. Research progress on polyphenol of <italic>Canarium album</italic>(lour.) raeusch [J]. <italic>Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops</italic>, 2018, 39(12): 2532−2541.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2018.12.029 [11] 黎英, 曾珍清, 张薇, 等. 漳平水仙茶饼多酚的纯化及其体外活性研究 [J]. 热带作物学报, 2017, 38(8):1456−1463. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2017.08.014LI Y, ZENG Z Q, ZHANG W, et al. Separation and purification of polyphenols from Zhangping Shuixian tea cake by macroporous resin and its vitro activity [J]. <italic>Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops</italic>, 2017, 38(8): 1456−1463.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2017.08.014 [12] 陆广念, 朱志雄, 宋晓敏. 常见蔬菜抗氧化活性与总酚含量的研究 [J]. 食品科技, 2009, 34(9):68−71.LU G N, ZHU Z X, SONG X M. Antioxidant activity and total phenolic of vegetables commonly consumed [J]. <italic>Food Science and Technology</italic>, 2009, 34(9): 68−71.(in Chinese) [13] 林宝妹, 邱珊莲, 郑开斌, 等. 嘉宝果叶片总多酚提取工艺优化及其体外降糖活性 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2019, 34(5):587−594.LIN B M, QIU S L, ZHENG K B, et al. Process optimization and <italic>in vitro</italic> hypoglycemic effect of polyphenols extracted from jaboticaba leaves [J]. <italic>Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences</italic>, 2019, 34(5): 587−594.(in Chinese) [14] 张东峰, 陈家豪, 郭静, 等. 7种柑橘多酚、黄酮含量及其抗氧化活性比较研究 [J]. 食品研究与开发, 2019, 40(6):69−74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2019.06.013ZHANG D F, CHEN J H, GUO J, et al. Comparative study on the polyphenol, flavonoid and antioxidant activity of seven varieties of <italic>Citrus</italic> [J]. <italic>Food Research and Development</italic>, 2019, 40(6): 69−74.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2019.06.013 [15] 吴琼, 王明月, 吕岱竹, 等. 紫皮豇豆多酚类物质的含量及其降糖活性研究 [J]. 中国调味品, 2019, 44(10):59−62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2019.10.013WU Q, WANG M Y, LYU D Z, et al. Study on polyphenols content and hypoglycemic activity of <italic>Vigna unguiculata</italic> [J]. <italic>China Condiment</italic>, 2019, 44(10): 59−62.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2019.10.013 [16] HAMMERSCHMIDT P A, PRATT D E. Phenolic antioxidants of dried soybeans [J]. <italic>Journal of Food Science</italic>, 1978, 43(2): 556−559. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.1978.tb02353.x [17] STRUMEYERDH, MALINMJ. Condensed tannins in grain sorghum isolation, fractionation and characterization [J]. <italic>Agric. Food Chem</italic>, 1975, 23: 909−914. doi: 10.1021/jf60201a019 [18] 朱叶梅, 张雯, 杨少杰, 等. HPLC法测定茶叶中的7种多酚类化合物的含量 [J]. 云南化工, 2018, 45(9):66−68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-275X.2018.09.029ZHU Y M, ZHANG W, YANG S J, et al. Simultaneous determination of nine polyphenols colorants in paper-making reconstituted tobacco by HPLC [J]. <italic>Yunnan Chemical Technology</italic>, 2018, 45(9): 66−68.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-275X.2018.09.029 [19] 隋华嵩, 杨燕, 侯英, 等. 紫红豇豆色素组成及体外抗氧化活性研究 [J]. 食品研究与开发, 2014, 35(24):34−38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2014.24.009SUI H S, YANG Y, HOU Y, et al. Studies on Primary Identification and in Vitro Antioxidant Activity of Pigments from Purple-red Cowpea [J]. <italic>Yunnan Chemical Technology</italic>, 2014, 35(24): 34−38.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2014.24.009 -







 下载:
下载: