Effects of Heavy Metal Pollution in Soil on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Two Major Oil Crops
-
摘要:
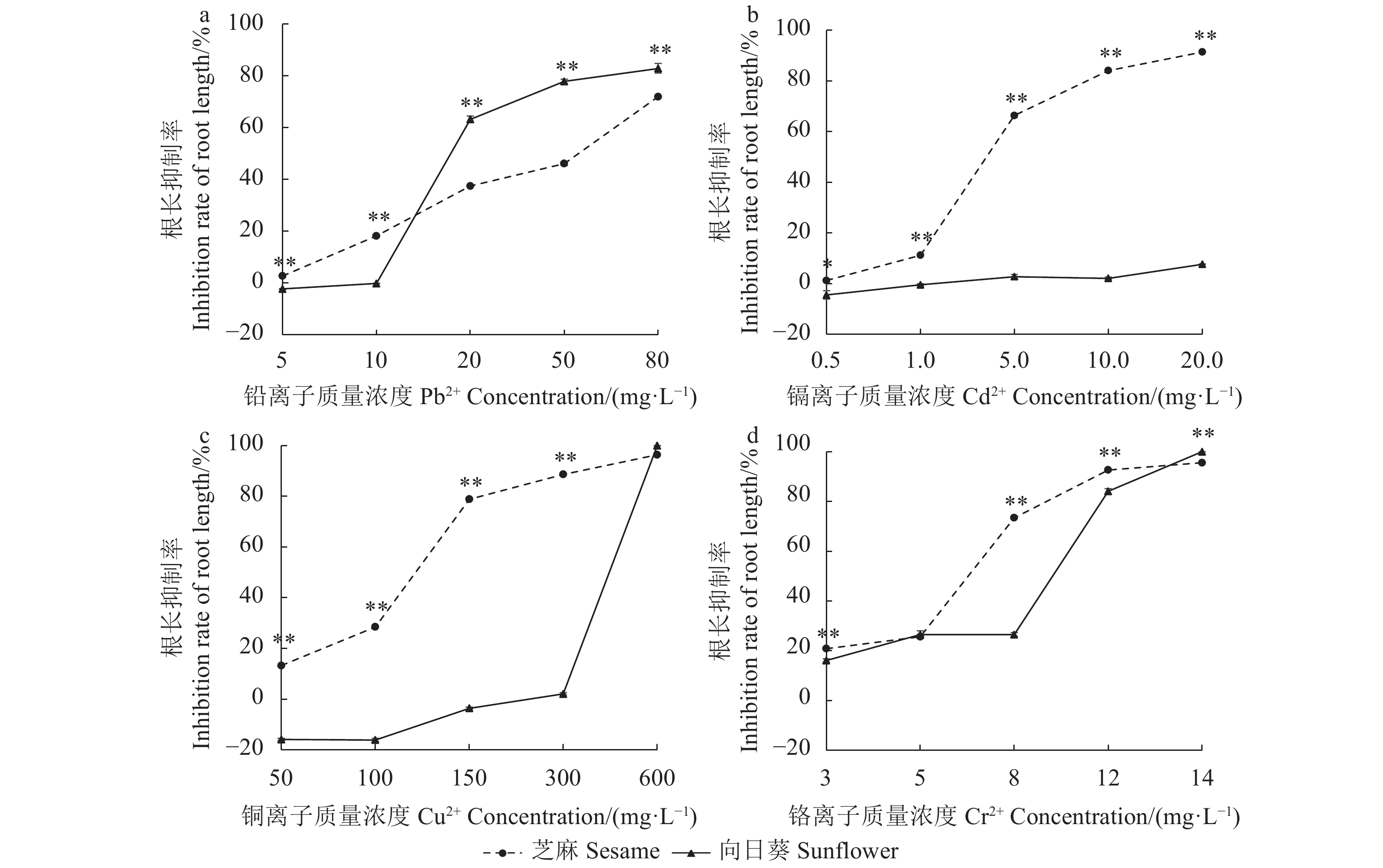
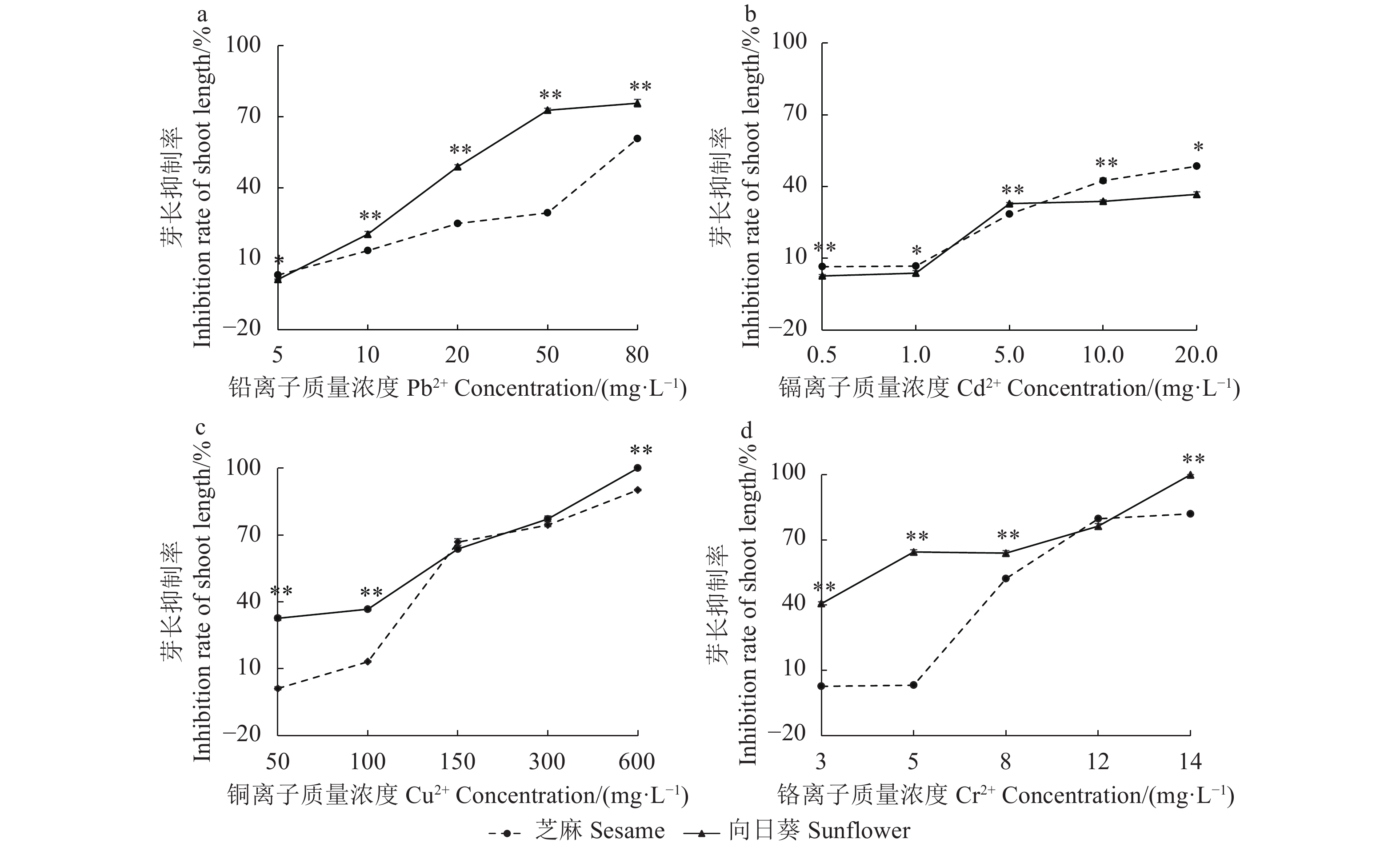
目的 探究2种主要油料作物芝麻(Sesamum indicum)、向日葵(Helianthus annuus)在铅(Pb2+)、镉(Cd2+)、铬(Cr6+)、铜(Cu2+)污染农田综合利用上的可能性。 方法 以2种油料作物主栽品种为试验材料,采用水培法研究 Pb2+(0.0、5.0、10.0、20.0、50.0、80.0 mg·L−1)、Cd2+(0.0、0.5、1.0、5.0、10.0、20.0 mg·L−1)、Cr6+(0.0、3.0、5.0、8.0、12.0、14.0 mg·L−1)、Cu2+(0.0、50.0、100.0、150.0、300.0、600.0 mg·L−1)对油料作物种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响。 结果 对2种作油料物种子萌发率的影响:2种油料作物的种子萌发率均随着Pb2+、Cd2+、Cr6+、Cu2+浓度的升高而降低,各处理芝麻种子的萌发率均极显著高于向日葵(P<0.01)。低浓度的4种重金属污染物对2种油料作物的发育与形态建成无明显影响,高质量浓度处理Pb2+(20.0 ~ 80.0 mg·L−1)、Cd2+ (5.0 ~ 20.0 mg·L−1)、Cr6+(5.0 ~14.0 mg·L−1)、Cu2+ (150.0 ~ 600.0 mg·L−1)时2种油料作物无法形成正常的根或芽。对2种油料作物幼苗根生长的影响:Pb2+胁迫(5.0~10.0 mg·L−1)、Cd2+胁迫(0.5~20.0 mg·L−1)、Cu2+胁迫(50~300.0 mg·L−1)、Cr6+胁迫(8.0~12.0mg·L−1)对芝麻根生长的抑制作用极显著大于向日葵(P<0.01),而Pb2+胁迫(20.0~80.0 mg·L−1)、Cr6+胁迫(14.0 mg·L−1)与上述作用相反。对2种油料作物种子芽生长的影响:Pb2+胁迫(10.0~80.0 mg·L−1)、Cd2+胁迫(5 mg·L−1)、Cu2+胁迫(50~100.0 mg·L−1和600.0 mg·L−1)、Cr6+胁迫(3.0~8.0 mg·L−1和14.0 mg·L−1)对向日葵种子芽生长的抑制作用大于芝麻,Cd2+胁迫(0.5~1.0 mg·L−1和10.0~20.0 mg·L−1)与上述作用相反。 结论 农田铅(Pb2+)、镉(Cd2+)、铬(Cr6+)、铜(Cu2+)污染对芝麻种子萌发率的影响极显著小于向日葵。综合4种重金属污染下根、芽生长状况,芝麻相对于向日葵对Pb2+(20.0~80.0 mg·L−1)、Cr6+(14.0 mg·L−1)的耐受性更强;向日葵相对于芝麻对Cd2+ (0.5~1.0 mg·L−1和10.0~20.0 mg·L−1)的耐受性更强。 Abstract:Objective Possibility of growing sesame(Sesamum indicum) and sunflower(Helianthus annuus) crops on the soil polluted by Pb2+, Cd2+, Cr6+, and/or Cu2+ was explored in a hydroponic experimentation in laboratory with the respects of seed germination and seedling growth of the plants. Method Seeds of sesame and sunflower cultivars were planted in hydroponics to examine the effects of heavy metals, Pb2+ (at 0, 5.0, 10.0, 20.0, 50.0, and 80.0 mg·L−1), Cd2+ (at 0, 0.5, 1.0, 5.0, 10.0, and 20.0 mg·L−1), Cr6+ (at 0, 3.0, 5.0, 8.0, 12.0, and 14.0 mg·L−1) and Cu2+ (at 0, 50.0, 100.0, 150.0, 300.0, and 600.0 mg·L−1) on the germination and seedling growth. Result The artificially added heavy metals in the medium decreased the seed germination rates (GR) of both cultivars as the Pb2+, Cd2+, Cr6+, and Cu2+ concentrations increased. The effect was significantly higher on the sesame seeds than the sunflower seeds (P<0.01). At lower levels of the heavy metal concentrations, the development and morphogenesis of either seeds were significantly affected. However, as the pollutants were increased in the medium (i.e., Pb2+>80.0 mg·L−1, Cd2+>20.0 mg·L−1, Cr6+>14.0 mg·L−1, and Cu2+>600.0 mg·L−1), normal root or bud formation was inhibited on both cultivars. For the growth of the seedlings, the heavy metals exerted greater reductions with Pb2+ at 5.0-10.0 mg·L−1, Cd2+ at 0.5-20.0 mg·L−1, Cu2+ at 50-300.0 mg·L−1, and Cr6+ at 8.0-12.0 mg·L−1 on the root length of sesame than sunflower plants (P<0.01), but at 20.0-80.0 mg·L−1 of Pb2+ or 14.0 mg·L−1 of Cr6, the opposite was observed. For the growth of seedling shoots, Pb2+ at 10.0-80.0 mg·L−1, Cd2+ at 5.0 mg·L−1, Cu2+ at 50.0-100.0 mg·L−1 and 600.0 mg·L−1 or Cr6+ at 3.0-8.0 mg·L−1 and 14.0 mg·L−1 inhibited it on sunflower more than on sesame, while the opposite was found with Cd2+ at 0.5-1.0 mg·L−1 or 10.0-20.0 mg·L−1. Conclusion Heavy metals, Pb2+, Cd2+, Cr6+, and/or Cu2+, in a hydroponic medium induced greater germination inhibition effect on the sunflower than the sesame seeds. The growth of roots and buds of sesame seedlings appeared more tolerant to Pb2+ at 20.0-80.0 mg·L−1, Cr6+ at 14.0 mg·L−1, and Cu2+ at 150.0-300.0 mg·L−1 than that of the sunflower counterparts, while the sunflower seedlings were more tolerant to Cd2+ at 0.5-1.0 mg·L−1 and 10.0-20.0 mg·L−1. -
Key words:
- Oil crop /
- heavy metal pollution in soil /
- germination rate /
- seedling growth
-
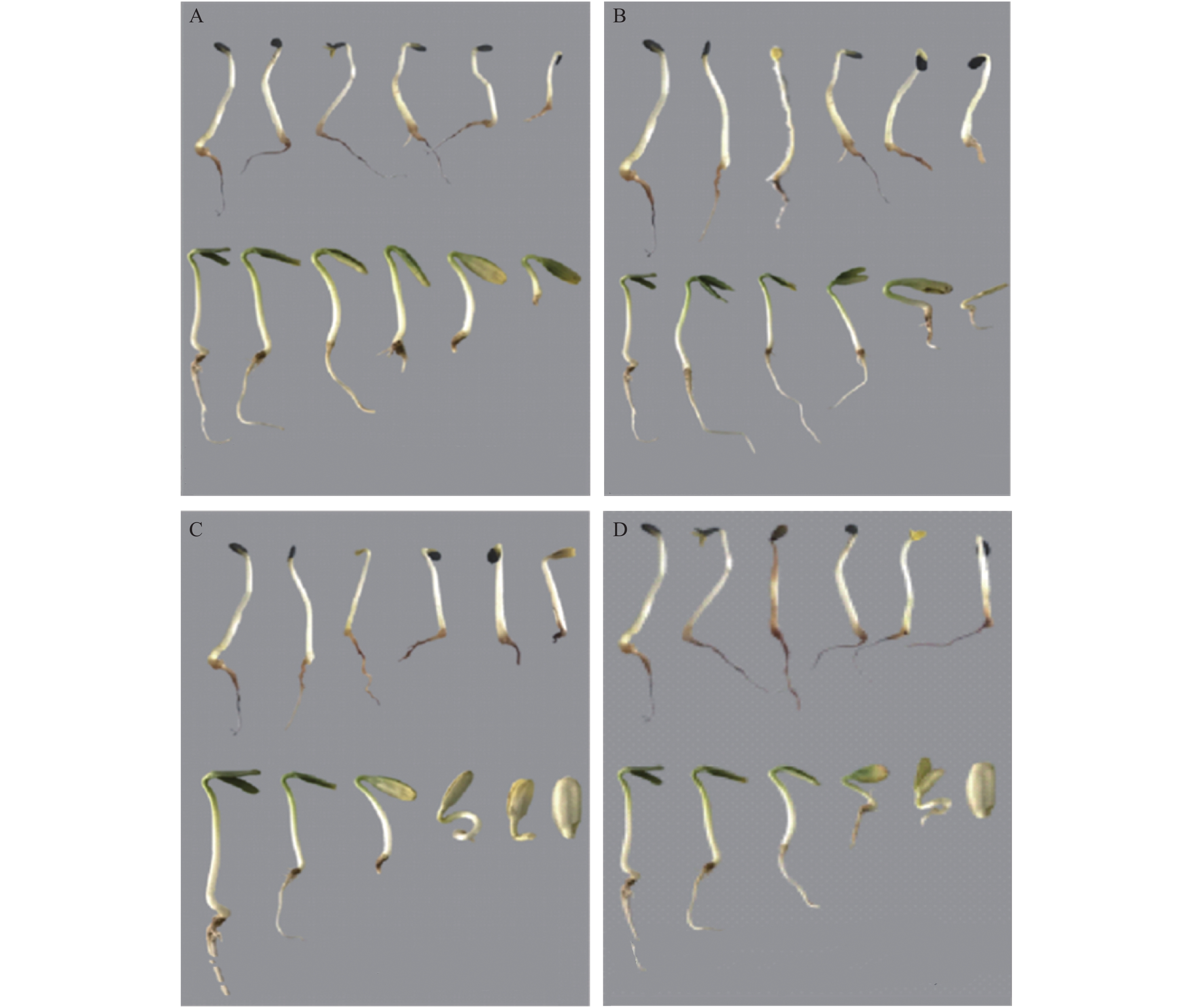
图 2 不同处理芝麻、向日葵幼苗生长状况
A. Pb2+ 浓度从左至右依次为0、5、10、20、50、80 mg·L−1;B. Cd2+ 浓度从左至右依次为0、0.5、1.0、5.0、10.0、20.0 mg·L−1;C. Cr6+ 浓度从左至右依次为0、3、5、8、12、14 mg·L−1;D. Cu2+ 浓度从左至右依次为0、50、100、150、300、600 mg·L−1
Figure 2. Growth of sesame and sunflower seedlings under treatments
A. The concentration of Pb2+ was 0, 5, 10, 20, 50, 80 mg·L−1 from left to right; B. The concentration of Cd2+ was 0, 0.5, 1.0, 5.0, 10.0, 20.0 mg·L−1 from left to righ; C. The concentration of Cr6+ was 0, 3, 5, 8, 12, 14 mg·L−1 from left to right; D. The concentration of Cr6+ was 0, 3, 5, 8, 12, 14 mg·L−1 from left to right
-
[1] MONTANARELLA L, CHUDE V, YAGI K, et al. Rome, Italy: Food and agriculture organization of the united nations and intergovernmental technical panel on soils[M]. Rome: Status of the World's Soil Resources (SWSR) - Main Report, 2015, 476–519. [2] 陈世宝, 王萌, 李杉杉, 等. 中国农田土壤重金属污染防治现状与问题思考 [J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(6):35−41.CHEN S B, WANG M, LI S S, et al. Current status of and discussion on farmland heavy metal pollution pre-ventionin China [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(6): 35−41.(in Chinese) [3] MCGRATH S P, LOMBI E, GRAY C W, et al. Field evaluation of Cd and Zn phytoextraction potential by the hyperaccumulators Thlaspi caerulescens and Arabidopsis halleri [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2006, 141(1): 115−125. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2005.08.022 [4] 陈惠君, 谭玲, 李取生, 等. Cr/Pb低累积菜心品种筛选及其根际机理研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2016, 35(7):1249−1256. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2016.07.004CHEN H J, TAN L, LI Q S, et al. Screening and preliminary rhizosphere mechanisms of low Cr/Pb accumulation cultivars of Chinese flowering cabbages(Brassica parachinensis L.) [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2016, 35(7): 1249−1256.(in Chinese) doi: 10.11654/jaes.2016.07.004 [5] VAMERALI T, BANDIERA M, COLETTO L, et al. Phytoremediation trials on metal- and arsenic-contaminated pyrite wastes (Torviscosa, Italy) [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2009, 157(3): 887−894. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2008.11.003 [6] 代全林. 重金属对植物毒害机理的研究进展 [J]. 亚热带农业研究, 2006, 2(2):129−133.DAI Q L. A review of toxicant mechanisms of heavy metals against plants [J]. Subtropical Agriculture Research, 2006, 2(2): 129−133.(in Chinese) [7] 黎红亮, 杨洋, 陈志鹏, 等. 花生和油菜对重金属的积累及其成品油的安全性 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2015, 9(5):2488−2494. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.20150574LI H L, YANG Y, CHEN Z P, et al. Accumulation of heavy metals by peanut and rapeseed and safety of their refined oil [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2015, 9(5): 2488−2494.(in Chinese) doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.20150574 [8] 张惠娟. 植物油料和食用油脂中砷含量的研究[D]. 郑州: 河南工业大学, 2013.ZHANG H J. The Studies On The Content Of Arsenic In Vegetable Oilseeds And Oils[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan University of Technology, 2013. (in Chinese). [9] GINNEKEN L V, MEERS E, GUISSON R, et al. Phytoremediation for heavy metal-contaminated soils combined with bioenergy production [J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering & Landscape Management, 2007, 15(4): 227−236. [10] 孙建, 颜小文, 乐美旺, 等. 芝麻不同抗旱基因型对花期干旱胁迫的生理响应机理 [J]. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(7):1215−1226. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.07.009SUN J, YAN X W, LE M W, et al. Physiological response mechanism of drought stress in different drought-tolerance genotypes of sesame during flowering period [J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2019, 52(7): 1215−1226.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.07.009 [11] 温蕊, 侯建华, 张艳芳, 等. 干旱胁迫对向日葵种子萌发的影响及其抗旱性鉴定 [J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2018, 36(2):186−191. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2018.02.27WEN R, HOU J H, ZHANG Y F, et al. Effect of drought stress on seed germination of sunflower on and identification of drought resistance of main variety [J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2018, 36(2): 186−191.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2018.02.27 [12] 杨丹娜, 骆夜烽, 谢家琪, 等. 酸、铝胁迫对苜蓿种子发芽和幼苗生长的影响 [J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(8):103−109.YANG D N, LUO Y F, XIE J Q, et al. Effects of acidity and/or aluminum stress on seed germination and seedling growth of alfalfa [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(8): 103−109.(in Chinese) [13] 田如男, 于双, 王守攻. 铜、镉胁迫下荻种子的萌发和幼苗生长 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2011, 20(8):1332−1337. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2011.08.024TIAN R N, YU S, WANG S G. Germination and seedling growth of Triarrhena sacchariflora (Maxim.) Nakai under Copper and Cadmium stress [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2011, 20(8): 1332−1337.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2011.08.024 [14] 曾庆玲, 黄晓华, 周青. 酸雨对水稻、小麦和油菜种子萌发的影响 [J]. 环境科学, 2005, 26(1):181−184. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2005.01.039ZENG Q L, HUANG X H, ZHOU Q. Effect of acid rain on seed germination of rice, wheat and rape [J]. Environmental Science, 2005, 26(1): 181−184.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2005.01.039 [15] 周健民, 沈仁芳. 土壤学大辞典[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013. [16] 王文萍, 黄占斌, 毕涛, 等. 再生水及重金属Pb/Cd对种子萌发和成苗的影响 [J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2010, 29(2):81−84.WANG W P, HUANG Z B, BI T, et al. Effects of reclaimed water and heavy metals Pb/Cd on seed germination and seedling [J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2010, 29(2): 81−84.(in Chinese) [17] 曲同宝, 杨塍希, 马文育, 等. 铅(Pb2+)和镉(Cd2+)对火炬树种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响 [J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2020, 40(1):30−36.QU T B, YANG C X, MA W Y, et al. Effects of Pb2+ and Cd2+ on seed germination and seedling growth of Rhus typhina [J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2020, 40(1): 30−36.(in Chinese) [18] 王新新, 吴亮, 朱生凤, 等. 镉胁迫对碱蓬种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2013, 32(2):238−243.WANG X X, WU L, ZHU S F, et al. Effects of cadmium stress on seed germination and seedling growth of Suaeda glauca [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2013, 32(2): 238−243.(in Chinese) [19] 刘春艳, 储玲, 沈兴江, 等. 酒石酸对Cd胁迫下油菜种子萌发和生长的影响 [J]. 安徽师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 34(5):467−471.LIU C Y, CHU L, SHEN X J, et al. The effects of tartaric acid on the seed germination and growth of rape under Cd stress [J]. Journal of Anhui Normal University (Natural Science), 2011, 34(5): 467−471.(in Chinese) [20] 王忠全, 温琰茂, 黄兆霆, 等. 几种植物处理含重金属废水的适应性研究 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2005, 14(4):540−544. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2005.04.019WANG Z Q, WEN Y M, HUANG Z T, et al. Adaptability of several plant to heavy metal wastewater treatment [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2005, 14(4): 540−544.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2005.04.019 [21] 江行玉, 赵可夫. 植物重金属伤害及其抗性机理 [J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2001, 7(1):92−99. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-687X.2001.01.022JIANG X Y, ZHAO K F. Mechanism of heavy metal injury and resistance of plants [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 2001, 7(1): 92−99.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-687X.2001.01.022 [22] ZHANG Y X, CHAI T Y, BURKARD G. Research advances on the mechanisms of heavy metal tolerance in plants [J]. Acta Botanica Sinica, 1999, 41(5): 453−457. [23] 张锡洲, 李廷轩, 王永东. 植物生长环境与根系分泌物的关系 [J]. 土壤通报, 2007, 38(4):785−789. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2007.04.034ZHANG X Z, LI T X, WANG Y D. Relationship between growth environment and root exudates of plants: a review [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2007, 38(4): 785−789.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2007.04.034 [24] 夏海威, 施国新, 黄敏, 等. 一氧化氮对植物重金属胁迫抗性的影响研究进展 [J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(10):3139−3147.XIA H W, SHI G X, HUANG M, et al. Advances on effects of nitric oxide on resistances of plants to heavy metal stress [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(10): 3139−3147.(in Chinese) [25] MENCH M, MOREL J L, GUCKERT A. Metal binding properties of high molecular weight soluble exudates from maize (Zea mays L.) roots [J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 1987, 3(3): 165−169. doi: 10.1007/BF00255778 [26] SEREGIN I V, KOZHEVNIKOVA A D. Roles of root and shoot tissues in transport and accumulation of cadmium, lead, nickel, and strontium [J]. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology, 2008, 55(1): 1−22. doi: 10.1134/S1021443708010019 [27] LIU J G, HE C H, CAO C X, et al. Variations between Two Rice Genotypes in Root Secretion of Organic Acids and Plant Pb Uptake[C]. 3rd International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, iCBBE 2009, 2009. [28] 张振海, 陈琰, 韩胜芳, 等. 低磷胁迫对大豆根系生长特性及分泌H+和有机酸的影响 [J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2011, 33(2):135−140.ZHANG Z H, CHEN Y, HAN S, et al. Effect of P deficiency stress on soybean root system and its secretion of H+ and organic acid [J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences,, 2011, 33(2): 135−140.(in Chinese) -








 下载:
下载: