Optimized Medium Utilizing Distiller's Grains Polypeptide for High-density Culture of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
-
摘要:
目的 研发适用于酿酒酵母菌剂生产的高密度低成本培养基。 方法 以酿酒酵母JH301为对象菌,以糖蜜为基础培养基,采用单因素试验筛选适宜的碳源、氮源、无机盐和天然产物增殖因子,通过U16(88)均匀试验优化培养基成分。 结果 研究筛选出适宜的碳源为棉籽糖、葡萄糖和海藻糖,氮源为胰蛋白胨,无机盐为磷酸二氢钾,天然产物增殖因子为酒糟多肽、大米糖化液和大豆多糖。获得优化培养基配方为:在可溶性固形物含量为10%的糖蜜中添加酒糟多肽23.72 g·L−1、大米糖化液44.15 g·L−1、大豆多糖31.88 g·L−1、棉籽糖22.45 g·L−1、葡萄糖13.97 g·L−1、海藻糖15.00 g·L−1、胰蛋白胨27.25 g·L−1、磷酸二氢钾3.00 g·L−1,调节pH至4.5±0.2。酵母细胞增殖培养生物量可达1.48×108 cfu·mL−1,比基础糖蜜培养基提高了1个数量级。 结论 酒糟多肽中富含多种对酿酒酵母细胞增殖起促进作用的小分子多肽成分,作为天然产物添加到糖蜜培养基中可显著提高酵母产量,是一种来源丰富、低成本的优良复合营养源,相关研究内容可为高活力酵母菌剂制备提供思路和参考依据。 Abstract:Objective An optimized low-cost medium for high-density culture of Saccharomyces cerevisiae was formulated. Method S. cerevisiae JH301 was cultured on the basic molasses media of varied compositions to determine the optimal carbon source, nitrogen source, inorganic salt, and natural growth promoters for the yeast preparation in a single factor test. Optimization models using different statistical analyses were compared for the formulation finalization. Result From a U16(88) uniform experiment, the optimized medium formulation was determined to apply the carbon source that included glucose, cottonseed sugar, and trehalose, tryptone for the nitrogen source, K2HPO4 as the inorganic salt, and the natural growth promoters that consisted of distiller's grains polypeptide, rice saccharification solution, and soybean polysaccharide. The finalized formula called for 23.72 g·L−1 distiller's grains polypeptide, 44.15 g·L−1 rice saccharification solution, 31.88 g·L−1 soybean polysaccharide, 22.45 g·L−1 cottonseed sugar, 13.97 g·L−1 glucose, 15.00 g·L−1 trehalose, 27.25 g·L−1 tryptone, and 3.00 g·L−1 K2HPO4, in addition to 10% soluble solids molasses. The resulting yeast biomass reached 1.48×108 cfu·mL−1, which was one order of magnitude higher than the culture obtained from the basic molasses medium. Conclusion Rich in small molecular polypeptides capable of promoting the cell proliferation of S. cerevisiae, the natural distiller's grains polypeptide was formulated in the medium to yield a low-cost preparation for the yeast. -
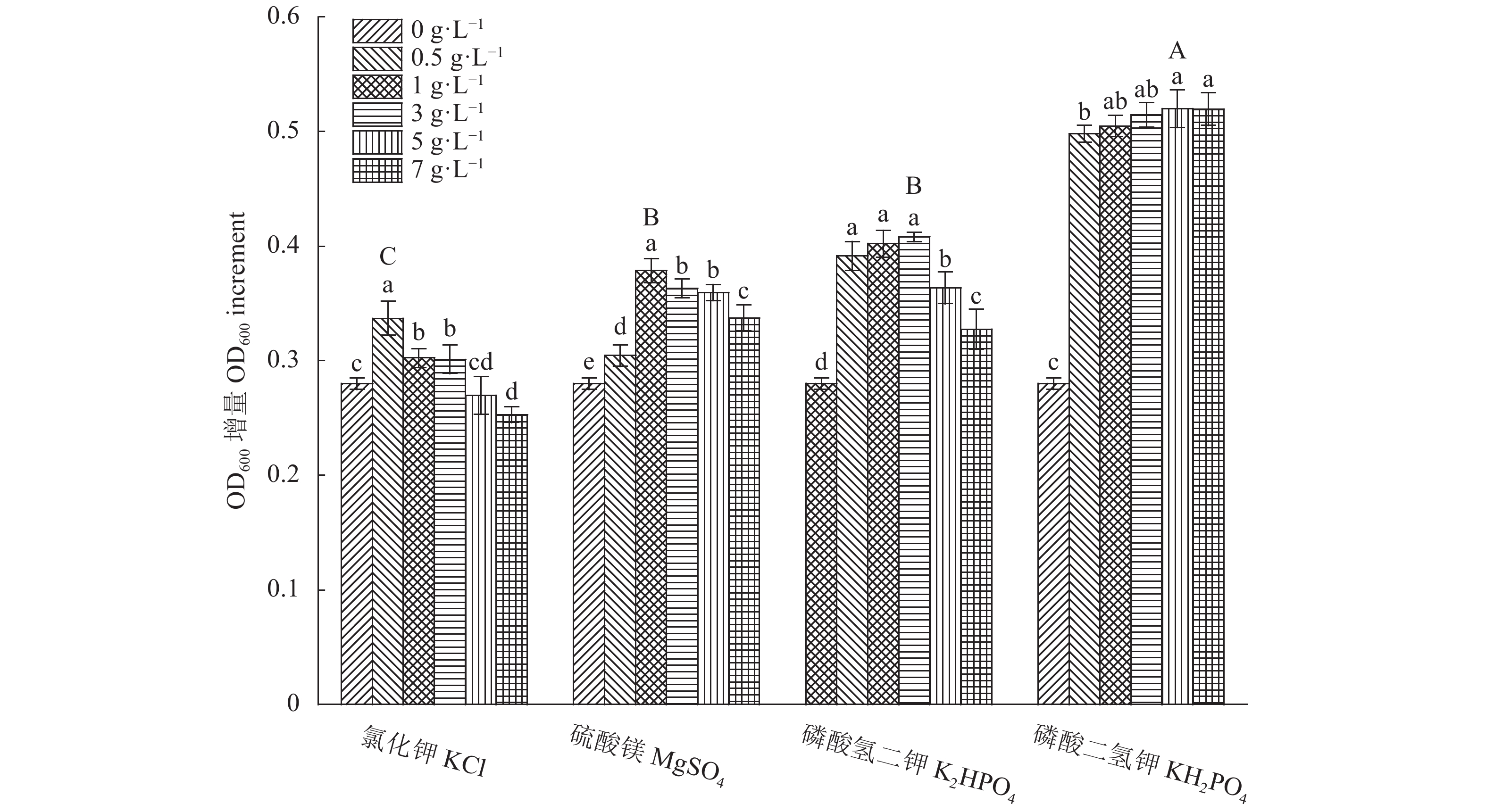
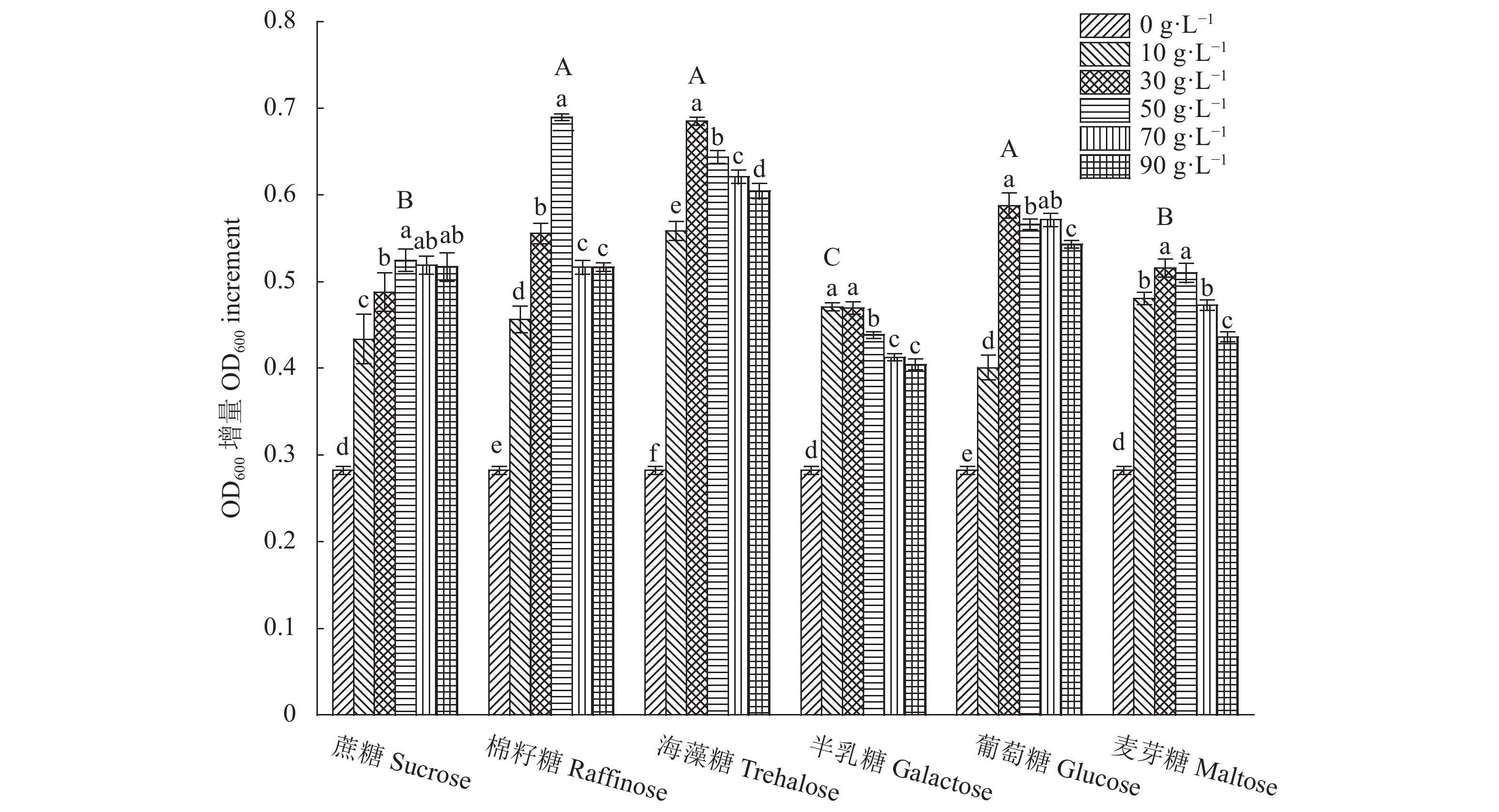
图 1 碳源种类及质量浓度对JH301生长的影响
注:图中不同小写字母表示同一处理不同质量浓度之间差异显著(P<0.05),不同大写字母表示不同处理组中最高OD600增量组间的差异显著(P<0.05)。图2~4同。
Figure 1. Effects of C sources and concentrations on growth of JH301
Note: Data with different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different concentrations under same treatment; data with different capital letters, significant differences on highest OD600 increment group between different treatments (P<0.05). Same for Fig.2–4.
表 1 U16(88)均匀试验结果
Table 1. Results of U16(88) uniform test
因子
Factorx1磷酸二氢钾
KH2PO4 /
(g·L−1)x2胰蛋白胨
Tryptone/
(g·L−1)x3海藻糖
Trehalose/
(g·L−1)x4葡萄糖
Glucose/
(g·L−1)x5棉籽糖
Raffinose/
(g·L−1)x6酒糟多肽
(Distiller's grains
polypeptide, DGP)/
(g·L−1)x7大豆多糖
(Soybean
polysaccharide,
SP)/
(g·L−1)x8大米糖化液
(Rice
saccharification
solution, RSS)/
(g·L−1)菌体密度
对数值
Cell
densityN1 5.5 10 55 10 30 40 20 60 7.29 N2 4.5 45 55 10 5 5 20 40 7.19 N3 5.5 30 45 30 15 10 40 65 7.44 N4 6.0 15 35 25 10 25 10 40 7.50 N5 4.5 20 75 30 40 35 40 45 7.58 N6 4.0 40 35 5 35 25 30 65 7.51 N7 3.0 15 65 5 10 20 45 50 7.71 N8 5.0 25 15 0 40 15 15 45 7.57 N9 4.0 25 15 35 5 30 25 55 7.60 N10 3.5 10 25 20 35 10 35 35 7.64 N11 5.0 35 85 0 15 30 35 35 7.86 N12 3.0 30 45 15 20 40 15 30 7.57 N13 6.0 40 65 35 35 20 25 30 7.48 N14 6.5 20 85 15 20 5 30 55 7.62 N15 6.5 45 25 20 25 35 45 50 7.59 N16 3.5 35 75 25 25 15 10 60 7.47 表 2 模型1优选培养基组合
Table 2. Medium formulation optimization by stepwise regression of multiple factors and square terms
成分
Factors磷酸二氢钾
KH2PO4胰蛋白胨
Tryptone海藻糖
Trehalose葡萄糖
Glucose棉籽糖
Raffinose酒糟多肽
DGP大豆多糖
SP大米糖化液
RSS水平编码值 Level 1.00 4.45 1.00 3.79 4.49 4.74 5.38 3.83 质量浓度 Concentration/(g·L−1) 3.00 27.25 15.00 13.97 22.45 23.72 31.88 44.15 表 3 模型2优选培养基组合
Table 3. Medium formulation optimization by stepwise regression of multiple factors and interaction
成分
Factors磷酸二氢钾
KH2PO4胰蛋白胨
Tryptone海藻糖
Trehalose葡萄糖
Glucose棉籽糖
Raffinose酒糟多肽
DGP大豆多糖
SP大米糖化液
RSS水平编码值 Level 8.00 8.00 1.00 8.00 8.00 8.00 1.00 8.00 质量浓度 Concentration/(g·L−1) 6.50 45.00 15.00 35.00 40.00 40.00 10.00 65.00 表 4 模型3优选培养基组合
Table 4. Medium formulation optimization by quadratic polynomial stepwise regression analysis
成分
Factors磷酸二氢钾
KH2PO4胰蛋白胨
Tryptone海藻糖
Trehalose葡萄糖
Glucose棉籽糖
Raffinose酒糟多肽
DGP大豆多糖
SP大米糖化液
RSS水平编码值 Level 8.00 8.00 1.00 8.00 8.00 8.00 1.00 8.00 质量浓度 Concentration/(g·L−1) 6.50 45.00 15.00 35.00 40.00 40.00 10.00 65.00 -
[1] 赵欠, 王巧碧, 周才琼. 酿酒酵母相关营养功能成分的研究及应用进展 [J]. 中国酿造, 2015, 34(6):15−18.ZHAO Q, WANG Q B, ZHOU C Q. Application research status on the nutritional and functional compositions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. China Brewing, 2015, 34(6): 15−18.(in Chinese) [2] PANNAKAL S T, JÄGER S, DURANTON A, et al. Longevity effect of a polysaccharide from Chlorophytum borivilianum on Caenorhabditis elegans and Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(7): e0179813. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179813 [3] WANG G K, HUANG M T, NIELSEN J. Exploring the potential of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for biopharmaceutical protein production [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2017, 48: 77−84. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2017.03.017 [4] BRANCO P, FRANCISCO D, MONTEIRO M, et al. Antimicrobial properties and death-inducing mechanisms of saccharomycin, a biocide secreted by Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 101(1): 159−171. doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-7755-6 [5] BAI R, YAN C Y, WAN R X, et al. Structure of the post-catalytic Spliceosome from Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Cell, 2017, 171(7): 1589−1598. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.10.038 [6] IZAH S C, BASSEY S E, OHIMAIN E I. Amino acid and proximate composition of Saccharomyces cerevisiae biomass cultivated in cassava mill effluents [J]. Molecular Microbiology Research, 2017, 7: 20−29. doi: 10.5376/mmr.2017.07.0003 [7] PERLI T, WRONSKA A K, ORTIZ-MERINO R A, et al. Vitamin requirements and biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Yeast (Chichester, England), 2020, 37(4): 283−304. doi: 10.1002/yea.3461 [8] 何海燕. 甘蔗糖蜜发酵培养富铁酵母的研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2007.HE H Y. Fermenting cultivation of high-iron yeast by using sugar cane molasses[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2007. (in Chinese) [9] 卢敏. 促酵母生长代谢活性肽的分离纯化与结构鉴定研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2017.LU M. Purification and identification of active peptides that promote yeast growth and metabolism[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2017. (in Chinese) [10] 周永婧. 小麦面筋蛋白源促酵母增殖与代谢活性肽的分离纯化与结构鉴定研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2018.ZHOU Y J. Purification and identification of peptides with growth-and fermentation-promoting activity of brewer's yeast from wheat gluten protein[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2018.(in Chinese) [11] LEI H J, ZHENG L Y, WANG C X, et al. Effects of worts treated with proteases on the assimilation of free amino acids and fermentation performance of lager yeast [J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 2013, 161(2): 76−83. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2012.11.024 [12] 雷宏杰. 高浓麦汁氮源组成对酵母氨基酸同化及发酵调控影响的研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2014.LEI H J. Study of the effects of nitrogen composition in high gravity wort on the assimilation of amino acids by lager yeast and fermentation control[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2014. (in Chinese) [13] 赵小丽, 甄玉国, 王兰惠, 等. 酿酒酵母有氧发酵培养基的研究 [J]. 中国酿造, 2014, 33(7):43−47. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2014.07.009ZHAO X L, ZHEN Y G, WANG L H, et al. Aerobic fermentation culture medium of Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. China Brewing, 2014, 33(7): 43−47.(in Chinese) doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2014.07.009 [14] 林晓婕, 何志刚, 梁璋成, 等. 红曲黄酒糟蛋白酶解物制备工艺优化及营养评价 [J]. 中国粮油学报, 2019, 34(1):43−49.LIN X J, HE Z G, LIANG Z C, et al. Optimization of preparation technology of Hongqu glutinous rice wine grains protein hydrolysate and nutrition value [J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2019, 34(1): 43−49.(in Chinese) [15] 梁璋成, 何志刚, 窦芳娇, 等. 红曲黄酒糟酶解液美拉德反应增香条件优选 [J]. 中国酿造, 2018, 37(10):57−60. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2018.10.011LIANG Z C, HE Z G, DOU F J, et al. Optimization of flavour-enhancing conditions by Maillard reaction in enzymatic hydrolysis solution of Hongqu Huangjiu lees [J]. China Brewing, 2018, 37(10): 57−60.(in Chinese) doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2018.10.011 [16] WANG L, HE Y T, SWANSON C S, et al. Optimization of medium composition and culture conditions for cell multiplication of a high quality milk beer fermentation yeast (Kluyveromyces marxianus) [J]. Food Science and Technology Research, 2020, 26(3): 351−361. doi: 10.3136/fstr.26.351 [17] 梁璋成, 任香芸, 林晓姿, 等. 低产尿素、杂醇油红曲黄酒酵母的筛选及鉴定 [J]. 中国食品学报, 2018, 18(2):265−271.LIANG Z C, REN X Y, LIN X Z, et al. Screening and identification of the yeast stains with low urea and fusel oil production for brewing in Hong qu(glutinous rice wine) [J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2018, 18(2): 265−271.(in Chinese) [18] 蒋艾廷, 李新玲, 姜淑娟, 等. 一株优选酿酒酵母增殖培养条件优化及发酵动力学模型的构建 [J]. 食品科学技术学报, 2018, 36(1):45−52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-6002.2018.01.006JIANG A T, LI X L, JIANG S J, et al. Optimizing on proliferation conditions of preferred Saccharomyces cerevisiae and construction of fermentation kinetics model [J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 2018, 36(1): 45−52.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-6002.2018.01.006 [19] VAN V M L, STREHAIANO P, NGUYEN D L, et al. Microbial protease or yeast extract-alternative additions for improvement of fermentation performance and quality of beer brewed with a high rice content [J]. Journal of the American Society of Brewing Chemists, 2001, 59(1): 10−16. doi: 10.1094/ASBCJ-59-0010 [20] 奚宽鹏, 钱海峰, 张晖, 等. 小麦面筋蛋白酶解物对酵母增殖的影响 [J]. 食品与生物技术学报, 2016, 35(6):597−603. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2016.06.006XI K P, QIAN H F, ZHANG H, et al. Effects of wheat gluten hydrolysates on the proliferation of yeast [J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2016, 35(6): 597−603.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2016.06.006 [21] 刘梦兰, 李游, 张健, 等. 大豆多肽对酵母细胞增殖及耐冻性的影响 [J]. 食品科学技术学报, 2016, 34(6):17−23.LIU M L, LI Y, ZHANG J, et al. Influence of soy peptides on yeast cells' proliferation and tolerance to freeze-thaw stress [J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 2016, 34(6): 17−23.(in Chinese) [22] IZAWA S, IKEDA K, TAKAHASHI N, et al. Improvement of tolerance to freeze-thaw stress of baker's yeast by cultivation with soy peptides [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2007, 75(3): 533−537. doi: 10.1007/s00253-007-0855-6 [23] KITAGAWA S, MUKAI N, FURUKAWA Y, et al. Effect of soy peptide on brewing beer [J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2008, 105(4): 360−366. doi: 10.1263/jbb.105.360 [24] 王颖, 何宁, 李清彪, 等. 酿酒酵母S. cerevisiae高密度培养条件优化研究 [J]. 工业微生物, 2007, 37(1):34−38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6678.2007.01.007WANG Y, HE N, LI Q B, et al. Optimization of high cell density cultivation conditions of Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Industrial Microbiology, 2007, 37(1): 34−38.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6678.2007.01.007 [25] 汪芳, 吴晖, 余以刚, 等. 酿酒酵母S. cerevisiae YQ-7的高密度发酵 [J]. 中国酿造, 2010, 29(10):113−117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5071.2010.10.034WANG F, WU H, YU Y G, et al. High density fermentation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae YQ-7 [J]. China Brewing, 2010, 29(10): 113−117.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5071.2010.10.034 [26] 陈雪, 甄玉国, 赵小丽. 以糖蜜为碳源的酿酒酵母培养基的优化 [J]. 中国酿造, 2014, 33(4):35−38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5071.2014.04.009CHEN X, ZHEN Y G, ZHAO X L. Optimization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae medium with molasses as carbon source [J]. China Brewing, 2014, 33(4): 35−38.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5071.2014.04.009 [27] 邵明, 王家林, 张颖, 等. 废弃黄酒糟的开发利用 [J]. 中国酿造, 2011, 30(9):15−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5071.2011.09.005SHAO M, WANG J L, ZHANG Y, et al. Exploitation and utilization of rice wine lees [J]. China Brewing, 2011, 30(9): 15−18.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5071.2011.09.005 [28] 李倩, 裴朝曦, 王之盛, 等. 不同类型酒糟营养成分组成差异的比较研究 [J]. 动物营养学报, 2018, 30(6):2369−2376.LI Q, PEI Z X, WANG Z S, et al. Comparative study on nutrients compositions of different types of distillers' grains [J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2018, 30(6): 2369−2376.(in Chinese) -







 下载:
下载: