Response Surface Optimization of ISSR-PCR Reaction for Genetic Study on Phyllanthus Emblica
-
摘要:
目的 优化余甘子种质资源ISSR-PCR反应体系,为余甘子种质资源遗传多样性及亲缘关系研究提供基础。 方法 以缅甸、印度、广东、云南、福建等5份来源不同的余甘子种质资源的基因组DNA组成混合的DNA模板,综合单因素试验和响应面分析法,分析引物浓度、2×Taq Master Mix添加量、DNA模板量、退火温度等反应条件对ISSR-PCR反应体系的影响,优化建立余甘子ISSR-PCR反应体系。 结果 引物浓度和2×Taq Master Mix添加量对扩增效果有较大影响,DNA模板量影响较小;引物浓度和DNA模板量交互作用明显;余甘子ISSR反应体系为引物浓度0.4 μmol·L−1,2×Taq Master Mix添加量13 μL,DNA模板量30 ng,扩增结果与响应面分析模型理论值相对误差仅为9.39%;退火温度为50.5~52.7 ℃时,随着温度的升高,条带质量变好,数量变多,退火温度为52.7 ℃时可获得多样性好的清晰条带。 结论 获得ISSR-PCR反应体系为引物浓度0.4 μmol·L−1,2×Taq Master Mix添加量13 μL,DNA模板量30 ng,退火温度52.7 ℃,扩增循环数35循环,扩增获得的条带清晰、稳定,多样性好,该体系适于余甘子种质资源的遗传多样性和亲缘关系等分析研究。 Abstract:Objective ISSR-PCR reaction system for genetic study on Phyllanthus emblica germplasms was optimized. Methods A mixed DNA template composed of genomic DNA of P. emblica germplasms came from Myanmar, India, Guangdong, Yunnan, and Fujian was obtained. The single factor test and response surface analysis were used to optimize the ISSR-PCR reaction conditions including primer concentration, amount of 2×Taq Master Mix, DNA template amount, and annealing temperature. Result The primer concentration and addition amount of 2×Taq Master Mix had a greater impact on the amplification than did the DNA template amount. A significant interaction between the primer concentration and DNA template amount was found. The optimized system with a primer concentration of 0.4 μmol·L−1, a 2×Taq Master Mix of 13 μL, and a DNA template concentration of 30 ng was established that achieved a low relative error of 9.39% in predicting the theoretical response. Within the annealing temperature between 50.5 ℃ and 52.7 ℃, increasing temperature improved the number and quality of bands. When the annealing temperature is 50.5-52.7 ℃, the number of strips increases, and the quality of the strips becomes better with the increase of temperature. The annealing temperature is 52.7 ℃ to obtain good diversity and clear bands. Conclusion The optimized ISSR-PCR reaction system was established applying a primer concentration of 0.4 μmol·L−1, a 2×Taq Master Mix of 13 L, a DNA template concentration of 30 ng at the annealing temperature of 52.7 ℃ for 35 amplification cycles. The methodology could be used to study the genetic diversity and relationship of P. emblica germplasms. -
Key words:
- Phyllanthus emblica /
- ISSR-PCR /
- response surface methodology /
- system optimization
-
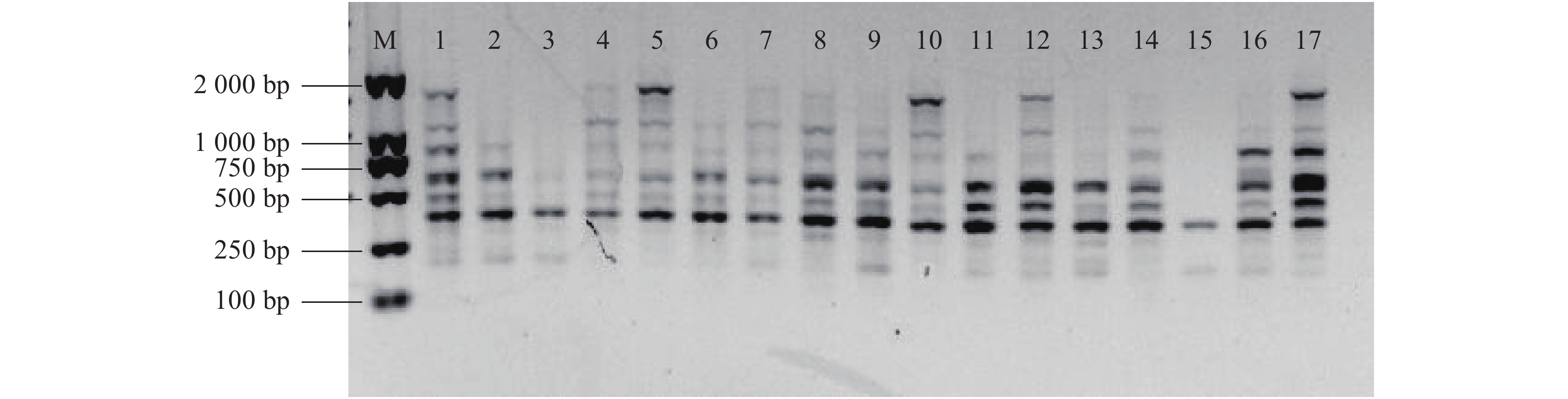
图 2 引物浓度(UBC 841)、2×Taq Master Mix添加量、DNA模板量对ISSR反应体系的影响
注:M为DL15K DNA Maker;A、B、C分别表示引物浓度、2×Taq Master Mix添加量、DNA模板量单因素试验,1~15代表不同处理。
Figure 2. Effect of primer concentration, 2×Taq Master Mix addition, and DNA template amount on ISSR reaction
Note: M: DL15K DNA maker; A, B, and C: primer concentration, 2×Taq Master Mix addition, and DNA template amount, respectively, in single factor test; and 1-15: various treatments.
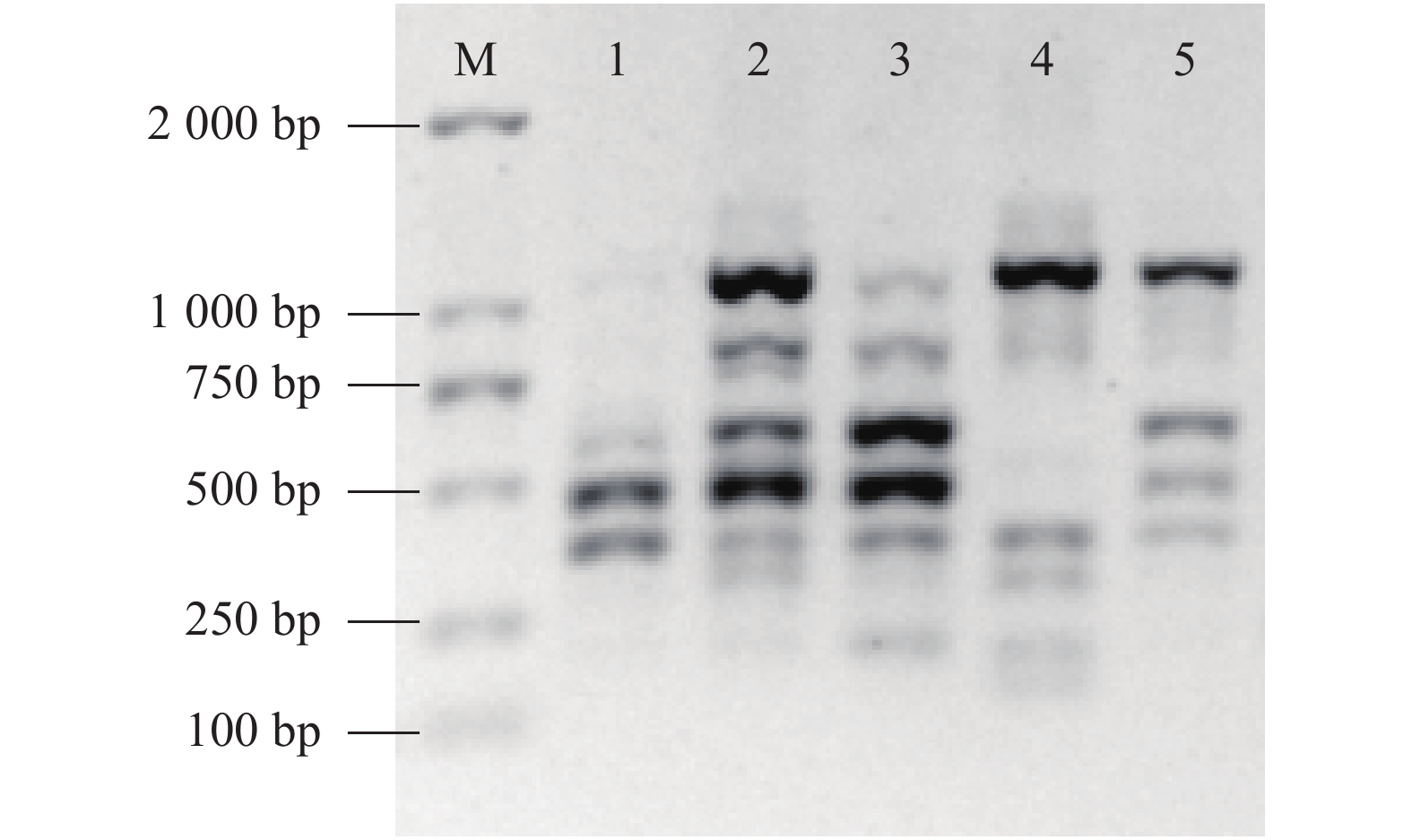
图 6 退火温度对ISSR反应体系的影响
注:M为DL2K DNA Marker;电泳谱1~8依次表示50.5 、50.7、51.2 、51.9 、52.7 、53.3、53.7 和54.0 ℃退火温度下扩增效果。
Figure 6. Effect of annealing temperature on ISSR assay
Note: M: DL2K DNA marker; Electrophoresis 1-8: at ISSR annealing temperatures of 50.5 , 50.7 , 51.2 , 51.9, 52.7, 53.3 , 53.7 and 54.0 ℃, respectively.
表 1 试验材料来源
Table 1. Sources of testing materials
编号
Code品种(系)名
Name来源
Source采样地
Sample Site1 缅甸实生 Myanmar seedling 缅甸 Myanmar 余甘子种质资源圃 Field genebank for Phyllanthus emblica 2 印度大果 India species 印度 India 余甘子种质资源圃 Field genebank for Phyllanthus emblica 3 甜种 Tianzhong 中国广东 Guangdong, China 余甘子种质资源圃 Field genebank for Phyllanthus emblica 4 盈玉 Yingyu 中国云南 Yunnan, China 余甘子种质资源圃 Field genebank for Phyllanthus emblica 5 福建本地种 Fujian native specie 中国福建 Fujian, China 余甘子种质资源圃 Field genebank for Phyllanthus emblica 表 2 单因素试验设计
Table 2. Simple factor experiment
序号
Number编号
Code引物浓度
Primer
concentration/
(μmol·L−1)2×Taq Master Mix
添加量
2×Taq Master Mix
addition amount/μLDNA模板量
DNA template
amount/ng1 A 0.2 12 45 2 0.3 12 45 3 0.4 12 45 4 0.5 12 45 5 0.6 12 45 6 B 0.4 8 45 7 0.4 10 45 8 0.4 12 45 9 0.4 14 45 10 0.4 16 45 11 C 0.4 12 15 12 0.4 12 30 13 0.4 12 45 14 0.4 12 60 15 0.4 12 75 注:在整个反应过程中,随着比较因素梯度的设置变动,相应的调整ddH2O的量以保证反应体系为25 μL。
Note: During reaction process, amount of added ddH2O was continually adjusted to maintain volume of reaction system at 25 μL as gradient of comparison factor changed.表 3 响应面分析因子及水平表
Table 3. Factors and levels of response surface design
反应条件
Reation Condition编码
Code水平 Levels −1 0 1 引物浓度
Primer concentration/(μmol·L−1)X1 0.30 0.35 0.40 2×Taq Master Mix 添加量
2×Taq Master Mix addition amount/μLX2 12 13 14 DNA模板量
DNA template amount/ngX3 25 30 35 表 4 响应面分析方案及试验结果
Table 4. Design and results on factors and levels of response surface test
序号
Order numberX1 X2 X3 评分
Score1 0 0 0 14.2±1.41 2 0 1 −1 4.25±1.26 3 1 0 1 2.12±1.26 4 1 −1 0 9.25±0.5 5 −1 −1 0 10.25±0.82 6 1 0 −1 6.75±0.96 7 0 −1 1 6.38±1.60 8 1 1 0 9.38±0.95 9 0 −1 −1 8.13±0.85 10 0 0 0 13.55±2.46 11 0 1 1 7.38±1.38 12 0 0 0 10.00±1.83 13 1 0 1 5.13±0.82 14 0 1 0 8.75±0.96 15 −1 0 −1 2.25±0.50 16 −1 0 1 7.50±1.29 17 0 0 0 14.75±5.19 表 5 验证试验与结果
Table 5. Validation test results
序号
Number理论解决方案
Theoretical solution实际解决方案
Practical solution理论评分
Theoretical score实际评分
Actual score相对误差
Relative error/%1 X1:0.36 μmol·L−1,X2:13.46 μL,X3:29.41 ng X1:0.35 μmol·L−1,X2:13.5 μL,X3:30 ng 13.1149 11.4±0.55 9.58 2 X1:0.37 μmol·L−1,X2:13.09 μL,X3:29.06 ng X1:0.40 μmol·L−1,X2:13.0 μL,X3:30 ng 13.1304 12.5±0.79 9.39 -
[1] 潘慧清, 朱平, 魏学明, 等. 藏药余甘子研究概况 [J]. 甘肃中医药大学学报, 2019, 36(2):84−88.PAN H Q, ZHU P, WEI X M, et al. On Tibetan medicine Yuganzi (Phylianthi fructus) [J]. Journal of Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, 2019, 36(2): 84−88.(in Chinese) [2] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典: 一部[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020: 186-187. [3] 赵谋明, 刘晓丽, 崔春, 等. 余甘子多酚响应面法优化提取及其抗氧化活性研究 [J]. 食品工业科技, 2007, 28(6):117−120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0306.2007.06.034ZHAO M M, LIU X L, CUI C, et al. Study on the optimizing extraction processing of polyphenol from Phyllanthus emblica L. fruit by method of response surface analysis and its antioxidant activity [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2007, 28(6): 117−120.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0306.2007.06.034 [4] GANTAIT S, MAHANTA M, BERA S, et al. Advances in biotechnology of Emblica officinalis Gaertn. syn. Phyllanthus emblica L. : A nutraceuticals-rich fruit tree with multifaceted ethnomedicinal uses [J]. 3 Biotech, 2021, 11(2): 1−25. [5] ZIETKIEWICZ E, RAFALSKI A, LABUDA D. Genome fingerprinting by simple sequence repeat (SSR)-anchored polymerase chain reaction amplification [J]. Genomics, 1994, 20(2): 176−183. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1151 [6] SARWAT M, DAS S, SRIVASTAVA P S. Analysis of genetic diversity through AFLP, SAMPL, ISSR and RAPD markers in Tribulus terrestris, a medicinal herb [J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2008, 27(3): 519−528. doi: 10.1007/s00299-007-0478-5 [7] 杨培奎, 郑道序, 马瑞君, 等. 潮汕橄榄地方品种(系)遗传多样性的ISSR分析 [J]. 广东农业科学, 2013, 40(23):129−132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2013.23.031YANG P K, ZHENG D X, MA R J, et al. Genetic diversity analysis of Canarium album L. landrances in Chaoshan area by ISSR [J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 40(23): 129−132.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2013.23.031 [8] 张安世, 韩臣鹏, 齐秀娟, 等. 基于ISSR标记的猕猴桃品种遗传多样性分析及指纹图谱构建 [J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 2017, 26(3):19−26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7895.2017.03.03ZHANG A S, HAN C P, QI X J, et al. Genetic diversity analysis and fingerprinting construction of cultivars of Actinidia spp. based on ISSR marker [J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 2017, 26(3): 19−26.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7895.2017.03.03 [9] 李国田, 张美勇, 相昆, 等. 基于ISSR标记的16个核桃品种遗传多样性分析及分子身份构建 [J]. 核农学报, 2015, 29(10):1884−1892. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2015.10.1884LI G T, ZHANG M Y, XIANG K, et al. Analysis of genetic diversity and establishment of molecular ID for 16 walnut varieties based on ISSR markers [J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 29(10): 1884−1892.(in Chinese) doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2015.10.1884 [10] 刘晓生, 郑道序, 周春娟, 等. 潮汕余甘子种质资源遗传多样性与亲缘关系的ISSR分析 [J]. 中国南方果树, 2014, 43(1):18−22.LIU X S, ZHENG D X, ZHOU C J, et al. Analysis of genetic diversity and genetic relationship of Phyllanthus emblica L. Germplasm in Chaoshan area with ISSR [J]. South China Fruits, 2014, 43(1): 18−22.(in Chinese) [11] 周春娟, 詹潮安, 刘晓生, 等. 粤东余甘子种质资源遗传多样性与亲缘关系的ISSR分析[C]//广东省植物学会年会2012年年会论文集. 2012: 16-16.ZHOU C J, ZHAN C A, LIU X S, et al. ISSR Analysis of genetic diversity and genetic relationship of Phyllanthus emblica germplasm resources in eastern Guangdong[C] //Annual meeting of Guangdong Botany Society. 2012: 16-16. (in Chinese) [12] 邵雪花, 刘牛, 赖多, 等. 28份余甘子品种遗传多样性的ISSR分析及指纹图谱构建 [J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 48(8):129−136.SHAO X H, LIU N, LAI D, et al. Genetic diversity analysis and DNA fingerprint mapping of 28 varieties of Phyllanthus emblica L. based on ISSR molecular marker [J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(8): 129−136.(in Chinese) [13] 李巧明, 赵建立. 云南干热河谷地区余甘子居群的遗传多样性研究 [J]. 生物多样性, 2007, 15(1):84−91. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-0094.2007.01.009LI Q M, ZHAO J L. Genetic diversity of Phyllanthus emblica populations in dry-hot valleys in Yunnan [J]. Biodiversity Science, 2007, 15(1): 84−91.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-0094.2007.01.009 [14] 李金璐, 王硕, 于婧, 等. 一种改良的植物DNA提取方法 [J]. 植物学报, 2013, 48(1):72−78. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1259.2013.00072LI J L, WANG S, YU J, et al. A modified CTAB protocol for plant DNA extraction [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2013, 48(1): 72−78.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1259.2013.00072 [15] 尚小红, 严华兵, 曹升, 等. 葛根SCoT-PCR反应体系优化及引物筛选 [J]. 南方农业学报, 2018, 49(1):1−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2018.01.01SHANG X H, YAN H B, CAO S, et al. Optimization of SCoT-PCR reaction system and primer selection for Pueraria DC [J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2018, 49(1): 1−7.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2018.01.01 [16] 阚琦缤, 刘瑞雪, 王晓娅, 等. 响应面优化刺五加总黄酮提取工艺及体外抗氧化研究 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2021, 36(3):358−368.KAN Q B, LIU R X, WANG X Y, et al. Process optimization and in vitro antioxidant activity of flavonoids extracted from Acanthopanax senticosus [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 36(3): 358−368.(in Chinese) [17] 郑良, 李越凡, 赵强, 等. 基于响应面分析的聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯表面微观生物污损超声防除研究 [J]. 表面技术, 2021, 50(4):319−327.ZHENG L, LI Y F, ZHAO Q, et al. Research on removal of microfouling on polymethyl methacrylate surface by ultrasonic antifouling technology based on response surface analysis [J]. Surface Technology, 2021, 50(4): 319−327.(in Chinese) [18] YEH F C. Population genetic analysis of codominant and dominant markers and quantitative traits [J]. Belgian Journal of Botany, 1997: 129. [19] 王建波. ISSR分子标记及其在植物遗传学研究中的应用 [J]. 遗传, 2002, 24(5):613−616. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9772.2002.05.022WANG J B. ISSR markers and their applications in plant genetics [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2002, 24(5): 613−616.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9772.2002.05.022 [20] 黄晓慧, 巫伟峰, 陈春, 等. 中国兰ISSR-PCR反应体系优化及引物筛选 [J]. 南方农业学报, 2018, 49(7):1282−1288. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2018.07.04HUANG X H, WU W F, CHEN C, et al. Optimization and primer screening of ISSR-PCR reaction system for Chinese Orchids [J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2018, 49(7): 1282−1288.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2018.07.04 [21] 刘凤书, 侯开卫, 李绍家, 等. 余甘子的保健价值及开发利用前景 [J]. 自然资源学报, 1993, 8(4):299−306. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3037.1993.04.002LIU F S, HOU K W, LI S J, et al. The health-protecting value of Phyllanthus emblica L. and its prospects for exploitation and utilization [J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 1993, 8(4): 299−306.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3037.1993.04.002 [22] 钟凤林, 王江波, 潘东明, 等. 余甘子ISSR反应体系的优化 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2008(3):166−169.ZHONG F L, WANG J B, PAN D M, et al. Optimization of ISSR reaction system in Phyllanthus emblica L [J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2008(3): 166−169.(in Chinese) -







 下载:
下载: