Sequences and Spatiotemporal Expressions of Vitellogenin and Vitellogenin Receptor Genes of Tessaratoma papillosa
-
摘要:
目的 为荔枝蝽Tessaratoma papillosa的产卵繁殖行为提供分子层面的理论基础,并为荔枝蝽防治的靶点筛选提供有益思路。 方法 采用转录组测序的方法,对荔枝蝽不同发育时期及组织进行转录组测序。通过筛选荔枝蝽的转录组数据和分子克隆的方法获得荔枝蝽卵黄原蛋白及其受体基因,并利用实时荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)分析其在不同发育阶段和组织部位的时空表达情况。 结果 获得荔枝蝽3个卵黄原蛋白基因(T.papi_Vg1,T.papi_Vg2,T.papi_Vg3)和1个卵黄原受体蛋白基因(T.papi_VgRs)。对4个基因进行分析,发现其均具有典型的保守结构域,是典型的昆虫Vg和VgRs基因。从进化关系看,荔枝蝽的Vg和VgRs基因的分子进化与物种之间的进化关系较为匹配。qRT-PCR结果显示Vg1基因在雌虫各个组织中表达量都比较高,雄成虫中仅在淋巴液中表达量较高,而Vg2和Vg3基因仅在雌虫脂肪体中较高表达。VgRs的表达与Vg的表达部位基本一致,在雌虫卵巢中表达量最高,其次是雌虫、雄虫淋巴液和若虫的脂肪体当中,在若虫触角、雄虫触角和雄虫精巢中也有少量表达。 结论 获得了荔枝蝽3个卵黄原蛋白基因和1个卵黄原蛋白受体基因,对其结构和进化关系进行探讨,并对其时空表达情况进行分析,为后续对荔枝蝽新防治靶标的筛选奠定基础。 Abstract:Objective Molecular information associated with the oviposition and reproduction of Tessaratoma papillosa was studied for control of the pest on lychee trees. Method Transcriptome sequencing of T. papillosa in various tissues and developmental stages was conducted. The vitellogenin and vitellogenin receptor genes were obtained by screening the transcriptome database and applying molecular cloning methods. Temporal and spatial expressions of the genes were analyzed using qRT-PCR. Result Three vitellogenin genes (i.e., T. papi_Vg1 , Vg2, and Vg3) and one receptor gene, T. papi_VgRs, were obtained after screening. Homologous analysis showed the genes contained conserved domains typical in the Vg and VgRs of insects. The molecular evolution of Vg and VgRs of T. papillosa paralleled that of the species. The temporal and spatial expressions of Vg1 shown by qRT-PCR were relatively high in all female tissues, but only the lymphatic fluid in adult males, whereas those of Vg2 and Vg3 highly expressed only in female adipose tissue. The expression of VgRs, as well as Vg, was highest in female ovary, followed by female, male lymph fluid, nymph adipose tissue, and minute in nymph antenna, male antenna, and male testis. Conclusion The structures and evolution of the 3 vitellogenin genes and one vitellogenin receptor gene were analyzed. The information on the spatiotemporal expressions of the genes would aid target selection in study for the control ofT. papillosa. -
Key words:
- Vitellogenin gene /
- vitellogenin receptor gene /
- transcriptome /
- evolutionary analysis /
- gene expression
-
图 2 荔枝蝽3个卵黄原蛋白的氨基酸序列一致性分析
注:红色方框标记为信号肽序列,紫色横线为LPD_N结构域,绿色横向标记为DUF1943结构域,粉色横线为VWD结构域,红色横线标记为low complexity结构域。
Figure 2. Homology of amino acid sequences of 3 T. papillosa vitellogenin genes
Note: Red box contains signal peptide sequence; purple line indicates LPD_N domain; green line indicates DUF1943 domain; pink line indicates VWD domain; and red line indicates low complexity domain.
图 1 荔枝蝽3个卵黄原蛋白及1个卵黄原受体蛋白的结构域
注:3个卵黄原蛋白典型的卵黄原蛋白的结构域[LPD_N(紫色),DUF1943(绿色)和VWD结构域(红色)];Vg2在DUF1943结构域前面,包含一个low complexity(774-785)结构域(粉红色);Vg3在VWD结构域之后,包含一个low complexity(1752-1756)结构域(粉红色);卵黄原受体蛋白包含了8个LDLR,3个EGF,7个LY和1个GRAM结构域。
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the structural domains of three vitellogenin and one vitellogenin receptor protein in T. papillosa
Note: Three typical vitellogenin domains [LPD_N (purple), DUF1943 (green) and VWD domain (red)]. Vg2 has one low complexity (774-785) domain (pink) before DUF1943 domain, while Vg3 contains a low complexity (1752-1756) domain (pink)after the VWD domain, and vitellogenin receptor protein contains 8 LDLRs, 3 EGFs, and 7 LY and 1 GRAM domain.
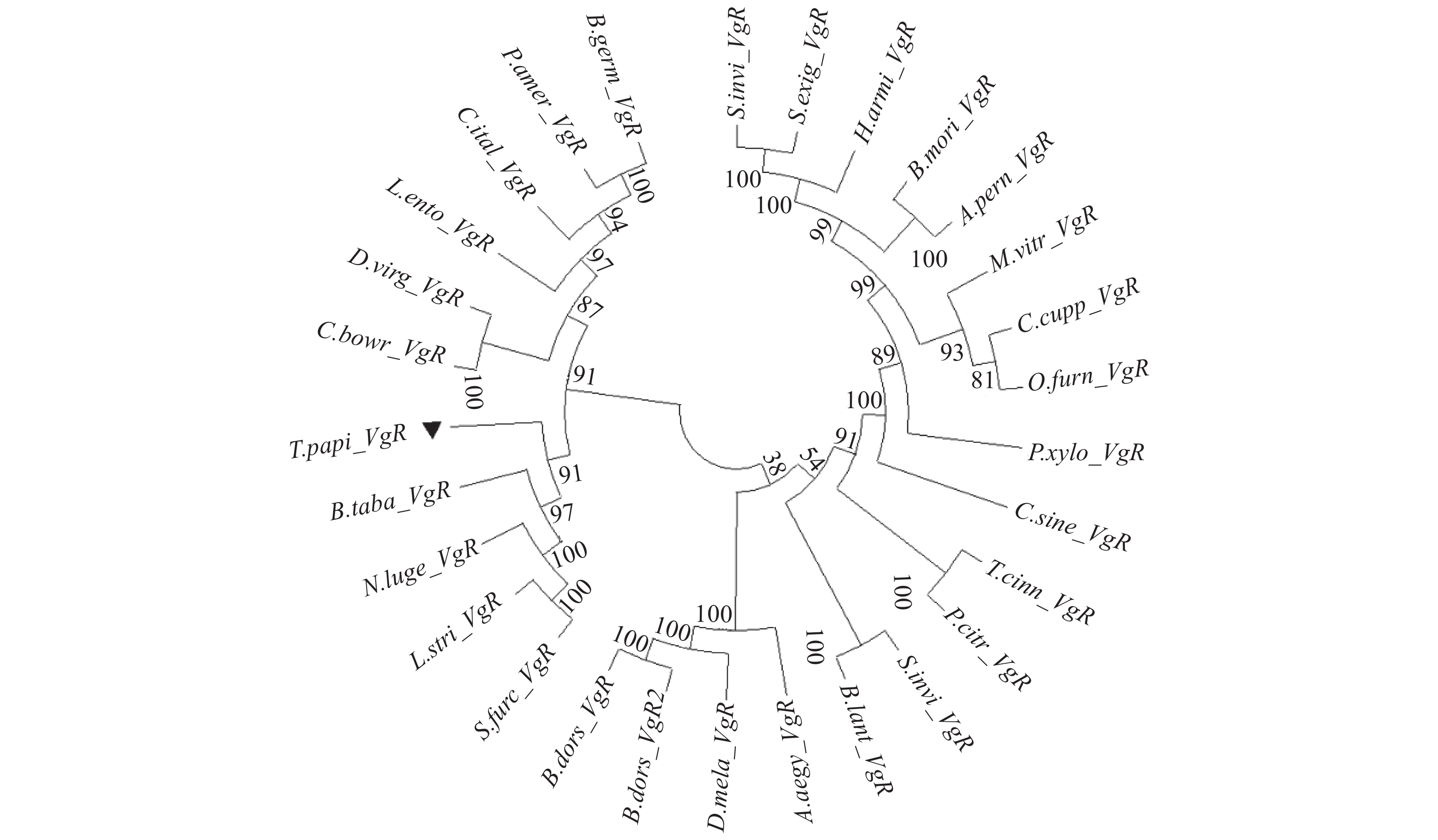
图 3 部分昆虫Vg蛋白进化树
注:构建系统发育树所用到的基因信息见表3,利用MEGA X构建NJ树(Bootstrap值1000),黑色三角形标记为荔枝蝽3个Vg基因。
Figure 3. Phylogenetic tree of partial T. papillosa Vg
Note: Genes used to construct phylogenetic tree are shown in Table 3; MEGA X used to construct NJ tree had a Bootstrap value of 1 000; and 3 T. papillosa Vg are marked by black triangles.
图 4 部分昆虫VgRs蛋白进化树
注:构建系统发育树所用到的基因信息见表4,利用MEGA X构建NJ树(Bootstrap值1000),黑色三角型标记为荔枝蝽VgRs基因。
Figure 4. Phylogenetic tree of partial T. papillosa VgRs
Note: Genes used to construct phylogenetic tree are shown in Table 4; MEGA X used to construct NJ tree had a Bootstrap value of 1 000; and T. papillosa VgRs is marked by black triangle.
图 5 荔枝蝽卵黄原蛋白基因在不同组织、不同发育时期中的表达分析
注:a、c、e分别为Vg1、Vg2、Vg3基因在不同发育时期表达量分析,不同发育时期以若虫为基础进行比较。b、d、f分别为Vg1、Vg2、Vg3基因在不同组织表达量分析,不同组织以若虫触角为基础进行比较。组织部位标注见表1, 18S rRNA基因作为内参基因,图中数据为平均值±标准误,相对表达量差异显著(LSD法多重比对,P<0.05)。
Figure 5. Expressions of vitellogenin genes of T. papillosa in tissues at developmental stages
Note: a, c, and e are expression levels of Vg1, Vg2, and Vg3, respectively, at different developmental stages, and the comparison is based on nymph in different development stages. b, d, and f respectively show the expression levels of Vg1 , Vg2 , and Vg3 genes in different tissues, and the different tissues are compared on the basis of nymph antennae. Tissues abbreviations are shown in Table 1; 18S rRNA gene is internal reference gene used; data are mean±standard error; and relative expression is significantly different determined by multiple comparison by LSD method at P<0.05.
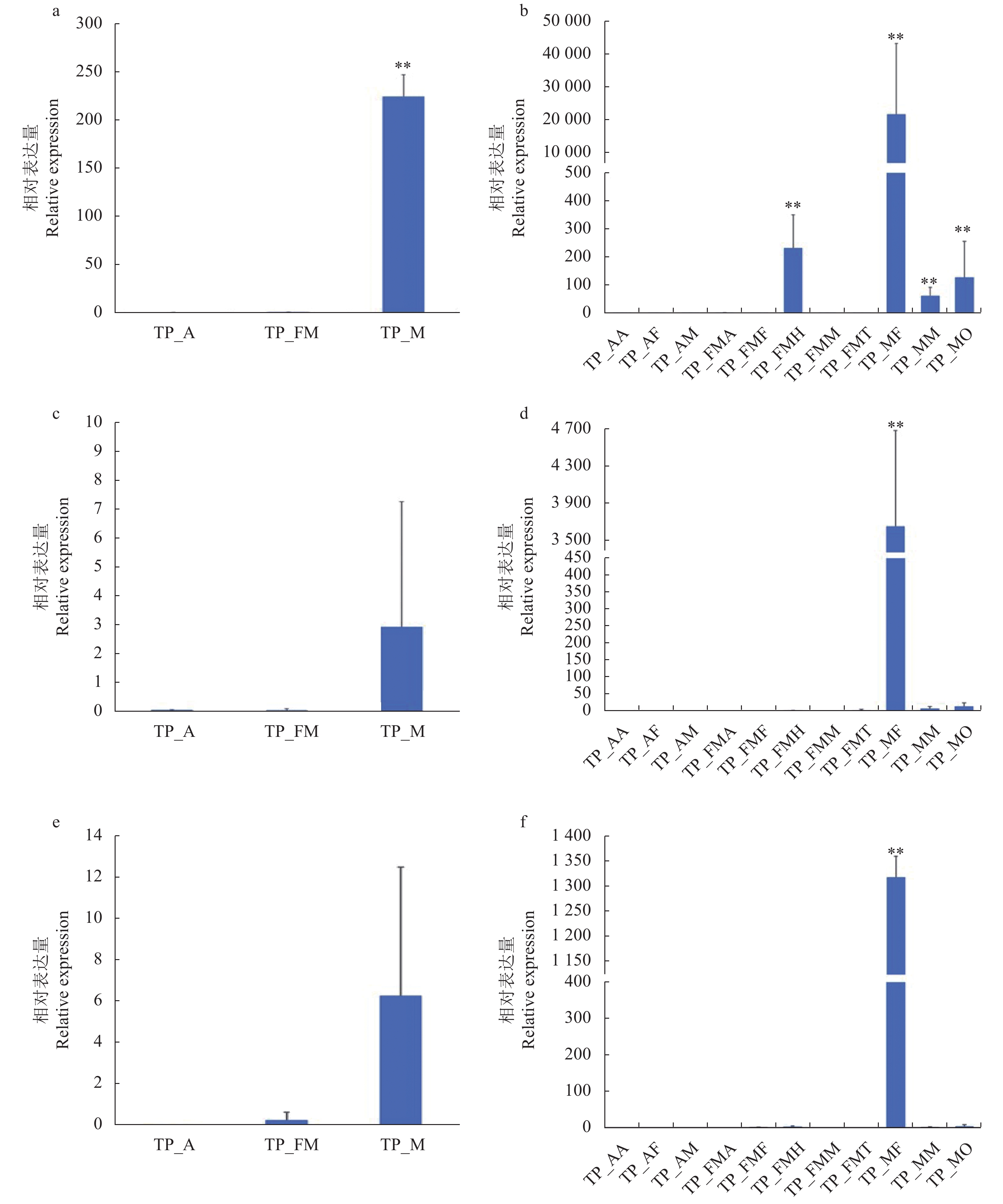
图 6 荔枝蝽卵黄原蛋白受体基因在不同组织,不同发育时期中的表达分析
注:a为VgR基因在不同发育时期表达量分析,不同发育时期以幼虫为基础进行比较。b为VgR基因在不同组织表达量分析,不同组织是以幼虫触角为基础进行比较。组织部位标注见表1, 18S rRNA基因作为内参基因,图中数据为平均值±标准误,相对表达量差异显著(LSD法多重比对,P<0.05)。
Figure 6. Expressions of vitellogenin receptor gene of T. papillosa in tissues at developmental stages
Note: a is VgR expressions at different developmental stages, and the comparison is based on nymph in different development stages.b is VgR expressions in different tissues, and the different tissues are compared on the basis of nymph antennae. Tissues abbreviations are shown in Table 1; 18S rRNA gene is internal reference gene used; data are mean±standard error; and relative expression is significantly different as determined by multiple comparison by LSD method at P<0.05.
表 1 供试荔枝蝽组织
Table 1. Tissues of T. papillosa under study
组织 Tissue 名称 Name 雌虫 Female insect TP_M 雌虫卵巢 Female ovary TP_MO 雌虫中肠 Female midgut TP_MM 雌虫脂肪体 Female fat body TP_MF 雄虫 Male insect TP_FM 雄虫触角 Male antenna TP_FMA 雄虫精巢 Male testis TP_FMT 雄虫中肠 Male midgut TP_FMM 雄虫脂肪体 Male fat body TP_FMF 雄虫淋巴液 Male lymph TP_FMH 若虫触角 Nymph antennae TP_AA 若虫中肠 Nymph midgut TP_AM 若虫脂肪体 Nymph fat body TP_AF 若虫 Nymph TP_A 表 2 PCR扩增引物序列
Table 2. PCR primer sequences
引物名 Primer name 序列 Sequence Vg1-R-all ATGGCGTGGAGTACAGCCCTTCTC Vg1-F-all TCAGCTTGAAATACAGGCCTCTGG Vg2-R-all CATGTGCTGGTCAAGAACACTT Vg2-F-all TTACAAACTGGAAACACA Vg3-R-all ATGTGGACACAAATTTCACTG Vg3-F-all TTACAAACTGGAAACACATT VgR-R-all AGGCACCAAAGGCTTCCAGTTCG VgR-F-all TTACTCTCATCACTCCCATCACGG 表 3 PCR扩增引物序列
Table 3. qRT-PCR primer sequences
引物名 Primer name 序列 Sequence Vg1-R-RT TTTCGCCGCATCCTACGCCG Vg1-F- RT ACAGGACCTGCCGCCATCCT Vg2-R- RT CTGGGCCAGTTCCGGCTTGG Vg2-F- RT GCAGCCTTGACGAGCGCAGT Vg3-R- RT CGGTGCTGTGAGCTAAGGCGG Vg3-F- RT CGGCCCGGCCCTTGTTTCAA VgR-R- RT TGTTCCAATGCACCAGCGGCA VgR-F- RT GTCGCTTCCGTCAGCGCAGT 表 4 荔枝蝽Vg和VgRs序列分析
Table 4. Sequencing of T. papillosa Vg and VgRs
名称
Name序列长度
Sequence
length/bpORF长度
ORF
length/bp编码氨基酸起始位点
Coded amino
acid start site/bp编码氨基酸长度
Coded amino
acid length/bp信号肽长度
Signal peptide
length/个Sec/SPI pI/Mw T. papi_Vg1 5 764 5 541 118-5 658 1 846 11 0.9868 6.53 / 209748.39 T. papi_Vg2 6 216 5 514 6 200-687 1 837 18 0.9214 6.28/209455.11 T. papi_Vg3 6 278 5 577 6 263-687 1 858 21 0.9721 7.89/208177.72 T. papi_VgRs 3 239 3 207 32-3 238 1 068 29 0.9033 4.96/119486.53 表 5 用于进化树分析的Vg基因序列
Table 5. Vg sequences for phylogenetic tree analysis
序号
Serial number缩写
Abbreviations物种名称
Species name分类地位
Classification status学名
Latin name基因ID
Genebank NO.序列长度
Sequence length/bp1 A.aegy_UGALA_Vg 埃及伊蚊 双翅目,蚊科 Aedes aegypti AAU02548 6 504 2 A.luco_Vg1 绿盲蝽 半翅目,盲蝽科 Apolygus lucorum JQ867181 6 122 3 A.luco_Vg2 绿盲蝽 半翅目,盲蝽科 Apolygus lucorum KC136271 6 097 4 A.mell_Vg 意大利蜜蜂 膜翅目,蜜蜂科 Apis mellifera NM_001011578 5 441 5 A.rosa_Vg 黄翅菜叶蜂 膜翅目,叶蜂科 Athalia rosae AB007850 5 783 6 B.germ_Vg 德国小蠊 蜚蠊目,蜚蠊科 Blattella germanica AJ005115 5 749 7 B.Hypo_Vg 小峰熊蜂 膜翅目,蜜蜂科 Bombus hypocrita GQ340749 5 478 8 B.mori_Vg 家蚕 鳞翅目,蚕蛾科 Bombyx mori NM_001043844 5 734 9 B.taba_Q_Vg Q型烟粉虱 半翅目,粉虱科 Bemisia tabaci biotype Q GU332722 6 552 10 B.taba_B_Vg B型烟粉虱 半翅目,粉虱科 Bemisia tabaci biotype B GU332720 6 474 11 C.livi_Vg 黑肩绿盲蝽 半翅目,盲蝽科 Cyrtorhinus lividipennis KJ652904 5 912 12 C.medi_Vg 稻纵卷叶螟 鳞翅目,螟蛾科 Cnaphalocrocis medinalis JN408698 5 779 13 C.sept_Vg 大草蛉 脉翅目,草蛉科 Chrysopa septempunctata JX286617 5 664 14 C.sine_Vg 荔枝蒂蛀虫 鳞翅目,细蛾科 Conopomorpha sinensis MH553377 5 430 15 C.supp_Vg 二化螟 鳞翅目,草螟蛾科 Chilo suppressalis KT724958 5 373 16 D.vari_Vg 变异革蜱 寄螨目,硬蜱科 Dermacentor variabilis AY885250 5 744 17 G.nigr_Vg 油蝉 半翅目,蝉科 Graptopsaltria nigrofuscata AB026848 6 205 18 G.pall_Vg 大眼长蝽 半翅目,长蝽科 Geocoris pallidipennis KP688587 5 667 19 H.armi_Vg 棉铃虫 鳞翅目,夜蛾科 Helicoverpa armigera JX504706 5 271 20 H.axyr_Vg 异色瓢虫 鞘翅目,瓢甲科 Harmonia axyridis KX442718 5 403 21 L.deyr_Vg 大田负蝽 半翅目,土蝽科 Lethocerus deyrollei AB425334 5 865 22 L.disp_Vg 舞毒蛾 鳞翅目,毒蛾科 Lymantria dispar U60186 5 579 23 L.stri_Vg1 灰飞虱 半翅目,飞虱科 Laodelphax striatella KC469580 6 415 24 L.stri_Vg2 灰飞虱 半翅目,飞虱科 Laodelphax striatella KC469581 6 265 25 N. luge_Vg 褐飞虱 半翅目,飞虱科 Nilaparvata lugens AB353856 6 314 26 O.corn_Vg 角额壁蜂 膜翅目,切叶蜂科 Osmia cornifrons KM387561 5 477 27 P.amer_Vg 美洲蟑螂 蜚蠊目,蜚蠊科 Periplaneta americana AB034804 5 854 28 P.nipp_Vg 日本黑瘤姬蜂 膜翅目,姬蜂科 Pimpla nipponica AF026789 5 604 29 R.clav_Vg 豆类点蜂缘蝽 半翅目,缘蝽科 Riptortus clavatus RCU97277 5 736 30 S.exig_Vg 甜菜夜蛾 鳞翅目,夜蛾科 Spodoptera exigua KT599434 5 286 31 S.invi_Vg 红火蚁 膜翅目,蚁科 Solenopsis invicta AF512520 5 638 32 S.litu_Vg 斜纹夜蛾 鳞翅目,夜蛾科 Spodoptera litura EU095334 5 247 33 T.pui_Vg 蒲氏钩蝠蛾 鳞翅目,蝙蝠蛾科 Thitarodes pui MF622538 5 566 34 Z.atra_Vg 大麦虫 鞘翅目,拟步甲科 Zophobas atratus MK890211 5 457 表 6 用于进化树分析的VgRs基因序列
Table 6. VgRs sequences for phylogenetic tree analysis
序号
Serial number缩写
Abbreviations物种名称
Species name分类地位
Classification status学名
Latin name基因ID
Genebank NO.序列长度
Sequence length/bp1 S.invi_VgR 红火蚁 膜翅目,蚁科 Solenopsis invicta NM_001304596.1 5 764 2 B.mori_VgR 家蚕 鳞翅目,蚕蛾科 Bombyx mori NM_001197251.1 5 746 3 A.aegy_VgR 埃及伊蚊 双翅目,蚊科 Aedes aegypti L77800.1 5 544 4 P.amer_VgR 美洲大蠊 蜚蠊目,蜚蠊科 Periplaneta americana AB077047.2 5 722 5 B.germ_VgR 德国小蠊 蜚蠊目,蜚蠊科 Blattella germanica AM050637.1 5 768 6 T.cinn_VgR 棉花红蜘蛛 蜱螨目,叶螨科 Tetranychus cinnabarinus KR090060.1 5 559 7 B.dors_VgR 桔小实蝇 双翅目,实蝇科 Bactrocera dorsalis JX469118.1 6 595 8 D.mela_VgR 黑腹果蝇 双翅目,果蝇科 Drosophila melanogaster U13637.1 6 254 9 S.invi_VgR 红火蚁 膜翅目,蚁科 Solenopsis invicta AY262832.1 5 764 10 L.ento_VgR 嗜虫书虱 啮虫目,虱啮科 Liposcelis entomophila MN398904.1 5 916 11 S.furc_VgR 白背飞虱 半翅目,飞虱科 Sogatella furcifera MN327568.1 5 796 12 B.lant_VgR 兰州熊蜂 膜翅目,蜜蜂科 Bombus lantschouensis MN217253.1 5 519 13 C.cupp_VgR 二化螟 鳞翅目,草螟蛾科 Chilo suppressalis MN227162.1 5 484 14 C.sine_VgR 荔枝蒂蛀虫 鳞翅目,细蛾科 Conopomorpha sinensis KX987145.1 5 424 15 L.stri_VgR 灰飞虱 半翅目,飞虱科 Laodelphax striatella MH347273.1 6 065 16 C.bowr_VgR 大猿叶虫 鞘翅目,叶甲科 Colaphellus bowringi MH104867.1 5 774 17 B.taba_VgR 烟粉虱 半翅目,粉虱科 Bemisia tabaci complex sp. Asia KR818562.2 5 430 18 S.litu_VgR 斜纹夜蛾 鳞翅目,夜蛾科 Spodoptera litura GU983858.1 5 370 19 P.citr_VgR 柑橘全爪螨 蜱螨目,叶螨科 Panonychus citri KC978894.1 5 676 20 H.armi_VgR 棉铃虫 鳞翅目,夜蛾科 Helicoverpa armigera KC181922.2 5 891 21 A.pern_VgR 姬透目天蚕蛾 鳞翅目,天蚕蛾科 Antheraea pernyi JN003583.1 5 847 22 N.luge_VgR 褐飞虱 半翅目,飞虱科 Nilaparvata lugens GU723297.1 6 174 23 C.ital_VgR 意大利蝗 直翅目,蝗科 Calliptamus italicus MK358118.1 5 589 24 S.exig_VgR 甜菜夜蛾 鳞翅目,夜蛾科 Spodoptera exigua KT899978.1 5 445 25 O.furn_VgR 亚洲玉米螟 鳞翅目,螟蛾科 Ostrinia furnacalis MN058042.1 6 289 26 P.xylo_VgR 小菜蛾 鳞翅目,菜蛾科 Plutella xylostella MN044389.1 5 418 27 M.vitr_VgR 豆野螟 鳞翅目,螟蛾科 Maruca vitrata MG799569.1 5 397 28 D.virg_VgR 玉米根萤叶甲 鞘翅目,叶甲科 Diabrotica virgifera KY373243.1 5 612 -
[1] 陈景耀, 柯冲, 陈菁瑛. 荔枝鬼帚病的初步调查及传病试验 [J]. 植物病理学报, 1992(1):26.CHEN J Y, KE C, CHEN J Y. A preliminary study on the incidence and transmission of litchi witches broom [J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 1992(1): 26.(in Chinese) [2] 许长藩, 陈景耀, 夏雨华, 等. 荔枝蝽传播龙眼鬼帚病的研究 [J]. 植物病理学报, 1994, 2(2):60−64.XU C F, CHEN J Y, XIA Y H, et al. On transmission of Longyan witches broom by Tessaratoma papillosa(Drury) [J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 1994, 2(2): 60−64.(in Chinese) [3] 黎荣欣, 赵冬香, 王玉洁, 等. 荔枝蝽防治研究进展 [J]. 热带作物学报, 2013, 34(1):195−200.LI R X, ZHAO D X, WANG Y J, et al. Research progress of controlling Tessaratoma papillosa(Drury) [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2013, 34(1): 195−200.(in Chinese) [4] AMDAM G V, PAGE JR R E, FONDRK M K, et al. Hormone response to bidirectional selection on social behavior [J]. Evolution & Development, 2010, 12(5): 428−436. [5] 戈林泉, 吴进才. 昆虫卵黄蛋白及其激素调控的研究进展 [J]. 昆虫知识, 2010, 47(2):236−246.GE L Q, WU J C. Research progress in insect vitellin and its hormone regulation [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Entomology, 2010, 47(2): 236−246.(in Chinese) [6] MATOZZO V, GAGNÉ F, MARIN M G, et al. Vitellogenin as a biomarker of exposure to estrogenic compounds in aquatic invertebrates: A review [J]. Environment International, 2008, 34(4): 531−545. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2007.09.008 [7] TUFAIL M, TAKEDA M. Molecular characteristics of insect vitellogenins [J]. Journal of Insect Physiology, 2008, 54(12): 1447−1458. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2008.08.007 [8] TUFAIL M, TAKEDA M. Insect vitellogenin/lipophorin receptors: Molecular structures, role in oogenesis, and regulatory mechanisms [J]. Journal of Insect Physiology, 2009, 55(2): 87−103. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2009.01.009 [9] TUFAIL M, TAKEDA M. Molecular cloning, characterization and regulation of the cockroach vitellogenin receptor during oogenesis [J]. Insect Molecular Biology, 2005, 14(4): 389−401. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2583.2005.00570.x [10] CIUDAD L, PIULACHS M D, BELLÉS X. Systemic RNAi of the cockroach vitellogenin receptor results in a phenotype similar to that of the Drosophila yolkless mutant [J]. The FEBS Journal, 2006, 273(2): 325−335. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.05066.x [11] LIU Q N, ZHU B J, LIU C L, et al. Characterization of vitellogenin receptor (VgR) from the Chinese oak silkworm, Antheraea pernyi [J]. Bulletin of Insectology, 2011, 64(2): 167−174. [12] QIAN C, FU W W, WEI G Q, et al. Identification and expression analysis of vitellogenin receptor from the wild silkworm, Bombyx mandarina [J]. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 2015, 89(4): 181−192. doi: 10.1002/arch.21235 [13] WEINSTOCK G M, ROBINSON G E, GIBBS R A, et al. Insights into social insects from the genome of the honeybee Apis mellifera [J]. Nature, 2006, 443(7114): 931−949. doi: 10.1038/nature05260 [14] CHO K H, RAIKHEL A S. Organization and developmental expression of the mosquito vitellogenin receptor gene [J]. Insect Molecular Biology, 2001, 10(5): 465−474. doi: 10.1046/j.0962-1075.2001.00285.x [15] LU K, SHU Y, ZHOU J, et al. Molecular characterization and RNA interference analysis of vitellogenin receptor from Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) [J]. Journal of Insect Physiology, 2015, 73: 20−29. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2015.01.007 [16] BROWN M S, GOLDSTEIN J L. A receptor‐mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis (Nobel lecture) [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English, 1986, 25(7): 583−602. doi: 10.1002/anie.198605833 [17] SAPPINGTON T W, RAIKHEL A S. Molecular characteristics of insect vitellogenins and vitellogenin receptors [J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 1998, 28(5-6): 277−300. doi: 10.1016/S0965-1748(97)00110-0 [18] TUFAIL M, TAKEDA M. Vitellogenin of the cockroach, Leucophaea maderae: Nucleotide sequence, structure and analysis of processing in the fat body and oocytes [J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2002, 32(11): 1469−1476. doi: 10.1016/S0965-1748(02)00067-X [19] HIRAI M, WATANABE D, KIYOTA A, et al. Nucleotide sequence of vitellogenin mRNA in the bean bug, Riptortus clavatus: Analysis of processing in the fat body and ovary [J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 1998, 28(8): 537−547. doi: 10.1016/S0965-1748(98)00052-6 [20] RAIKHEL A S, DHADIALLA T S. Accumulation of yolk proteins in insect oocytes [J]. Annual Review of Entomology, 1992, 37: 217−251. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.37.010192.001245 [21] SNIGIREVSKAYA E S, RAIKHEL A S. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of yolk proteins in insect oocytes[J]. Progress in vitellogenesis[J]. Reproductive biology of invertebrates, 2005, 12(Part B): 199-228. [22] ROEHRKASTEN A, FERENZ H J. Role of the lysine and arginine residues of vitellogenin in high affinity binding to vitellogenin receptors in locust oocyte membranes [J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1992, 1133(2): 160−166. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90064-I [23] 张维球, 刘秀琼. 荔枝蝽象血淋巴物理性状及“还原能”季节性变化的研究 [J]. 昆虫学报, 1973, 16(1):15−24.ZHANG W Q, LIU X Q. Studies on the seasonal changes of the physical properties and the reducing power of the haemolymph of the lychee stinkbug, Tessaratoma papillsoa drury (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) [J]. Acta entomologica sinica, 1973, 16(1): 15−24.(in Chinese) [24] 佘春仁, 潘蓉英, 古德祥, 等. 利用平腹小蜂防治荔枝蝽若干技术问题探讨 [J]. 福建农业大学学报, 1997, 26(4):441−445.SHE C R, PAN R Y, GU D X, et al. Several technological problems of applying Anastatus sp. to control Tessaratoma papillosa [J]. Journal of Fujian Agricultural University, 1997, 26(4): 441−445.(in Chinese) [25] 佘春仁, 潘蓉英. 荔枝蝽的系统解剖及其在测报上的应用 [J]. 福建农学院学报, 1993(1):59−63.SHE C R, PAN R Y. Systematic dissection for forecasting the pest Tessaratoma papillosa Drury [J]. Journal of Fujian Agricultural college, 1993(1): 59−63.(in Chinese) [26] LIVAK K J, SCHMITTGEN T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method [J]. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402−408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 [27] TUFAIL M, NAGABA Y, ELGENDY A M, et al. Regulation of vitellogenin genes in insects [J]. Entomological Science, 2014, 17(3): 269−282. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2008.08.007 [28] UPADHYAY S K, SINGH H, DIXIT S, et al. Molecular characterization of vitellogenin and vitellogenin receptor of Bemisia tabaci [J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(5): e0155306. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155306 [29] HU K, TIAN P, TANG Y, et al. Molecular characterization of vitellogenin and its receptor in Sogatella furcifera, and their function in oocyte maturation [J]. Frontiers in Physiology, 2019, 10: 1532. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01532 [30] ROBERTSON J L, PREISLER H K. Pesticide bioassays with arthropods[M]. CRC Press, 1992: 127. [31] THOMPSON J R, BANASZAK L J. Lipid-protein interactions in lipovitellin [J]. Biochemistry, 2002, 41(30): 9398−9409. doi: 10.1021/bi025674w [32] HUSAIN M, RASOOL K G, TUFAIL M, et al. RNAi-mediated silencing of vitellogenin gene curtails oogenesis in the almond moth Cadra cautella [J]. PloS one, 2021, 16(2): e0245928. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245928 [33] MORANDIN C, HAVUKAINEN H, KULMUNI J, et al. Not only for egg yolk—functional and evolutionary insights from expression, selection, and structural analyses of Formica ant vitellogenins [J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2014, 31(8): 2181−2193. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msu171 [34] PIULACHS M D, GUIDUGLI K R, BARCHUK A R, et al. The vitellogenin of the honey bee, Apis mellifera: Structural analysis of the cDNA and expression studies [J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2003, 33(4): 459−465. doi: 10.1016/S0965-1748(03)00021-3 [35] CORONA M, LIBBRECHT R, WURM Y, et al. Vitellogenin underwent subfunctionalization to acquire caste and behavioral specific expression in the harvester ant Pogonomyrmex barbatus [J]. PLoS Genetics, 2013, 9(8): e1003730. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003730 [36] YANO K, SAKURAI M T, WATABE S, et al. Structure and expression of mRNA for vitellogenin in Bombyx mori [J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1994, 1218(1): 1−10. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(94)90094-9 [37] MARTÍN D, PIULACHS M D, COMAS D, et al. Isolation and sequence of a partial vitellogenin cDNA from the cockroach, Blattella germanica (L.) (Dictyoptera, Blattellidae), and characterization of the vitellogenin gene expression [J]. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 1998, 38(3): 137−146. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6327(1998)38:3<137::AID-ARCH4>3.0.CO;2-P [38] TUFAIL M, HATAKEYAMA M, TAKEDA M. Molecular evidence for two vitellogenin genes and processing of vitellogenins in the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana [J]. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 2001, 48(2): 72−80. doi: 10.1002/arch.1059 [39] SHEN Y, CHEN Y Z, LOU Y H, et al. Vitellogenin and vitellogenin-like genes in the brown planthopper [J]. Frontiers in Physiology, 2019, 10: 1181. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01181 [40] ROMANS P, TU Z, KE Z, et al. Analysis of a vitellogenin gene of the mosquito, Aedes aegypti and comparisons to vitellogenins from other organisms [J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 1995, 25(8): 939−958. doi: 10.1016/0965-1748(95)00037-V [41] SMITH C D, ZIMIN A, HOLT C, et al. Draft genome of the globally widespread and invasive Argentine ant (Linepithema humile) [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2011, 108(14): 5673−5678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1008617108 [42] COLETTA A, PINNEY J W, SOLÍS D Y W, et al. Low-complexity regions within protein sequences have position-dependent roles [J]. BMC Systems Biology, 2010, 4(1): 1−13. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-4-1 [43] LYNCH M, CONERY J S. The evolutionary fate and consequences of duplicate genes [J]. Science, 2000, 290(5494): 1151−1155. doi: 10.1126/science.290.5494.1151 [44] CONG L, YANG W J, JIANG X Z, et al. The essential role of vitellogenin receptor in ovary development and vitellogenin uptake in Bactrocera dorsalis (hendel) [J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2015, 16(8): 18368−18383. doi: 10.3390/ijms160818368 [45] ZHANG W, MA L, XIAO H, et al. Molecular characterization and function analysis of the vitellogenin receptor from the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae) [J]. PloS ONE, 2016, 11(5): e0155785. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155785 [46] YAO Q, XU S, DONG Y Z, et al. Characterization of vitellogenin and vitellogenin receptor of Conopomorpha sinensis Bradley and their responses to sublethal concentrations of insecticide [J]. Frontiers in Physiology, 2018, 9: 1250. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01250 [47] SAYAH F, FAYET C, IDAOMAR M, et al. Effect of azadirachtin on vitellogenesis of Labidura riparia (Insect Dermaptera) [J]. Tissue and Cell, 1996, 28(6): 741−749. doi: 10.1016/S0040-8166(96)80077-2 [48] AMIR M. Histopathological effect of some toxicants on the female reproductive system of Sarcophaga ruficornis Fabricius (Diptera: Sarcophagidae) [J]. Cibtech Journal of Zoology ISSN, 2014, 3(2): 2319−38831. [49] ZHOU C, YANG X B, YANG H, et al. Effects of sublethal concentrations of insecticides on the fecundity of Sogatella furcifera (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) via the regulation of vitellogenin and its receptor [J]. Journal of Insect Science, 2020, 20(5): 14. doi: 10.1093/jisesa/ieaa099 -








 下载:
下载: