Effects of Tannic Acid Supplement on Growth, Slaughter Performance, and Gut Microbiota of Broilers
-
摘要:
目的 旨在探讨饲粮中添加单宁酸对白羽肉鸡生长性能、屠宰性能和肠道微生物菌群组成的影响。 方法 将384只1日龄健康、体重相近的白羽肉鸡,随机分成4组,每组12个重复,每个重复8只。空白对照组饲喂基础饲粮,试验组在基础饲粮中分别添加100、150和200 mg·kg−1的单宁酸,试验期为42 d。 结果 (1)饲粮中添加TA呈现提高肉鸡体重的趋势(P<0.05),添加200 mg·kg−1的TA可显著提高肉鸡的日采食量(P<0.05),且呈现降低料肉比的趋势(P>0.05)。(2)各组间屠宰重、屠宰率、全净膛率和胸肌率差异均不显著(P>0.05);与对照组相比,添加150 mg·kg−1的单宁酸可显著提高腿肌率(P<0.05)。(3)基础饲粮中添加单宁酸对肉鸡的肠道菌群的Alpha多样性无显著影响(P>0.05),添加200 mg·kg−1的单宁酸可显著提高肠道中乳酸杆菌属的相对丰度(P<0.05)。 结论 基础饲粮中添加单宁酸可提高肉鸡的生长性能和腿肌率,增加肠道中有益菌乳酸杆菌属的数量。 Abstract:Objective Effects of tannic acid (TA) supplementation in diet on the growth, slaughter performance, and gut microbiota of broilers were studied. Method A total of 384 one-day-old healthy broilers with similar body weight were randomly divided into 4 groups with 12 replicates per group and 8 broilers per replicate. The birds were given either a control diet free of TA or diets containing 100, 150, or 200 mg·kg−1 of TA for 42 d prior to slaughtering and testing. Result (1) The TA supplementation tended to increase the broiler weight (P<0.05). The inclusion of 200 mg·kg−1 of TA in forage significantly increased the average daily feed intake of the broilers over control (P<0.05). The feed/weight gain ratios decreased as the supplement increased on the 4 treatment groups (P>0.05). (2) No significant effects of the TA supplementation were found on the dressing weight and the rate of dressing, evisceration, or breast muscle of the slaughtered broilers (P>0.05). However, the presence of 150 mg·kg−1of TA in diet significantly increased the muscle yield (P<0.05). (3) TA exerted no significant effect on the α diversity of gut microbiota (P>0.05), but a 200 mg·kg−1 supplementation significantly increased the relative abundance of Lactobacillus in the intestines of the broilers. Conclusion The dietary TA supplement improved the growth, proportionally increased the leg muscle, and boosted the population of beneficial enteric Lactobacillus of the broilers. -
Key words:
- Tannic acid /
- broilers /
- growth /
- slaughter performance /
- gut microbiota
-
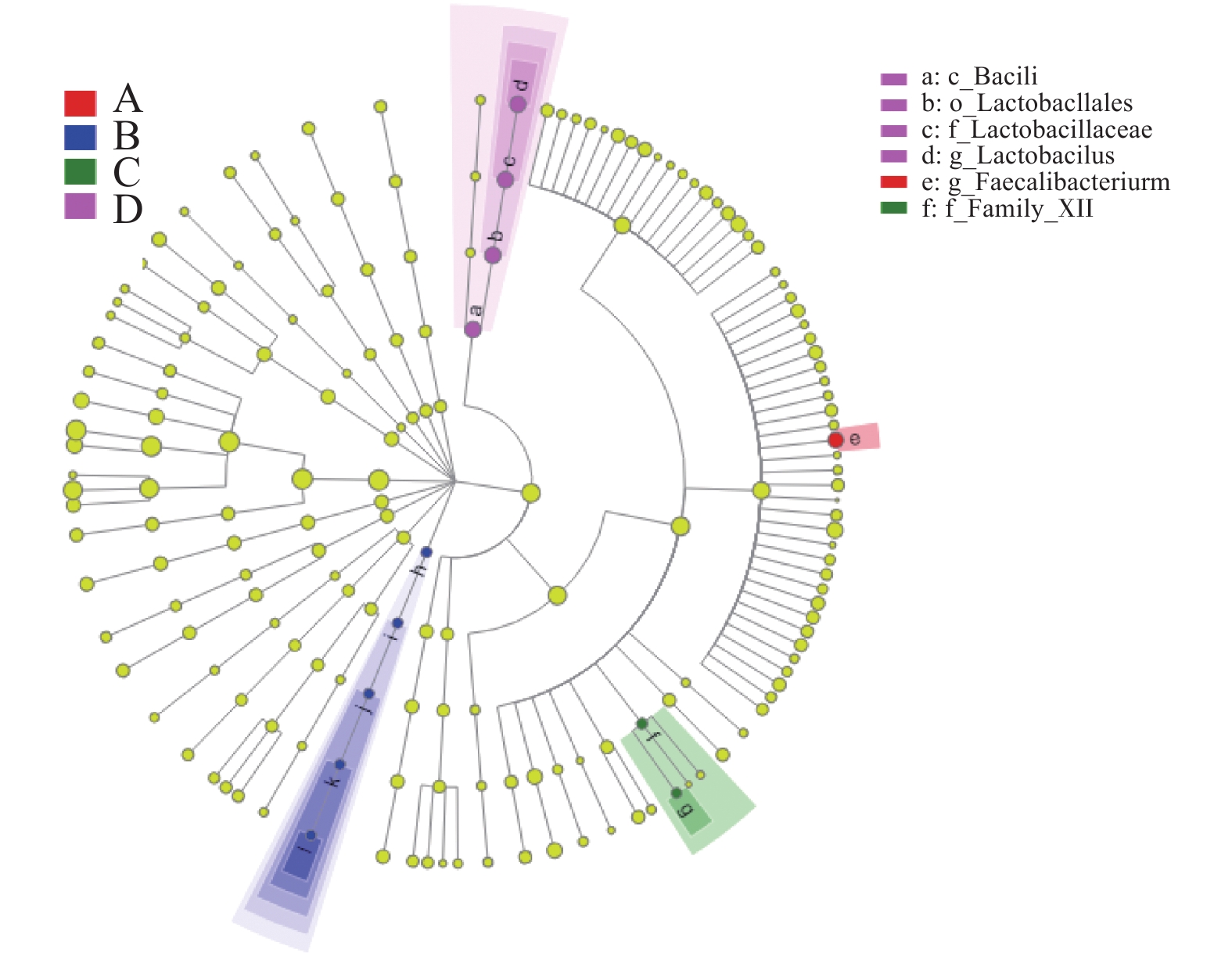
图 4 LEfSe分析差异物种
注:圆圈由里到外表示物种分类水平由门到属,差异物种用彩色圆圈和扇形表示,每个圆圈的直径与该物种的相对丰度成比例,黄色圆圈表示差异不显著。
Figure 4. LEfSe analysis on different microbes
Note: Concentric circles represent phylum (inside) to genus (outside). Biomarker taxa are shown with colored circles and shaded areas. Diameter of a circle is proportional to relative abundance of that taxa in a community. Yellow circle indicates no significance.
表 1 基础饲粮组成及营养水平(风干基础)
Table 1. Composition and nutrient levels of basal diet used in trial (on air-dry basis)
% 原料
Ingredients含量
Content1~3周
1–3 weeks4~6周
4–6 weeks玉米 Corn 52.00 58.00 豆粕 Soybean meal 34.70 27.30 膨化大豆 Extruded soybean 3.00 3.00 国产鱼粉 Domestic fish meal 2.00 1.50 豆油 Soybean oil 4.00 6.00 石粉 Limestone 1.21 1.21 磷酸氢钙 CaHPO4 1.53 1.43 DL-蛋氨酸 DL-Met 0.26 0.26 预混料 Premix1) 1.00 1.00 氯化钠 NaCl 0.30 0.30 合计 Total 100.00 100.00 营养水平 Nutrient levels 2) 代谢能 ME/(MJ·kg−1) 12.46 13.23 粗蛋白 CP 22.14 19.17 钙 Ca 1.05 0.98 有效磷 AP 0.51 0.44 赖氨酸 Lys 1.16 0.97 蛋氨酸+半胱氨酸 Met + Cys 1.08 0.99 注:① 预混料为每千克饲粮提供:VA 9500 IU,VD 3 000 IU,VE 22.5 mg,VK 3.0 mg,VB1 3.0 mg,VB2 7.5 mg,VB6 3.0 mg,VB12 0.22 mg,泛酸钙 15.0 mg,烟酸 30.0 mg,叶酸 1.5 mg,生物素 0.12 mg,胆碱 400 mg,碘 0.40 mg。② 营养水平均为计算值。
Note: ① The premix provided the following per kg of the diet: VA 9500 IU,VD 3 000 IU,VE 22.5 mg,VK 3.0 mg,VB1 3.0 mg,VB2 7.5 mg,VB6 3.0 mg,VB12 0.22 mg,calcium pantothenate 15.0 mg,nicotinic acid 30.0 mg,folic acid 1.5 mg,biotin 0.12 mg,chloride 400 mg,I 0.40 mg. ② Nutrient levels were calculated.表 2 TA对白羽肉鸡生长性能的影响
Table 2. Effect of feeding TA-containing diets on growth of broilers
项目
Items0(CK) 100 mg·kg−1 TA 150 mg·kg−1 TA 200 mg·kg−1 TA P值
P value初重 IBM/g 47.00±0.47 47.78±1.26 48.00±1.15 46.89±0.51 0.125 末重 FBM/g 2303.41±248.95 c 2327.67±255.48 ab 2343.07±261.72 ab 2476.67±230.78 a 0.031 1~3周 1–3 weeks 日采食量 ADFI/g 36.09±2.49 37.00±2.66 36.99±3.47 38.47±2.38 0.149 日增重 ADG/g 41.91±1.18 41.41±3.72 40.95±2.16 42.75±2.25 0.216 料重比 F/G 1.16±0.17 1.12±0.12 1.11±0.24 1.11±0.16 0.067 4~6周 4–6 weeks ADFI 73.59±4.96 b 73.84±3.34 b 74.58±5.26 ab 79.51±4.15 a 0.021 ADG 118.10±6.15 115.65±3.55 115.69±6.13 118.47±4.87 0.061 F/G 1.60±0.25 a 1.57±0.18 ab 1.55±0.14 ab 1.49±0.22 b 0.046 1~6周 1–6 weeks ADFI 53.72±2.76 b 54.28±2.31 b 54.64±2.52 b 57.85±3.19 a 0.016 ADG 78.44±1.95 77.62±2.33 76.50±3.83 79.26±2.71 0.379 F/G 1.46±0.21 1.43±0.14 1.40±0.11 1.37±0.16 0.631 注:同行数据后的不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),相同或无字母表示差异不显著(P>0.05)。下表同。
Note: Within a row, values with different small letters indicate significantly different between dietary treatments (P<0.05), while with the same letter or no letter means no significant difference (P>0.05). The same as below.表 3 TA对肉鸡屠宰性能的影响
Table 3. Effect of dietary TA supplement on slaughter performance of broilers
项目
Items0(CK) 100 mg·kg−1 TA 150 mg·kg−1 TA 200 mg·kg−1 TA P值
P value屠宰重 Dressing weight/g 2190.67±87.46 2287.33±59.68 2322±85.84 2556.67±80.05 0.761 屠宰率 Dressing rate/% 94.9±1.66 93.55±0.72 93.47±1.07 94.61±1.08 0.218 全净膛率 All eviscerated rate/% 81.97±4.66 78.5±1.26 77.16±1.97 80.01±0.77 0.126 胸肌率 Breast muscle rate/% 27.08±3.45 27.95±3.97 24.98±1.85 28.32±2.34 0.433 腿肌率 Leg muscle rate/% 12.06±0.48 b 12.36±0.78 b 13.43±1.03 a 12.56±0.98 b 0.037 表 4 TA对肉鸡肠道微生物Alpha多样性指数的影响
Table 4. Effect of dietary TA supplement on α diversity of enteric microbiota in broilers
项目
Items0(CK) 100 mg·kg−1 TA 150 mg·kg−1 TA 200 mg·kg−1 TA P值
P valueACE指数 ACE index 259.88±13.25 251.53±17.97 265.62±14.03 259.42±16.98 0.634 Chao 1指数 Chao 1 index 261.70±11.70 257.64±18.58 270.01±15.19 257.58±17.08 0.494 Shannon指数 Shannon index 2.44±0.05 2.61±0.43 2.57±0.19 2.39±0.39 0.332 Simpson指数 Simpson index 0.26±0.05 0.23±0.05 0.21±0.03 0.25±0.06 0.235 覆盖度指数 Coverage index 0.999 0.999 0.999 0.999 0.270 -
[1] 王吉, 张琳玉, 刘翔燕, 等. 单宁酸诱导猪肾细胞氧化损伤和凋亡 [J]. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32(9):4327−4336.WANG J, ZHANG L Y, LIU X Y, et al. Tannic acid induces oxidative damage and apoptosis in pig kidney cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32(9): 4327−4336.(in Chinese) [2] HUANG Q Q, LIU X L, ZHAO G Q, et al. Potential and challenges of tannins as an alternative to in-feed antibiotics for farm animal production [J]. Animal Nutrition, 2018, 4(2): 137−150. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2017.09.004 [3] 李光先, 孙侠, 李敏, 等. 五倍子单宁酸对SD大鼠的皮肤毒性研究 [J]. 毒理学杂志, 2020, 34(4):348−351.LI G X, SUN X, LI M, et al. Dermatological toxicity of gallnut tannic acid on SD rats [J]. Journal of Toxicol, 2020, 34(4): 348−351.(in Chinese) [4] 苟昌勇, 施晓丽, 孙澄慧, 等. 五倍子单宁酸对断奶仔猪生长性能、腹泻和养分消化的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32(12): 1-8GOU C Y, SHI X L, SUN C H, et al. Effects of gallnut tannic acid on growth performance, diarrhea and nutrient digestion in weaned piglets[J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32(12): 1−8[2020-08-10]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.5461.S.20200807.0940.008.html. (in Chinese) [5] ESPINOSA-GÓMEZ F C, SERIO-SILVA J C, SANTIAGO-GARCÍA J D, et al. Salivary tannin-binding proteins are a pervasive strategy used by the folivorous/frugivorous black howler monkey [J]. American Journal of Primatology, 2018(2): e22737. [6] BIONDI L, RANDAZZO C L, RUSSO N, et al. Dietary supplementation of tannin-extracts to lambs: effects on meat fatty acids composition and stability and on microbial characteristics [J]. Foods, 2019, 8(10): 469. doi: 10.3390/foods8100469 [7] BRUS M, DOLINŠEK J, CENCIČ A, et al. Effect of chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.) wood tannins and organic acids on growth performance and faecal microbiota of pigs from 23 to 127 days of age [J]. Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 2013, 19(4): 841−847. [8] STARČEVIĆ K, KRSTULOVIĆ L, BROZIĆ D, et al. Production performance, meat composition and oxidative susceptibility in broiler chicken fed with different phenolic compounds [J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2015, 95(6): 1172−1178. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.6805 [9] WANG M W, HUANG H J, LIU S, et al. Tannic acid modulates intestinal barrier functions associated with intestinal morphology, antioxidative activity, and intestinal tight junction in a diquat-induced mouse model [J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(55): 31988−31998. doi: 10.1039/C9RA04943F [10] ENGSTRÖM M T, ARVOLA J, NENONEN S, et al. Structural features of hydrolyzable tannins determine their ability to form insoluble complexes with bovine serum albumin [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2019, 67(24): 6798−6808. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b02188 [11] CHUNG K T, WONG T Y, WEI C I, et al. Tannins and human health: a review [J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 1998, 38(6): 421−464. doi: 10.1080/10408699891274273 [12] CHAMORRO S, VIVEROS A, REBOLÉ A, et al. Influence of dietary enzyme addition on polyphenol utilization and meat lipid oxidation of chicks fed grape pomace [J]. Food Research International, 2015, 73: 197−203. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2014.11.054 [13] EBRAHIM R, LIANG J, JAHROMI M, et al. Effects of tannic acid on performance and fatty acid composition of breast muscle in broiler chickens under heat stress [J]. Italian Journal of Animal Science, 2015, 14(4): 2015−3956. [14] 陈赛娟, 谷新晰, 刘涛, 等. 单宁酸对家兔肠道形态和内源酶活性的影响 [J]. 饲料工业, 2015, 36(9):14−16.CHEN S J, GU X X, LIU T, et al. Effect of tannic acid on intestinal morphology and endogenous enzyme activity of rabbits [J]. Feed Industry, 2015, 36(9): 14−16.(in Chinese) [15] WANG M W, HUANG H, HU Y P, et al. Effects of dietary microencapsulated tannic acid supplementation on the growth performance, intestinal morphology, and intestinal microbiota in weaning piglets [J]. Journal of Animal Science, 2020, 98(5): 1−12. [16] 毛亚芳, 周振波, 杜红岩, 等. 杜仲叶粉对绿壳蛋鸡蛋品质、血清生化指标、屠宰性能及肉质性状的影响 [J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2021, 48(1):161−171.MAO Y F, ZHOU Z B, DU H Y, et al. Effects of Eucommia ulmoides leaves power on egg quality, serum biochemical indexes, slaughtering performance and meat quality in green-shell layers [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2021, 48(1): 161−171.(in Chinese) [17] 陈秀琴, 黄梅清, 郑敏, 等. 病毒感染与肠道菌群关系的研究进展 [J]. 中国兽医学报, 2019, 39(6):1239−1244.CHEN X Q, HUANG M Q, ZHENG M, et al. Research progress of the relationship between viral infection and gut microbiota [J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2019, 39(6): 1239−1244.(in Chinese) [18] 徐静, 张子儒, 王德贺, 等. 饮水中添加大蒜精油对蛋鸡生长性能、肠道组织形态及盲肠菌群的影响 [J]. 动物营养学报, 2021, 33(1):308−316. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2021.01.031XU J, ZHANG Z R, WANG D H, et al. Effects of adding garlic essential oil into drinking water on growth performance, intestinal tissue morphology and cecum microbial flora of layer hens [J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2021, 33(1): 308−316.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2021.01.031 [19] 杨曾乔, 丁雪梅, 白世平, 等. 不同产蛋水平肉种鸡繁殖性能、肠道组织形态、卵巢功能和盲肠微生物区系差异研究 [J]. 动物营养学报, 2021, 33(1):270−284. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2021.01.028YANG C Q, DING X M, BAI S P, et al. Differences in reproductive performance, intestinal tissue morphology, ovarian function and caecal microbiota of broiler [J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2021, 33(1): 270−284.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2021.01.028 [20] 陈秀琴, 黄梅清, 郑敏, 等. 动物肠道菌群与病原微生物感染关系的研究进展 [J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2019, 46(2):628−634.CHEN X Q, HUANG M Q, ZHENG M, et al. Research progress on the relationship between gut microbiota of animals and pathogenic microorganism infection [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2019, 46(2): 628−634.(in Chinese) [21] JUMPERTZ R, LE D S, TURNBAUGH P J, et al. Energy-balance studies reveal associations between gut microbes, caloric load, and nutrient absorption in humans [J]. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2011, 94(1): 58−65. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.110.010132 [22] BIAGI G, CIPOLLINI I, PAULICKS B R, et al. Effect of tannins on growth performance and intestinal ecosystem in weaned piglets [J]. Archives of Animal Nutrition, 2010, 64(2): 121−135. doi: 10.1080/17450390903461584 [23] DANIELSON A D, PEO JR E R, SHAHANI K M, et al. Anticholesteremic property of Lactobacillus Acidophilus yogurt fed to mature boars [J]. Journal of Animal Science, 1989, 67(4): 966−974. doi: 10.2527/jas1989.674966x -







 下载:
下载: