Inhibitory Activity and Mechanism of Bacillus velezensi Strains against Soil-borne Pathogens
-
摘要:
目的 明确6株贝莱斯芽胞杆菌(Bacillus velezensi)对7种土传病原菌的抑制活性,探究其拮抗机理,为土传病害的生物防治提供菌种资源和理论依据。 方法 采用平板对峙法测定拮抗菌株对7种土传病原菌的抑菌活性,用显微镜观察拮抗菌对病原物菌丝形态的影响;采用叶片离体接种法测定其防治效果,鉴别性培养基测定拮抗菌株产生的胞外酶,并用PCR扩增技术检测拮抗菌携带抗生素相关基因(mycB、fenB、ituA、sfp、bamC、erisA、spaS、bacA、yndJ和qk)。 结果 所有测试菌株(NN01、NN02、NN04、NN05、NN88和NN95)对核盘菌(Sclerotinia sclerotiorum)、灰葡萄孢菌(Botrytis cinerea)、立枯丝核菌(Rhizoctonia solani)、尖孢镰刀菌古巴专化型(Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense)、齐整小核菌(Scleritium rolfsii )和烟草疫霉(Phytophthora nicotianae)等土传病原菌的菌丝生长均具有明显的抑制作用,其中对齐整小核菌抑制作用最明显;NN01、NN02、NN04和NN88对尖孢镰刀菌菌丝有较好的抑制效果,菌丝生长抑制率为40.56%~56.30%;抑菌带边缘菌丝的形态发生明显改变,原生质浓缩或外泄、菌丝破裂和颜色加深;所有拮抗菌株均能较好抑制桑白绢病和莴苣菌核病病斑的发展,防治效果分别为53.40%~71.32%和43.57%~65.68%,高于或与枯草芽胞杆菌对照防治效果相当;所有拮抗菌都能产纤维素酶和蛋白酶,除了NN95基因组不携带fenB,其余所有菌株都携带mycB、ituA、 fenB、bacA和yndJ等脂肽类抗生素相关基因。 结论 所有测定的贝莱斯芽胞杆菌对6种土传病原菌均具有抑菌活性,能产纤维素酶和蛋白酶,携带mycB、ituA、fenB、 bacA和yndJ等5种抗生素相关基因,具有防治土传病害的潜力。 Abstract:Objective Inhibitory activities and antagonistic mechanisms of Bacillus velezensi (Bv) strains against certain soil-borne pathogens were studied in search for new venues of biological disease control. Method Antagonism of 6 Bv strains, NN01, NN02, NN04, NN05, NN88, and NN95, on 7 soil-borne pathogens, Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, Scleritium rolfsii, Botrytis cinerea, Rhizoctonia solani, and Phytophthora nicotianae, were studied using a plate confrontation test. Morphological responses of the pathogen mycelia to the Bv strains were observed under an optic microscope, and the control efficacy verified in vitro on mulberry and lettuce leaves. Activities of the extracellular enzymes (e.g., cellulase, protease, and β-1,3-glucanase) produced by the Bv strains were identified with differential media, and 10 antibiotic-related genes (i.e., mycB, fenB, ituA, sfp, bamC, Erisa, spaS, bacA, yndJ, and Qk ) in the bacteria detected by PCR amplification with specific primers. Result To varying extents the 6 Bv strains inhibited the mycelia growth of the 6 target pathogens. The strongest effect was shown on S. rolfsii. NN01, NN02, NN04, and NN88 displayed inhibition rates ranging from 40.56% to 56.30% on F. oxysporum. The appearance of mycelia on edge of inhibition rings changed significantly with broken, leaking intracellular substances, and darked color. In vitro the Bv strains significantly inhibited disease development on the plant leaves by S. sclerotiorum with a control effect of 53.40-71.32% and 43.57-65.68% by S. rolfsii, which were higher than or equal to the inhibition by B. subtilis. All 6 Bv strains secreted proteases and cellulases with the presence of 5 lipopeptide antibiotic-related genes (i.e., mycB, fenB, ituA, bacA, and yndJ), except no fenB found in NN95. Conclusion All 6 Bv strains had varying inhibitory effects against the 7 soil-borne pathogens. They showed extracellular protease and cellulase activities, and almost all of them carried 5 lipopeptide antibiotic-related genes. These Bv strains could potentially be applied as biocontrol agents for control of diseases caused by the soil-borne pathogens. -
图 1 贝莱斯芽胞杆菌(A)及其无菌发酵液(B)对 7 种土传病害病原菌菌丝生长的抑制效果
注:CK,LB 培养基;1,核盘菌;2,灰葡萄孢;3,立枯丝核菌;4,尖孢镰刀菌古巴专化;5,齐整小核菌;6,烟草疫霉;7,终极腐霉。
Figure 1. Inhibitory effects of Bv culture liquid (A) and cell-free fermentation broth (B) against 7 soil-borne pathogens
Note: CK, LB medium;1, S. sclerotiorum; 2, B. cinerea; 3, R. solani;4, F. oxysporum f. sp. cubense; 5, S. rolfsii; 6, P.a nicotianae; 7, P. ultimum.
图 4 拮抗贝莱斯芽胞杆菌的纤维素酶、蛋白酶和β-1,3-葡聚糖酶活性检测
注:①1:NN01;2:NN02;3:NN04;4:NN05;5:NN88;6:NN95。②A:纤维素酶;B:蛋白酶;C:β-1,3-葡聚糖酶。
Figure 4. Determination of cellulase, protease, and amylase activities in Bv strains
Note: ①1: NN01; 2: NN02; 3: NN04; 4: NN05; 5: NN88; 6: NN95. ② A: Cellulase; B: Protease; C: β-1,3-glucanase.
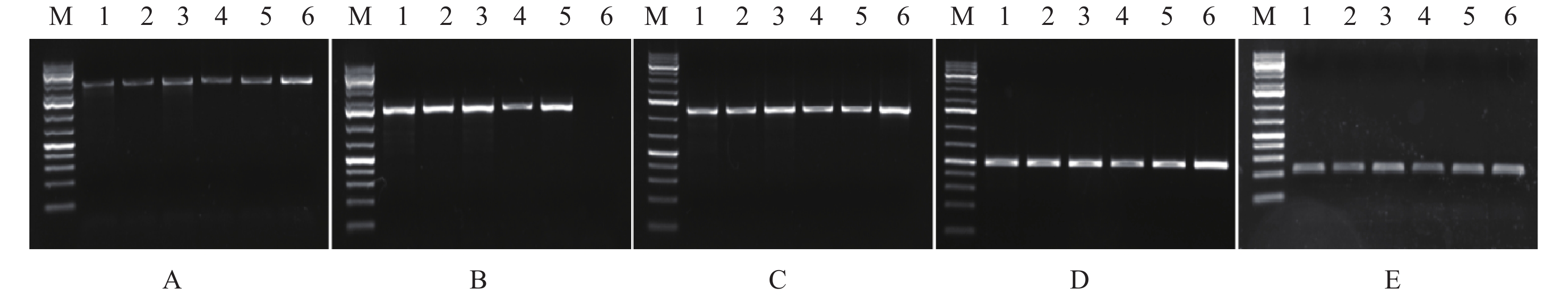
图 5 贝莱斯芽胞杆菌菌株中抗生素合成基因电泳检测结果
注:①M:1 kb DNA marker;1:NN01;2:NN02;3:NN04;4:NN05;5:NN88;6:NN95。② A:mycB (2 024 bp);B:fenB (1 400 bp);C:ituA (1 150 bp);C:mycB (2 024 bp);D:bacA (498 bp);E:yndj (212 bp)。
Figure 5. Detection of antibiotic-related genes in Bv strains by PCR amplification
Note: ①M: 1 kb DNA marker; 1: NN01; 2: NN02; 3: NN04; 4: NN05; 5: NN88; 6: NN95. ② A: mycB (2 024 bp); B: fenB (1 400 bp); C: ituA (1 150 bp); C: mycB (2 024 bp); D: bacA (498 bp); E: yndj (212 bp).
表 1 用于检测拮抗贝莱斯芽胞杆菌抗生素相关基因的引物
Table 1. Primers used to detect antibiotic-related genes in Bv strains
基因
Genes引物名称及其序列(5′→3′)
Primers and the sequences片段大小
Product size/bp抑菌物质
Antifungal substancesmycB MycB-F:ATGTCGGTGTTTAAAAATCAAGTAACG
MycB-R:TTAGGACGCCAGCAGTTCTTCTATTGA2 024 抗霉枯草菌素
MycosubtilinfenB FenB-F:CTATAGTTTGTTGACGGCTC
FenB-R:CAGCACTGGTTCTTGTCGCA1 600 丰原素
FengycinituA ItuA-F:ATGTATACCAGTCAATTCC
ItuA-R:GATCCGAAGCTGACAATAG1 047 伊枯草菌素
Iturinsfp Sfp-F:ATGAAGATTTACGGAATTTA
Sfp-R:TTATAAAAGCTCTTCGTACG675 表面活性素
SurfactinbamC Bamc-F:AGTAAATGAACGCGCCAATC
Bamc-R:CCCTCTCCTGCCACATAGAG957 杆菌霉素
BacillomycinerisA Erisa-f:TTCGATGARTTCGATTTGGA
Erisa-r:GCAGCCCTTTTTCTTTTATTTC357 Ericin spaS Spas-f:GGTTTGTTGGATGGAGCTGT
Spas-r:GCAAGGAGTCAGAGCAAGGT375 枯草菌素
SubtilinbacA Baca-f:CAGCTCATGGGAATGCTTTT
Baca-r:CTCGGTCCTGAAGGGACAAG498 溶杆菌素
Bacylisinyndj 147-F:CAGAGCGACAGCAATCACAT
148-147-R:TGAATTTCGGTCCGCTTATC212 假定蛋白
Yndjqk Qk1-F:CTTAAACGTCAGAGGCGGAG
Qk1-R:ATTGTGCAGCTGCTTGTACG704 枯草杆菌蛋白酶
Subtilisin表 2 拮抗贝莱斯芽胞杆菌对土传病原菌菌丝生长的影响
Table 2. Effect of Bv strains on in vitro growth of soil-borne pathogens
病原菌
Pathogens菌株及抑制率
B. velezensi strains and Inhibition rate /%NN01 NN02 NN04 NN05 NN88 NN95 齐整小核菌(S. rolfsii ) 67.59±4.12 a 76.11±0.61 a 74.81±6.11 a 46.67±6.70 a 62.41±2.57 a 28.70±3.88 a 核盘菌(S. sclerotiorum) 34.07±16.19d 52.22±3.14 b 19.44±8.85 c 14.81±2.18 b 13.50±2.58 d 10.93±3.47 b 灰葡萄孢菌(B. cinerea) 56.39±1.67 b 11.11±4.16 c 13.056±2.46 c 13.89±5.20 b 12.78±3.20 d 22.78±4.11 ab 尖孢镰刀菌古巴专化型(F. oxysporum f. sp. cubense) 47.78±1.41 c 46.67±0.99 b 56.30±3.63 b 11.67±1.53 b 40.56±9.65 b 11.67±1.17 b 烟草疫霉(P. nicotianae) 10.00±4.97 e 12.96±1.67 c 13.70±1.67 c 15.74±1.30 b 19.26±2.69 c 15.37±3.02 b 注:表中数据为3次重复的平均值±标准差,同列的相同小写字母表示在 0.05 水平上无显著差异。 Note: Data presented as mean±standard deviations were calculated from three independent experiments.Values followed by the same letter within a row were not significantly different at 0.05 level. 表 3 离体条件下6株贝莱斯芽胞杆菌桑白绢病和生菜菌核病的防治效果
Table 3. In vitro control efficacy of Bv strains against S. rolfsii and S. sclerotiorum
桑叶 mulberry 生菜叶 lettuce 菌株
Strain病斑直径
Lesion diameter/cm防治效果
Control efficacy/%菌株
Strain病斑直径
Lesion diameter/cm防治效果
Control efficacy/%NN01 1.61±0.12 71.32±2.26 a NN01 1.97±0.45 65.68±0.08 a NN05 1.91±0.28 65.65±3.70 b NN02 2.42±0.75 57.82±0.13 b NN02 1.95±0.20 65.05±5.12 b NN05 2.52±0.82 56.08±0.14 b NN95 2.15±0.10 61.46±1.87 c NN88 2.77±1.35 51.72±0.23 c CK2 2.25±0.39 59.67±7.00 c NN04 2.93±1.02 48.81±0.18 c NN04 2.33±0.23 58.18±4.19 c NN95 3.23±0.25 43.57±0.04 d NN88 2.60±0.26 53.40±4.67 c CK2 4.05±1.15 29.32±0.20 e CK1 5.58±0.12 — CK1 5.73±0.91 — 注:① 表中数据为3次重复的平均值±标准差,同列的相同小写字母表示在 0.05 水平上无显著差异。② CK1:无菌水;CK2:枯草芽胞杆菌。
Note: ① Data presented as mean±standard deviations were calculated from three independent experiments. Values followed by the same letter within a row were not significantly different at 0.05 level. ② CK1:sterilized water;CK2:B. subtilis. -
[1] MARK M, SHIRI F. Prospects for biological soilborne disease control: Application of indigenous versus synthetic microbiomes [J]. Phytopathology, 2017, 107(3): 256−263. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-09-16-0330-RVW [2] 黄新琦, 蔡祖聪. 土壤微生物与作物土传病害控制 [J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2017, 32(6):593−600.HUANG X Q, CAI Z C. Soil microbes and control of soil-borne diseases [J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017, 32(6): 593−600.(in Chinese) [3] 李文静, 王秋霞, 李园, 等. 我国防治主要土传病害的农药登记和推广情况 [J]. 农药, 2021, 60(8):547−554,570.LI W J, WANG Q X, LI Y, et al. Current situation of pesticides for control of mainly soil-borne diseases registration, extension and application in China [J]. Agrochemicals, 2021, 60(8): 547−554,570.(in Chinese) [4] 曹坳程, 刘晓漫, 郭美霞, 等. 作物土传病害的危害及防治技术 [J]. 植物保护, 2017, 43(2):6−16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-1542.2017.02.002CAO A C, LIU X M, GUO M X, et al. Incidences of soil-borne diseases and control measures [J]. Plant Protection, 2017, 43(2): 6−16.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-1542.2017.02.002 [5] 李兴龙, 李彦忠. 土传病害生物防治研究进展 [J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(3):204−212. doi: 10.11686/cyxb20150321LI X L, LI Y Z. Research advances in biological control of soil-borne disease [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(3): 204−212.(in Chinese) doi: 10.11686/cyxb20150321 [6] 高游慧, 郑泽慧, 张越, 等. 根际微生态防治作物土传真菌病害的机制研究进展 [J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2021, 26(6):100−113. doi: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2021.06.11GAO Y H, ZHENG Z H, ZHANG Y, et al. Mechanism of rhizosphere micro-ecology in controlling soil-borne fungal diseases: A review [J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2021, 26(6): 100−113.(in Chinese) doi: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2021.06.11 [7] 刘磊, 梁昌聪, 曾迪, 等. 芽胞杆菌次生代谢产物及其在土传病害防控中的应用研究进展 [J]. 热带作物学报, 2017, 38(4):775−782. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2017.04.030LIU L, LIANG C C, ZENG D, et al. Research progress on secondary metabolites of Bacillus spp. and their applications in biocontrol of soil-borne diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2017, 38(4): 775−782.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2017.04.030 [8] BUBICI G, KAUSHAL M, PRIGIGALLO M I, et al. Biological control agents against Fusarium wilt of banana [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10: 616. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00616 [9] MILJAKOVIC D, MARINKOVIC J, BALESEVIC TUBIC S. The Significance of Bacillus spp. in disease suppression and growth promotion of field and vegetable crops [J]. Microorganisms, 2020, 8(7): 1037. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8071037 [10] NIU B, WANG W X, YUAN Z B, et al. Microbial interactions within multiple-strain biological control agents impact soil-borne plant disease [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2020, 11: 585404. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.585404 [11] ADENIJI A A, LOOTS D T, BABALOLA O O. Bacillus velezensis: Phylogeny, useful applications, and avenues for exploitation [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2019, 103(9): 3669−3682. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-09710-5 [12] JIANG C H, LIAO M J, WANG H K, et al. Bacillus velezensis, a potential and efficient biocontrol agent in control of pepper gray mold caused by Botrytis cinereal [J]. Biological Control, 2018, 126: 147−157. doi: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2018.07.017 [13] 陶永梅, 潘洪吉, 黄健, 等. 新型生防微生物因子贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(Bacillus velezensis)的研究与应用 [J]. 中国植保导刊, 2019, 39(9):26−33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6820.2019.09.004TAO Y M, PAN H J, HUANG J, et al. Research and application of a novel bio-control microbial factor Bacillus velezensis [J]. China Plant Protection, 2019, 39(9): 26−33.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6820.2019.09.004 [14] 张彩文, 程坤, 张欣, 等. 贝莱斯芽胞杆菌(Bacillus velezensis)分类学及功能研究进展 [J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2019, 45(17):258−265.ZHANG C W, CHENG K, ZHANG X, et al. Taxonomy and functions of Bacillus velezensis: A review [J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2019, 45(17): 258−265.(in Chinese) [15] FAN B, WANG C, SONG X F, et al. Bacillus velezensis FZB42 in 2018: The gram-positive model strain for plant growth promotion and biocontrol [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9: 2491. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02491 [16] 沙月霞, 隋书婷, 曾庆超, 等. 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌E69预防稻瘟病等多种真菌病害的潜力 [J]. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(11):1908−1917. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.11.006SHA Y X,SUI S T, ZENGQ C, et al. Biocontrol potential of Bacillus velezensis strain E69 against rice blast and other fungal diseases [J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2019, 52(11): 1908−1917.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.11.006 [17] 赵昱榕, 李磊, 谢学文, 等. 贝莱斯芽胞杆菌ZF2对多主棒孢病菌防治效果 [J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2019, 35(2):217−225.ZHAO Y R, LI L, XIE X W, et al. Biocontrol effect of Bacillus velezensis strain ZF2 against Corynespora cassiicola [J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2019, 35(2): 217−225.(in Chinese) [18] 崔文会, 孙雪, 梁承宇, 等. 土传真菌病害拮抗菌的筛选及其生防效果研究 [J]. 工业微生物, 2020, 50(2):41−47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6678.2020.02.007CUI W H, SUN X, LIANG C Y, et al. Screening of antagonistic bacteria against soil-borne pathogenic fungi and evaluation of their biocontrol effects [J]. Industrial Microbiology, 2020, 50(2): 41−47.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6678.2020.02.007 [19] 王瑞昊, 邓业成, 陈广桂, 等. 罗汉果土传病害拮抗细菌的筛选及鉴定 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2021, 36(8):927−935.WANG R H, DENG Y C, CHEN G G, et al. Antagonistic bacteria against soil-borne diseases on Siraitia grosvenorii [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 36(8): 927−935.(in Chinese) [20] 许帅, 谢学文, 张昀, 等. 马铃薯枯萎病生防芽胞杆菌筛选及生防效果研究 [J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2020, 36(5):761−770.XU S, XIE X W, ZHANG Y, et al. Screening of biocontrol Bacillus isolate against potato Fusarium wilt and its biocontrol effect [J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2020, 36(5): 761−770.(in Chinese) [21] MARTÍNEZ-RAUDALES I, DE LA CRUZ-RODRÍGUEZ Y, ALVARADO-GUTIÉRREZ A, et al. Draft genome sequence of Bacillus velezensis 2A-2B strain: A rhizospheric inhabitant of Sporobolus airoides (Torr. ) Torr., with antifungal activity against root rot causing phytopathogens [J]. Standards in Genomic Sciences, 2017, 12: 73. doi: 10.1186/s40793-017-0289-4 [22] 蒙月月. 桑树细菌性枯萎病菌生物学特性研究及其拮抗细菌和防治药剂筛选 [D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2014.MENG Y Y. Research on biological characteristics of mulberry bacterial wilt pathogens, and screening of its antagonistic bacterials and bactericides [D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2014. (in Chinese) [23] 宋文欣, 陈清华, 杨惠贞, 等. 桑枝枯菌核病病菌拮抗芽孢杆菌的筛选和鉴定 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(22):106−110.SONG W X, CHEN Q H, YANG H Z, et al. Screening and identification of antagonistic Bacillus spp. against Sclerotinia sclertiorum [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(22): 106−110.(in Chinese) [24] 夏京津, 陈建武, 宋怿, 等. 解淀粉芽孢杆菌HE活性成分鉴定及抗菌特性分析 [J]. 南方水产科学, 2019, 15(3):41−49.XIA J J, CHEN J W, SONG Y, et al. Identification of antibacterial substances from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens HE and analysis of antibacterial characteristics [J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2019, 15(3): 41−49.(in Chinese) [25] 曲晓旭, 刘洪霞, 高玲, 等. 芽孢杆菌产抗菌脂肽调控基因快速检测 [J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2016, 39(5):858−864. doi: 10.7685/jnau.201601042QU X X, LIU H X, GAO L, et al. Rapid identification of the encoding genes of antimicrobial lipopeptides producted by Bacillus [J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2016, 39(5): 858−864.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7685/jnau.201601042 [26] 冉军舰, 徐剑宏, 胡晓丹, 等. 1株产脂肽类抗生素芽孢杆菌的鉴定及脂肽类抗生素相关基因克隆 [J]. 食品科学, 2016, 37(17):127−132. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201617021RAN J J, XU J H, HU X D, et al. Identification of a Bacillus strain producing lipopeptide and cloning of genes related to lipopeptide [J]. Food Science, 2016, 37(17): 127−132.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201617021 [27] 武利勤, 尚宏忠, 顾海科. 拮抗匍枝根霉的生防菌R1B的筛选鉴定和抑菌活性分析 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2019, 35(4):29−35.WU L Q, SHANG H Z, GU H K. Screening, identification of biocontrol bacterium R1B against Rhizopus stolonifer and analysis of its antagonistic characteristics? [J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2019, 35(4): 29−35.(in Chinese) [28] JOSHI R, MCSPADDEN GARDENER B B. Identification and characterization of novel genetic markers associated with biological control activities in Bacillus subtilis [J]. Phytopathology, 2006, 96(2): 145−154. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-96-0145 [29] 程凯, 江欢欢, 沈标, 等. 棉花黄萎病拮抗菌的筛选及其生物防治效果 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(1):166−174. doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2011.0123CHENG K, JIANG H H, SHEN B, et al. Isolation and biological control effects of cotton Verticilium wilt antagonist [J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2011, 17(1): 166−174.(in Chinese) doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2011.0123 [30] RABBEE M F, ALI M S, CHOI J, et al. Bacillus velezensis: A valuable member of bioactive molecules within plant microbiomes [J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(6): 1046. doi: 10.3390/molecules24061046 [31] MARDANOVA AM, FANISOVNA HADIEVA G, TAFKILEVICH LUTFULLIN M, et al. Bacillus subtilis strains with antifungal activity against the phytopathogenic fungi [J]. Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 8(1): 1−20. doi: 10.4236/as.2017.81001 [32] 邓永卓, 张家宁, 邓爽, 等. 伊枯草菌素类抗菌肽抑菌活性及机理研究进展 [J]. 中国抗生素杂志, 2020, 45(7):639−645. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8689.2020.07.002DENG Y Z, ZHANG J N, DENG S, et al. Progress on the antibacterial activity and antibacterial mechanisms of iturins [J]. Chinese Journal of Antibiotics, 2020, 45(7): 639−645.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8689.2020.07.002 [33] NANNAN C, VU H Q, GILLIS A, et al. Bacilysin within the Bacillus subtilis group: Gene prevalence versus antagonistic activity against Gram-negative foodborne pathogens [J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2021, 327: 28−35. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2020.12.017 [34] 吴黎明, 李曦, 伍辉军, 等. 芽胞杆菌抗菌二肽溶杆菌素的研究进展 [J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2018, 41(5):778−783. doi: 10.7685/jnau.201803047WU L M, LI X, WU H J, et al. Research advances on bacilysin from Bacillus [J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2018, 41(5): 778−783.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7685/jnau.201803047 [35] 杨迪, 杜婵娟, 张晋, 等. 香蕉枯萎病拮抗菌贝莱斯芽胞杆菌的筛选鉴定及其生物学特性 [J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2021, 37(1):165−171.YANG D, DU C J, ZHANG J, et al. Screening, identification and biological characteristics of Bacillus velezensis with antagonst activity against banana Fusarium wilt [J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2021, 37(1): 165−171.(in Chinese) [36] 赵鹏鹏, 雷淑珍, 徐晓光, 等. 培养基组成对贝莱斯芽孢杆菌产抑真菌成分的影响 [J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2020, 46(5):147−151.ZHAO P P, LEI S Z, XU X G, et al. Effect of medium compositions on the production of antifungal components by Bacillus velezensis [J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(5): 147−151.(in Chinese) [37] LECLÈRE V, BÉCHET M, ADAM A, et al. Mycosubtilin overproduction by Bacillus subtilis BBG100 enhances the organism's antagonistic and biocontrol activities [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2005, 71(8): 4577−4584. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.8.4577-4584.2005 [38] 黄伟, 张丽娟, 秦新政, 等. 贝莱斯芽胞杆菌JK19发酵液稳定性及抑菌物质初步分析 [J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2021, 38(1): 73-80.HUANG W, ZHANG L J, QIN X Z, et al. Preliminary analysis of stability and antimicrobial substances in fermentation broth of Bacillus velezensis JK19[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2021, 38(1): 73-80. -








 下载:
下载: