Biological Characteristics and Fungicides of Cherry Leaf Spot Disease Pathogen
-
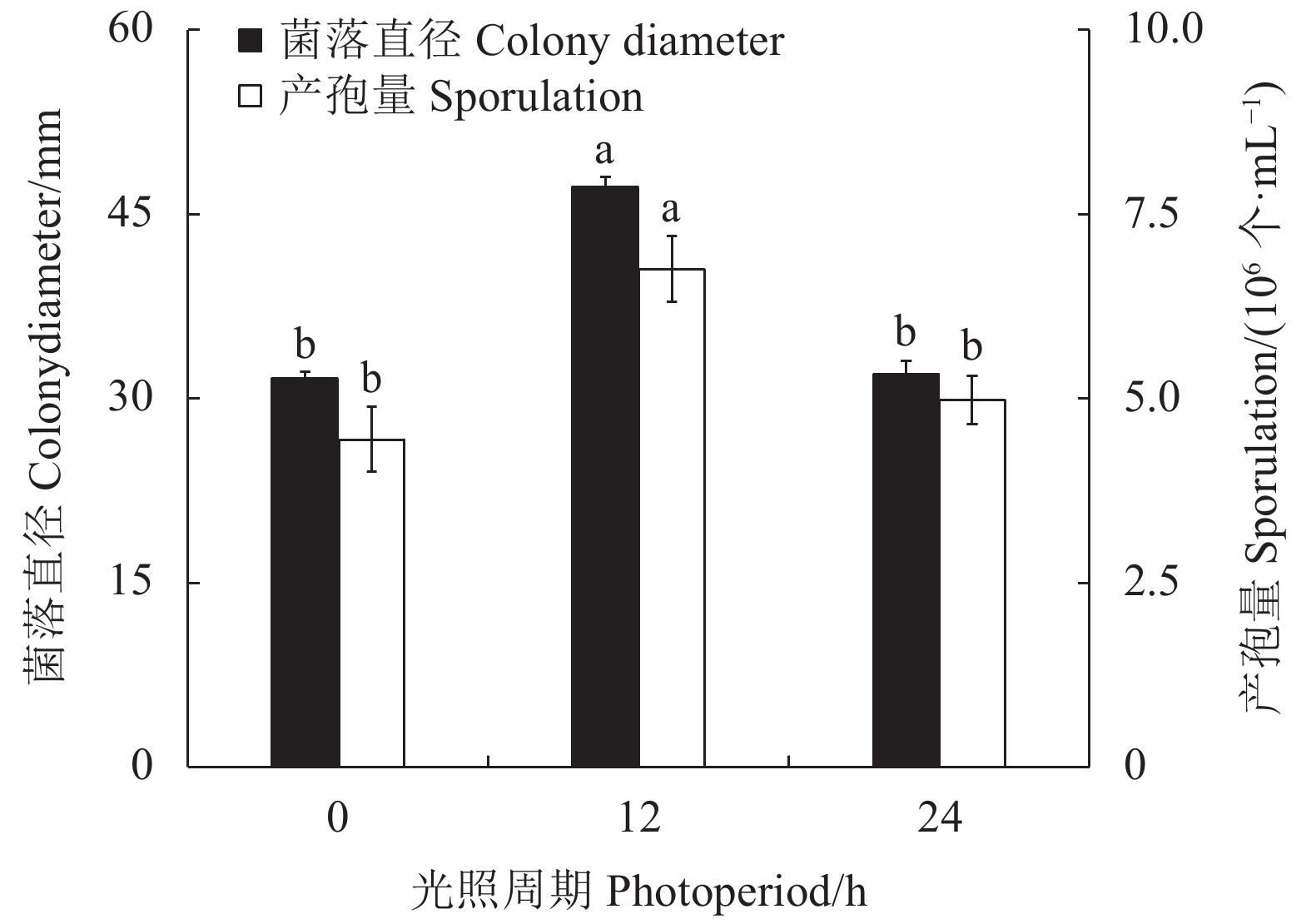
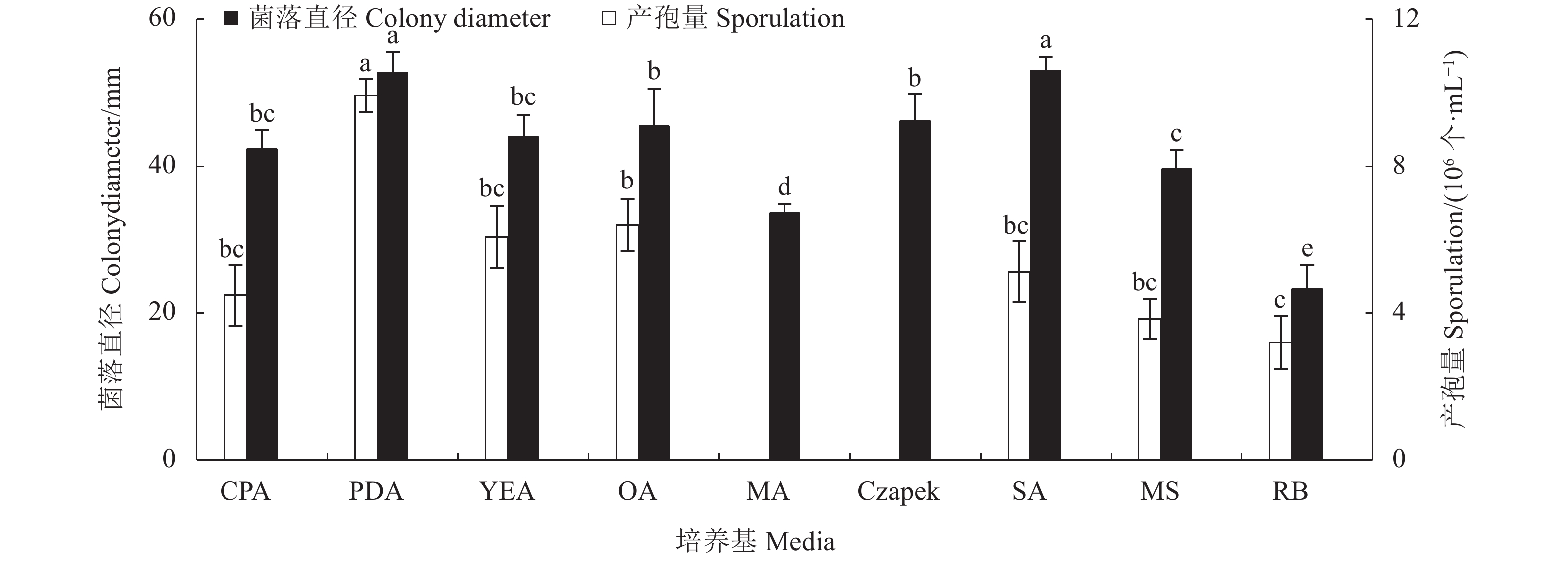
摘要:
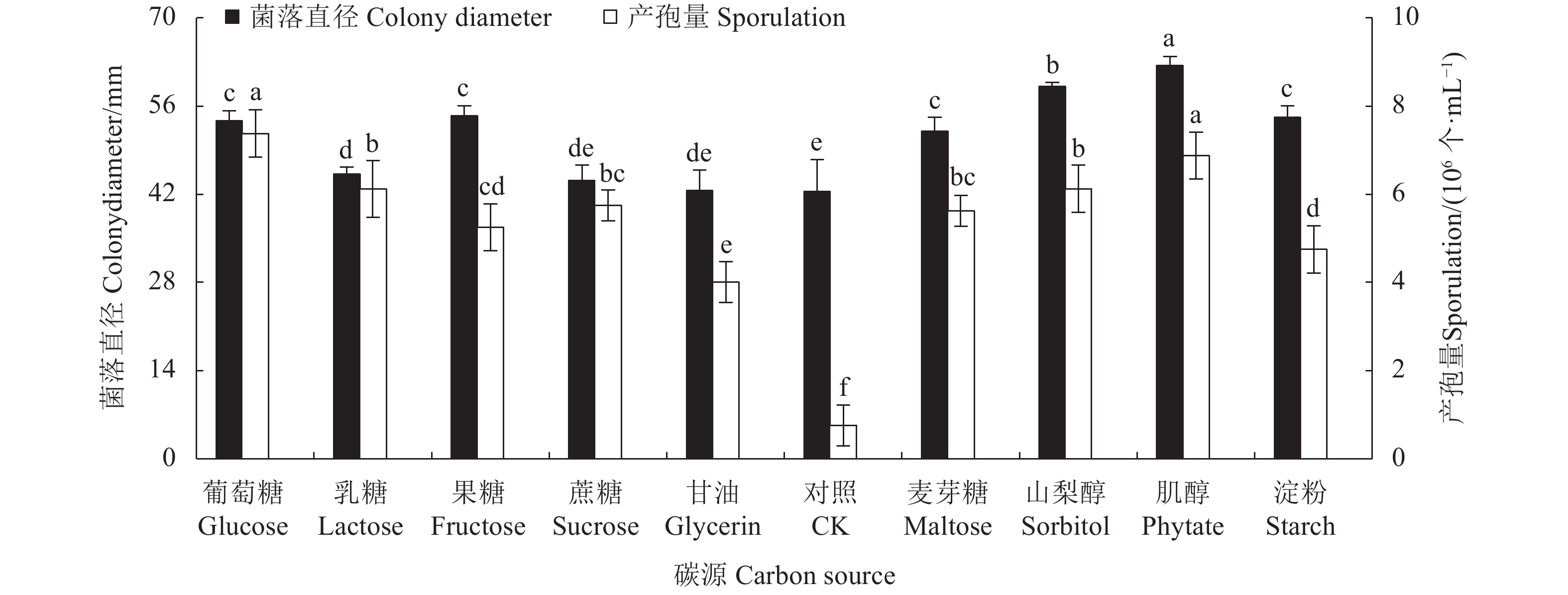
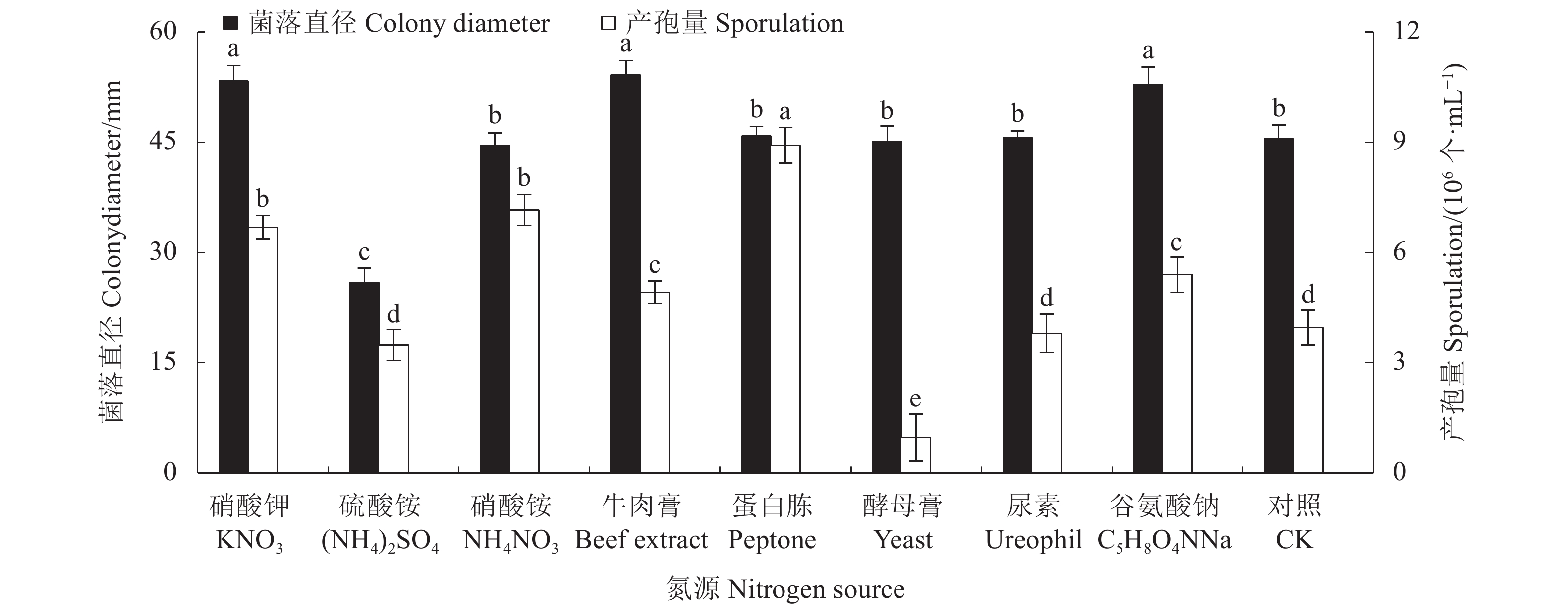
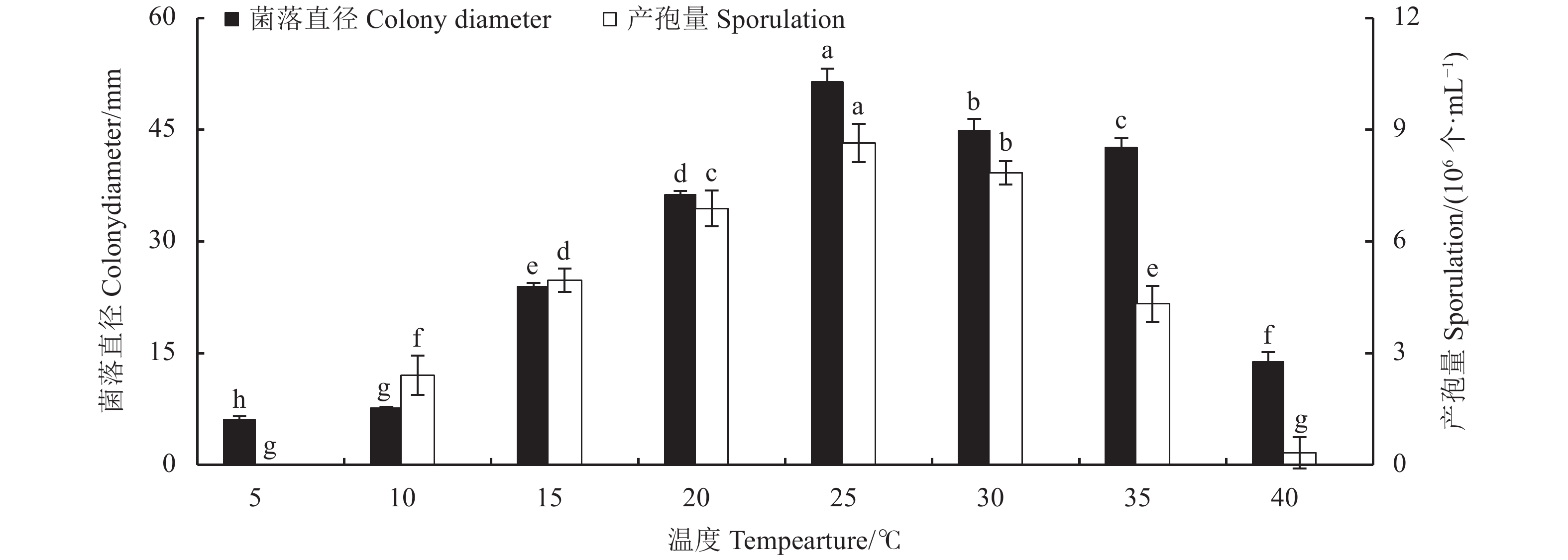
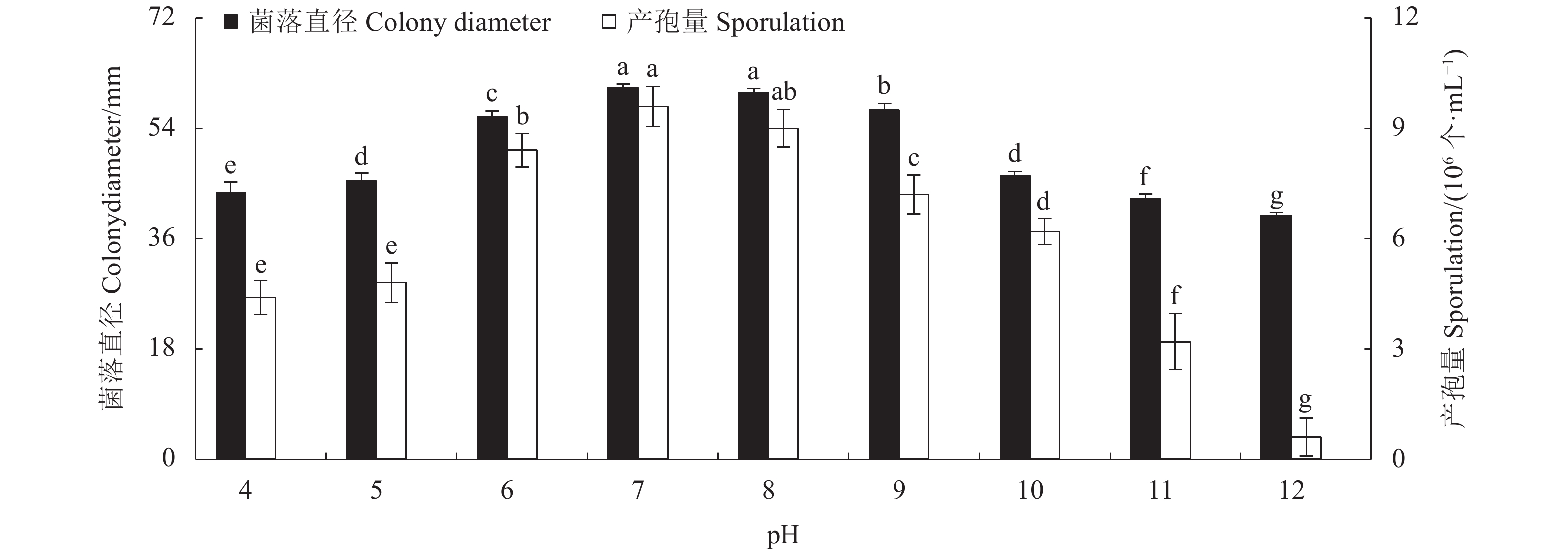
目的 明确青海省樱桃叶斑病菌杨柳炭疽菌Colletotrichum salicis的生物学特性,并筛选出高效的杀菌剂。 方法 采用十字交叉法及孢子计数法研究了病原菌的生物学特性,并用生长速率法测定病原菌对26种杀菌剂的敏感性。 结果 该病原菌的最适培养基为PDA;菌落生长和产孢的最适碳源分别为肌醇和葡萄糖,菌落生长和产孢的最适氮源分别为牛肉膏和蛋白胨。该菌在5~40 ℃条件下均能生长,且最适温度为25 ℃,致死条件为58 ℃水浴处理10 min;在pH值为4~12内均可生长和产孢,最适pH值为7;在12 h /12 h光暗交替下,菌落生长快且产孢多。供试杀菌剂中化学与生物杀菌剂抑菌效果最好的分别是10%苯醚甲环唑WG和0.3%丁子香酚SL,其EC50值分别为0.6、1.15 mg∙L−1;20%乙蒜素EC、80%代森锰锌WP和500 g∙L−1异菌脲SC的抑菌效果较差,EC50值高达301.44、679.36、1012.52 mg∙L−1。 结论 明确了樱桃叶斑病病原菌生长和产孢的最适培养条件和营养物质,并筛选出抑菌效果较好的杀菌剂。 Abstract:Objective Biological characteristics of Colletotrichum salicis, the pathogen that causes the leaf spot disease on cherry plants in Qinghai Province, were studied and effective fungicides evaluated for the control. Methods C. salicis were examined by the cross and spore counting methods. Its sensitivity to 26 fungicides was determined in the laboratory according to the growth inhibition on culture media. Results PDA medium was found to be optimal for the C. salicis mycelial growth and sporulation. Inositol and glucose were the optimal carbon sources for sporulation, while beef extract the nitrogen for colony growth and peptone for spore production. The pathogen could grow between 5 ℃ and 40 ℃ but most rapidly at 25 ℃ and died at 58 ℃ in 10 min; between pH 4 and 12 but optimally at pH 7; and well under a photoperiod cycle of 12 h light/12 h dark. Among the tested antifungal agents, 10% phentermine methiconazole aqueous dispersion or 0.3% eugenol dissolvable solution had the greatest inhibition with EC50 of 0.6 mg·L−1 and 1.151 mg·L−1, respectively, whereas 20% allicin oil emulsion, 80% manganese zinc wettable powder, and 500 g·L−1 isobaric urea suspension the least efficacies with EC50 up to 301.44 mg·L−1, 679.36 mg·L−1, and 1 012.52 mg·L−1, respectively. Conclusion The conditions and nutrients for optimal C. salicis culture were determined and the effective fungicides were identified. -
图 7 杀菌剂对杨柳炭疽菌的菌丝生长的抑制效果
注:A,10%苯醚甲环唑水分散粒剂;B,325 g∙L-1苯甲∙嘧菌酯悬浮剂;C,430 g∙L-1戊唑醇悬浮剂;D,60%唑醚∙代森联水分散粒剂;E,75%肟菌∙戊唑醇水分散粒剂;F,46%氢氧化铜水分散粒剂;G,25 g∙L-1咯菌腈悬浮种衣剂;H,30%吡唑醚菌酯悬浮剂;I,250 g∙L-1嘧菌酯悬浮剂;J,40%腈菌唑悬浮剂;K,50%啶酰菌胺水分散粒剂;L,75%百菌清可湿性粉剂;M,70%甲基硫菌灵可湿性粉剂;N,15%三唑酮可湿性粉剂;O,250 g∙L-1丙环唑乳油;P,80%丙森锌可湿性粉剂;Q,80%多菌灵可湿性粉剂;R,300 g∙L-1苯甲∙丙环唑乳油;S,80%代森锰锌可湿性粉剂;T,500 g∙L-1异菌脲悬浮剂;U,0.3%丁子香酚可溶液剂;V,3%中生菌素可湿性粉剂;W,8%宁南霉素水剂;X,6%春雷霉素水剂;Y,6%寡糖∙链蛋白可湿性粉剂;Z,20%乙蒜素乳油;CK,空白PDA培养基。
Figure 7. Inhibitory effect of fungicides on C. salicis
Note: A, 10% dioxoconazole WG;B, 325 g∙L-1 benzoyl azoxystrobin SC;C, 430 g∙L-1 tebuconazole SC;D, 60% zolyl ether combination WG;E, 75% oxime∙tebuconazole WG;F, 46%copper hydroxide WG;G, 25 g∙L-1 fludioxonil FS;H, 30% pyraclostrobin SC;I, 250 g∙L-1 azoxystrobin SC;J, 40% myclobutanil SC;K, 50% boscalid WG;L, 75% chlorothalonil WP;M, 70% thiophanate-methyl WP;N, 15% triadimefon WP;O, 250 g∙L-1 propiconazole EC;P, 80% propineb WP;Q, 80% carbendazim WP;R, 300 g∙L-1 benzoyl propiconazole EC;S, 80% mancozeb WP;T, 500 g∙L-1 iprodione SC;U, 0.3% eugenol SL;V, 3% zhongshengmycin WP;W, 8% ningnanmycin WA;X, 6% kasugamycin WA;Y, 6% oligose catenin WP;Z, 20% ethylicin EC;CK, Blank PDA medium.
表 1 参试药剂及其稀释倍数
Table 1. Dilutions of tested fungicides
药剂 Fungicides 生产厂家 Manufacturers 稀释倍数 Diluted multiples 80%代森锰锌可湿性粉剂 80% mancozeb WP 印度科门德国际有限公司 400、800、1200、1600、2000 250 g∙L−1丙环唑乳油 250 g∙L−1 propiconazole EC 先正达(苏州)作物保护有限公司 300、600、900、1200、1500 15%三唑酮可湿性粉剂 15% triadimefon WP 江苏剑牌农化股份有限公司 400、800、1200、1600、2000 250 g∙L−1嘧菌酯悬浮剂 250 g∙L−1 azoxystrobin SC 先正达南通作物保护有限公司 500、1000、2000、3000、4000 46%氢氧化铜水分散粒剂 46%copper hydroxide WG 美国杜邦中国集团有限公司 1000、2000、3000、4000、5000 300 g∙L−1苯甲∙丙环唑乳油 300 g∙L−1 benzoyl propiconazole EC 瑞士先正达作物保护有限公司 200、400、800、1600、3200 80%多菌灵可湿性粉剂 80% carbendazim WP 浙江一帆化工有限公司 400、800、1200、1600、2000 70%甲基硫菌灵可湿性粉剂 70% thiophanate-methyl WP 陕西亿农高科药业有限公司 1000、2000、3000、4000、5000 40%腈菌唑悬浮剂 40% myclobutanil SC 江西禾益化工股份有限公司 500、1000、2000、3000、4000 50%啶酰菌胺水分散粒剂 50% boscalid WG 巴斯夫欧洲公司 500、1000、2000、3000、4000 325 g∙L−1苯甲∙嘧菌酯悬浮剂 325 g∙L−1 benzoyl azoxystrobin SC 先正达南通作物保护有限公司 500、1000、2000、4000、8000 60%唑醚∙代森联水分散粒剂 60% zolyl ether combination WG 巴斯夫欧洲公司 300、600、1200、2400、4800 10%苯醚甲环唑水分散粒剂 10% dioxoconazole WG 先正达南通作物保护有限公司 500、1000、2000、3000、4000 430 g∙L−1戊唑醇悬浮剂 430 g∙L−1 tebuconazole SC 澳大利亚拜耳股份公司 400、800、1600、3200、6400 75%肟菌∙戊唑醇水分散粒剂 75% oxime∙tebuconazole WG 山东京博农化科技有限公司 300、600、1200、2400、4800 75%百菌清可湿性粉剂 75% chlorothalonil WP 陕西亿农高科药业有限公司 300、600、1200、2400、4800 30%吡唑醚菌酯悬浮剂 30% pyraclostrobin SC 河南勇冠乔迪农业科技有限公司 1000、2000、3000、4000、5000 80%丙森锌可湿性粉剂 80% propineb WP 江苏利民化学有限责任公司 500、1000、2000、3000、4000 500 g∙L−1异菌脲悬浮剂 500 g∙L−1 iprodione SC 江苏辉丰物业股份有限公司 300、600、1200、2400、4800 25 g∙L−1咯菌腈悬浮种衣剂 25 g∙L−1fludioxonil FS 先正达南通作物保护有限公司 100、200、300、400、500 20%乙蒜素乳油 20% ethylicin EC 南阳新卧龙生物化工有限公司 200、400、800、1600、3200 8%宁南霉素水剂 8% ningnanmycin WA 哈尔滨德强生物股份有限公司 100、200、400、800、1600 6%春雷霉素水剂 6% kasugamycin WA 北京三浦百草绿色植物制剂有限公司 100、200、400、800、1600 6%寡糖∙链蛋白可湿性粉剂 6% oligose catenin WP 河北中保绿农作物科技有限公司 100、200、400、800、1600 0.3%丁子香酚可溶液剂 0.3% eugenol SL 保定市亚达益农农业科技有限公司 100、200、300、400、500 3%中生菌素可湿性粉剂 3% zhongshengmycin WP 河北中保绿农作物科技有限公司 400、800、1200、1600、2000 表 2 26种杀菌剂对病原菌的毒力测定
Table 2. Toxicity of 26 individual fungicides on C. salicis
供试药剂
Fungicides毒力回归方程
Regression equation相关系数
Correlation coefficient抑制中浓度
EC50/(mg∙L−1)80%代森锰锌可湿性粉剂 80% mancozeb WP y=2.22x−1.287 2 0.949 7 679.360 250 g∙L−1丙环唑乳油 250 g∙L−1 propiconazole EC y=1.104 9x+2.527 1 0.968 8 173.021 15%三唑酮可湿性粉剂15% triadimefon WP y=1.012 6x+2.951 2 0.992 9 105.487 250 g∙L−1嘧菌酯悬浮剂 250 g∙L−1 azoxystrobin SC y=0.698 7x+3.860 8 0.997 7 44.844 46%氢氧化铜水分散粒剂 46%copper hydroxide WG y=0.504 3x+4.316 9 0.975 6 22.615 300 g∙L−1苯甲∙丙环唑乳油 300 g∙L−1 benzoyl propiconazole EC y=0.389 8x+4.097 4 0.995 2 206.871 80%多菌灵可湿性粉剂 80% carbendazim WP y=0.657 6x+3.524 2 0.945 1 175.55 70%甲基硫菌灵可湿性粉剂 70% thiophanate-methyl WP y=0.841 5x+3.306 2 0.985 2 102.96 40%腈菌唑悬浮剂 40% myclobutanil SC y=0.578 7x+4.022 0.979 6 48.978 50%啶酰菌胺水分散粒剂 50% boscalid WG y=0.576 8x+3.995 6 0.988 6 55.106 325 g∙L−1苯甲∙嘧菌酯悬浮剂 325 g∙L−1 benzoyl azoxystrobin SC y=0.701x+4.605 7 0.994 7 3.652 60%唑醚∙代森联水分散粒剂 60% zolyl ether combination WG y=0.692 8x+4.444 0.998 3 6.347 10%苯醚甲环唑水分散粒剂 10% dioxoconazole WG y=0.621 8x+5.138 0.991 1 0.600 430 g∙L−1戊唑醇悬浮剂 430 g∙L−1 tebuconazole SC y=0.691 3x+4.554 0.990 0 4.418 75%肟菌∙戊唑醇水分散粒剂 75% oxime∙tebuconazole WG y=0.691 4x+4.350 6 0.988 2 8.690 75%百菌清可湿性粉剂 75% chlorothalonil WP y=0.711 3x+3.674 3 0.958 2 73.097 30%吡唑醚菌酯悬浮剂30% pyraclostrobin SC y=0.862 4x+3.715 6 0.973 1 30.846 80%丙森锌可湿性粉剂 0% propineb WP y=1.195 9x+2.309 7 0.996 6 177.664 500 g∙L−1异菌脲悬浮剂 500 g∙L−1 iprodione SC y=0.657 5x+3.024 0.978 6 1012.512 25 g∙L−1咯菌腈悬浮种衣剂 25 g∙L−1fludioxonil FS y=0.782 7x+3.838 8 0.935 6 30.451 20%乙蒜素乳油 20% ethylicin EC y=0.548 5x+3.640 2 0.916 8 301.439 8%宁南霉素水剂 8% ningnanmycin WA y=0.319 1x+4.375 5 0.980 8 90.615 6%春雷霉素水剂 6% kasugamycin WA y=0.704 3x+3.452 6 0.998 2 157.389 6%寡糖∙链蛋白可湿性粉剂 6% oligose catenin WP y=0.615 9x+3.600 4 0.969 9 187.284 0.3%丁子香酚可溶液剂0.3% eugenol SL y=0.413 7x+4.974 7 0.949 2 1.151 3%中生菌素可湿性粉剂 3% zhongshengmycin WP y=0.468 3x+4.432 8 0.963 1 16.236 -
[1] 孙杨, 付全娟, 孙玉刚, 等. 樱桃褐斑病病原菌生物学特性及品种抗性评价 [J]. 植物保护, 2017, 43(4):110−114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-1542.2017.04.020SUN Y, FU Q J, SUN Y G, et al. Identification of cherry cultivar resistance to leaf spot and biological characteristics of Passalora circumscissa [J]. Plant Protection, 2017, 43(4): 110−114.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-1542.2017.04.020 [2] MCCUNE L M, KUBOTA C, STENDELL-HOLLIS N R, et al. Cherries and health: A review [J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2011, 51(1): 1−12. [3] 王琴, 王建友, 韩宏伟, 等. 南疆地区甜樱桃品种果实品质测定与评价 [J]. 食品工业科技, 2019, 40(8):215−220.WANG Q, WANG J Y, HAN H W, et al. Determination and evaluation of fruit quality of sweet cherry cultivars in southern Xinjiang [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2019, 40(8): 215−220.(in Chinese) [4] 黄贞光, 刘聪利, 李明, 等. 近20年国内外甜樱桃产业发展动态及对未来的预测 [J]. 果树学报, 2014(S1):1−6.HUANG Z G, LIU C L, LI M, et al. The development situation of sweet cherry industry in China and abroad during recent two decates and prognostication for the future [J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2014(S1): 1−6.(in Chinese) [5] 张艳婷, 仇智灵, 李阿根, 等. 浙江省樱桃褐腐病病原菌种类及其对常见药剂的抗性检测 [J]. 果树学报, 2020, 37(9):1394−1403.ZHANG Y T, QIU Z L, LI A G, et al. Species of pathogens causing cherry brown rot and their resistance to common fungicides in Zhejiang Province [J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2020, 37(9): 1394−1403.(in Chinese) [6] 徐丽, 王甲威, 陈新, 等. 甜樱桃流胶病原菌的分子鉴定和致病性检测 [J]. 植物病理学报, 2015, 45(4):350−355.XU L, WANG J W, CHEN X, et al. Identification and pathogenicity detection of the cherry gummosis pathogen [J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 2015, 45(4): 350−355.(in Chinese) [7] 王娟, 邓朋, 李中学, 等. 5种樱桃果病害的发生规律与防治 [J]. 现代园艺, 2018(19):159−160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4958.2018.19.085WANG J, DENG P, LI Z X, et al. Occurrence regularity and control of five cherry fruit diseases [J]. Xiandai Horticulture, 2018(19): 159−160.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4958.2018.19.085 [8] LOPEZ-CARBONELL M, MORET A, NADAL M. Changes in cell ultrastructure and zeatin riboside concentrations in Hedera helix, Pelargonium zonale, Prunus avium, and Rubus ulmifolius leaves infected by fungi [J]. Plant Disease, 1998, 82(8): 914−918. doi: 10.1094/PDIS.1998.82.8.914 [9] 刘俏. 青海省樱桃叶斑病病原种类鉴定及防治药剂室内筛选研究[D]. 西宁: 青海大学, 2020.LIU Q. Identification of the pathogens causing sweet cherry leaf spot in Qinghai province and screening fungicides in laboratory [D]. Xining: Qinghai University, 2020. (in Chinese) [10] 刘一贤, 蔡志英, 施玉萍, 等. 辣木果腐病病原菌兰生炭疽菌(Colletotrichum chlorophyti)生物学特性及其防治药剂室内毒力测定 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2019, 47(20):133−137.LIU Y X, CAI Z Y, SHI Y P, et al. Biological characteristics of Colletotrichum chlorophyti, a pathogen of moringa oleifera fruit rot disease, and laboratory virulence determination of its control agents [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(20): 133−137.(in Chinese) [11] 李文, 何月秋, 王佳莹, 等. 百日草炭疽病病原菌的分离鉴定及防治药剂筛选 [J]. 农药学学报, 2021, 23(2):341−347.LI W, HE Y Q, WANG J Y, et al. Isolation and identification of pathogen causing anthracnose on Zinnia elegans Jacq. and fungicides screening [J]. Chinese Journal of Pesticide Science, 2021, 23(2): 341−347.(in Chinese) [12] 张琳, 占浩鑫, 冯志伟, 等. 人参生炭疽菌Colletotrichum panacicola和线列炭疽菌C. lineola的生物学特性及其对不同杀菌剂的敏感性研究[J/OL]. 植物病理学报: 1-14[2021-10-22]. Doi: 10.13926/j.cnki.apps.000769.ZHANG L, ZHAN H X, FENG Z W, et al. Biological characteristics and fungicide sensitivity of Colletotrichum panacicola and C. lineola causing anthracnose on ginseng [J/OL]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica: 1-14. [2021-10-22]. Doi: 10.13926/j.cnki.apps.000769 (in Chinese). [13] 邵慧慧, 张西梅, 刘紫祺, 等. 引起西洋参锈腐病的Ilyonectria属4种病原菌的生物学特性及其对不同杀菌剂的敏感性[J/OL]. 植物病理学报: 1-11[2021-09-16]. Doi: 10.13926/j.cnki.apps.000746.SHAO H H, ZHANG X M, LIU Z Q, et al. Biological characteristics and fungicide sensitivity of four Ilyonectria species causing root rot on American ginseng [J/OL]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica: 1-11. [2021-09-16]. Doi: 10.13926/j.cnki.apps.000746 (in Chinese). [14] 张秀伟, 蔡甫格, 潘中涛, 等. 金刺梨黑斑病病原菌生物学特性及室内药剂毒力测定 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2018, 46(18):98−100.ZHANG X W, CAI F G, PAN Z T, et al. Biological characteristics of the pathogenic bacteria of rosa roxburghii black spot disease and determination of indoor toxicity [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 46(18): 98−100.(in Chinese) [15] 吴松, 陈全助, 张晓阳, 等. 樟树溃疡病原菌生物学特性及室内毒力测定 [J]. 森林与环境学报, 2021, 41(3):308−317.WU S, CHEN Q Z, ZHANG X Y, et al. Studies on biological characteristics of a Camphor tree canker pathogen (Neofusicoccum Parvum) and fungicide laboratory toxicity [J]. Journal of Forest and Environment, 2021, 41(3): 308−317.(in Chinese) [16] 郭宁, 胡清玉, 刘粤阳, 等. 玉米叶斑病菌麦根腐平脐蠕孢的生物学特性及其对杀菌剂的敏感性 [J]. 华北农学报, 2019, 34(S1):289−295. doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.20190188GUO N, HU Q Y, LIU Y Y, et al. Biological characteristics and sensitivity to fungicides of Bipolaris sorokiniana causing maize leaf spot [J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2019, 34(S1): 289−295.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.20190188 [17] 范文忠, 王振, 顾园园, 等. 水蜡叶斑病病原菌鉴定及对药剂的敏感性 [J]. 农药, 2020, 59(1):60−64.FAN W Z, WANG Z, GU Y Y, et al. Pathogen identification of Ligustrum obtusifolium leaf spot and fungicides susceptibility [J]. Agrochemicals, 2020, 59(1): 60−64.(in Chinese) [18] 孔琼, 袁盛勇, 郭建伟, 等. 野蚕豆根根腐病原菌、生物学特性及其有效杀菌剂研究 [J]. 西南农业学报, 2020(7):1480−1485.KONG Q, YUAN S Y, GUO J W, et al. Identification, biological characteristics and fungicides screening of pathogen on root-rot disease in Centranthera grandiflora [J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2020(7): 1480−1485.(in Chinese) [19] 孙宇, 白庆荣. 吉林省水稻鞘枯病病菌生物学特性及药剂敏感性 [J]. 农药, 2018, 57(10):757−761,767.SUN Y, BAI Q R. Pathogen identification and biological characteristics of rice sheath blight caused by Nigrospora oryzae in Jilin Province and susceptibility to fungicides [J]. Agrochemicals, 2018, 57(10): 757−761,767.(in Chinese) [20] 田华, 朱艳梅, 董瑜, 等. 烟草麻孢根腐病菌生理学特性及药剂毒力测定 [J]. 植物保护学报, 2017, 44(3):488−494.TIAN H, ZHU Y M, DONG Y, et al. Physiological characteristics of Gelasinospora reticulata and toxicity test of 11 fungicides [J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2017, 44(3): 488−494.(in Chinese) [21] 魏蜜, 朱洁倩, 张伟, 等. 玛咖根腐病菌的生物学特性及防治药剂室内筛选 [J]. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 32(5):787−792.WEI M, ZHU J Q, ZHANG W, et al. Biological characteristics of pathogen causing maca root rot disease and its fungicides laboratory screening [J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University(Natural Science Edition), 2017, 32(5): 787−792.(in Chinese) [22] 常佳迎, 田兰芝, 刘树森, 等. 新月弯孢变种的生物学特性及其对药剂的敏感性 [J]. 植物保护学报, 2020, 47(5):1038−1047.CHANG J Y, TIAN L Z, LIU S S, et al. Biological characteristics of fungal pathogen Curvularia lunata varieties and its sensitivity to fungicides [J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2020, 47(5): 1038−1047.(in Chinese) [23] 王春伟, 王燕, 张曦倩, 等. 越橘镰孢果腐病菌的生物学特性测定及防治药剂初步筛选 [J]. 园艺学报, 2017, 44(8):1589−1598.WANG C W, WANG Y, ZHANG X Q, et al. Determination of biological characteristics and preliminary screening of control fungicides of Fusarium acuminatum causing Fusarium fruit rot on blueberry [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2017, 44(8): 1589−1598.(in Chinese) [24] 李润根, 卢其能, 何咪, 等. 百合新病原菌假短孢弯孢生物学特性及其对杀菌剂的敏感性 [J]. 植物保护, 2020, 46(6):41−46.LI R G, LU Q N, HE M, et al. The biological characteristics of Curvularia pseudobrachyspora, a new causal agent of lily leaf spot, and its sensitivity to fungicides [J]. Plant Protection, 2020, 46(6): 41−46.(in Chinese) [25] 陈宏州, 杨敬辉, 肖婷, 等. 12种杀菌剂对葡萄灰霉病菌的毒力测定 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2015, 43(1):124−126,127.CHEN H Z, YANG J H, XIAO T, et al. Determination of virulence of 12 fungicides against Botrytis cinerea [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 43(1): 124−126,127.(in Chinese) [26] 刘丽萍, 高洁, 李玉. 植物炭疽菌属Colletotrichum真菌研究进展 [J]. 菌物研究, 2020, 18(4):266−281.LIU L P, GAO J, LI Y. Advances in knowledge of the fungi referred to the genus Colletotrichum [J]. Journal of Fungal Research, 2020, 18(4): 266−281.(in Chinese) [27] 向梅梅, 张云霞, 刘霄. 炭疽菌属真菌分类的研究进展 [J]. 仲恺农业工程学院学报, 2017, 30(1):59−66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5663.2017.01.012XIANG M M, ZHANG Y X, LIU X. Research progress on the taxonomy of Colletotrichum [J]. Journal of ZhongKai University of Agriculture and Technology, 2017, 30(1): 59−66.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5663.2017.01.012 [28] KOELSCH M C, COLE J C, VONBROEMBSEN S L. First report of leaf spots and stem lesions on common periwinkle caused by Colletotrichum gloeosporioides [J]. Plant Disease, 1995, 79(1): 83. [29] GAUTAM A K, AVASTHI S, BHADAURIA R. First report of anthracnose caused by Colletotrichum gloeosporioides on Boehravia diffusa in India [J]. Archives of Phytopathology and Plant Protection, 2012, 45(20): 2502−2506. doi: 10.1080/03235408.2012.730888 [30] BI Y, GUO W, ZHANG G J, et al. First report of Colletotrichum boninense causing anthracnose of strawberry in China (Article) [J]. Plant Disease, 2017, 101(1): 250−251. [31] OKORSKI A, PSZCZOLKOWSKA A, SULIMA P, et al. First report of willow anthracnose caused by Colletotrichum salicis in Poland (Note) [J]. Plant Disease, 2018, 102(10): 2036−2041. [32] KARAMNEJADI T, SOLHIZADEH A, SHENAVAR O, et al. First report of leaf spot caused by Colletotrichum coccodes on viola tricolor in Iran (Note) [J]. Journal of Plant Pathology, 2017, 99(2): 536. [33] 孙洁, 池振江, 赵思峰. 新疆红枣缩果病菌生物学特性及室内药剂筛选研究 [J]. 北方园艺, 2013(24):126−129.SUN J, CHI Z J, ZHAO S F. Study on biological characteristics of Alternaria alternata caused jujube shrink disease and screening of fungicides in Xinjiang [J]. Northern Horticulture, 2013(24): 126−129.(in Chinese) [34] 杨佳文, 赵尊练, 张管曲, 等. 陕西线辣椒炭疽病原菌的鉴定及生物学特性研究 [J]. 西北农业学报, 2017, 26(11):1695−1705. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1004-1389.2017.11.017YANG J W, ZHAO Z L, ZHANG G Q, et al. Identification and biological characterization of Anthrax bacteria in xianlajiao chili pepper in Shaanxi Province [J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2017, 26(11): 1695−1705.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1004-1389.2017.11.017 [35] 秦健, 黄如葵, 黄熊娟, 等. 苦瓜双色平脐蠕孢叶斑病病原菌的生物学特性及其抑菌药剂筛选 [J]. 热带作物学报, 2020, 41(12):2507−2512. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2020.12.019QIN J, HUANG R K, HUANG X J, et al. Biological characteristics of Momordica charantia leaf spot pathogen Bipolaris bicolor and bacteriostatic agents screening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2020, 41(12): 2507−2512.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2020.12.019 [36] 冯思琪, 张亚玲. 黑龙江水稻胡麻叶斑病病原菌的分离鉴定及生物学特性 [J]. 中国植保导刊, 2019, 39(2):17−23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6820.2019.02.004FENG S Q, ZHANG Y L. Pathogen isolation and identification of rice brown spot and its biological characteristics in Heilongjiang [J]. China Plant Protection, 2019, 39(2): 17−23.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6820.2019.02.004 [37] 姜苏月, 靳俊媛, 刘静, 等. 羽扇豆炭疽病病原鉴定及室内药剂筛选 [J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2021, 49(5):136−141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2021.05.024JIANG S Y, JIN J Y, LIU J, et al. Pathogen identification and screening of fungicides of anthracnose of Lupinus micranthus by Colletotrichum Lupi-ni [J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2021, 49(5): 136−141.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2021.05.024 [38] 邓洁, 莫飞旭, 石金巧, 等. 钩藤炭疽病病原鉴定、生物学特性及防治药剂筛选 [J]. 中药材, 2020, 43(6):1303−1307.DENG J, MO F X, SHI J Q, et al. Pathogen identification, biological characteristics of anthracnose in Uncaria hirsuta and screening of control fungicides [J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2020, 43(6): 1303−1307.(in Chinese) [39] 孟珂, 张亚波, 常君, 等. 8种杀菌剂对9种薄壳山核桃炭疽病病原菌的毒力测定 [J]. 林业科学研究, 2021, 34(1):153−164.MENG K, ZHANG Y B, CHANG J, et al. Toxicity Test with 8 Fungicides Against 9 Pathogens of Pecan Anthracnose (Colletotrichum spp. ) [J]. Forest Research, 2021, 34(1): 153−164.(in Chinese) -







 下载:
下载: