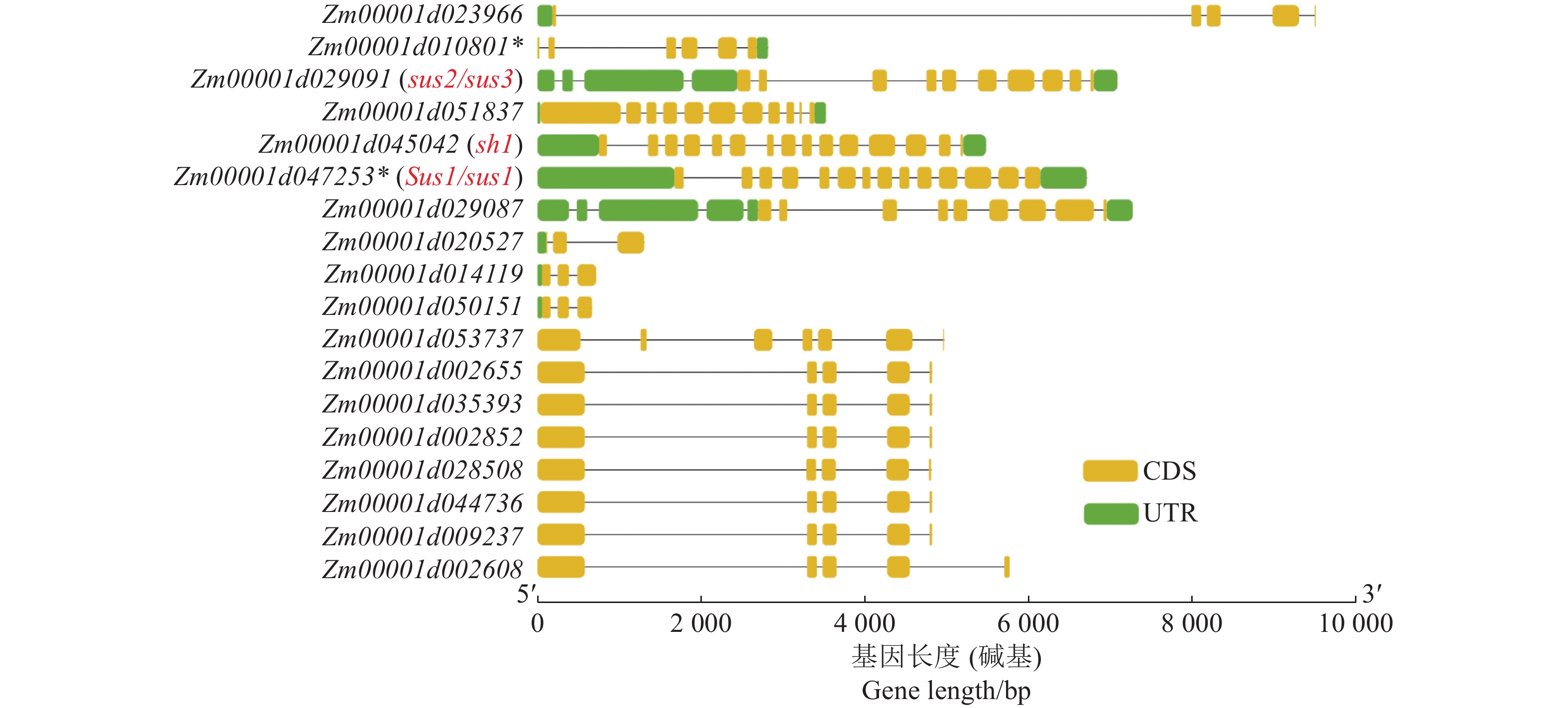
Genetic Basis of Sweetness of Super-sweet Corn, Minshuangse No. 6
-
摘要:
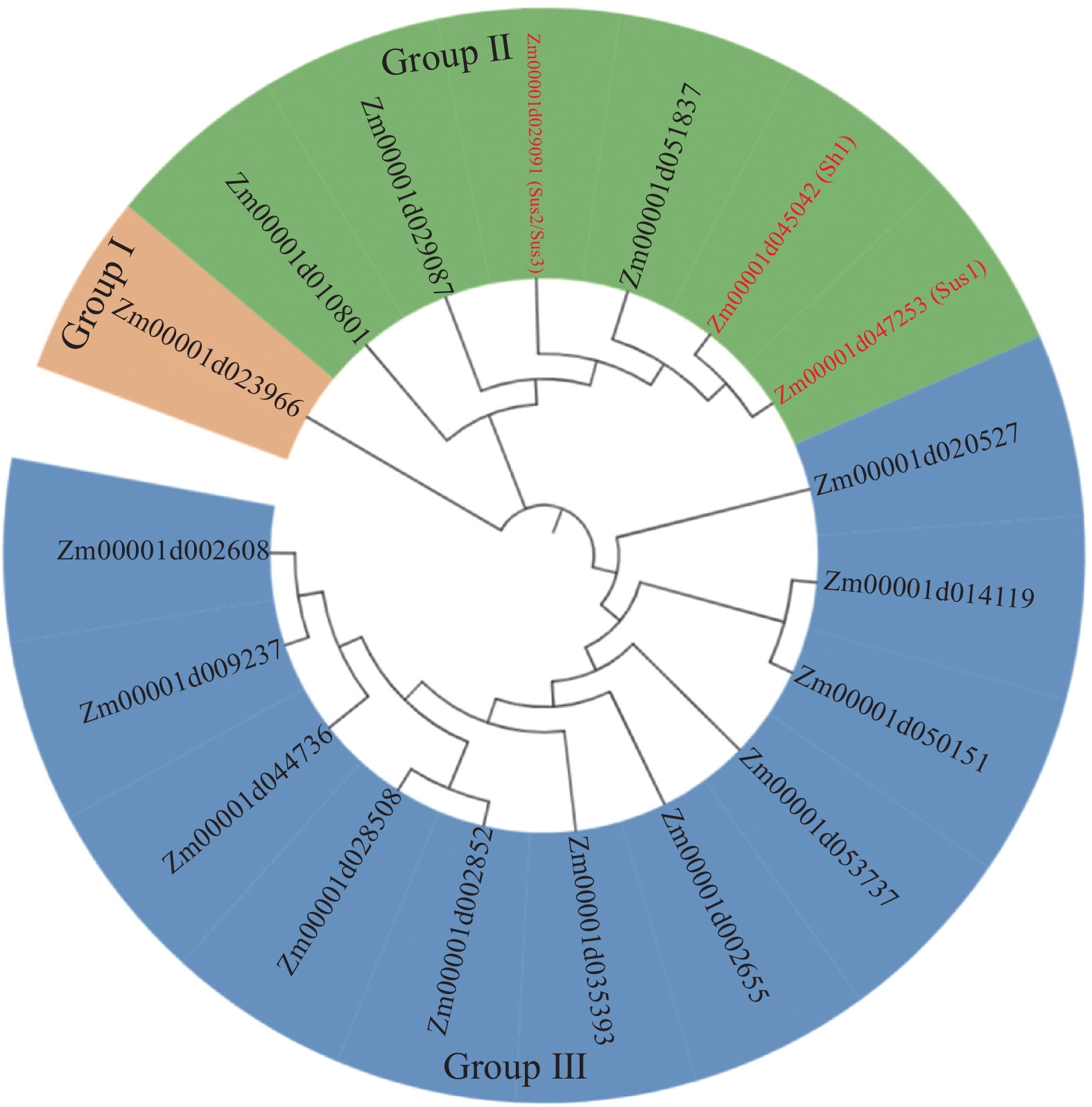
目的 深入探究甜玉米甜度形成的关键基因及可能涉及的杂种优势分子机制。 方法 以超甜玉米品种闽双色6号及其双亲为研究材料,利用生物信息学,重测序,转录组等技术对蔗糖合酶基因家族进化、甜度相关基因分型及表达模式进行分析。 结果 玉米中存在18个蔗糖合酶基因;其中,Zm0001d029087与Sh1、Sus1和Sus2/3同属一个亚家族,进化上亲缘关系较近,表明Zm0001d029087可能在籽粒糖代谢中发挥功能;在双亲与B73的变异分析中发现,Sh1、Sus1和Sus2/3均存在突变,共同构成闽双色6号的超甜特性的遗传物质基础;表达分析发现,18个基因中仅Zm0001d029087与Sh1、Sus1和Sus2/3在籽粒中有表达。进一步对4个基因在闽双色6号及其双亲中的表达进行分析,结果显示,除Sh1基因外,其他3个基因在闽双色6号中的表达显著低于双亲或之一,表明闽双色6号在糖代谢途径上存在超亲遗传的分子机制。 结论 解析了闽双色6号籽粒超甜特性的遗传特性,发现1个潜在的功能基因Zm0001d029087,并初步探究杂种优势在闽双色6号超甜特性形成中的遗传机制。 Abstract:Objective This study explored the key genes of sweet corn sweetness formation and the possible molecular mechanism of heterosis. Method Genotypes and expressions of sucrose synthase gene family of a super-sweet corn variety, Minshuangse No.6, and its parents were analyzed using bioinformatics, resequencing, transcriptome, and other techniques to unveil the underlining basis of the sweet taste of corns. Result Eighteen sucrose synthase genes were isolated from the corn kernels. Among them, Zm0001d029087 was found to belong to the same subfamily as Sh1, Sus1, and Sus2/3 with close evolution relationships. It might play a role in the sugar metabolism of the corn. Comparing both parents with B73, mutations were found in Sh1, Sus1, and Sus2/3. Of the 18 genes, only Zm0001d029087 and those 4 genes expresses in the kernels. Further analyses showed the 4 genes, except Sh1, had significantly lower expressions in Minshuangse No.6 than in both or one of the parents. Conclusion The genetic variations in the super-sweet Minshuangse No.6 revealed a unique characteristic of Zm0001d029087 that might relate to the sweetness of the corn kernels. A preliminary role of heterosis in sugar formation by that gene was proposed for further investigation. -
Key words:
- Minshuangse No. 6 /
- sucrose synthase /
- genetic variation /
- expression analysis /
- heterosis
-
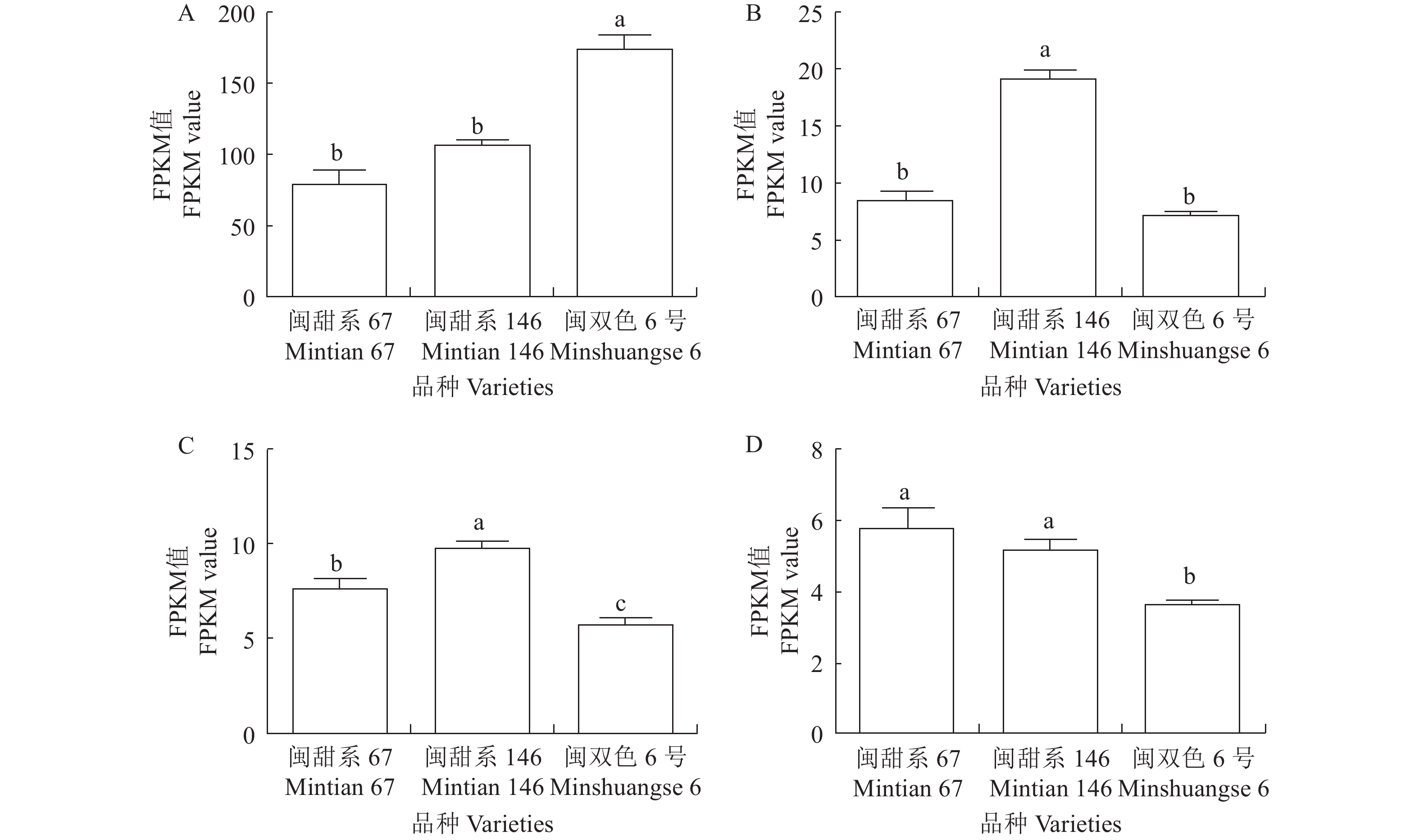
图 4 不同品种籽粒间蔗糖合酶基因的差异表达分析
A、B、C、D分别为Zm00001d045042(Sh1)、Zm00001d047253( Sus1 )、Zm00001d029091 ( Sus2/3 )、Zm00001d029087;不同小写字母表示该基因在不同品种籽粒中的表达差异性。
Figure 4. Differential expressions of sucrose synthase genes in kernels of different corn varieties
A, B and C represent Mintian 67, Mintian 146, and Minshuangse No. 6, respectively; different lowercase letters represent expression differences of respective genes in kernels of different corn varieties.
表 1 双亲与B73的基因型对比分析
Table 1. Comparison on genotypes between parents and B73
基因号
Gene ID染色体
Chromosome位置
Position突变类型
Mutation typeB73
闽甜系146 Mintian 146 闽甜系67 Mintian 67 Zm00001d029087 1 57458900 非同义突变nonsynonymous A — G 1 57459090 非同义突变nonsynonymous G A G 1 57459108 非同义突变nonsynonymous C T C 1 57459240 非同义突变nonsynonymous G T G 1 57459287 非同义突变nonsynonymous T C T 1 57459517 终止子缺失Stoploss A C T 1 57459532 非同义突变nonsynonymous A A G 1 57462132 非同义突变nonsynonymous C G C Zm00001d029091
(Sus2/3)1 57487288 非同义突变nonsynonymous T T C 1 57487312 非同义突变nonsynonymous A — G 1 57487334 非同义突变nonsynonymous G — C 1 57487573 提前终止Stopgain G T T 1 57487653 非同义突变nonsynonymous G T G 1 57487700 非同义突变nonsynonymous T C T 1 57490727 移码突变frameshift C CAT CAT Zm00001d002608 2 16655931 移码突变frameshift TATACGTG T T 2 16655939 非移码突变 No-frameshift ATAC A T 2 16655944 移码突变frameshift TCC TCC T Zm00001d050151 4 69443338 非同义突变nonsynonymous C T C Zm00001d051837 4 171682444 非同义突变nonsynonymous C C T 4 240099563 非同义突变nonsynonymous A A T 4 240099712 非同义突变nonsynonymous T C C 4 240099721 非同义突变nonsynonymous C C T 4 240099732 非同义突变nonsynonymous T T C 4 240103694 非同义突变nonsynonymous C A C Zm00001d014119 5 33044977 非同义突变nonsynonymous A — T 5 33045010 非同义突变nonsynonymous G — A Zm00001d010801 8 128221424 非同义突变nonsynonymous A G A 8 128221755 非同义突变nonsynonymous G G A 8 128221768 移码突变frameshift CCG C CCG 8 128223803 移码突变frameshift C CA C 8 128223824 非同义突变nonsynonymous G G A Zm00001d045042
(Sh1)9 10912802 非同义突变nonsynonymous C C G 9 10912803 移码突变frameshift TCG TCG T Zm00001d047253
(Sus1)9 124178618 移码突变frameshift C CTT C 9 124178640 非同义突变nonsynonymous G A G 9 124178644 移码突变frameshift A AGAAG A 9 124179054 非同义突变nonsynonymous G C C 9 124182253 非同义突变nonsynonymous T T G Zm00001d023966 10 32431873 非同义突变nonsynonymous C C T 基因型中“—”表示重测序数据中未检测到。
The "—" in the genotype indicates that it is not detected in the resequencing data. -
[1] 李坤, 黄长玲. 我国甜玉米产业发展现状、问题与对策 [J]. 中国糖料, 2021, 43(1):67−71. doi: 10.13570/j.cnki.scc.2021.01.012LI K, HUANG C L. Current production status, problem and countermeasure on sweet corn industry in China [J]. Sugar Crops of China, 2021, 43(1): 67−71.(in Chinese) doi: 10.13570/j.cnki.scc.2021.01.012 [2] 杨茂材. 甜玉米品种的生态适应性及主要栽培技术 [J]. 耕作与栽培, 1987(2):22−24. doi: 10.13605/j.cnki.52-1065/s.1987.02.008YANG M C. Ecological adaptability and main cultivation techniques of sweet maize varieties [J]. Tillage and Cultivation, 1987(2): 22−24.(in Chinese) doi: 10.13605/j.cnki.52-1065/s.1987.02.008 [3] 王义发. 甜玉米营养保健作用 [J]. 食品与生活, 1999(3):53.WANG Y F. Nutrition and health care function of sweet corn [J]. Food and Life, 1999(3): 53.(in Chinese) [4] 魏俊杰. 甜玉米育种现状与发展对策 [J]. 福建农业, 2015(6):83.WEI J J. Present situation and development countermeasures of sweet corn breeding [J]. FuJian Agriculture, 2015(6): 83.(in Chinese) [5] 赵守光. 超甜玉米育种现状及发展方向探讨 [J]. 广东农业科学, 2007, 34(12):14−16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2007.12.005ZHAO S G. Discussion on breeding status and development direction of super sweet corn [J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2007, 34(12): 14−16.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2007.12.005 [6] 韩金龙, 王同燕, 徐立华, 等. 我国甜玉米育种现状与种质创新思路 [J]. 现代农业科技, 2010(11):77−78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2010.11.046HAN J L, WANG T Y, XU L H, et al. Thinking of the present situation and germplasm innovation of sweet corn breeding in China [J]. Modern Agricultural Sciences and Technology, 2010(11): 77−78.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2010.11.046 [7] 李坤, 李高科, 肖颖妮, 等. 甜玉米品质遗传改良研究进展 [J]. 广东农业科学, 2020, 47(11):70−77. doi: 10.16768/j.issn.1004-874x.2020.11.008LI K, LI G K, XIAO Y N, et al. Research progresses in genetic improvement of sweet corn quality [J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 47(11): 70−77.(in Chinese) doi: 10.16768/j.issn.1004-874x.2020.11.008 [8] 郑大浩, 李艳茹, 郭彦. 甜玉米遗传育种研究进展 [J]. 延边大学农学学报, 2003, 25(3):213−217. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7999.2003.03.013ZHENG D H, LI Y R, GUO Y. Progress of studying on heredity and breeding of sweet corn [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science Yanbian University, 2003, 25(3): 213−217.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7999.2003.03.013 [9] ANDREW R H. Factors influencing early seedling vigor of shrunken‐2 Maize1 [J]. Crop Science, 1982, 22(2): 263−266. doi: 10.2135/cropsci1982.0011183X002200020015x [10] CHOUREY P S, NELSON O E. Interallelic complementation at the sh locus in maize at the enzyme level [J]. Genetics, 1979, 91(2): 317−325. doi: 10.1093/genetics/91.2.317 [11] GEIGENBERGER P, STITT M. Sucrose synthase catalyses a readily reversible reaction in vivo in developing potato tubers and other plant tissues [J]. Planta, 1993, 189(3): 329−339. doi: 10.1007/BF00194429 [12] HEIM U, WEBER H, BÄUMLEIN H, et al. A sucrose-synthase gene of Vicia faba L. : Expression pattern in developing seeds in relation to starch synthesis and metabolic regulation [J]. Planta, 1993, 191(3): 394−401. [13] 陈慧敏, 李敏慧, 冯送联, 等. 甜玉米蔗糖合成酶基因ZmSus6和ZmSus7的克隆及组织表达特异性检测 [J]. 南方农业学报, 2020, 51(5):1098−1107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2020.05.014CHEN H M, LI M H, FENG S L, et al. Cloning and tissue expression specificity analysis of sucrose synthase genesZmSus6 and ZmSus7 in sweet corn [J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2020, 51(5): 1098−1107.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2020.05.014 [14] 来艳华, 赵亚中. 玉米蔗糖合成酶基因Sh1生物信息学分析 [J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2019(10):4−10. doi: 10.11942/j.issn1002-2767.2019.10.0004LAI Y H, ZHAO Y Z. Bioinformatics analysis on Sh1 gene of maize sucrose synthase [J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019(10): 4−10.(in Chinese) doi: 10.11942/j.issn1002-2767.2019.10.0004 [15] WERR W, FROMMER W B, MAAS C, et al. Structure of the sucrose synthase gene on chromosome 9 of Zea mays L [J]. The EMBO Journal, 1985, 4(6): 1373−1380. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03789.x [16] GUPTA M, CHOUREY P S, BURR B, et al. cDNAs of two non-allelic sucrose synthase genes in maize: Cloning, expression, characterization and molecular mapping of the sucrose synthase-2 gene [J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 1988, 10(3): 215−224. doi: 10.1007/BF00027398 [17] CARLSON S J, CHOUREY P S, HELENTJARIS T, et al. Gene expression studies on developing kernels of maize sucrose synthase (SuSy) mutants show evidence for a third SuSy gene [J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2002, 49(1): 15−29. doi: 10.1023/A:1014457901992 [18] WEI Y Y, XU F, SHAO X F. Changes in soluble sugar metabolism in loquat fruit during different cold storage [J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 2017, 54(5): 1043−1051. doi: 10.1007/s13197-017-2536-5 [19] ZHU X D, WANG M Q, LI X P, et al. Genome-wide analysis of the sucrose synthase gene family in grape (Vitis vinifera): Structure, evolution, and expression profiles [J]. Genes, 2017, 8(4): 111. doi: 10.3390/genes8040111 [20] CHEN C J, XIA R, CHEN H, et al. TBtools, a Toolkit for Biologists integrating various HTS-data handling tools with a user-friendly interface[J]. bioRxiv, 2018,DOI: 10.1101/289660. [21] POREBSKI S, BAILEY L G, BAUM B R. Modification of a CTAB DNA extraction protocol for plants containing high polysaccharide and polyphenol components [J]. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 1997, 15(1): 8−15. doi: 10.1007/BF02772108 [22] 何艺涛, 王广亚, 范春芬, 等. 植物蔗糖合酶研究进展 [J]. 植物生理学报, 2020, 56(6):1165−1176. doi: 10.13592/j.cnki.ppj.2019.0230HE Y T, WANG G Y, FAN C F, et al. Research progress of sucrose synthase in plants [J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2020, 56(6): 1165−1176.(in Chinese) doi: 10.13592/j.cnki.ppj.2019.0230 [23] 乔亮. 水稻蔗糖合成酶基因家族的初步研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2012QIAO L. Preliminary study of the rice sucrose synthase gene family[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2012. (in Chinese) [24] 李丽娜, 孔建强. 植物蔗糖合酶的结构、功能及应用 [J]. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2015, 31(9):904−913. doi: 10.13865/j.cnki.cjbmb.2015.09.03LI L N, KONG J Q. Gene organization, function and application of plant sucrose synthase [J]. Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2015, 31(9): 904−913.(in Chinese) doi: 10.13865/j.cnki.cjbmb.2015.09.03 [25] REN X D, ZHANG J J. Research progresses on the key enzymes involved in sucrose metabolism in maize [J]. Carbohydrate Research, 2013, 368: 29−34. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2012.10.016 -







 下载:
下载: