Breeding Haploid-induced Corn Lines for Fresh Consumption in Fujian
-
摘要:
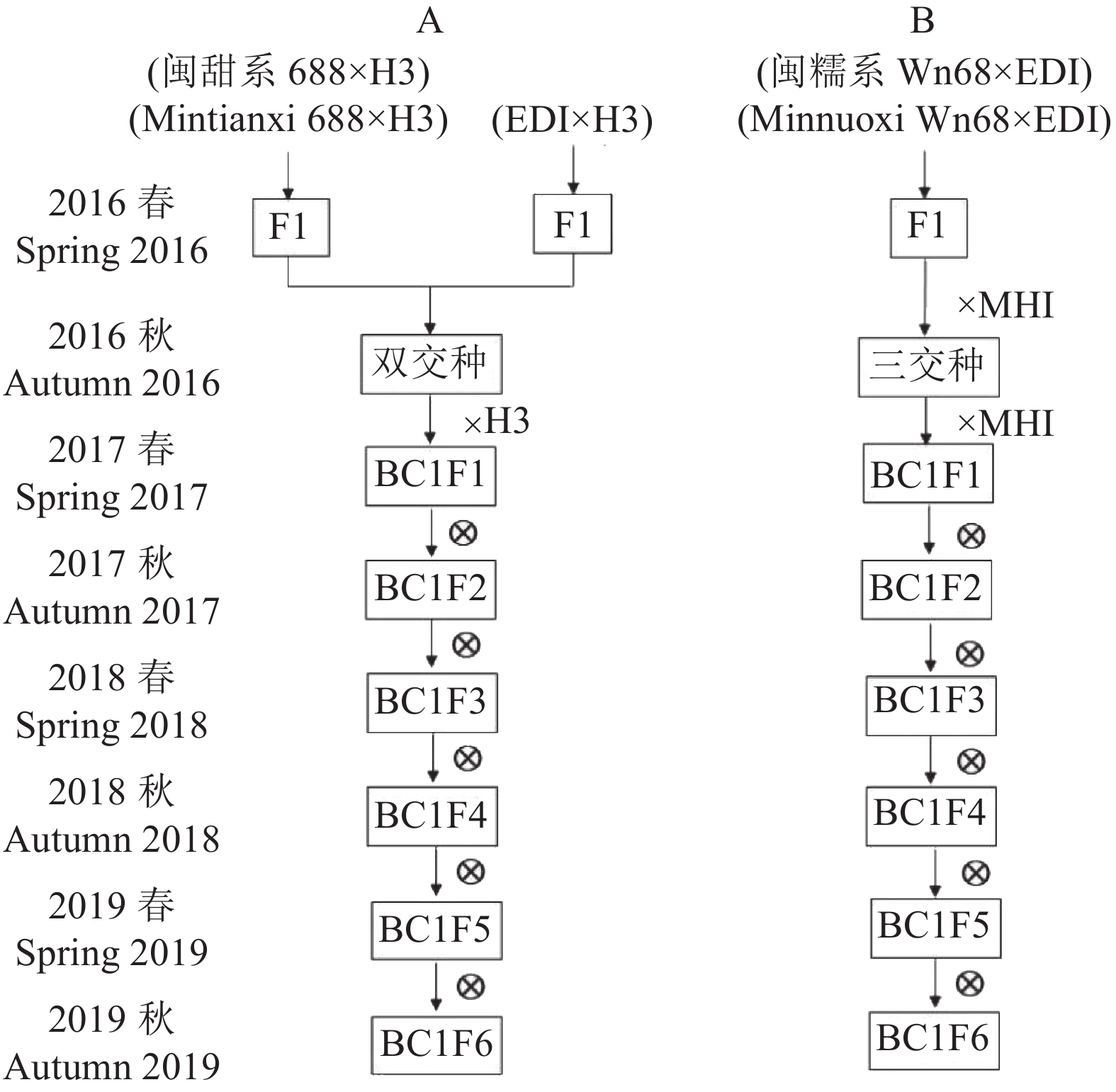
目的 玉米单倍体技术已成功应用于玉米商业化育种,极大地提高了玉米育种效率。针对福建省玉米单倍体育种起步晚、缺乏适应本地的诱导系等问题,开展适应福建气候特点的玉米单倍体诱导系选育,为福建鲜食玉米单倍体育种提供材料。 方法 利用外引高频单倍体诱导系MHI和EDI、高油型诱导系H3为基础材料,分别加入甜、糯玉米种质构建基础群体,在自交纯合的同时进行适应性、油分和诱导率测定。 结果 选育出适合福建省鲜食玉米单倍体育种的诱导系2份,分别命名为FSI-4和FWI-2。其中FSI-4为高油型甜质诱导系,平均诱导率为10.32%,农艺性状及抗病性优良,花粉量大,油分含量8.99%,可采用油分标记进行筛选;FWI-2为糯质型单倍体诱导系,该系诱导率平均为11.08%,植株农艺性状及抗病性优良,花粉量大,颜色标记清晰,适合糯玉米单倍体诱导。 结论 选育出的诱导系FSI-4和FWI-2具有综合农艺性状优良、抗病性好、花粉量大、颜色标记及含油量高等优点,可用于福建省鲜食玉米单倍体高效育种。 Abstract:Objective The haploid technology for high-efficient commercial corn breeding was applied to provide an exemplary breeding program in Fujian. Method The external high-frequency induction MHI and EDI and the oil-rich induction H3 were combined with the materials from local adaptive sweet and waxy corn cultivars to establish a base population. Through continuous testing for oil content, adaptability, and haploid induction rate during breed self-purification, new corn varieties were obtained. Result Two haploid-induced corn lines suitable for fresh consumption were selected. FSI-4 had a relatively high oil content with an average induction rate of 10.32%. It displayed desirable agronomic characters, large amount of pollen, and strong overall resistance. The 8.99% oil content could be further improved by selective breeding using the target markers. The haploid-induced common waxy corn FWI-2 had an average induction rate of 11.08%. It also demonstrated with desirable agronomic characters, large amount of pollen, strong overall resistance, and distinct color markers. The two breeds were both applicable for haploid induction of new corn variety breeding program. Conclusion Two haploid-induced corn lines were obtained to be used as a material for haploid breeding of fresh-consumption corn cultivars in Fujian. -
Key words:
- Fresh-consumption corn /
- haploid /
- induced line /
- breeding
-
表 1 玉米诱导系及其他基础材料
Table 1. Induced corn lines and other basic materials
材料名称
Material系谱/血缘
Pedigree特征特性
Characteristic来源
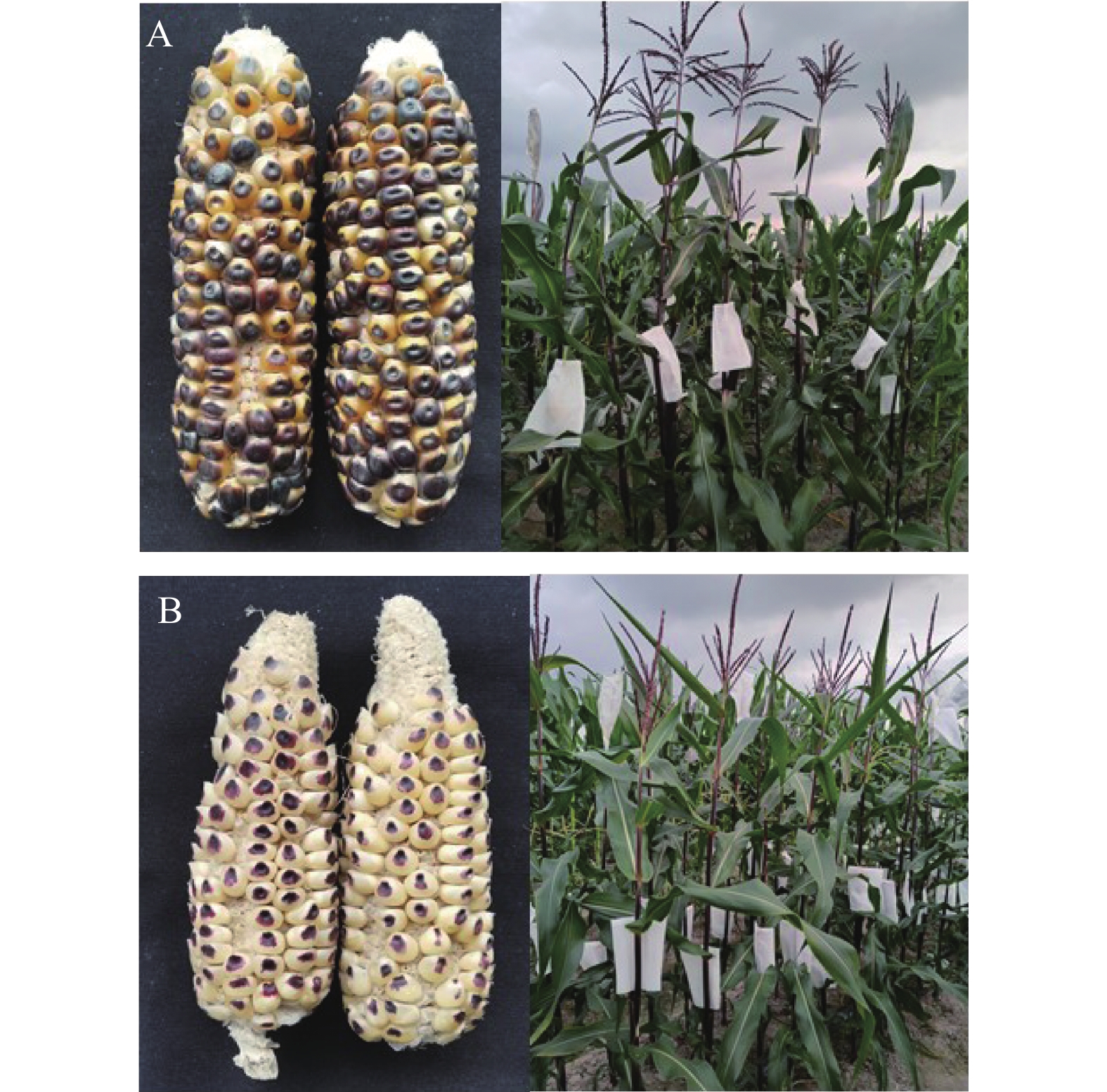
OriginEDI 温带诱导系 诱导率9%~13%,颜色标记清晰,抗倒性好,花粉量少,抗病性和结实性较差 美国 MHI 温热诱导系 诱导率8%~12%,颜色标记清晰,农艺性状较好,抗病性、抗倒性较差 欧洲 H3 温带诱导系 高油型诱导系,诱导率7%~10%左右,花粉量大,抗倒性和颜色标记较差 中国农业大学 闽甜系688 Mintianxi688 甜玉米种质 热带甜玉米种质,抗性好,散粉量大,适应性强,无诱导性 福建省农业科学院 闽糯系Wn68 MinnuoxiWn68 糯玉米种质 热带糯玉米种质,抗性好,散粉量大,适应性强,无诱导性 福建省农业科学院 闽甜685 Mintian6855 杂交种 甜玉米杂交种,温热种质,母本材料 福建省农业科学院 万糯2000 Wannuo2000 杂交种 热源糯玉米杂交种,母本材料 河北省万全种业 表 2 高油型玉米诱导系不同世代油分含量分布
Table 2. Oil content in generations of oil-rich induced corn lines
世代
Offspring样本量
Sample
Number
/粒变幅
Amplitude/%油分含量0%
Oil content 0%油分含量
0.01%~3.00%
Oil content
0.01%~3.00%油分含量
3.01%~6.00%
Oil content
3.01%~6.00%油分含量
6.01%~8.00%
Oil content
6.01%~8.00%油分含量
8.01%~9.00%
Oil content
8.01%~9.00%油分含量>9.00%
Oil content >9.00%种子数
Number占比
Percentage/%种子数
Number占比
Percentage/%种子数
Number占比
Percentage/%种子数
Number占比
Percentage/%种子数
Number占比
Percentage/%种子数
Number占比
Percentage/%双交种
Double hybrid1345 0~8.23 78 5.8 432 32.1 623 46.3 167 12.4 45 3.3 0 0.0 BC1F1 7651 0~9.42 892 11.7 1072 14.0 2987 39.0 1937 25.3 656 8.6 107 1.4 BC1F2 3644 0~9.25 527 14.5 298 8.2 592 16.2 1733 47.6 432 11.9 62 1.7 BC1F3 2241 0~9.49 252 11.2 132 5.9 321 14.3 1243 55.5 281 12.5 12 0.5 BC1F4 2948 0~9.32 278 9.4 127 4.3 392 13.3 1448 49.1 672 22.8 31 1.1 BC1F5 1781 0~8.35 174 9.8 88 4.9 241 13.5 692 38.9 543 30.5 43 2.4 BC1F6 1590 0~8.29 188 11.8 62 3.9 212 13.3 527 33.1 550 34.6 51 3.2 表 3 高油型玉米诱导系不同世代单倍体诱导率分布
Table 3. Haploid induction rate of oil-rich induced corn lines in generations
世代
Offspring株数
Number变幅
Amplitude/
%平均值
Average/
%诱导率0%
Haploid induction rate 0%诱导率
0.01%~3.00%
Haploid
induction rate
0.01%~3.00%诱导率
3.01%~6.00%
Haploid
induction rate
3.01%~6.00%诱导率
6.01%~8.00%
Haploid
induction rate
6.01%~8.00%诱导率
8.01%~9.00%
Haploid
induction rate
8.01%~9.00%诱导率>9.00%
Haploid induction
rate>9.00%株数
Number比例
Percentage/%株数
Number比例
Percentage/%株数
Number比例
Percentage/%株数
Number比例
Percentage/%株数
Number比例
Percentage/%株数
Number比例
Percentage/%双交种
Double hybrid125 0~9.22 4.71 6 4.8 11 8.8 72 57.6 30 24.0 5 4.0 1 0.8 BC1F1 143 0~9.81 5.52 3 2.1 9 6.3 48 33.6 64 44.8 16 11.2 3 2.1 BC1F2 76 1.17~11.35 6.18 0 0.0 6 7.9 19 25.0 30 39.5 14 18.4 7 9.2 BC1F3 90 2.31~12.18 7.39 0 0.0 6 6.7 13 14.4% 43 47.8 19 21.1 9 10.0 BC1F4 48 4.39~11.24 7.66 0 0.0 3 6.3 5 10.4 19 39.6 13 27.1 8 16.7 BC1F5 46 5.88~11.19 8.33 0 0.0 0 0.0 3 6.5 7 15.2 28 60.9 8 17.4 BC1F6 16 7.92~11.96 8.77 0 0.0 0 0.0 0 0.0 1 6.3 11 50.0 5 43.8 表 4 糯质型单倍体诱导系不同世代单倍体诱导率分布
Table 4. Haploid induction rate of haploid-induced waxy corn lines in generations
世代
Offspring株数
Number变幅
Amplitude/
%平均值
Average/
%单倍体诱导率
0.01%~3.00%
Haploid induction rate
0.01%~3.00%单倍体诱导率
3.01%~6.00%
Haploid induction
3.01%~6.00%单倍体诱导率
6.01%~8.00%
Haploid induction
6.01%~8.00%单倍体诱导率
8.01%~9.00%
Haploid induction
8.01%~9.00%单倍体诱导率>9.00%
Haploid induction >9.00%株数
Number比例
Percentage/
%株数
Number比例
Percentage/
%株数
Number比例
Percentage/
%株数
Number比例
Percentage/
%株数
Number比例
Percentage/
%三交种
Trible hybrid160 0.85~8.29 3.21 83 51.9 47 29.4 25 15.6 5 3.1 0 0.8 BC1F1 125 2.35~11.04 6.42 7 5.6 28 22.4 42 33.6 36 28.8 12 2.1 BC1F2 212 5.43~11.29 7.82 0 0.0 9 4.2 57 26.9 117 55.2 29 9.2 BC1F3 110 7.31~12.58 8.42 0 0.0 0 0.0 23 20.9 58 52.7 29 10.0 BC1F4 79 7.65~11.88 8.79 0 0.0 0 0.0 9 11.4 21 26.6 49 16.7 BC1F5 86 8.21~12.37 9.23 0 0.0 0 0.0 0 0.0 19 22.1 67 17.4 BC1F6 10 8.92~12.66 9.47 0 0.0 0 0.0 0 0.0 7 70.0 3 30.00 表 5 普通型糯质单倍体诱导系不同世代农艺性状
Table 5. Agronomic characteristics of haploid-induced common waxy corn line in generations
编号
Number株高
Plant height/cm穗位高
Ear height/cm雄穗分支数
Tassel number/个穗长
Ear length/cm穗粗
Ear width/cm穗行数
Rows per ear/行行粒数
Kernels per row/粒油分含量
Oil content/%诱导率
HIR/%综合抗性
Comprehensive resistanceFSI-1F 183.4 76.5 9.3 12.4 4.4 10.6 21.4 9.18 9.15 优 FSI-1Y 179.3 79.5 8.8 11.7 4.6 9.8 22.7 8.87 8.92 优 FSI-2F 197.5 81.3 8.4 15.4 4.5 10.2 19.5 10.03 9.32 优 FSI-2Y 185.6 82.5 8.3 16.3 4.7 10.7 22.6 9.48 11.45 良 FSI-3F 172.8 64.4 9.2 13.3 4.2 8.8 19.6 8.83 11.32 优 FSI-3Y 177.6 68.7 9.4 12.7 3.9 8.4 21.2 9.31 10.27 中等 FSI-4F 199.2 80.1 10.3 16.5 5.2 12.2 21.9 8.93 9.76 优 FSI-4Y 201.9 83.3 9.8 15.7 4.9 11.6 22.2 9.04 10.87 优 FSI-5F 181.6 72.5 7.8 13.2 4.4 11.8 22.3 8.85 9.25 中等 FSI-5Y 179.7 68.9 7.2 12.6 4.5 9.8 18.5 9.33 9.72 良 FWI-1F 159.4 64.4 6.8 11.2 4.1 10.6 20.5 2.33 10.35 良 FWI-1Y 166.5 71.2 7.4 12.3 4.5 9.7 21.2 3.17 9.21 良 FWI-2F 184.3 73.4 6.7 16.8 5.6 12.7 23.1 2.19 11.32 优 FWI-2F 190.5 76.2 7.1 15.7 5.3 12.3 21.9 1.85 10.84 优 FWI-3F 174.5 69.2 7.5 13.4 4.6 10.8 19.3 1.67 8.62 中等 FWI-3Y 176.6 71.3 6.9 12.5 4.7 11.3 18.5 2.03 8.93 优 F、Y分别代表福建(F)和云南(Y)。
F: Fujian; Y: Yunnan. -
[1] 刘纪麟. 玉米育种学[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2002. [2] 杜何为, 戴景瑞, 李建生. 玉米单倍体育种研究进展 [J]. 玉米科学, 2010, 18(6):1−7.DU H W, DAI J R, LI J S. Study proceeding in haploid breeding of maize [J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2010, 18(6): 1−7.(in Chinese) [3] CHANG M T, COE E H Jr. Doubled haploids[M]//Molecular Genetic Approaches to Maize Improvement. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2009: 127-142. [4] 陈绍江, 黎亮, 李浩川. 玉米单倍体育种技术[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2012. [5] COE E H Jr. A line of maize with high haploid frequency [J]. The American Naturalist, 1959, 93(873): 381−382. doi: 10.1086/282098 [6] CHASE S S. Monoploids and monoploid-derivatives of maize (Zea mays L. ) [J]. The Botanical Review, 1969, 35(2): 117−168. doi: 10.1007/BF02858912 [7] GEIGER H H, GORDILLO G A. Doubled haploids in hybrid maize breeding [J]. Maydica, 2009, 54(4): 485−499. [8] ROTARENCO V, DICU G, FUIA S. New inducers of maternal haploids in maize [J]. Maize Genetics Cooperation Newsletter, 2010, 84: 1−7. [9] SHATSKAYA O A, ZABIROVA E R, SHCHERBAK V S, et al. Mass induction of maternal haploids in corn [J]. Maize Genetics Cooperation Newsletter, 1994, 68: 51. [10] EDER J, CHALYK S. In vivo haploid induction in maize [J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2002, 104(4): 703−708. doi: 10.1007/s00122-001-0773-4 [11] ROEBER F, GORDILLO G A, GEIGER H H. In vivo haploid induction in maize-Performance of new inducers and significance of doubled haploid lines in hybrid breeding [J]. Maydica, 2005, 50(3): 275−283. [12] 刘志增, 宋同明. 玉米高频率孤雌生殖单倍体诱导系的选育与鉴定 [J]. 作物学报, 2000, 26(5):570−574. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0496-3490.2000.05.009LIU Z Z, SONG T M. The breeding and identification of haploid inducer with high frequency parthenogenesis in maize [J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2000, 26(5): 570−574.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0496-3490.2000.05.009 [13] 才卓, 徐国良, 刘向辉, 等. 玉米高频率单倍生殖诱导系吉高诱系3号的选育 [J]. 玉米科学, 2007, 15(1):1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0906.2007.01.001CAI Z, XU G L, LIU X H, et al. The breeding of JAAS3-haploid inducer with high frequency parthenogenesis in maize [J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2007, 15(1): 1−4.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0906.2007.01.001 [14] ZHANG Z L, QIU F Z, LIU Y Z, et al. Chromosome elimination and in vivo haploid production induced by Stock 6-derived inducer line in maize (Zea mays L. ) [J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2008, 27(12): 1851−1860. doi: 10.1007/s00299-008-0601-2 [15] 岳尧海, 路明, 张建新, 等. 玉米单倍体高频诱导系吉诱101号的选育 [J]. 作物杂志, 2017(3):35−38.YUE Y H, LU M, ZHANG J X, et al. The breeding of Jiyou 101 haploid inducer with high frequency parthenogenesis in maize [J]. Crops, 2017(3): 35−38.(in Chinese) [16] 陈绍江, 宋同明. 利用高油分的花粉直感效应鉴别玉米单倍体 [J]. 作物学报, 2003, 29(4):587−590. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0496-3490.2003.04.020CHEN S J, SONG T M. Identification haploid with high oil Xenia effect in maize [J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2003, 29(4): 587−590.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0496-3490.2003.04.020 [17] 董昕. 玉米单倍体诱导基因qhir1精细定位与新型诱导系选育研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2014.DONG X. Fine mapping haploid induction rate gene Qhir1and marker assisted selection of Qhir1in haploid breeding in maize[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese) [18] LIU C X, LI J L, CHEN M, et al. Development of high-oil maize haploid inducer with a novel phenotyping strategy [J]. The Crop Journal, 2022, 10(2): 524−531. doi: 10.1016/j.cj.2021.07.009 [19] 刘金, 郭婷婷, 杨培强, 等. 玉米单倍体核磁共振自动分拣系统的开发(英文) [J]. 农业工程学报, 2012(S2):233−236.LIU J, GUO T T, YANG P Q, et al. Development of automatic nuclear magnetic resonance screening system for haploid kernels in maize [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2012(S2): 233−236.(in Chinese) [20] 陈宝建, 刘丽威, 徐丽, 等. 玉米单倍体幼胚加倍效果观察 [J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2016, 21(5):10−16. doi: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2016.05.002CHEN B J, LIU L W, XU L, et al. Observation on doubling effects of immature haploid embryo in maize [J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2016, 21(5): 10−16.(in Chinese) doi: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2016.05.002 [21] DONG L, LI L N, LIU C L, et al. Genome editing and double-fluorescence proteins enable robust maternal haploid induction and identification in maize [J]. Molecular Plant, 2018, 11(9): 1214−1217. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2018.06.011 [22] 段民孝, 刘新香, 邢锦丰, 等. 玉米高频单倍体诱导系选育研究 [J]. 玉米科学, 2020, 28(4):8−14.DUAN M X, LIU X X, XING J F, et al. Study on breeding the high frequency haploid inducer in maize [J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2020, 28(4): 8−14.(in Chinese) [23] 任军, 郭琦, 刘小丹, 等. 玉米杂交诱导单倍生殖育种工具材料: 单倍体诱导系 [J]. 玉米科学, 2020, 28(1):9−16,24.REN J, GUO Q, LIU X D, et al. Tool material for maize in vivo haploid induction: Inducers [J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2020, 28(1): 9−16,24.(in Chinese) [24] 杨耀迥, 张述宽, 滕辉升, 等. 玉米单倍体诱导系Y8的选育 [J]. 大众科技, 2012, 14(9):106−107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1151.2012.09.045YANG Y J, ZHANG S K, TENG H S, et al. Breeding of corn haploid induction system Y8 [J]. Popular Science & Technology, 2012, 14(9): 106−107.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1151.2012.09.045 [25] 江禹奉, 覃兰秋, 程伟东, 等. 桂诱系列热带玉米单倍体诱导系选育 [J]. 广东农业科学, 2015, 42(10):11−15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2015.10.002JIANG Y F, QIN L Q, CHENG W D, et al. Breeding of Gui inducer series for in vivo haploid production in tropical maize [J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 42(10): 11−15.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2015.10.002 [26] LASHERMES P, BECKERT M. Genetic control of maternal haploidy in maize (Zea mays L. ) and selection of haploid inducing lines [J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 1988, 76(3): 405−410. doi: 10.1007/BF00265341 -







 下载:
下载:


