Biological Characteristics and Fungicides for Effective Control of Colletotrichum destructivum on Echeveria Perle von Nürnberg
-
摘要:
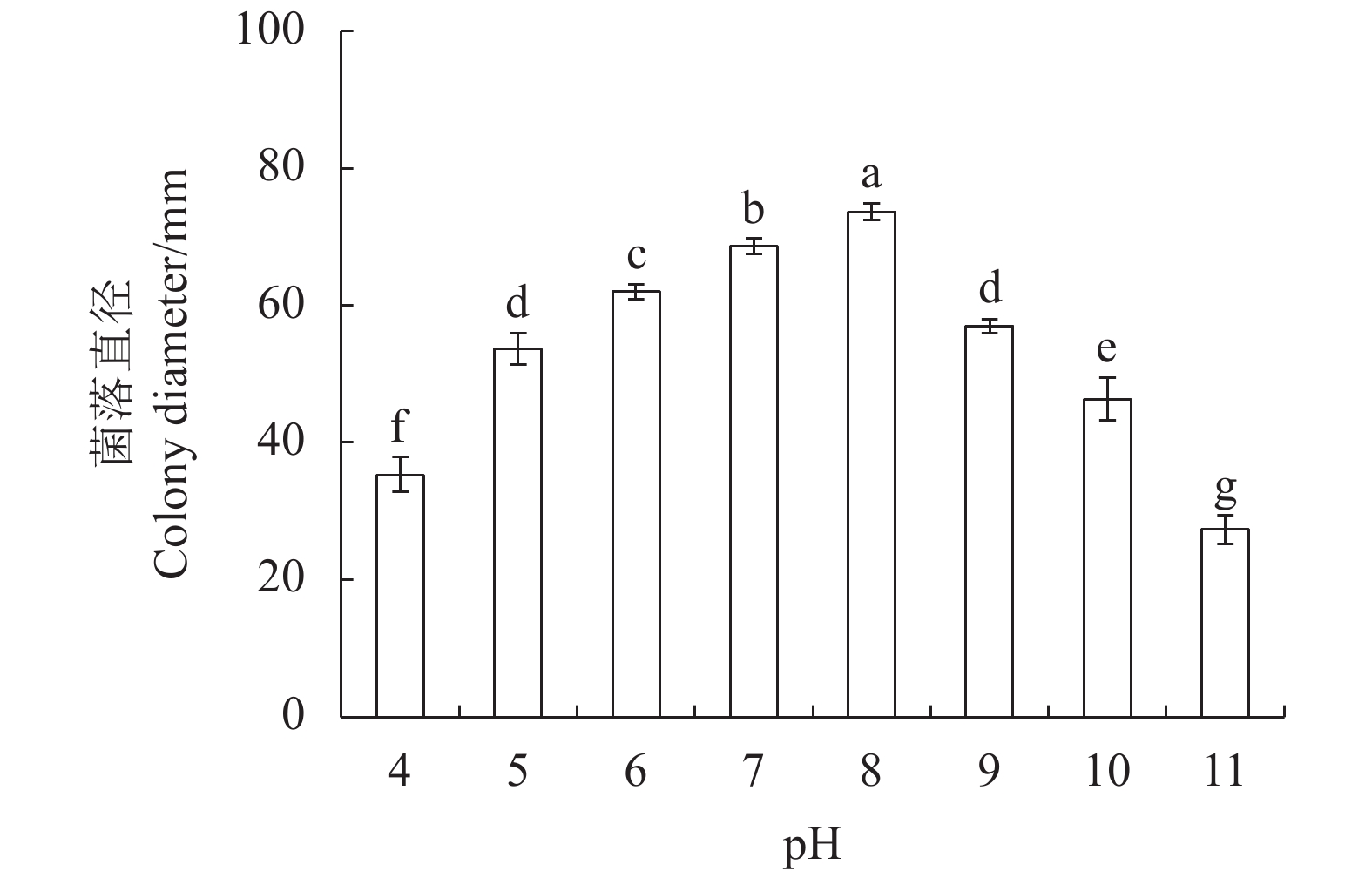
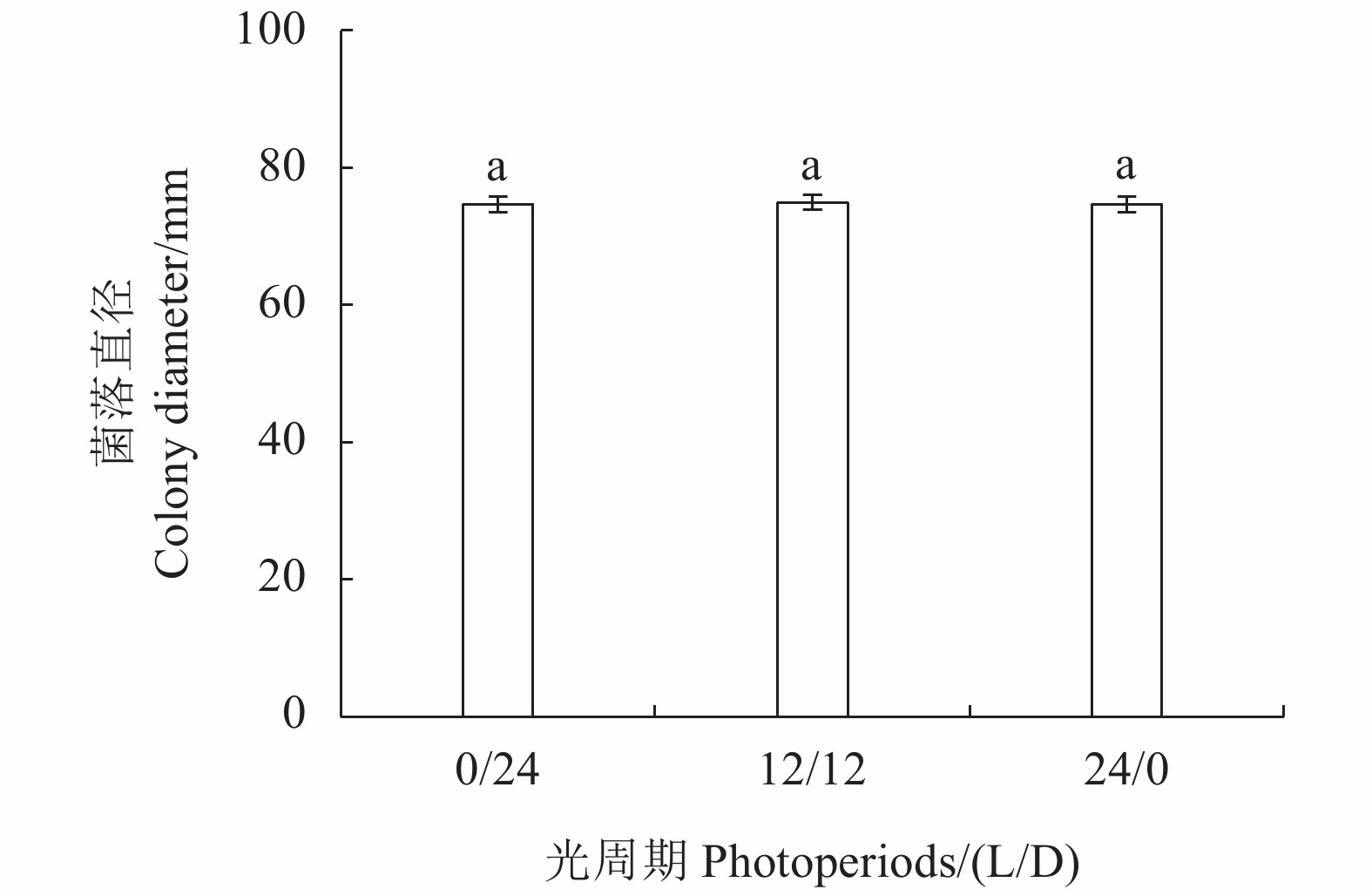
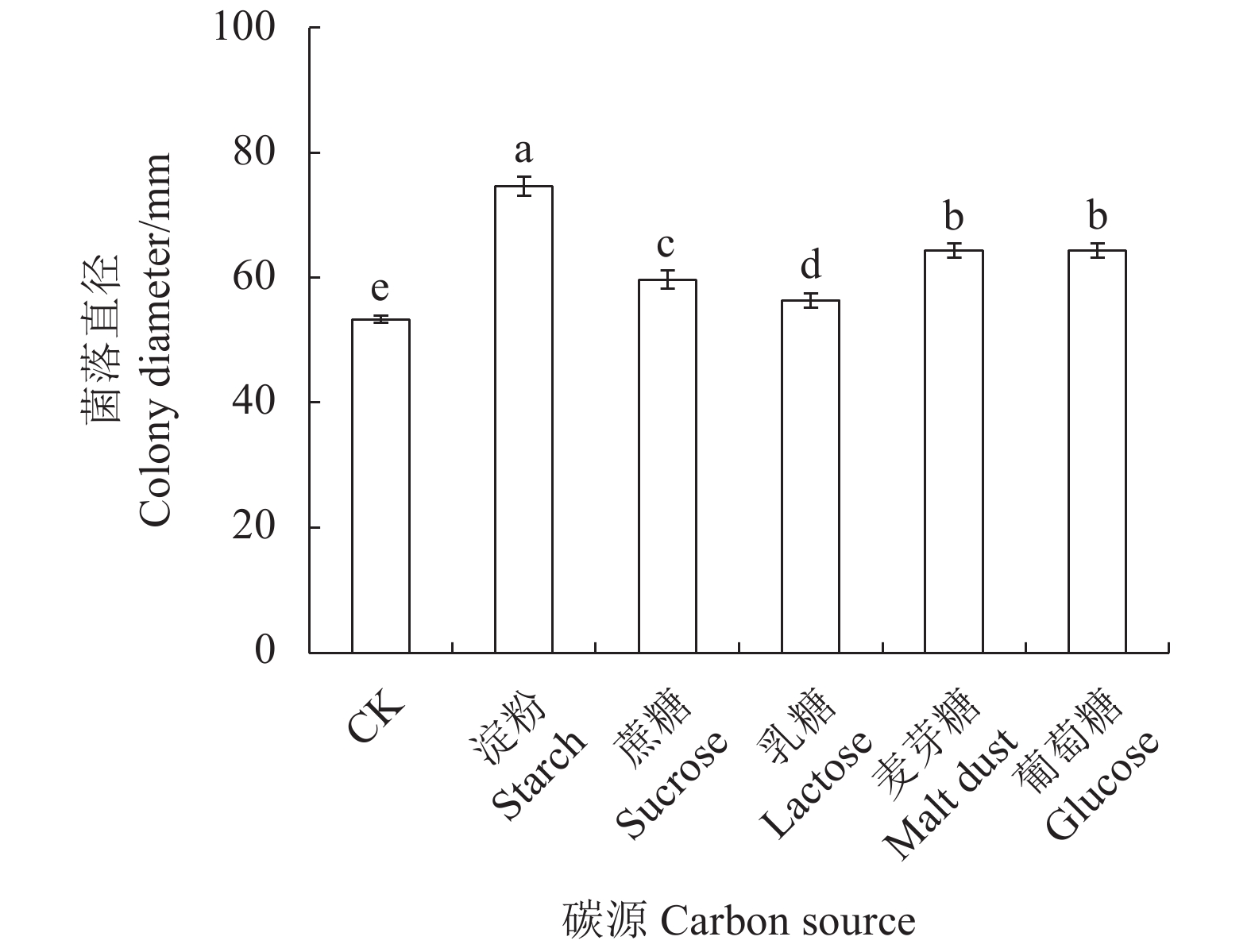
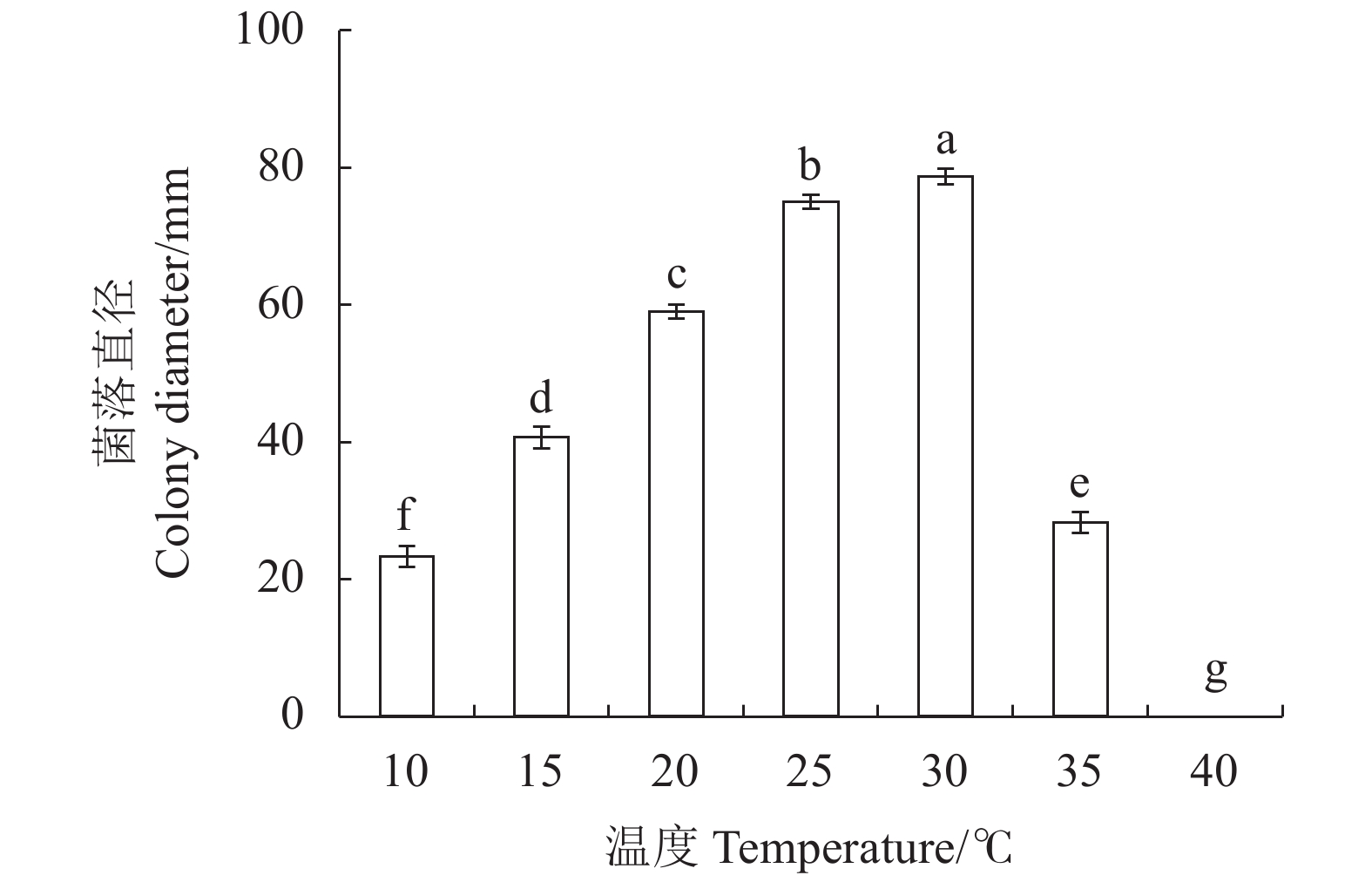
目的 明确红心莲炭疽病菌毁灭炭疽菌(Colletotrichum destructivum)的生物学特性。测定不同化学结构和作用机制的6种杀菌剂对毁灭炭疽菌的室内毒力,筛选高效安全杀菌剂。 方法 采用菌丝生长速率法测定温度、pH、光周期和碳、氮源对菌丝生长的影响,以及6种杀菌剂对毁灭炭疽菌抑制效果。 结果 毁灭炭疽菌菌丝生长最适温度为30 ℃、最适pH为8,光周期对菌丝生长影响小,最适碳、氮源分别为淀粉和酵母。室内毒力测定结果表明,所选的6种杀菌剂对病原菌毒力差异大,其中咯菌腈的毒力最强,EC50为0.0236 mg·L−1;其次为咪鲜胺和吡唑醚菌酯,EC50分别为0.0306 和0.0487 mg·L−1;甲基硫菌灵和苯醚甲环唑的毒力较弱,EC50分别为0.1526和0.1955 mg·L−1;多菌灵的毒力最弱,EC50为0.2199 mg·L−1。 结论 温度、pH、碳氮源对毁灭炭疽菌菌丝生长具有一定影响。咯菌腈、咪鲜胺和吡唑醚菌酯等杀菌剂对毁灭炭疽菌有较好的室内毒力。 Abstract:Objective Biological characteristics of Colletotrichum destructivum that infects Echeveria Perle von Nürnberg and in vitro toxicity of 6 fungicides on the pathogen were studied for the disease control. Method Effects of temperature, pH, photoperiods, carbon, and nitrogen on the growth and 6 fungicides on their legality on C. destructivum were determined by an in vitro culture method. Result The optimum growth conditions for C. destructivum were 30 ℃ at pH 8 on medium using starch for carbon and yeast for nitrogen resources. Photoperiods did not significant affect the mycelial growth. The 6 selected fungicides exhibited varying degrees of efficacy against C. destructivum. The EC50 of fludioxonil at 0.023 6 mg·L−1 was the most potent of them. It was followed by prochloraz at 0.030 6 mg·L−1, pyraclostrobin at 0.048 7 mg·L−1, thiophanate-methyl at 0.152 6 mg·L−1, difenoconazole at 0.195 5 mg·L−1, and carbendazim at 0.219 9 mg·L−1. Conclusion The growth of C. destructivum was affected by temperature, pH, carbon, and nitrogen and inhibited by fludioxonil, prochloraz, and pyraclostrobin. -
表 1 6种杀菌剂对毁灭炭疽病菌的室内毒力
Table 1. Toxicities of 6 fungicides against C. destructivum
供试药剂
Fungicides毒力回归方程
Toxicity regression equationEC50/(mg·L−1) 95% 置信区间
95% confidence interval
/(mg·L−1)相关系数 r
Correlation coefficient r甲基硫菌灵
Thiophanate-Methyly=5.556 4+0.681 6x 0.152 6 0.122 9~0.189 6 0.996 8 咪鲜胺
Prochlorazy=5.772 6+0.510 1x 0.030 6 0.024 6~0.038 0 0.997 4 吡唑醚菌酯Pyraclostrobin y=5.789 9+0.601 9x 0.048 7 0.042 6~0.055 7 0.998 9 咯菌腈
Fludioxonily=5.817 3+0.502 2x 0.023 6 0.019 8~0.028 0 0.998 4 苯醚甲环唑Difenoconazole y=5.520 3+0.733 9x 0.195 5 0.145 4~0.262 8 0.994 3 多菌灵
Carbendazimy=5.472 8+0.718 9x 0.219 9 0.181 0~0.267 2 0.997 5 -
[1] GRIFFITHS H, MALES J. Succulent plants[J]. Current Biology, 2017, 27(17): R890–R896. [2] 中国花卉协会. 2018年12月各地盆花市场行情 [J]. 中国花卉园艺, 2019(3):51−52.CHINA FLOWER ASSOCIATION. Potted flower market in December 2018 [J]. China Flowers & Horticulture, 2019(3): 51−52.(in Chinese) [3] YAO J A, HUANG P, CHEN H X, et al. Anthracnose pathogen of the succulent plant Echeveria ‘Perle von Nürnberg’ [J]. Australasian Plant Pathology, 2020, 49(2): 209−212. doi: 10.1007/s13313-020-00693-w [4] TOMIOKA K, NISHIKAWA J, MORIWAKI J, et al. Anthracnose of snapdragon caused by Colletotrichum destructivum [J]. Journal of General Plant Pathology, 2011, 77(1): 60−63. doi: 10.1007/s10327-010-0278-6 [5] VASIĆ T, KRNJAJA V, JEVREMOVIĆ D, et al. Morphological and Molecular Identification of Colletotrichum destructivum from alfalfa[C]. 7th Congress on Plant Protection, 2014: 24−28. [6] MACDONALD J L, PUNJA Z K. Identification of Colletotrichum destructivum causing anthracnose of Wasabia japonica in British Columbia[C]. Canadian Phytopathological Society British Columbia Regional Meeting, 2015: 38. [7] 冉飞, 陈佳, 莫飞旭, 等. 百香果炭疽病菌生物学特性及室内药剂筛选 [J]. 热带作物学报, 2021, 42(4):1080−1085. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2021.04.025RAN F, CHEN J, MO F X, et al. Biological characteristics of the pathogen and fungicides screening in laboratory for anthracnose of Passiflora edulia Sims [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2021, 42(4): 1080−1085.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2021.04.025 [8] CROUCH J A, CROUCH J A. Anthracnose of cereals and grasses [J]. Fungal Diversity, 2009, 39: 19−44. [9] BERTETTI D, GULLINO M, GARIBALDI A. Effect of leaf wetness duration, temperature and inoculum concentration on infection of evergreen azalea by Colletotrichum acutatum, the causal agent of anthracnose [J]. Journal of Plant Pathology, 2009, 91(3): 763−766. [10] 王芳, 王晓立, 韩浩章, 等. 多肉植物青星美人的黑腐病病原鉴定及生物学特性 [J]. 湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 47(5):540−546.WANG F, WANG X L, HAN H Z, et al. Identification and biological characteristics of black rot pathogen on succulent plant Pachyphytum ‘Dr Cornelius' [J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University (Natural Sciences), 2021, 47(5): 540−546.(in Chinese) [11] SUN H, TIAN J, STEINKELLNER S, et al. Identification and characterization of Colletotrichum destructivum causing anthracnose on sunflower [J]. Archives of Microbiology, 2020, 202(6): 1459−1467. doi: 10.1007/s00203-020-01861-8 [12] 张琳, 彭琳, 邵郅伟, 等. 南瓜炭疽病菌Colletotrichum brevisporum生物学特性及药剂防治 [J]. 植物保护, 2021, 47(4):59−65.ZHANG L, PENG L, SHAO Z W, et al. Biological characteristics and indoor fungicide screening of Colletotrichum brevisporum causing pumpkin anthracnose [J]. Plant Protection, 2021, 47(4): 59−65.(in Chinese) [13] 娄喜艳, 王欣阳, 裴冬丽. 河南商丘月季炭疽病的病原菌鉴定及生物学特性 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2021, 49(22):116−121.LOU X Y, WANG X Y, PEI D L. Identification and biological characteristics of pathogenic bacteria of rose anthracnose in Shangqiu Henan Province [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 49(22): 116−121.(in Chinese) [14] 孟珂, 张亚波, 常君, 等. 8种杀菌剂对9种薄壳山核桃炭疽病病原菌的毒力测定 [J]. 林业科学研究, 2021, 34(1):153−164. doi: 10.13275/j.cnki.lykxyj.2021.01.019MENG K, ZHANG Y B, CHANG J, et al. Toxicity test with 8 fungicides against 9 pathogens of pecan anthracnose (Colletotrichum spp. ) [J]. Forest Research, 2021, 34(1): 153−164.(in Chinese) doi: 10.13275/j.cnki.lykxyj.2021.01.019 [15] 高鹏, 刘琳, 刘昀鑫, 等. 不同作用机制杀菌剂对燕麦炭疽病病菌的室内毒力测定 [J]. 草业科学, 2021, 38(9):1737−1744.GAO P, LIU L, LIU Y X, et al. Toxicity testing of different fungicides for Colletotrichum cereale on oat anthracnose [J]. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(9): 1737−1744.(in Chinese) [16] 李少卡, 何凡, 陈哲, 等. 防治荔枝炭疽病的药剂筛选及田间应用 [J]. 农药, 2019, 58(10):773−776.LI S K, HE F, CHEN Z, et al. Effective fungicides screening and field application for Litchi anthracnose [J]. Agrochemicals, 2019, 58(10): 773−776.(in Chinese) -







 下载:
下载: