Fermentation Optimization and Antifungal Activity of Bacillus methylotrophicus Z21
-
摘要:
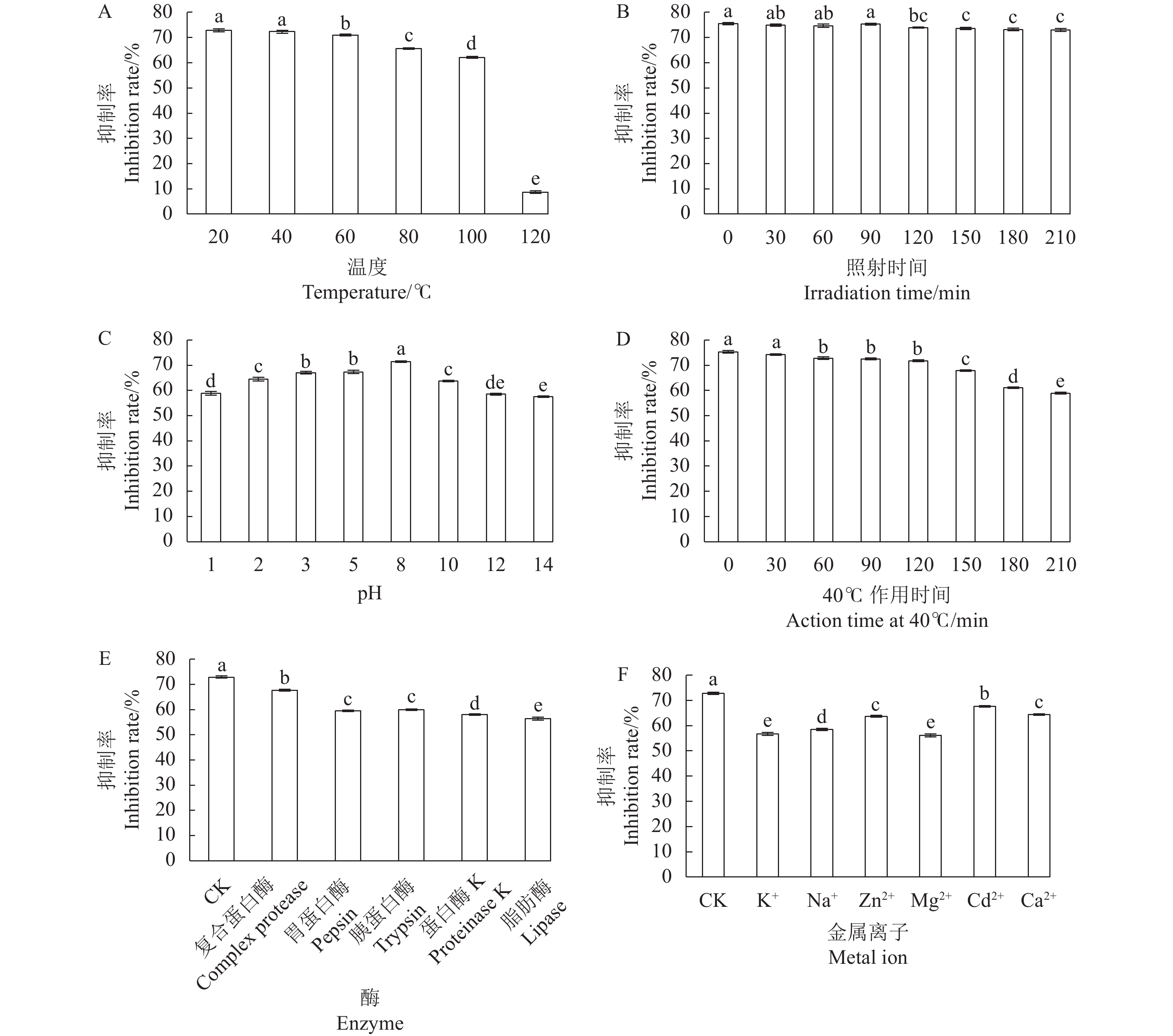
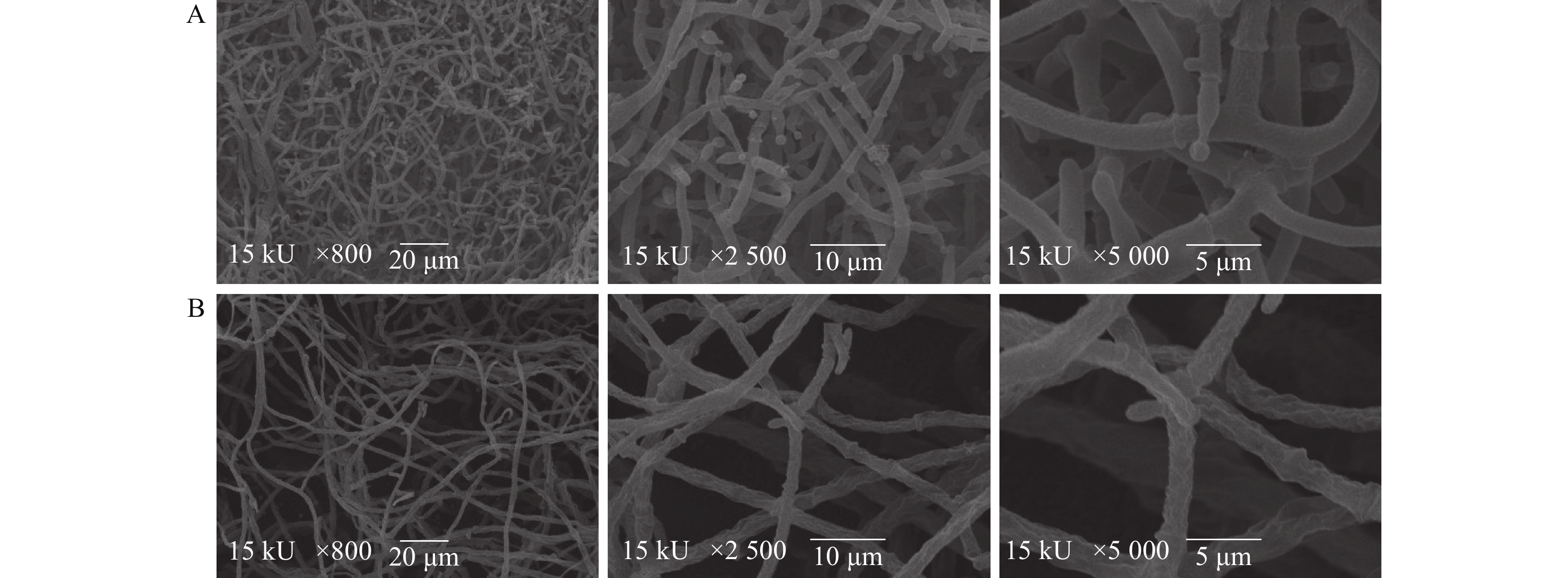
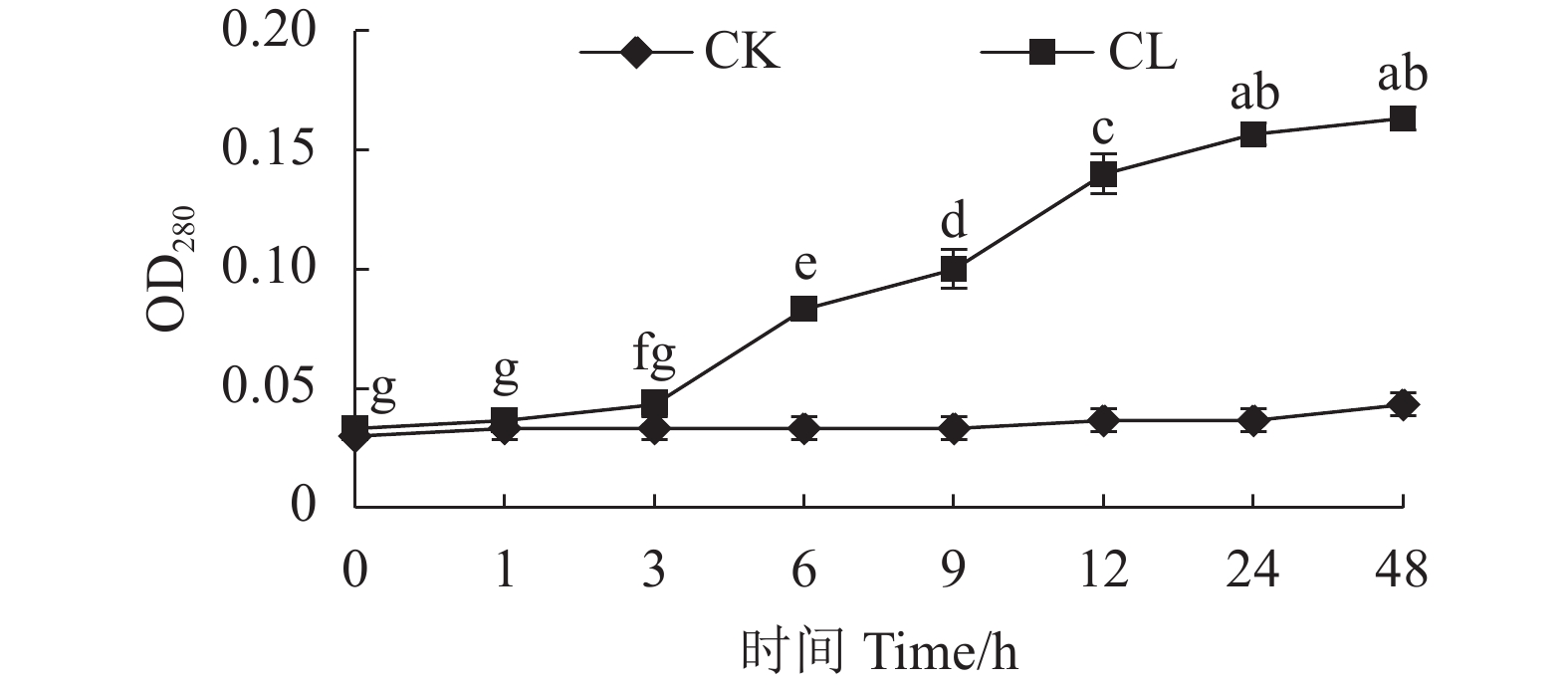
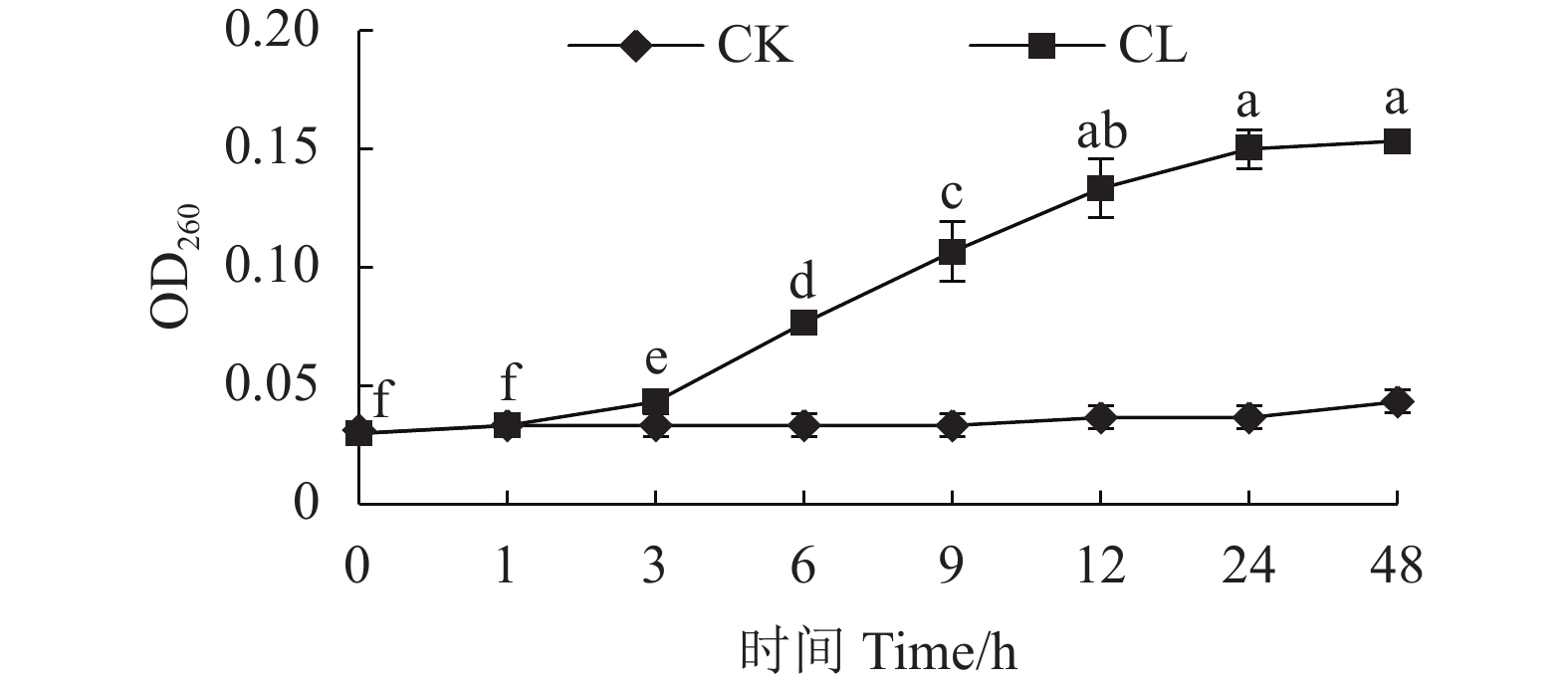
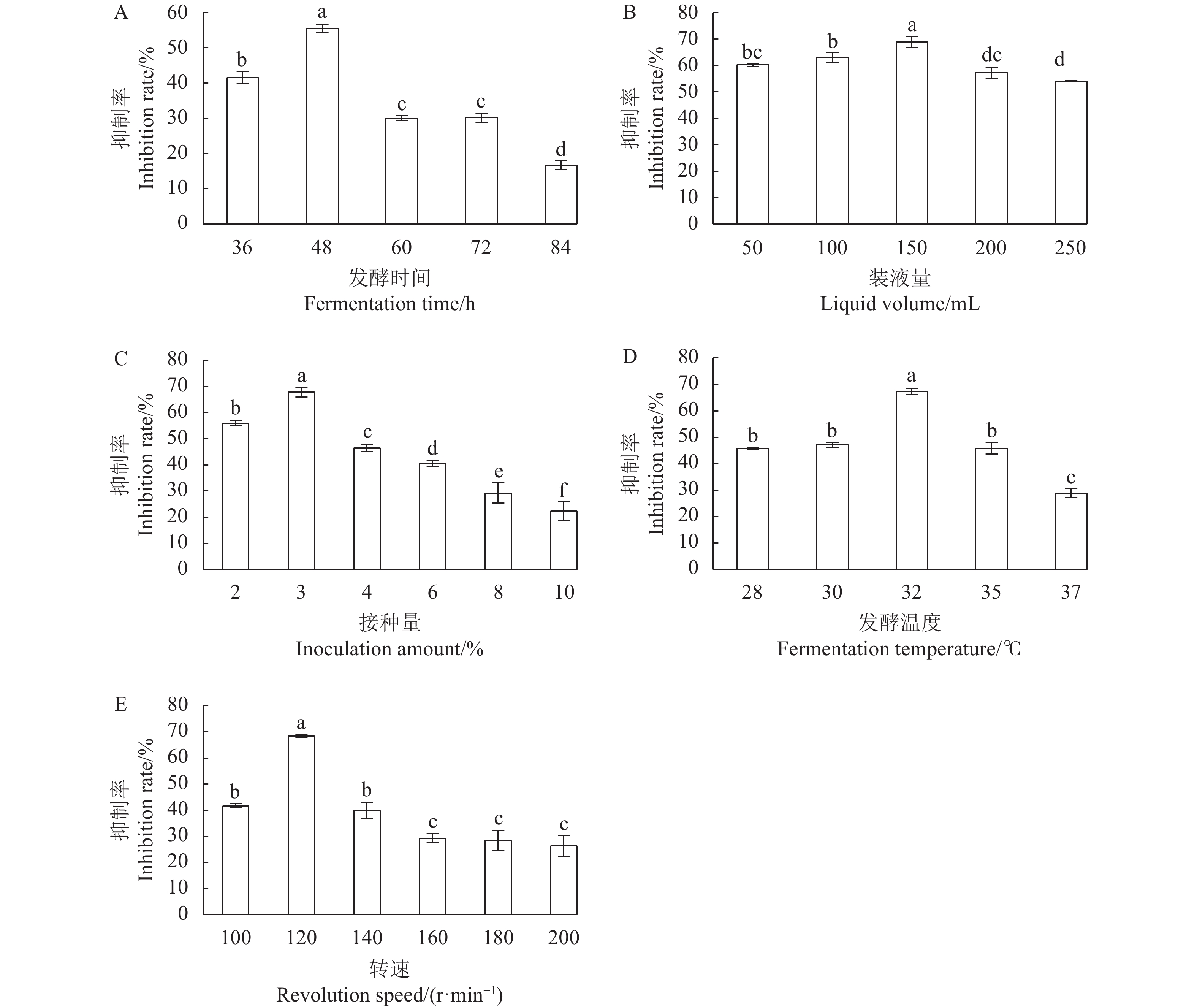
目的 芽孢杆菌Z21发酵液对黑曲霉、康氏木霉等真菌有拮抗性,探究Z21菌抑菌活性物质稳定性及抑菌活性分析,可为开发天然防腐剂提供参考。 方法 通过牛津杯法,以康氏木霉为指示菌,优化Z21菌产抑菌活性物质的发酵条件,探讨不同温度、紫外线、pH、作用时间、酶和金属离子对Z21菌抑菌活性物质稳定性的影响;测定硫酸铵沉淀法提取的粗提物MIC及对康氏木霉孢子萌发和菌丝生长的影响。 结果 当发酵条件为500 mL锥形瓶装液体培养基150 mL、接种量3%、发酵时间60 h、发酵温度30 ℃、转速140 r·min−1时,150 μL无菌发酵液对康氏木霉菌丝生长的抑制率为72%左右,粗提物的MIC为25 mg·mL−1。在紫外光波长为260 nm和280 nm时,经25 mg·mL−1的粗取物处理后的康氏木霉菌液紫外吸光值升高,说明菌丝的核酸和蛋白质有泄露。Z21菌发酵液耐热,耐酸、碱,对紫外线、许多酶和金属离子不敏感。扫描电镜观察显示:Z21菌处理后的康氏木霉菌丝比较纤细,不分化孢子梗。 结论 Z21菌发酵液对康氏木霉的生长和繁殖均受到抑制,抑菌活性物质稳定性良好。 Abstract:Objective Fermentation process of Bacillus methylotrophicus Z21, which exhibited antifungal activities on Aspergillus niger and Trichoderma koningii among others in a preliminary study, was optimized, and the stability and antibacterial properties of the broth as a nature preservative examined. Method The fermentation conditions, including temperature, UV, pH, time, enzymes, and metal ions, were optimized based on the antifungal activity of the broth against T. koningii determined by the Oxford cup method. Effects of the ammonium sulfate-precipitated crude extract on the MIC, inhibition rate, spore germination, and hypha growth of T. koningii were also examined. Result The optimized process was conducted in a 500 mL flask to hold 150 mL liquid medium with 3% inoculum for the 60 h fermentation at 30 ℃ under constant 140 r·min−1 stirring. The inhibition rate of the 150 μL sterile fermentation broth on the hypha growth was 72%. The increased UV absorbances of the T. koningii culture liquid at OD260 and OD280 by the treatment of the extract at MIC of 25 mg·mL−1 indicated a leakage of nucleic acids and proteins into the liquid from the mycelia. The Z21 fermentation broth was resistant to heat, acid, and alkali but insensitive to UV, enzymes, and metal ions. The scanning electron microscopic images showed that the hyphae of T. koningii treated by the broth became slender without spore stems. Conclusion The growth and reproduction of T. koningii were significantly inhibited by the presence of B. methylotrophicus Z21 fermentation broth. The antifungal activity of the broth remained stable under elevated temperature and/or acidic or alkali conditions. -
Key words:
- antifungal bacterium /
- fermentation optimization /
- anti-fungal property /
- stability
-
表 1 正交试验的因素及水平设计
Table 1. Factors and levels of orthogonal test
水平
LevelsA装液量
Liquid volume/mLB接种量
Inoculation amount/%C发酵时间
Fermentation time/hD发酵温度
Fermentation temperature/℃E转速
Revolution speed/(r·min−1)1 100 2 36 30 120 2 150 3 48 32 140 3 200 4 60 35 160 表 2 Z21菌发酵条件正交试验结果
Table 2. Orthogonal test results on Z21 fermentation conditions
试验
TestA装液量
Liquid
volume/mLB接种量
Inoculation
amount/%C发酵时间
Fermentation
time/hD发酵温度
Fermentation
temperature/℃E转速
Revolution speed/
(r·min−1)F空白
Blank抑制率
Inhibition
rate/%1 100 2 36 30 120 1 52.56 2 100 3 48 32 140 2 40.41 3 100 4 60 35 160 3 23.86 4 150 2 36 32 140 3 60.85 5 150 3 48 35 160 1 39.67 6 150 4 60 30 120 2 55.73 7 200 2 48 30 160 2 13.13 8 200 3 60 32 120 3 56.54 9 200 4 36 35 140 1 34.92 10 100 2 60 35 140 2 19.19 11 100 3 36 30 160 3 13.25 12 100 4 48 32 120 1 57.8 13 150 2 48 35 120 3 25.45 14 150 3 60 30 140 1 70.61 15 150 4 36 32 160 2 15.08 16 200 2 60 32 160 1 16.67 17 200 3 36 35 120 2 22.11 18 200 4 48 30 140 3 51.75 k1 34.512 31.308 33.128 42.838 45.032 45.372 k2 44.565 40.432 38.035 41.225 46.288 27.608 k3 32.52 39.857 40.433 27.533 20.277 38.617 R 12.045 9.124 7.305 15.305 26.011 17.764 主次因素
Secondary factorsE>D>A>B>C 最优方案
Optimal alterativeA2B2C3D1E2 表 3 正交试验结果方差分析
Table 3. ANOVA analysis on orthogonal test results
方差来源
Variance Source平方和
Squares自由度
Freedom均方
Mean
squareF值
F valueP值
P value校正模型 Calibration model 4410.504 10 441.050 1.708 0.246 A 500.237 2 250.118 0.968 0.425 B 313.280 2 156.640 0.607 0.572 C 166.381 2 83.190 0.322 0.735 D 848.615 2 424.308 1.643 0.260 E 2581.992 2 1290.996 4.999 0.045* 残差 Residuals 1807.867 7 258.267 总和 Sum 31126.004 18 表 4 Z21菌发酵液粗提物抑制康氏木霉孢子萌发的MIC
Table 4. MIC of crude Z21 fermentation extract on T. koningii spore germination
不同质量浓度提取物的抑制效果
Antifungal effects of extracts of different concentrations/(mg·mL−1)0 1.56 3.125 6.25 12.5 25 50 100 200 400 800 1000 + + + + + − − − − − − − 注:“+”表示长菌,无抑制效果;“−”表示不长菌,有抑制效果。
Note: “+” means growth of bacteria with no inhibitory effect; “−” means inhibition on bacterial growth. -
[1] NAETS M, VAN DAEL M, VANSTREELS E, et al. To disinfect or not to disinfect in postharvest research on the fungal decay of apple? [J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 2018, 266: 190−199. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2017.12.003 [2] WINTER G, PEREG L. A review on the relation between soil and mycotoxins: Effect of aflatoxin on field, food and finance [J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 2019: ejss.12813. doi: 10.1111/ejss.12813 [3] 裴鹏钢, 熊科, 叶宏, 等. 粮油食品中微生物和真菌毒素污染预测模型研究进展 [J]. 中国粮油学报, 2020, 35(2):179−187. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2020.02.030PEI P G, XIONG K, YE H, et al. Advances in prediction models of microbial and mycotoxin contamination in the grain and oil foods [J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2020, 35(2): 179−187.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2020.02.030 [4] 邓义佳, 王润东, 王雅玲, 等. 鱼干制品中真菌及次生代谢产物污染现状 [J]. 卫生研究, 2019, 48(4):677−680.DENG Y J, WANG R D, WANG Y L, et al. Status of fungal and secondary metabolite contamination in dried fish products [J]. Journal of Hygiene Research, 2019, 48(4): 677−680.(in Chinese) [5] HU W Q, GAO Q X, HAMADA M S, et al. Potential of Pseudomonas chlororaphis subsp. aurantiaca strain Pcho10 as a biocontrol agent against Fusarium graminearum [J]. Phytopathology, 2014, 104(12): 1289−1297. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-02-14-0049-R [6] ESKOLA M, KOS G, ELLIOTT C T, et al. Worldwide contamination of food-crops with mycotoxins: Validity of the widely cited ‘FAO estimate’ of 25% [J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2020, 60(16): 2773−2789. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2019.1658570 [7] 刁益韶, 贾萌, 朱璐瑶. 食品防腐剂的使用现状及安全性分析 [J]. 河北化工, 2012, 35(10):63−66.DIAO Y S, JIA M, ZHU L Y. Application status of food preservatives and their security analysis [J]. Hebei Chemical Industry, 2012, 35(10): 63−66.(in Chinese) [8] 任建雯, 罗云艳, 冯印印, 等. 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌RJW-5-5的分离鉴定及细菌素、抗菌肽基因簇挖掘 [J]. 微生物学通报, 2021, 48(3):742−754.REN J W, LUO Y Y, FENG Y Y, et al. Isolation and identification of Bacillus velezensis RJW-5-5 and gene cluster·mining of bacteriocin and RiPPs [J]. Microbiology China, 2021, 48(3): 742−754.(in Chinese) [9] CHEN M C, WANG J P, ZHU Y J, et al. Antibacterial activity against Ralstonia solanacearum of the lipopeptides secreted from the Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain FJAT-2349 [J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2019, 126(5): 1519−1529. doi: 10.1111/jam.14213 [10] GUO Q G, DONG W X, LI S Z, et al. Fengycin produced by Bacillus subtilis NCD-2 plays a major role in biocontrol of cotton seedling damping-off disease [J]. Microbiological Research, 2014, 169(7/8): 533−540. [11] 许琳琳. 枯草芽孢杆菌环脂肽对海藻酸钠成膜性能以及蓝莓保鲜效果影响研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2020XU L L. Effects of cyclolipopeptides produced by Bacillus subtilis on the film-forming properties of sodium alginate and the fresh-keeping effect of blueberries[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2020. (in Chinese) [12] ANANDARAJ B, VELLAICHAMY A, KACHMAN M, et al. Co-production of two new peptide antibiotics by a bacterial isolate Paenibacillus alvei NP75 [J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2009, 379(2): 179−185. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.12.007 [13] 陈雅平. 生防菌海芋内生菌TNX-1的分离鉴定、发酵条件及发酵液抑菌物质研究[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2012.CHEN Y P. Isolation and identification, fermentation conditions of Alocasia endophyte TNX-1 and study on antifungal substances of the fermentation liquid[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2012. [14] 李培中, 许丽, 何惠霞, 等. 1株水蜜桃采后病害拮抗细菌的鉴定及抑菌作用 [J]. 食品科学, 2019(2):102−109. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20171226-323LI P Z, XU L, HE H X, et al. Identification and antifungal activity of an antagonistic strain against postharvest disease in honey peach [J]. Food Science, 2019(2): 102−109.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20171226-323 [15] 张楠楠. 产脂肽枯草芽孢杆菌的发酵优化以及在面包中的应用[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2017.ZHANG N N. Study on the production optimization of lipopepetide from Bacillus subtilis and application in bread[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2017. [16] HMIDET N, JEMIL N, NASRI M. Simultaneous production of alkaline amylase and biosurfactant by Bacillus methylotrophicus DCS1: Application as detergent additive [J]. Biodegradation, 2019, 30(4): 247−258. doi: 10.1007/s10532-018-9847-8 [17] SONTAKKE S, CADENAS M B, MAGGI R G, et al. Use of broad range16S rDNA PCR in clinical microbiology [J]. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 2009, 76(3): 217−225. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2008.11.002 [18] 李方舟. 普洱茶树叶片内生细菌Bacillus velezensis FZ06的基因组测序及抗菌活性代谢产物研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2020LI F Z. Study on genome sequencing and antimicrobial metabolites produced by endophytic bacterium Bacillus velezensis FZ06 isolated from leaves of Camellia assamica[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2020. (in Chinese) [19] 毛馨, 张桂真, 曲劲尧, 等. 芽孢杆菌中新型非核糖体肽类抗菌活性物质的发掘、分离鉴定及特性研究 [J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2020, 47(12):4093−4102.MAO X, ZHANG G Z, QU J Y, et al. Discovery, isolation, identification and characterization of novel non-ribosomal peptide antibacterial active substances in Bacillus [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2020, 47(12): 4093−4102.(in Chinese) [20] MADHAIYAN M, POONGUZHALI S, KWON S W, et al. Bacillus methylotrophicus sp. nov., a methanol-utilizing, plant-growth-promoting bacterium isolated from rice rhizosphere soil [J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2010, 60(Pt 10): 2490−2495. [21] HE C N, YE W Q, ZHU Y Y, et al. Antifungal activity of volatile organic compounds produced by Bacillus methylotrophicus and Bacillus thuringiensis against five common spoilage fungi on loquats [J]. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 2020, 25(15): 3360. doi: 10.3390/molecules25153360 [22] 程敏, 顾钢, 肖顺, 等. 芽孢杆菌(Bacillus)FJSC01对烟草土传病原菌的拮抗作用及其鉴定 [J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 50(2):164−169.CHENG M, GU G, XIAO S, et al. Antagonistic effects of Bacillus FJSC01 on soilborne pathogens of tobacco and its identification [J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 50(2): 164−169.(in Chinese) [23] 张可可, 席宇, 吴少雄, 等. 甲基营养型芽孢杆菌的分离鉴定及其广谱抗菌性能初步研究 [J]. 中国调味品, 2019, 44(10):31−34,45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2019.10.007ZHANG K K, XI Y, WU S X, et al. Isolation and identification of Bacillus methylotrophicus and preliminary study on its broad-spectrum antibacterial activity [J]. China Condiment, 2019, 44(10): 31−34,45.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2019.10.007 [24] 吴燕燕, 张岩, 李来好, 等. 甲基营养型芽孢杆菌抗菌肽对罗非鱼片保鲜效果的研究 [J]. 食品工业科技, 2013, 34(2):315−318.WU Y Y, ZHANG Y, LI L H, et al. Study on fresh-keeping effect of antimicrobial peptides from Bacillus methylotrophilus in Tilapia fillet preservation [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2013, 34(2): 315−318.(in Chinese) [25] 尹向田, 杨阳. 甲基营养型芽孢杆菌GSBM05产抗菌活性物质发酵条件优化 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2018(20):89−93.YIN X T, YANG Y. Optimization of fermentation conditions of antibacterial substance produced by Bacillus methylotrophicus GSBM05 [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2018(20): 89−93.(in Chinese) [26] 魏新燕, 黄媛媛, 黄亚丽, 等. 甲基营养型芽孢杆菌BH21对葡萄灰霉病菌的拮抗作用 [J]. 中国农业科学, 2018, 51(5):883−892.WEI X Y, HUANG Y Y, HUANG Y L, et al. Antagonism of Bacillus methylotrophicus strain BH21 to Botrytis cinerea [J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2018, 51(5): 883−892.(in Chinese) [27] 詹艺舒, 李婕, 褚秀丹, 等. 一株真菌拮抗细菌Z21的筛选与鉴定及其发酵条件优化 [J]. 微生物学通报, 2020, 47(5):1503−1514.ZHAN Y S, LI J, CHU X D, et al. Screen, identification and fermentation optimization of an antifungal bacterium Z21 [J]. Microbiology China, 2020, 47(5): 1503−1514.(in Chinese) [28] 李恩琛, 张文军, 张树武, 等. 生防细菌复配对苹果主要病原真菌抑菌活性筛选及其稳定性 [J]. 西北农业学报, 2020, 29(8):1270−1277.LI E C, ZHANG W J, ZHANG S W, et al. Screening of antimicrobial activities and stability of biocontrol bacteria combination against apple's main pathogenic fungi [J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2020, 29(8): 1270−1277.(in Chinese) [29] 徐润. 钝顶螺旋藻藻蓝蛋白储存稳定性研究[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学, 2017.XU R. Research of the storage stability of phycocyanin from Spirulina platensis[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science & Technology, 2017. [30] 王青华, 唐旭, 孙晓晖, 等. 深海贝莱斯芽孢杆菌DH82的抑菌活性物质初步分离纯化及其抑菌谱检测 [J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2020, 39(1):20−26.WANG Q H, TANG X, SUN X H, et al. Purification of antimicrobial substance produced by deep sea Bacillus velezensis strain DH82 and its inhibition spectrum [J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2020, 39(1): 20−26.(in Chinese) [31] 文娜. 拮抗轮枝镰刀菌的放线菌筛选及其活性代谢产物的初步研究[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学, 2020.WEN N. Screening of actinomycetes resistant to Fusarium verticillioide and preliminary study on their active metabolites[D]. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University, 2020. [32] 陶阳. Bacillus subtilis fmbJ抗菌脂肽对Rhizopus stolonifer作用机理研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2010.TAO Y. Antifungal mechanism of antimicrobial lipopeptide produced by Bacillus subtilis fmbJ against Rhizopus stolonifer[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2010. [33] 梁光杰, 车程川, 巩志金, 等. 一株海洋链霉菌发酵条件的优化及其抑菌活性物质的研究 [J]. 中国酿造, 2018, 37(12):101−105.LIANG G J, CHE C C, GONG Z J, et al. Optimization of fermentation conditions of a marine Streptomyces and its antibacterial activity substances [J]. China Brewing, 2018, 37(12): 101−105.(in Chinese) [34] 张薇. 烟草青枯菌拮抗放线菌的筛选、鉴定及发酵条件研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2009.ZHANG W. Screening and identifying of antagonistic actinomycetes against Ralstonia solancearum and optimizing of fermentation conditions[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2009. [35] 陈倩倩. 烟草根际土壤拮抗放线菌SA74菌株活性代谢产物的研究[D]. 洛阳: 河南科技大学, 2019.CHEN Q Q. Study on active metabolite of antagonistic actinomycete SA74 in rhizosphere soil of tobacco[D]. Luoyang: Henan University of Science and Technology, 2019. [36] 李雨虹, 耿鹏, 刘建民, 等. 重组枯草芽孢杆菌全细胞催化合成钙二醇的初步研究 [J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2021, 47(12):17−22.LI Y H, GENG P, LIU J M, et al. Whole-cell biosynthesis of 25-hydroxy vitamin D3 by recombinant Bacillus subtilis [J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2021, 47(12): 17−22.(in Chinese) [37] MORA I, CABREFIGA J, MONTESINOS E. Cyclic lipopeptide biosynthetic genes and products, and inhibitory activity of plant-associated Bacillus against phytopathogenic bacteria [J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(5): e0127738. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127738 [38] STEIN T. Bacillus subtilis antibiotics: Structures, syntheses and specific functions [J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2005, 56(4): 845−857. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04587.x [39] 武利勤, 顾海科, 王青, 等. 石斛内生甲基营养芽胞杆菌的拮抗和促生作用研究 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2016, 32(8):200−206.WU L Q, GU H K, WANG Q, et al. Antagonistic efficacy and growth-promoting effect of Bacillus methylotrophicus isolated from Dendrobium huoshanense [J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2016, 32(8): 200−206.(in Chinese) [40] 采俊香, 李月梅. 抱茎苦荬菜内生甲基营养型芽孢杆菌G-5抗菌蛋白抗真菌特性研究 [J]. 中国植保导刊, 2017, 37(4):20−26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6820.2017.04.003CAI J X, LI Y M. Studies on antifungal characteristics of endophytic Bacillus methylotrophicus G-5 from Ixeris sonchifolia hance [J]. China Plant Protection, 2017, 37(4): 20−26.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6820.2017.04.003 [41] ZHANG Q X, ZHANG Y, SHAN H H, et al. Isolation and identification of antifungal peptides from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens W10 [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2017, 24(32): 25000−25009. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-0179-8 [42] 姜威, 马银鹏, 陆佳, 等. 生防甲基营养型芽孢杆菌Hg18抗菌蛋白的分离纯化及性质研究 [J]. 化学与生物工程, 2021, 38(6):35−39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5425.2021.06.007JIANG W, MA Y P, LU J, et al. Separation, purification and characteristics of antibacterial protein produced by biocontrol Bacillus methylotrophicus Hg18 [J]. Chemistry & Bioengineering, 2021, 38(6): 35−39.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5425.2021.06.007 [43] LEE M H, LEE J, NAM Y D, et al. Characterization of antimicrobial lipopeptides produced by Bacillus sp. LM7 isolated from chungkookjang, a Korean traditional fermented soybean food [J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 2016, 221: 12−18. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2015.12.010 [44] 吴艳清, 王游游, 蒋继志, 等. 拮抗菌YQ5对致病疫霉的抑制作用及其抑菌稳定性研究 [J]. 中国植保导刊, 2018, 38(10):5−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6820.2018.10.001WU Y Q, WANG Y Y, JIANG J Z, et al. Inhibition effect of antagonistic bacteria YQ5 against Phytophthora infestans and its stability [J]. China Plant Protection, 2018, 38(10): 5−12.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6820.2018.10.001 -







 下载:
下载: