Heavy Metal Accumulation in Husk-removed Grains as Affected by Foliar Fertilizer Application and Rice Variety
-
摘要:
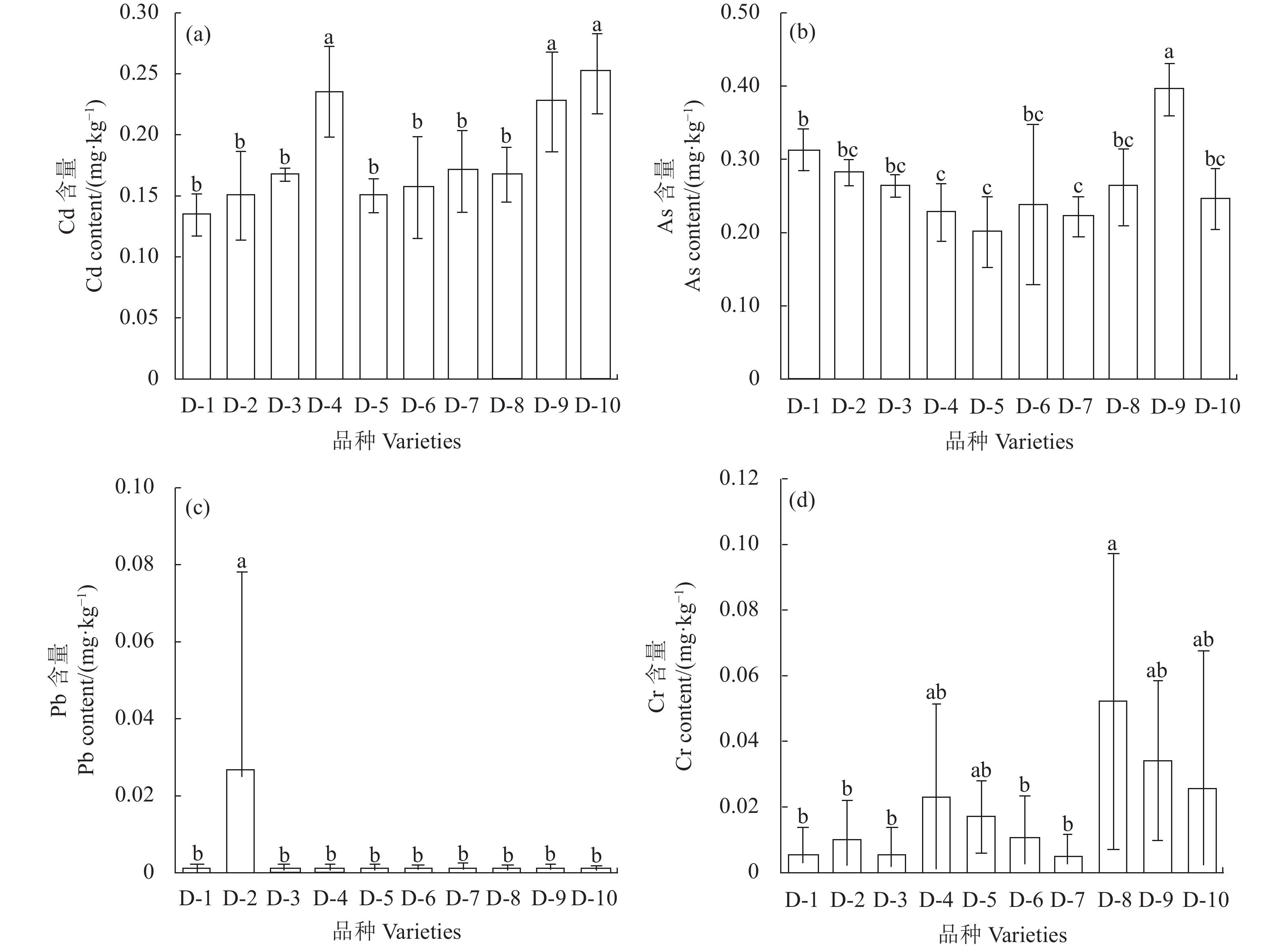
目的 研究不同水稻品种和叶面肥对水稻糙米富集多种重金属的影响。 方法 采用田间试验的方法,选用10个广西当地主要种植的晚稻品种,每个品种设置喷施硒肥(Se)、硅肥(Si)和CK施肥处理。测定和分析水稻糙米重金属As、Cd、Pb、Cr含量差异,比较不同晚稻品种As、Cd、Pb、Cr累积特性,筛选出适合广西当地种植的重金属低累积晚稻品种,同时分析出两种叶面肥对水稻糙米累积重金属的影响。 结果 不同水稻品种糙米对As、Cd、Pb、Cr的累积存在明显差异。其中桂育12糙米Cd含量最低,裕丰优158糙米As含量最低,荃香优822糙米Cr含量最低;10个水稻品种中,仅有华浙优1号检测出Pb含量。4种重金属在水稻糙米中富集能力大小依次为:Cd>As>Cr>Pb。喷洒硒肥(Se)和硅肥(Si)后水稻糙米Cd含量分别下降了44.8%和44.2%。富集系数分别降低了47.2%和47.4%。喷洒硅肥(Si)后,水稻糙米As含量及富集系数相较于对照处理分别降低了30.0%和19.0%。喷洒叶面肥后对水稻糙米Pb含量影响较小。 结论 选用品种桂育12在广西当地种植可以很好地降低糙米重金属中Cd的累积,选用裕丰优158可以很好地降低糙米中重金属As的累积,施用硅肥(Si)可显著降低As在水稻糙米中的累积,叶面喷施硒肥(Se)和硅肥(Si)均可以很好地阻控在水稻糙米中Cd的富集。 Abstract:Objective Effects of rice variety and applied foliar fertilizers on the accumulation of heavy metals in the husk-removed grains were studied. Method In a field experimentation, 10 major local late-season rice cultivars in Guangxi Province were sprayed with selenium (Se), silicon (Si), or water as CK. Contents of As, Cd, Pb, and Cr in the husk-removed grains were determined to identify the rice varieties with lower potential to retain heavy metals. Result Significant differences were found in the pollutants accumulation of rice grains. Among the 10 cultivars, Guiyu 12 was the lowest on Cd, Yufengyou 158 the lowest on As, Quanxiangyou 822 the lowest on Cr, and only Huazheyou No.1 detected with Pb. The greatest to the least heavy metal accumulated was in the order of Cd>As>Cr>Pb. On average, the application of Se foliar fertilizer reduced the Cd accumulation in grains by 44.8%, and that of Si by 44.2% with the enrichment coefficients decreased by 47.2% and 47.4%, respectively. Si application lowered the As content by 30.0% with an enrichment coefficient by 19.0% over CK, but less effective on Pb reduction. Conclusion The accumulation of Cd in the grains of Guiyu 12 could be significantly minimized, and also that of As in Yufengyou 158 rice, for the cultivation in Guangxi. Application of Si fertilizer on the leaves of a rice plant could decrease As accumulation and that of either Se or Si reduce Cd in the grains. -
Key words:
- Late-season rice /
- husk-removed rice grains /
- heavy metals /
- foliar fertilizer
-
表 1 供试水稻品种
Table 1. Rice varieties under study
品种 Varieties 编号Number 来源Source 桂育12
Guiyu 12D-1 当地农资店
Local agricultural materials store华浙优1号
Huazheyou No.1D-2 广西农科院提供
Provided by Guangxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences68优金占
68 YoujinzhangD-3 凯丰优158
Kaifengyou 158D-4 裕丰优158
Yufengyou 158D-5 y两优143
y Lliangyou 143D-6 荃香优822
Quanxiangyou 822D-7 又香优龙丝苗
Youxiang youlongsimiaoD-8 又香优雅丝苗
Youxiang youyasimiaoD-9 野香优明月丝苗
Yexiangyou mingyuesimiaoD-10 表 2 不同处理水稻糙米Cd含量
Table 2. Cd content of brown rice under treatments
品种
VarietiesCK 处理A Treatment A 处理B Treatment B 含量
Content/(mg·kg−1)含量
Content/(mg·kg−1)降幅
Decline/%含量
Content/(mg·kg−1)降幅
Decline/%D-1 0.1350±0.0173 a 0.0900±0.0141 b −33.3 0.0825±0.0150 b −38.9 D-2 0.1500±0.0365 a 0.0950±0.0054 a −36.7 0.0975±0.0450 a −35.0 D-3 0.1675±0.005 a 0.0975±0.025 b −41.8 0.0975±0.0125 b −41.8 D-4 0.2350±0.0369 a 0.1025±0.0095 b −56.4 0.1025±0.020 b −56.4 D-5 0.1500±0.0141 a 0.0975±0.0325 b −35.0 0.0950±0.0173 b −36.7 D-6 0.1575±0.0411 a 0.1275±0.0530 a −19.0 0.1400±0.0315 a −11.1 D-7 0.1700±0.0336 a 0.1000±0.0291 b −41.2 0.0850±0.0054 b −50.0 D-8 0.1675±0.0221 a 0.1050±0.0253 b −37.3 0.0975±0.0170 b −41.8 D-9 0.2275±0.0403 a 0.0825±0.0093 b −63.7 0.0950±0.0191 b −58.2 D-10 0.2520±0.0346 a 0.1025±0.0184 b −59.3 0.1175±0.0330 b −53.4 平均值 Average 0.1812±0.047 a 0.1000±0.0254 b −44.8 0.1010±0.0264 b −44.3 同行数据后不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05),下同。
Data with different letters on the same column indicate significant difference between different varieties (P<0.05). Same for the following tables.表 3 不同处理水稻糙米As含量
Table 3. As content of brown rice from different treatment groups
品种
VarietiesCK 处理A Treatment A 处理B Treatment B 含量
Content/(mg·kg−1)含量
Content/(mg·kg−1)降幅
Decline/%含量
Content/(mg·kg−1)降幅
Decline/%D-1 0.3125±0.0298 a 0.2250±0.0443 b −28.0 0.1425±0.0614 c −54.4 D-2 0.2800±0.0182 a 0.2450±0.0732 a −12.5 0.1950±0.0983 a −30.4 D-3 0.2625±0.015 a 0.2025±0.0222 ab −22.9 0.1725±0.0670 b −34.3 D-4 0.2275±0.0394 a 0.1925±0.0355 a −15.4 0.1675±0.1092 a −26.4 D-5 0.2000±0.0483 a 0.2325±0.0386 a 16.3 0.1800±0.0680 a −10.0 D-6 0.2375±0.1105 a 0.1900±0.0495 a −20.0 0.1675±0.0570 a −29.5 D-7 0.2200±0.0270 a 0.1950±0.0793 a −11.4 0.1800±0.0742 a −18.2 D-8 0.2625±0.0531 a 0.2250±0.0544 a −14.3 0.1825±0.0680 a −30.5 D-9 0.3950±0.0369 a 0.2850±0.0420 a −27.8 0.2650±0.1283 a −32.9 D−10 0.2450±0.0412 a 0.1975±0.0872 a −19.4 0.1975±0.0580 a −19.4 平均值 Average 0.2643±0.068 a 0.2195±0.0572 b −17.1 0.1850±0.07845 c −30.0 表 4 不同处理水稻糙米Pb含量
Table 4. Pb content of brown rice from different treatment groups
品种
VarietiesCK 处理A Treatment A 处理B Treatment B 含量
Content/(mg·kg−1)含量
Content/(mg·kg−1)降幅
Decline/%含量
Content/(mg·kg−1)降幅
Decline/%D-1 0.0010±0 a 0.0010±0 a 0 0.0168±0.031 a 1580.0 D-2 0.0268±0.0516 a 0.0010±0 a −96.3 0.0010±0 a −96.3 D-3 0.0010±0 a 0.0010±0 a 0 0.0010±0 a 0.0 D-4 0.0010±0 a 0.0010±0 a 0 0.0010±0 a 0.0 D-5 0.0010±0 a 0.0010±0 a 0 0.0010±0 a 0.0 D-6 0.0010±0 a 0.0010±0 a 0 0.0010±0 a 0.0 D-7 0.0010±0 a 0.0010±0 a 0 0.0010±0 a 0.0 D-8 0.0010±0 a 0.0010±0 a 0 0.0010±0 a 0.0 D-9 0.0010±0 a 0.0010±0 a 0 0.0010±0 a 0.0 D-10 0.0010±0 a 0.0010±0 a 0 0.0010±0 a 0.0 平均值 Average 0.0035±0.016 a 0.0010±0 a −72.1 0.0025±0.010 a −27.9 表 5 不同处理水稻糙米Cr含量
Table 5. Cr content of brown rice from different treatment groups
品种
VarietiesCK 处理A Treatment A 处理B Treatment B 含量
Content/(mg·kg−1)含量
Content/(mg·kg−1)降幅
Decline/%含量
Content/(mg·kg−1)降幅
Decline/%D-1 0.0051±0.0082 a 0.0144±0.0149 a 182.4 0.0178±0.0217 a 249.0 D-2 0.0097±0.0120 a 0.0335±0.045 a 245.4 0.0070±0.0119 a −27.8 D-3 0.0051±0.0081 a 0.0341±0.0421 a 568.6 0.0248±0.0307 a 386.3 D-4 0.0226±0.0284 a 0.0741±0.1362 a 227.9 0.0315±0.0523 a 39.4 D-5 0.0166±0.0109 a 0.0224±0.0078 a 34.9 0.0361±0.0512 a 117.5 D-6 0.0103±0.0127 a 0.0076±0.0082 a −26.2 0.0173±0.0266 a 68.0 D-7 0.0046±0.0071 a 0.0201±0.0134 a 337.0 0.0049±0.0078 a 6.5 D-8 0.0521±0.0452 a 0.0123±0.0076 a −76.4 0.0227±0.0375 a −56.4 D-9 0.0339±0.0241 a 0.0102±0.0065 a −69.9 0.0171±0.0207 a −49.6 D-10 0.0253±0.0422 a 0.0291±0.0504 a 15.0 0.0039±0.0057 a −84.6 平均值 Average 0.0185±0.025 a 0.0257±0.0481a 39.1 0.0183±0.0290a −1.2 表 6 不同品种水稻糙米重金属的富集系数
Table 6. Enrichment coefficients on heavy metals in brown rice of different varieties
品种
VarietiesCd As Pb Cr D-1 0.0601 0.0229 0.00003 0.0001 D-2 0.0684 0.0205 0.00089 0.0001 D-3 0.0901 0.0187 0.00004 0.0001 D-4 0.1065 0.0163 0.00003 0.0003 D-5 0.0677 0.0151 0.00003 0.0002 D-6 0.0733 0.0169 0.00003 0.0001 D-7 0.0767 0.0164 0.00003 0.0001 D-8 0.0784 0.0208 0.00003 0.0007 D-9 0.1056 0.0286 0.00004 0.0005 D-10 0.1178 0.0190 0.00003 0.0003 表 7 不同处理对水稻糙米重金属富集系数的影响
Table 7. Enrichment coefficients on heavy metals in brown rice from different treatment groups
处理
Treatment富集系数BCF Cd As Pb Cr CK 0.0844 a 0.0195 a 0.00012 a 0.0003 a 处理A Treatment A 0.0446 b 0.0186 a 0.00003 a 0.0004 a 处理B Treatment B 0.0444 b 0.0158 b 0.00009 a 0.0003 a 注:同列数据后不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Note: Data with different letters on same column indicate significant difference at P<0.05. -
[1] 周显, 韩毅, 陈霞, 等. 基于文献计量的土壤污染研究趋势分析 [J]. 长江科学院院报, 2021, 38(12):53−59.ZHOU X, HAN Y, CHEN X, et al. Trends of soil pollution research based on bibliometric analysis [J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2021, 38(12): 53−59.(in Chinese) [2] 王玉军, 刘存, 周东美, 等. 客观地看待我国耕地土壤环境质量的现状: 关于《全国土壤污染状况调查公报》中有关问题的讨论和建议 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(8):1465−1473.WANG Y J, LIU C, ZHOU D M, et al. A critical view on the status quo of the farmland soil environmental quality in china: discussion and suggestion of relevant issues on report on the national general survey of soil contamination [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2014, 33(8): 1465−1473.(in Chinese) [3] 全国土壤污染状况调查公报[J]. 中国环保产业, 2014(5): 10-11.Bulletin of the national survey of soil pollution[J]. China Environmental Protection Industry, 2014(5): 10-11. (in Chinese) [4] 宋波, 杨子杰, 张云霞, 等. 广西西江流域土壤镉含量特征及风险评估 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(4):1888−1900.SONG B, YANG Z J, ZHANG Y X, et al. Accumulation of Cd and its risks in the soils of the Xijiang River drainage basin in Guangxi [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(4): 1888−1900.(in Chinese) [5] 程菁靓, 赵龙, 杨彦, 等. 我国长江中下游水稻产区铅污染分区划分方法研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(1):70−78.CHENG J L, ZHAO L, YANG Y, et al. Classification methods for typical lead-contaminated rice production areas of the middle and Lower Yangtze River in China [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(1): 70−78.(in Chinese) [6] WU H P, LAI C, ZENG G M, et al. The interactions of composting and biochar and their implications for soil amendment and pollution remediation: A review [J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2017, 37(6): 754−764. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2016.1232696 [7] 文典, 江棋, 李蕾, 等. 重金属污染高风险农用地水稻安全种植技术研究 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(3):624−628.WEN D, JIANG Q, LI L, et al. Study on safe planting technology of rice in high risk farmland of heavy metal pollution [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2020, 29(3): 624−628.(in Chinese) [8] 薛涛, 廖晓勇, 王凌青, 等. 镉污染农田不同水稻品种镉积累差异研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(8):1818−1826.XUE T, LIAO X Y, WANG L Q, et al. Cadmium accumulation in different rice cultivars from cadmium-polluted paddy fields [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(8): 1818−1826.(in Chinese) [9] JIANG S L, SHI C H, WU J G. Studies on mineral nutrition and safety of wild rice (Oryza L. ) [J]. International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition, 2009, 60(S1): 139−147. [10] BOLAN N S, MAKINO T, KUNHIKRISHNAN A, et al. Cadmium contamination and its risk management in rice ecosystems[M]//Advances in Agronomy. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2013: 183–273. [11] 张潮海, 华村章, 邓汉龙, 等. 水稻对污染土壤中镉、铅、铜、锌的富集规律的探讨 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2003, 18(3):147−150.ZHANG C H, HUA C Z, DENG H L, et al. Investigation on the enrichment of Cd, Pb, Cu and Zn by rice in the field near a smelting plant [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2003, 18(3): 147−150.(in Chinese) [12] YANG Y J, CHEN J M, HUANG Q N, et al. Can Liming reduce cadmium (Cd) accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa) in slightly acidic soils? A contradictory dynamic equilibrium between Cd uptake capacity of roots and Cd immobilisation in soils [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 193: 547−556. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.061 [13] 陈喆, 铁柏清, 雷鸣, 等. 施硅方式对稻米镉阻隔潜力研究 [J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(7):2762−2770.CHEN Z, TIE B Q, LEI M, et al. Phytoexclusion potential studies of Si fertilization modes on rice cadmium [J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(7): 2762−2770.(in Chinese) [14] 谭周磁, 陈嘉勤, 薛海霞. 硒 (Se)对降低水稻重金属Pb, Cd, Cr污染的研究 [J]. 湖南师范大学自然科学学报, 2000, 23(3):80−83.TAN Z C, CHEN J Q, XUE H X. Studies on the pole of selenium (Se) in decreasing Pb, Cd and Cr pollution to rice [J]. Journal of Natural Science of Hunan Normal University, 2000, 23(3): 80−83.(in Chinese) [15] 方勇, 陈曦, 陈悦, 等. 外源硒对水稻籽粒营养品质和重金属含量的影响 [J]. 江苏农业学报, 2013, 29(4):760−765.FANG Y, CHEN X, CHEN Y, et al. Effects of exogenous selenium on nutritional quality and heavy metal content of rice grain [J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 29(4): 760−765.(in Chinese) [16] 王世华, 罗群胜, 刘传平, 等. 叶面施硅对水稻籽实重金属积累的抑制效应 [J]. 生态环境, 2007, 16(3):875−878.WANG S H, LUO Q S, LIU C P, et al. Effects of leaf application of nanometer silicon to the accumulation of heavy metals in rice grains [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2007, 16(3): 875−878.(in Chinese) [17] 周歆, 周航, 胡淼, 等. 不同杂交水稻品种糙米中重金属Cd、Zn、As含量的差异研究 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2013, 29(11):145−150.ZHOU X, ZHOU H, HU M, et al. The difference of Cd, Zn and As accumulation in different hybrid rice cultivars [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2013, 29(11): 145−150.(in Chinese) [18] 王林友, 竺朝娜, 王建军, 等. 水稻镉、铅、砷低含量基因型的筛选 [J]. 浙江农业学报, 2012, 24(1):133−138.WANG L Y, ZHU C N, WANG J J, et al. Screening for rice(Oryza sativa L. ) genotyeps with lower Cd, Pb and As contents [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2012, 24(1): 133−138.(in Chinese) [19] 林小兵, 周利军, 王惠明, 等. 不同水稻品种对重金属的积累特性 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(11):5198−5206.LIN X B, ZHOU L J, WANG H M, et al. Accumulation of heavy metals in different rice varieties [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(11): 5198−5206.(in Chinese) [20] 唐非, 雷鸣, 唐贞, 等. 不同水稻品种对镉的积累及其动态分布 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2013, 32(6):1092−1098.TANG F, LEI M, TANG Z, et al. Accumulation characteristic and dynamic distribution of Cd in different genotypes of rice(Oryza sativa L. ) [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2013, 32(6): 1092−1098.(in Chinese) [21] 王宇豪, 杨力, 康愉晨, 等. 镉污染大田条件下不同品种水稻镉积累的特征及影响因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(11):5545−5553.WANG Y H, YANG L, KANG Y C, et al. Characteristics and influencing factors of cadmium accumulation in different rice varieties under cadmium contaminated field conditions [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(11): 5545−5553.(in Chinese) [22] 陈慧茹, 董亚玲, 王琦, 等. 重金属污染土壤中Cd、Cr、Pb元素向水稻的迁移累积研究 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(12):236−241.CHEN H R, DONG Y L, WANG Q, et al. Distribution and transportation of Cd, Cr, Pb in rice with contamination in soil [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2015, 31(12): 236−241.(in Chinese) [23] 李林峰, 王艳红, 李义纯, 等. 调理剂耦合水分管理对双季稻镉和铅累积的阻控效应 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(1):472−480.LI L F, WANG Y H, LI Y C, et al. Inhibitory effects of soil amendment coupled with water management on the accumulation of Cd and Pb in double-cropping rice [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(1): 472−480.(in Chinese) [24] 张宇鹏, 谭笑潇, 陈晓远, 等. 无机硅叶面肥及土壤调理剂对水稻铅、镉吸收的影响 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(2):388−393.ZHANG Y P, TAN X X, CHEN X Y, et al. Effects of inorganic silicon foliar fertilizer and soil conditioner on plumbum and cadmium absorption in rice [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2020, 29(2): 388−393.(in Chinese) [25] 贾倩, 胡敏, 张洋洋, 等. 硅钙肥对水稻吸收铅、镉的影响研究 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2017, 40(6):24−30.JIA Q, HU M, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Effect of silicon-calcium fertilizer on Pb and Cd absorption by rice in heavy metal polluted farmland [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 40(6): 24−30.(in Chinese) [26] 戴青云, 刘代欢, 王德新, 等. 硅对水稻生长的影响及其缓解镉毒害机理研究进展 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(5):86−92.DAI Q Y, LIU D H, WANG D X, et al. A review on silicon: Effect on rice growth and its mechanism of relieving cadmium toxicity [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 36(5): 86−92.(in Chinese) [27] 张世杰, 付洁, 王晓美, 等. 叶面施硅对水稻吸收和转运无机砷和甲基砷的影响 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(7):1529−1536.ZHANG S J, FU J, WANG X M, et al. Effects of foliar application of silicon on uptake and transport of inorganic and methyl arsenic in rice [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(7): 1529−1536.(in Chinese) -







 下载:
下载:

