Nutrients and Microbial Community in Recirculating Aquaculture System for Plectropomus leopardus Aquaculture
-
摘要:
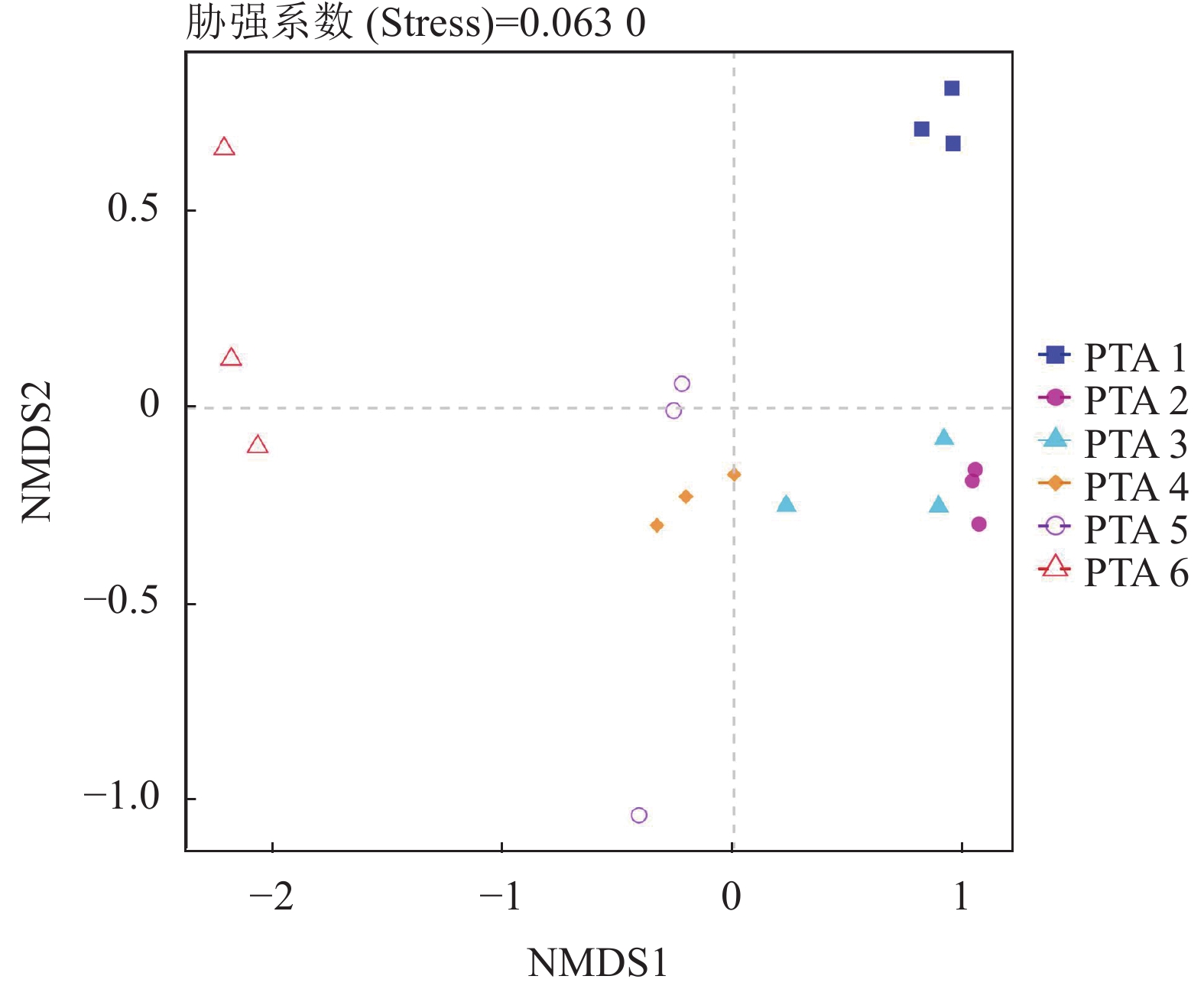
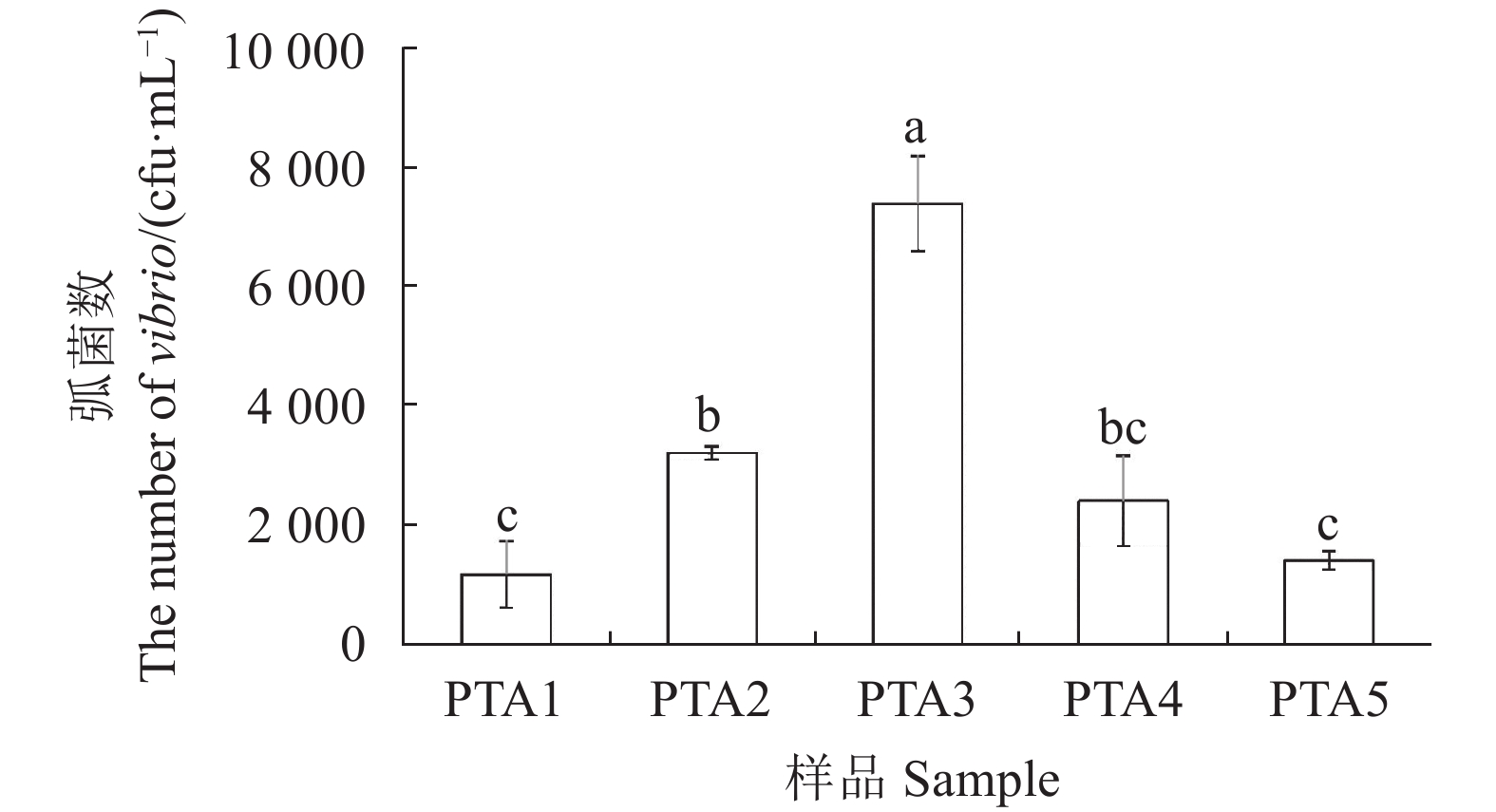
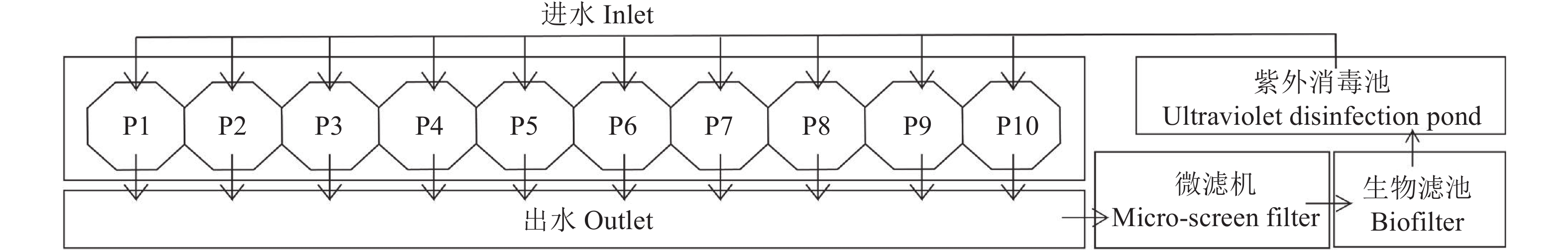
目的 明确循环水养殖系统(Recirculating aquaculture system,RAS)的营养盐及微生物组成特征,为东星斑循环水养殖系统的合理利用提供理论依据和技术参考。 方法 检测东星斑循环水养殖系统进水、养殖池、养殖池出水、生物滤池、紫外消毒池的水质指标、水体中弧菌数量,利用高通量测序技术对水体中微生物群落进行分析。 结果 氨氮、硝酸盐氮和磷酸盐的浓度从养殖环节至消毒环节呈现先上升后下降的变化趋势,亚硝酸盐氮则相反。外源海水样品中的弧菌数量小于循环水养殖系统中各个环节样品中的弧菌数量,弧菌数量经过养殖池后明显上升,经过生物滤池处理之后明显下降。在门分类水平上,循环水养殖系统中不同环节主要的微生物门类是变形菌门Proteobacteria、拟杆菌门Bacteroidota、厚壁菌门Firmicutes。在属分类水平上,主要为假交替单胞菌属Pseudoalteromonas、发光杆菌属Photobacterium、弧菌属Vibrio、乳杆菌属Lactobacillus,Vibrio中主要为Vibrio ponticus,占Vibrio总量的66.17%。 结论 循环水养殖系统的水处理环节可以有效降低养殖池出水中氨氮、硝酸盐氮以及磷酸盐的浓度和弧菌数量,同时揭示了循环水系统不同环节微生物组成特征。 Abstract:Objective Nutrients content and microbial community in a recirculating aquaculture system (RAS) for Plectropomus leopardus aquaculture were analyzed to provide theoretical and practical reference for the aquaculture operation. Method Indicators for the water quality of the influent, fish ponds, effluent, biological filter, and ultraviolet disinfection tank as well as the Vibrio count and microbial community at various stages of the RAS were determined based upon the high-throughput sequencing results. Result The concentrations of NH4+-N, NO3−-N and PO43−-P in the water increased at the stages where fish were present and declined where disinfection took place. It was the opposite on NO2−-N. Vibrio count was fewer in the exogenous seawater than in any downstream points of RAS which rose significantly after flowing through the fish ponds and diminished after the biofiltration treatment. At phylum level, the dominant microbes in the system were Proteobacteria, Bacteroidota, and Firmicutes. At genus level, there are mainly Pseudoalteromonas, Photobacterium, Vibrio, and Lactobacillus. The main Vibrio species was V. ponticus, the ration of which was 66.17%. Conclusion The RAS system was effective in reducing the $ {\rm{NH}}_4^+ $ -N, NO3−-N,${\rm{PO}}_4^{3-} $ -P, and vibrio population in the water. The composition of the microbial community in the circulating water was unveiled. -
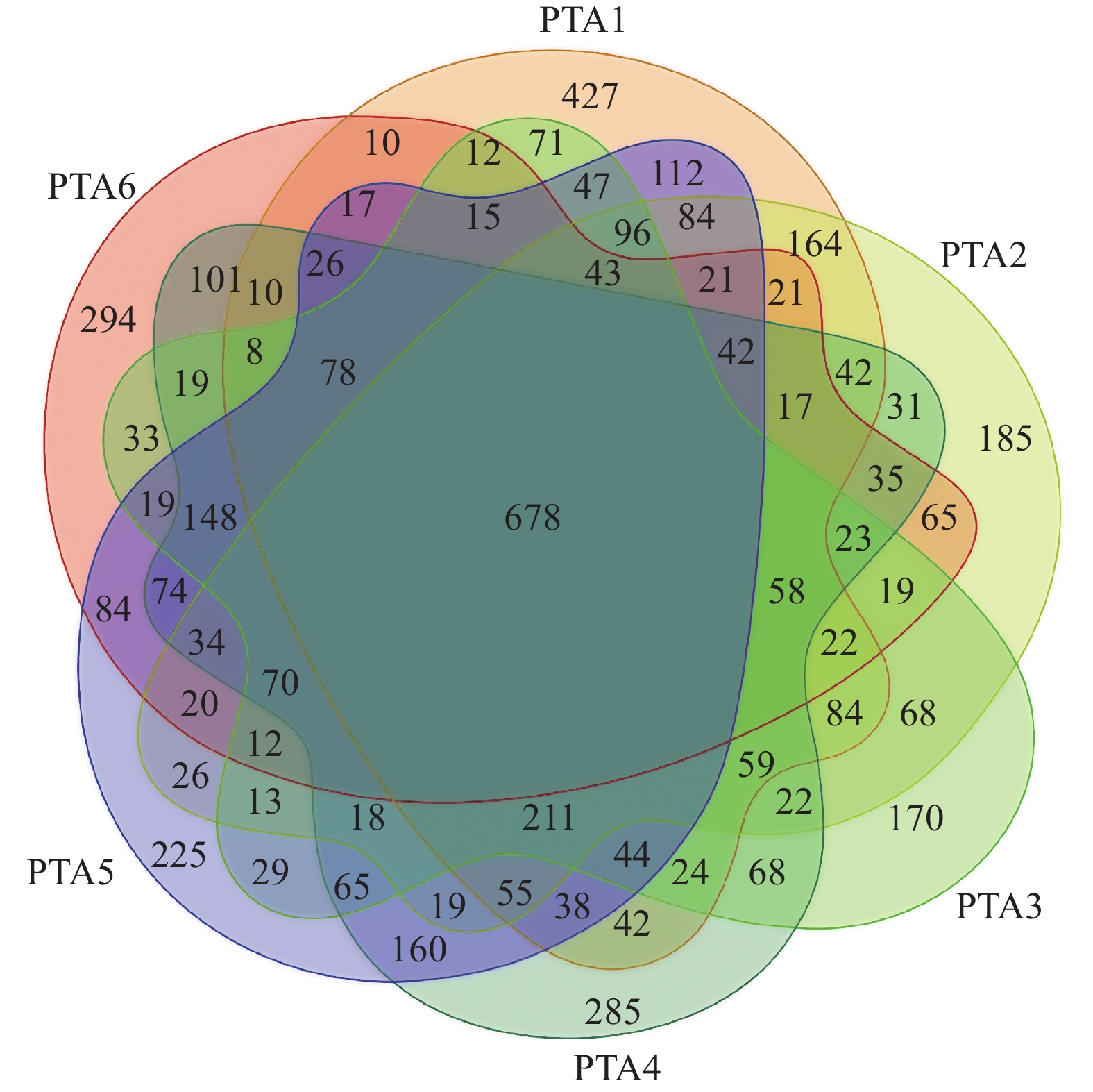
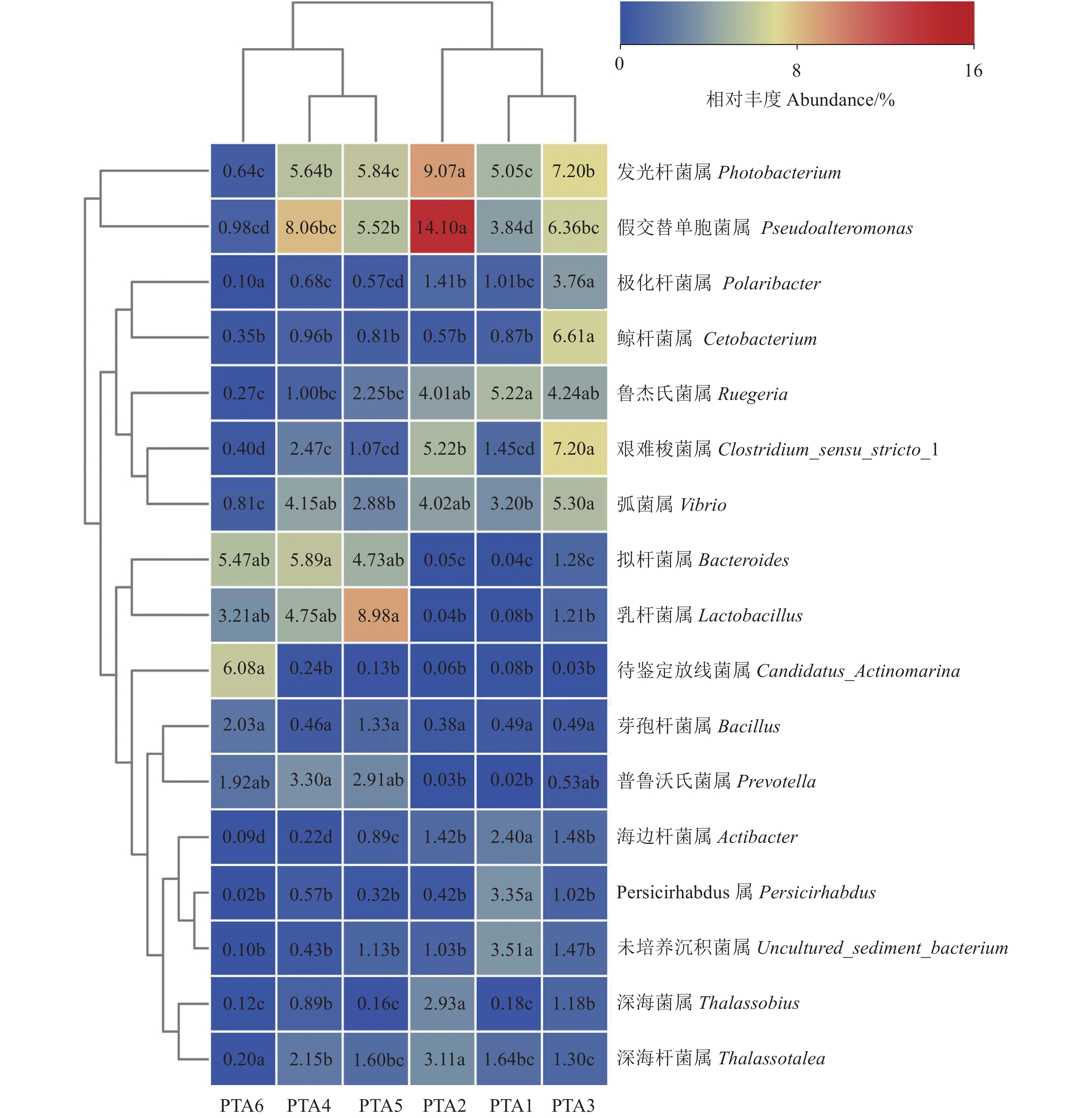
图 6 各样品优势菌物种丰度热图(属水平)
图中不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。图7同。
Figure 6. Heatmap of dominant bacteria in water samples at genus level
Data with different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at P<0.05. Same for Fig. 7.
表 1 循环水养殖系统不同环节的水质指标
Table 1. Water quality indicators for functional stages of RAS
样品
Sample盐度 Salinity pH 氨氮
NH4+-N/ (mg·L−1)亚硝酸盐氮
NO2−-N /(mg·L−1)硝酸盐氮
NO3−-N /(mg·L−1)磷酸盐
PO43−-P /(mg·L−1)PTA1(养殖池进水) 32.8 7.82 <0.001 0.393 26.80 0.521 PTA2(养殖池池水) 33.0 7.42 0.198 0.372 38.50 0.784 PTA3(养殖池出水) 32.9 7.42 0.679 0.202 58.60 0.794 PTA4(生物滤池池水) 33.1 7.53 0.080 0.416 26.20 0.652 PTA5(紫外消毒池池水) 32.6 7.41 <0.001 0.364 30.00 0.656 PTA6(外源海水) 32.6 8.00 <0.001 0.012 3.97 0.023 表 2 不同样品细菌群落的多样性
Table 2. Microbial community diversity at sampling spots
样品
SampleChao1指数
Chao1 index覆盖度
Good’s coverageShannon指数
Shannon indexSimpson指数
Simpson index有效序列数
Sequence numberOUT数目
OUT numberPTA1 2091.47 0.99 8.21 0.99 83738 1663 PTA2 1960.78 0.99 7.02 0.97 95738 1460 PTA3 1769.79 0.99 7.32 0.98 71625 1318 PTA4 1973.03 0.99 8.01 0.98 51304 1588 PTA5 2213.58 0.99 7.72 0.98 48207 1487 PTA6 1976.76 0.99 7.73 0.99 55228 1170 表 3 循环水养殖系统不同环节中优势菌的分布情况(属水平)
Table 3. Distribution of dominant bacteria at stages of RAS at genus level
优势菌
Dominant bacteria优势菌的占比
The proportion of dominant bacteria/%PTA1 PTA2 PTA3 PTA4 PTA5 不动杆菌属 Acinetobacter 1.14 海边杆菌属 Actibacter 2.40 1.42 1.48 Allobaculum属 Allobaculum 1.22 1.48 海水杆菌属 Aquimarina 1.81 芽孢杆菌属 Bacillus 1.33 拟杆菌属 Bacteroides 1.28 5.89 4.73 双歧杆菌属 Bifidobacterium 4.13 鲸杆菌属 Cetobacterium 6.61 艰难梭菌属
Clostridium_sensu_stricto_11.45 5.22 7.20 2.47 1.07 粪杆菌属 Faecalibacterium 1.03 1.08 克雷伯菌属 Klebsiella 1.02 乳杆菌属 Lactobacillus 1.21 4.75 8.98 列文氏菌属 Lewinella 1.33 1.55 Nautell属 Nautella 1.56 Persicirhabdus属 Persicirhabdus 3.35 1.02 发光杆菌属 Photobacterium 5.05 9.07 7.20 4.75 5.84 极化杆菌属 Polaribacter 1.01 1.41 3.76 普雷沃氏菌属 Prevotella 3.30 2.91 假交替单胞菌属 Pseudoalteromonas 3.84 14.10 6.36 8.06 5.52 玫瑰变色菌属 Roseovarius 1.37 Rubidimonas属 Rubidimonas 1.12 Rubritalea属 Rubritalea 1.27 1.38 鲁杰氏菌属 Ruegeria 5.22 4.01 4.24 1.00 2.25 亚硫酸杆菌属 Sulfitobacter 1.19 Sva0996海洋古菌属
Sva0996_marine_group1.77 黄杆菌属 Tenacibaculum 1.51 1.80 深海菌属 Thalassobius 2.93 1.18 深海杆菌属 Thalassotalea 1.64 3.11 1.30 2.15 1.60 弧菌属 Vibrio 3.20 4.02 5.30 4.15 2.88 -
[1] 王锐, 齐遵利, 张秀文, 等. 东星斑的生物学特性和人工养殖技术 [J]. 中国水产, 2011(4):33−34.WANG R, QI Z L, ZHANG X W, et al. Biological characteristics and artificial breeding techniques of Plectropomus leopardus [J]. China Fisheries, 2011(4): 33−34.(in Chinese) [2] 周可欣, 文鑫, 邓成, 等. 豹纹鳃棘鲈体色变异的色素细胞差异分析 [J]. 水生生物学报, 2021, 45(5):1164−1170. doi: 10.7541/2021.2020.291ZHOU K X, WEN X, DENG C, et al. Analysis of pigment cells difference in body color variation of Plectropomus leopardus [J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2021, 45(5): 1164−1170.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7541/2021.2020.291 [3] LAWSON T B. Recirculating aquaculture systems[M]//Fundamentals of Aquacultural Engineering. Boston, MA: Springer US, 1995: 192-247. [4] 侯婷婷, 钟志平, 刘缨, 等. 青石斑鱼海水循环水养殖水体的细菌群落特征 [J]. 微生物学报, 2016, 56(2):253−263.HOU T T, ZHONG Z P, LIU Y, et al. Bacterial community characterization of rearing water of marine recirculating aquaculture systems for yellow grouper (Epinephelus awoara) [J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2016, 56(2): 253−263.(in Chinese) [5] 黄志涛, 宋协法, 李勋, 等. 基于高通量测序的石斑鱼循环水养殖生物滤池微生物群落分析 [J]. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(S1):242−247.HUANG Z T, SONG X F, LI X, et al. Analysis of microbial diversity of submerged biofilters in recirculating aquaculture system(RAS) for grouper(Epinehelus moara) based on high-throughput DNA sequencing [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 32(S1): 242−247.(in Chinese) [6] 吴越, 马建忠, 郑伊诺, 等. 石斑鱼循环水养殖系统微生物群落结构 [J]. 中国水产科学, 2017, 24(5):1045−1054. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1118.2017.16349WU Y, MA J Z, ZHENG Y N, et al. Analysis of microbial community structure in recirculating aquaculture system for groupers (Epinephelus) [J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2017, 24(5): 1045−1054.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1118.2017.16349 [7] 崔云亮, 顾志峰, 郑兴, 等. 5种滤料在循环养殖系统中去除氨氮效果的比较 [J]. 热带生物学报, 2015, 6(3):235−241.CUI Y L, GU Z F, ZHENG X, et al. Comparison of five biofilter media in ammonia-removing efficiency in the recirculation aquaculture system [J]. Journal of Tropical Biology, 2015, 6(3): 235−241.(in Chinese) [8] 闫茂仓, 陈少波, 单乐州, 等. 海水养殖动物致病弧菌的研究进展 [J]. 水产科学, 2009, 28(8):475−481.YAN M C, CHEN S B, SHAN L Z, et al. A critical review: Pathogenic Vibrio in maricultural animals [J]. Fisheries Science, 2009, 28(8): 475−481.(in Chinese) [9] 金珊, 王国良, 薛良义, 等. 海水网箱养殖水域异养细菌和弧菌的数量动态 [J]. 海洋渔业, 1999, 21(4):154−156.JIN S, WANG G L, XUE L Y, et al. Variation of the number of heterotrophic bacteria and vibrios in marine cage - cultured waters [J]. Marine fisheries, 1999, 21(4): 154−156.(in Chinese) [10] 严俊贤, 李有宁, 吴开畅, 等. 豹纹鳃棘鲈池塘生态育苗试验 [J]. 广东农业科学, 2013, 40(1):127−130.YAN J X, LI Y N, WU K C, et al. Ecological breeding experiment of Plectropomus leopardus [J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 40(1): 127−130.(in Chinese) [11] 张欣, 孙向军, 梁拥军, 等. 北方地区东星斑工厂化养殖技术 [J]. 科学养鱼, 2011(7):35.ZHANG X, SUN X J, LIANG Y J, et al. Industrial culture technology of Plectropomus leopardus in Northern China [J]. Scientific Fish Farming, 2011(7): 35.(in Chinese) [12] 国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 海洋监测规范 第4部分: 海水分析: GB 17378.4—2007[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. [13] 中华人民共和国环境保护部. 水质 无机阴离子: HJ 84—2016[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2016. [14] 高亚峰, 孙洪杰. 氨氮对鱼类的危害 [J]. 河北渔业, 2014(8):62−63,67.GAO Y F, SUN H J. Harm of ammonia nitrogen to fish [J]. Hebei Fisheries, 2014(8): 62−63,67.(in Chinese) [15] 蔡真珍, 郑盛华, 王宪. 近海养殖水体硝化作用动力学研究 [J]. 闽南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 28(4):56−63. doi: 10.16007/j.cnki.issn2095-7122.2015.04.008CAI Z Z, ZHENG S H, WANG X. Research on kinetics of nitrification of coastal aquaculture water [J]. Journal of Minnan Normal University (Natural Science), 2015, 28(4): 56−63.(in Chinese) doi: 10.16007/j.cnki.issn2095-7122.2015.04.008 [16] 窦立军, 蒋进元, 黄永亨, 等. 两株自养型氨氧化细菌的分离、鉴定及系统发育分析 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2011, 24(11):1312−1317.DOU L J, JIANG J Y, HUANG Y H, et al. Separation, identification and phylogenetic analysis of two strains of autotrophic ammonia oxidizing bacteria [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2011, 24(11): 1312−1317.(in Chinese) [17] 蔡小龙, 林炜铁. 对虾养殖水体氨氧化菌的多样性分析与硝化作用的特征 [J]. 食品科学, 2011, 32(S1):52−57.CAI X L, LIN W T. Diversity of ammonia-oxidizing microorganism in waters of shrimp culture and nitrification characteristics [J]. Food Science, 2011, 32(S1): 52−57.(in Chinese) [18] 于党辉, 王秀华, 张宇哲, 等. 环境条件对1株假交替单胞菌脱氮效果的影响 [J]. 渔业科学进展, 2020, 41(4):144−150.YU D H, WANG X H, ZHANG Y Z, et al. Effect of environmental conditions on denitrification of Pseudomonas sp [J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2020, 41(4): 144−150.(in Chinese) [19] STARLIPER C. Bacterial coldwater disease of fishes caused by Flavobacterium psychrophilum [J]. Journal of Advanced Research, 2011, 2: 97−108. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2010.04.001 [20] 葛文杰. 复合铁酶促活性污泥强化脱氮除磷技术及其生物学机制研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛理工大学, 2018.GE W J. Study on enhanced nitrogen and Phosphorus removal by composite ferric enzymatic activated sludge and its biological mechanism[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao Tehcnology University, 2018. (in Chinese) [21] 冯国禄, 罗金飞, 廖永岩, 等. 不同盐度循环养殖水体微生物群落特征 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2020, 33(8):1838−1847.FENG G L, LUO J F, LIAO Y Y, et al. Microbial community characteristics in recirculating aquaculture waters at different salinity levels [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2020, 33(8): 1838−1847.(in Chinese) [22] 王晓甜. 南海好氧除磷菌多样性分析及除磷特性研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2017.WANG X T. Diversity and Phosphorus removal characteristic research of aerobic Phosphorus removal strains in South China Sea[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2017. (in Chinese) [23] 罗鸣, 陈傅晓, 刘龙龙, 等. 我国石斑鱼养殖疾病的研究进展 [J]. 水产科学, 2013, 32(9):549−554.LUO M, CHEN F X, LIU L L, et al. Progress in disease research of grouper aquaculture in China [J]. Fisheries Science, 2013, 32(9): 549−554.(in Chinese) [24] FERREIRA N C, BONETTI C, SEIFFERT W Q. Hydrological and water quality indices as management tools in marine shrimp culture [J]. Aquaculture, 2011, 318(3/4): 425−433. [25] XIE Z Y, HU C Q, ZHANG L P, et al. Identification and pathogenicity of Vibrio ponticus affecting cultured Japanese Sea bass, Lateolabrax japonicus (Cuvier in Cuvier and Valenciennes) [J]. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 2007, 45(1): 62−67. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2007.02141.x [26] 游剑涛. 大黄鱼烂鳃病病原菌的分离鉴定及药敏分析 [J]. 渔业研究, 2018, 40(6):425−433.YOU J T. Isolation, identification and antibiotic sensitivity analysis of bacterial pathogen from Larimichthys crocea with gill-rot disease [J]. Journal of Fisheries Research, 2018, 40(6): 425−433.(in Chinese) [27] 李岑鹏, 关瑞章, 江兴龙, 等. 循环水处理系统处理鳗鲡养殖污水的应用实验 [J]. 集美大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 14(2):126−130.LI C P, GUAN R Z, JIANG X L, et al. On the wastewater treatment in a recirculating system for eel aquaculture [J]. Journal of Jimei University (Natural Science), 2009, 14(2): 126−130.(in Chinese) [28] 周游, 黄滨, 吴凡, 等. 紫外线位置对循环水养殖半滑舌鳎水环境及生长影响 [J]. 中国工程科学, 2014, 16(9):78−85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2014.09.012ZHOU Y, HUANG B, WU F, et al. The influence of UV location on recirculating aquaculture Cynoglossus semilaevis's water environment and its growth [J]. Strategic study of CAE, 2014, 16(9): 78−85.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2014.09.012 [29] 张欢欢, 王秀华, 李晨, 等. 对虾养殖池中一株弧菌拮抗菌的分离鉴定 [J]. 渔业科学进展, 2016, 37(3):85−92.ZHANG H H, WANG X H, LI C, et al. Isolation and identification of a bacterial strain with vibrios-antagonism from shrimp ponds [J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2016, 37(3): 85−92.(in Chinese) [30] 刘鹏. 一株高效脱氮好氧适盐菌Photobacterium sp. LP的筛选及生物特性研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2015.LIU P. Screening and microbial characteristic study of a halophilic aerobic denitrification strain Photobacterium sp. LP[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2015. (in Chinese) [31] 陈世化, 夏延斌, 聂乾忠. 发酵蔬菜中乳酸菌抑菌性的研究 [J]. 食品工程, 2007(2):6−9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6044.2007.02.002CHEN S H, XIA Y B, NIE Q Z. Research on antibacterial capability of Lactic acid bacteria in fermented vegetables [J]. Food Engineering, 2007(2): 6−9.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6044.2007.02.002 [32] GRAM L, MELCHIORSEN J, BRUHN J B. Antibacterial activity of marine culturable bacteria collected from a global sampling of ocean surface waters and surface swabs of marine organisms [J]. Marine Biotechnology, 2010, 12(4): 439−451. doi: 10.1007/s10126-009-9233-y [33] 张芹, 周中凯, 任晓冲. 高通量测序技术研究高糖饮食对小鼠肠道菌群的影响 [J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2015, 6(5):1776−1782.ZHANG Q, ZHOU Z K, REN X C. Comparision of intestinal microbiota in mice with normal and high-sugar diet using Miseq high-throughput sequencing [J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2015, 6(5): 1776−1782.(in Chinese) [34] LUO Y H, PENG H W, WRIGHT A D G, et al. Broilers fed dietary vitamins harbor higher diversity of cecal bacteria and higher ratio of Clostridium, Faecalibacterium, and Lactobacillus than broilers with no dietary vitamins revealed by 16S rRNA gene clone libraries [J]. Poultry Science, 2013, 92(9): 2358−2366. doi: 10.3382/ps.2012-02935 [35] KOVATCHEVA-DATCHARY P, NILSSON A, AKRAMI R, et al. Dietary fiber-induced improvement in glucose metabolism is associated with increased abundance of Prevotella [J]. Cell Metabolism, 2015, 22(6): 971−982. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.10.001 [36] 朱宜平, 安东. 上海某水库水源水中微生物多样性表征初探 [J]. 复旦学报(自然科学版), 2021, 60(6):805−810,816.ZHU Y P, AN D. Characterization of microbial diversity in water source of a reservoir in Shanghai [J]. Journal of Fudan University (Natural Science), 2021, 60(6): 805−810,816.(in Chinese) [37] 高磊, 包卫洋, 张天文, 等. 水体碳氮比对芽孢杆菌、乳酸菌与弧菌生长、拮抗作用及菌体碳氮比的影响 [J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 43(1):34−40.GAO L, BAO W Y, ZHANG T W, et al. Effect of water C∶N ratio on the growth, antagonism and C∶N ratio of Bacillus, lactic acid bacteria and Vibrio [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2013, 43(1): 34−40.(in Chinese) [38] O'SULLIVAN L A, RINNA J, HUMPHREYS G, et al. Fluviicola taffensis Gen. nov. , sp. nov. , a novel freshwater bacterium of the family Cryomorphaceae in the Phylum ‘Bacteroidetes’[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2005, 55(Pt 5): 2189-2194. [39] FAN P X, LIU P, SONG P X, et al. Moderate dietary protein restriction alters the composition of gut microbiota and improves ileal barrier function in adult pig model [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 43412. doi: 10.1038/srep43412 -









 下载:
下载: