Growth, Yield, and Quality of Pseudostellaria heterophylla Affected by Different Viruses Infecting Seed Roots
-
摘要:
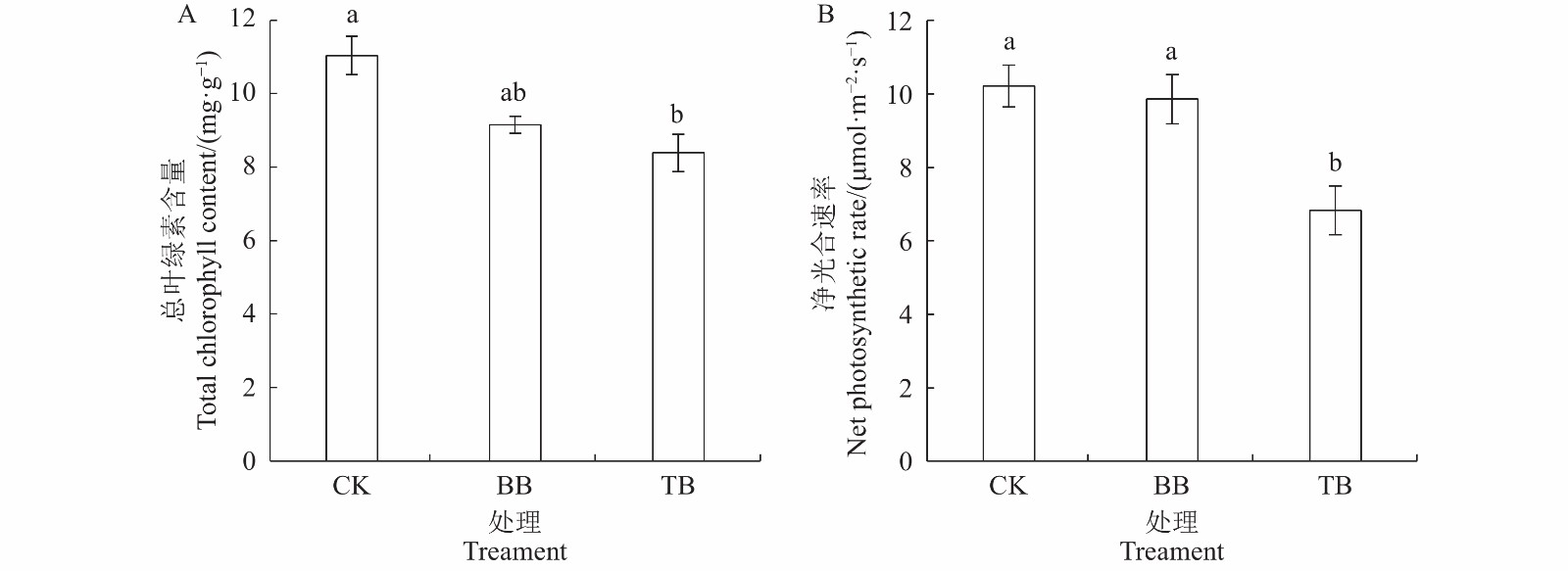
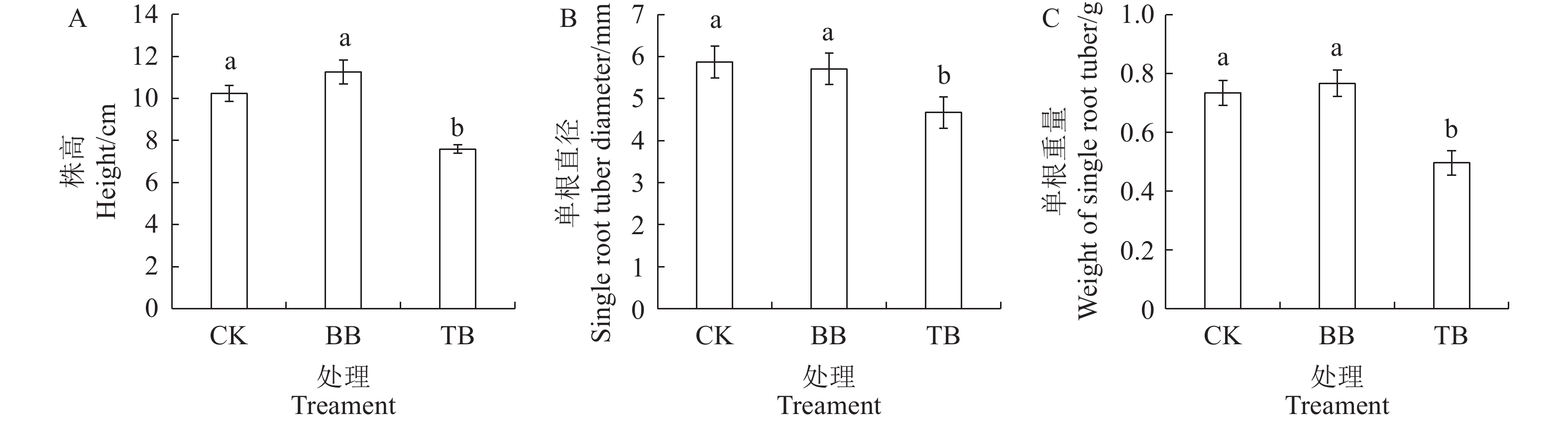
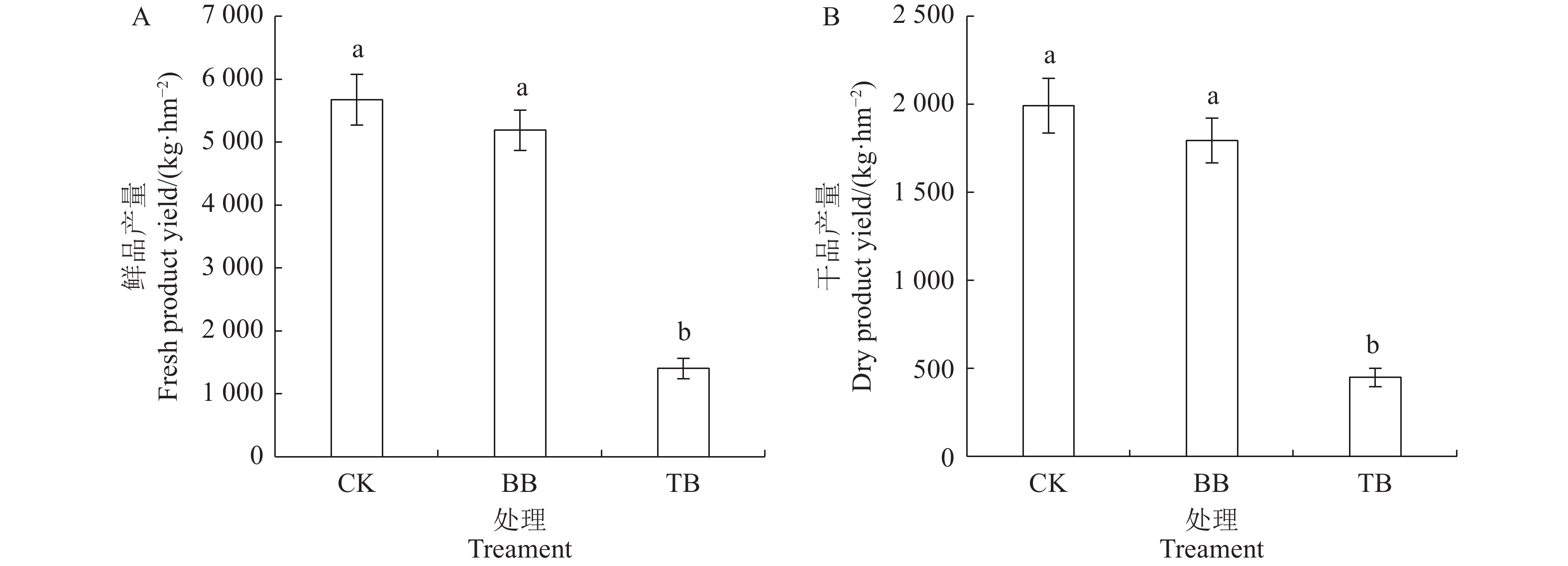
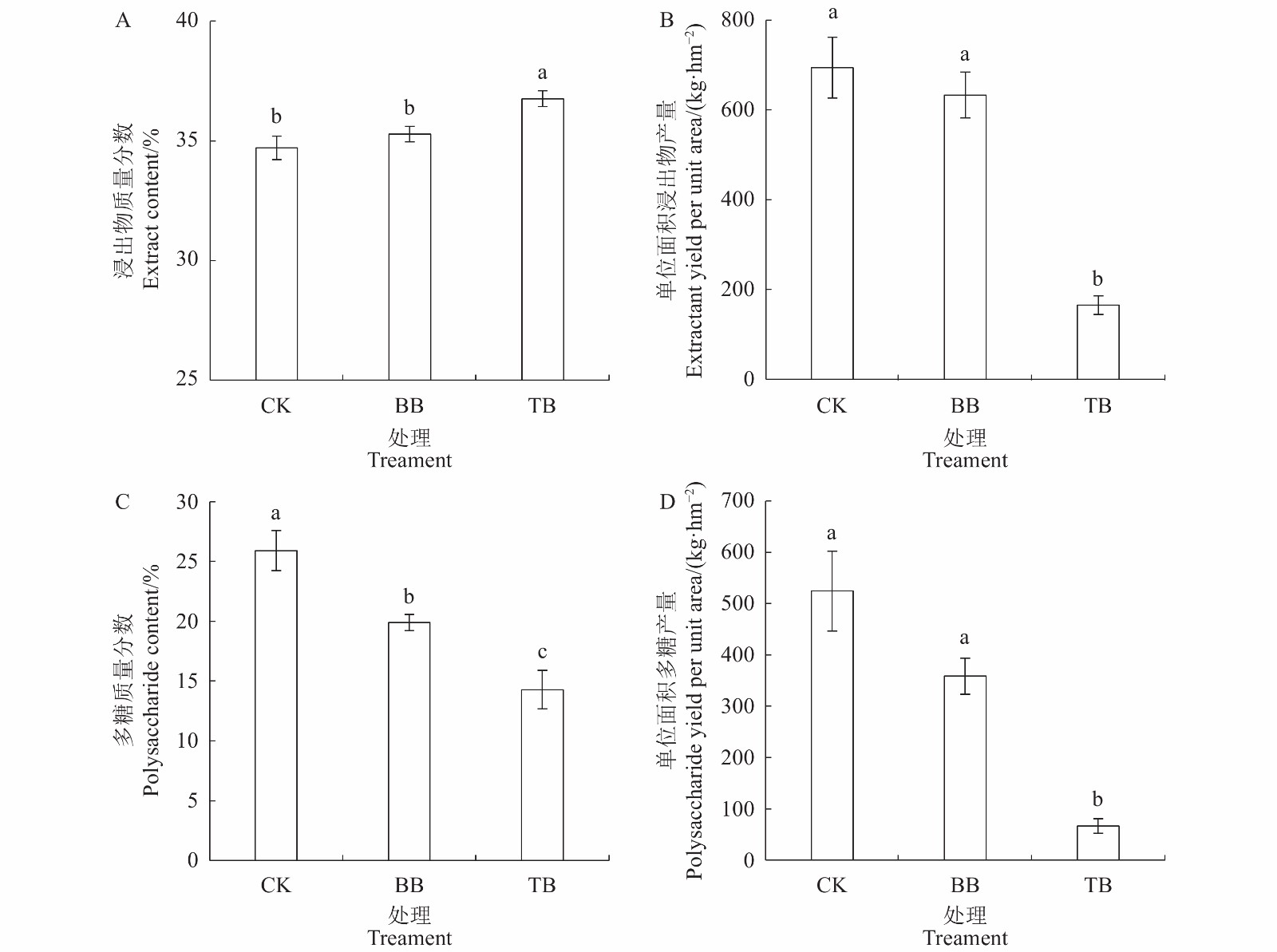
目的 探明不同病毒对太子参生长、产量及品质的影响。 方法 以柘参2号为试验材料,采用RT-PCR分子鉴定方法筛选出只携带一种常见病毒、携带两种常见病毒和不带病毒的太子参个体,经扩繁后,在田间使用随机区组的方法种植,探讨不同种类病毒对太子参的生长、产量和品质的影响。 结果 与未带病毒的植株相比,同时感染芜菁花叶病毒和蚕豆萎蔫病毒的植株总叶绿素含量、净光合速率和地上部株高分别降低了24%、33%和26%,单位面积的块根产量、浸出物含量和多糖含量分别降低了77.5%、76.2%和87.3%;而仅感染蚕豆萎蔫病毒的植株与未带病毒的植株相比,总叶绿素含量、净光合速率、地上部株高、块根产量、浸出物含量和多糖含量均无显著性差异。 结论 芜菁花叶病毒显著抑制太子参的生长,降低了太子参产量和品质,而蚕豆萎蔫病毒的影响不显著,在太子参脱病毒培养和脱毒苗的生产应用中应优先去除芜菁花叶病毒。 Abstract:Objective Effects on the photosynthesis, tuber yield, and tuber quality of Pseudostellaria heterophylla plants induced by infecting viruses were examined. Methods Identified by RT-PCR, virus-free P. heterophylla Zhenshen 2 plants and those infected by turnip mosaic virus (TMV) and/or broad bean wilt virus (BBWV) were propagated in the field in a random block experiment. Leaf photosynthesis as well as yield and quality of the medicinal roots of the plants were measured. Results The total chlorophyll content, net photosynthetic rate, and height of the plants infected by both TMV and BBWV were 24%, 33%, and 26%, respectively, and the tuber yield, water-soluble extracts, and polysaccharides on a per unit area basis 77.5%, 76.2%, and 87.3%, respectively, lower than those of the virus-free counterparts. But no significant effects on any of those monitored properties were detected in the plants infected by BBWV alone. Conclusion Unlike BBWV, TMV infection on P. heterophylla significantly reduced the photosynthesis, tuber yield, and tuber quality of the plants. Thus, it was imperative to avoid TMV contamination in handling P. heterophylla seedlings. -
Key words:
- Pseudostellaria heterophylla /
- virus /
- photosynthesis /
- yield /
- quality
-
图 2 不同病毒处理下太子参生理特性的比较
A: 总叶绿素含量;B:净光合速率。数据表示为平均值±标准误差,附不同小写英文字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05),下同。
Figure 2. Physiological characteristics of P. heterophylla plants with or without viral infection
A. Total chlorophyll contents ; B.Net photosynthetic rates . Data are expressed as mean ± standard error; those with lowercase letters represent significant difference ( P< 0.05). Same for below.
-
[1] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典(一部)[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020: 69. [2] 康传志, 周涛, 郭兰萍, 等. 全国栽培太子参生态适宜性区划分析 [J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(10):2934−2944.KANG C Z, ZHOU T, GUO L P, et al. Ecological suitability and regionalization of Pseudostellaria heterophylla (miq. ) Pax ex Pax et hoffm. in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2016, 36(10): 2934−2944.(in Chinese) [3] TORRICO A K, SALAZAR S M, KIRSCHBAUM D S, et al. Yield losses of asymptomatic strawberry plants infected with Strawberry mild yellow edge virus [J]. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 2018, 150(4): 983−990. doi: 10.1007/s10658-017-1337-z [4] NIHAD S A I, MANIDAS A C, HASAN K, et al. Genetic variability, heritability, genetic advance and phylogenetic relationship between rice tungro virus resistant and susceptible genotypes revealed by morphological traits and SSR markers [J]. Current Plant Biology, 2021, 25: 100194. doi: 10.1016/j.cpb.2020.100194 [5] 朱艳, 周小华, 秦民坚. 太子参病毒病及其脱病毒研究进展 [J]. 中国野生植物资源, 2005, 24(2):31−32,38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9690.2005.02.010ZHU Y, ZHOU X H, QIN M J. Advances of research on virus disease of Pseudostellaria heterophylla [J]. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 2005, 24(2): 31−32,38.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9690.2005.02.010 [6] 陈菁瑛, 黄颖桢, 刘保财, 等. 福建太子参常见病害与绿色防控技术 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2021, 49(12):152−155. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2021.12.038CHEN J Y, HUANG Y Z, LIU B C, et al. Common diseases and green control technique of Pseudostellaria heterophylla in Fujian Province [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 49(12): 152−155.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2021.12.038 [7] 徐宏辉. 闽东山区太子参两大病害发生特点及其绿色防控技术[J]. 中国植保导刊, 2015, 35(1): 39-42.XU H H. 2015. Occurrence characteristics and green control techniques of two diseases of pseudostellaria heterophylla in the mountainous area of eastern Fujian. China Plant Protection, 35(1): 39-42. (in Chinese) [8] 宋荣浩, 濮祖芹. 太子参病毒病的防治途径 [J]. 上海农业学报, 1995(3):59−62.SONG R H, PU Z Q. Control of Taizhishen virus diseases [J]. Acta Agricul Turae Shanghai, 1995(3): 59−62.(in Chinese) [9] 王蓉, 李勇, 魏若凡, 等. 我国太子参主产区病毒病发生情况调查 [J]. 植物保护, 2022(1):204−210,219.WANG R, LI Y, WEI R F, et al. Investigation on the occurrence of virus diseases in the main producing areas of Pseudostellaria heterophylla in China [J]. Plant Protection, 2022(1): 204−210,219.(in Chinese) [10] 蔡丽, 许泽永, 陈坤荣, 等. 芜菁花叶病毒研究进展 [J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2005(1):104−110. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-9084.2005.01.025CAI L, XU Z Y, CHEN K R, et al. Research progress on turnip mosaic virus [J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Scieves, 2005(1): 104−110.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-9084.2005.01.025 [11] 匡云波, 叶炜, 李金辉, 等. 太子参蚕豆萎蔫病毒2号CP基因的遗传多样性及分子进化分析 [J]. 植物病理学报, 2017, 47(4):470−478.KUANG Y B, YE W, LI J H, et al. Genetic polymorphism and phylogenetic analysis of Broad bean wilt virus 2 CP genes isolated from Pseudostellaria heterophylla [J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 2017, 47(4): 470−478.(in Chinese) [12] NIU Y B, SHI X L, ZHANG X M, et al. Molecular identification and sequence analysis of Broad bean wilt virus 2 isolates from Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz [J]. Chinese Journal of Virology, 2015, 31(1): 58−64. [13] 刘炜炜, 许文博, 刘升学, 等. 蚕豆萎蔫病毒2的分子鉴定及RNA1组分5'末端核苷酸序列分析 [J]. 石河子大学学报(自然科学版), 2012(6):695−699.LIU W W, XU W B, LIU S X, et al. Molecular identification of BBWV2 and sequence analysis of 5'-terminal region of genomic RNA1 [J]. Journal of Shihezi University (Natural Science), 2012(6): 695−699.(in Chinese) [14] MALIK A I, SOPHEARITH S, DELAQUIS E, et al. Susceptibility of Cassava Varieties to Disease Caused by Sri Lankan Cassava Mosaic Virus and Impacts on Yield by Use of Asymptomatic and Virus-Free Planting Material [J]. Agronomy, 2022, 12(7): 1658. doi: 10.3390/agronomy12071658 [15] YANG C B, YAN K R, MA C N, et al. Insight into the root growth, soil quality, and assembly of the root-associated microbiome in the virus-free Chrysanthemum morifolium [J]. Industrial Crops & Products, 2022, 176: 114362. [16] 袁济端. 太子参新品种柘参1号、柘参2号的选育 [J]. 广西热带农业, 2007(6):39−41.YUAN J D. Breeding of new varieties Zheshen 1 and Zheshen 2 of pseudostellaria heterophylla [J]. Guangxi Tropical Agriculture, 2007(6): 39−41.(in Chinese) [17] 匡云波, 陈满足, 陆伊荣, 等. 太子参芜菁花叶病毒和蚕豆萎蔫病毒的双重RT-PCR检测[J]. 园艺学报, 2017.44(4): 784-791.KUANG Y B, CHEN M Z, LU Y R, et al. 2017. Detection of Turnip mosaic virus and Broad bean wilt virus in Pseudostellaria heterophylla by Duplex RT-PCR. 44(4): 784-791. (in Chinese) [18] 黄冬寿. “柘荣太子参”规范化生产操作规程(SOP)[J]. 中国现代中药, 2009, 11(9): 15-17.HUANG D S. 2009. Standardized production and operation procedures of "Zherong Pseudostellaria heterophylla"(SOP)[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine, 11(9): 15-17. (in Chinese) [19] PORRA R J, THOMPSON W A, KRIEDEMANN P E. Determination of accurate extinction coefficients and simultaneous equations for assaying chlorophylls a and b extracted with four different solvents: verification of the concentration of chlorophyll standards by atomic absorption spectroscopy [J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics, 1989, 975(3): 384−394. doi: 10.1016/S0005-2728(89)80347-0 [20] 梁婷婷, 周英, 林冰, 等. 太子参多糖的水提醇沉工艺研究 [J]. 山地农业生物学报, 2013, 32(1):79−82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0457.2013.01.018LIANG T T, ZHOU Y, LIN B, et al. Polysaccharide extraction from Radix pseudostellariae with water extracting-ethanol precipitation method [J]. Journal of Mountain Agriculture and Biology, 2013, 32(1): 79−82.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0457.2013.01.018 [21] 赵学敏, 夏宏勋. 芜菁花叶病毒研究进展[J]. 现代农业科技, 2008(17): 170-173.ZHAO X M, XIA H X. Research progress of Turnip mosaic virus. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2008(17): 170-173. (in Chinese) [22] 党明青. 玉米褪绿斑驳病毒致病性分析及与甘蔗花叶病毒协同侵染机制研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2017.DANG M Q. Analysis of Maize chlorotic mottle virus pathogenicity and exploring the mechanism of synergistic infection with Sugarcane mosaic virus[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2017. (in Chinese) [23] 李亚囡, 李学华, 王广海, 等. 植物病毒在宿主内的拮抗效应及其分子机制 [J]. 华北农学报, 2021(S1):320−325. doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.20192624LI Y N, LI X H, WANG G H, et al. Antagonistic interactions between plant viruses within host and its molecular basis [J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2021(S1): 320−325.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.20192624 [24] 周翠姬. BrYV与PEMV2协生互作的生物学、转录组学和小RNA表达谱研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2017.ZHOU C J. Biologcal, transcriptomic and small RNA profiling analysis of synergistic interaction between Brassica yellows virus and Peaenation moscia virus 2[D].Beijing: China Agricultural University. 2017. (in Chinese) [25] TATINENI S, HEIN G L. Plant Viruses of Agricultural Importance: Current and Future Perspectives of Virus Disease Management Strategies. [J]. Phytopathology, 2022(10): 1943−7684. [26] 林巧美, 庞文生, 曾洁, 等. 福建柘荣不同品种太子参浸出物及多糖含量测定 [J]. 中国民族民间医药, 2019(3):21−23.LIN Q M, PANG W S, ZENG J, et al. Experimental study on the extracts and polysaccharides of different sarieties of Pseudostellaria heterophylla from zhelong Fujian Province [J]. Chinese Journal of Ethnomedicine and Ethnopharmacy, 2019(3): 21−23.(in Chinese) [27] 赵云青, 黄颖桢, 陈菁瑛, 等. 太子参芜菁花叶病毒时空动态定性初步检测 [J]. 福建农业科技, 2019(3):34−39.ZHAO Y Q, HUANG Y Z, CHEN J Y, et al. Preliminary qualitative detection on spatial and temporal dynamics of turnip mosaic virus in Radix pseudostellariae [J]. Fujian Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019(3): 34−39.(in Chinese) -








 下载:
下载: