Cadmium Decontamination of Polluted Yellow-brown Dryland Soil by Passivator
-
摘要:
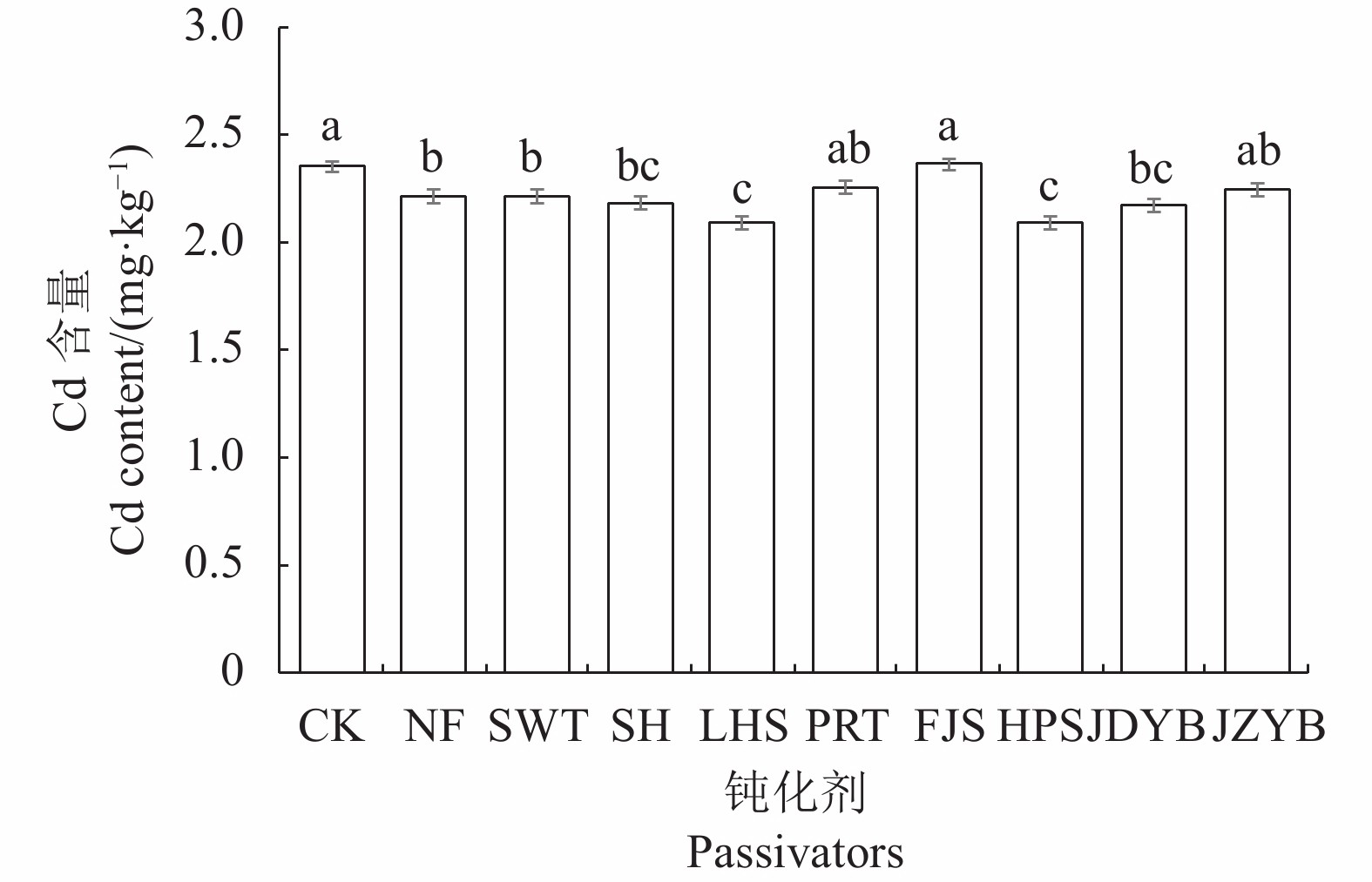
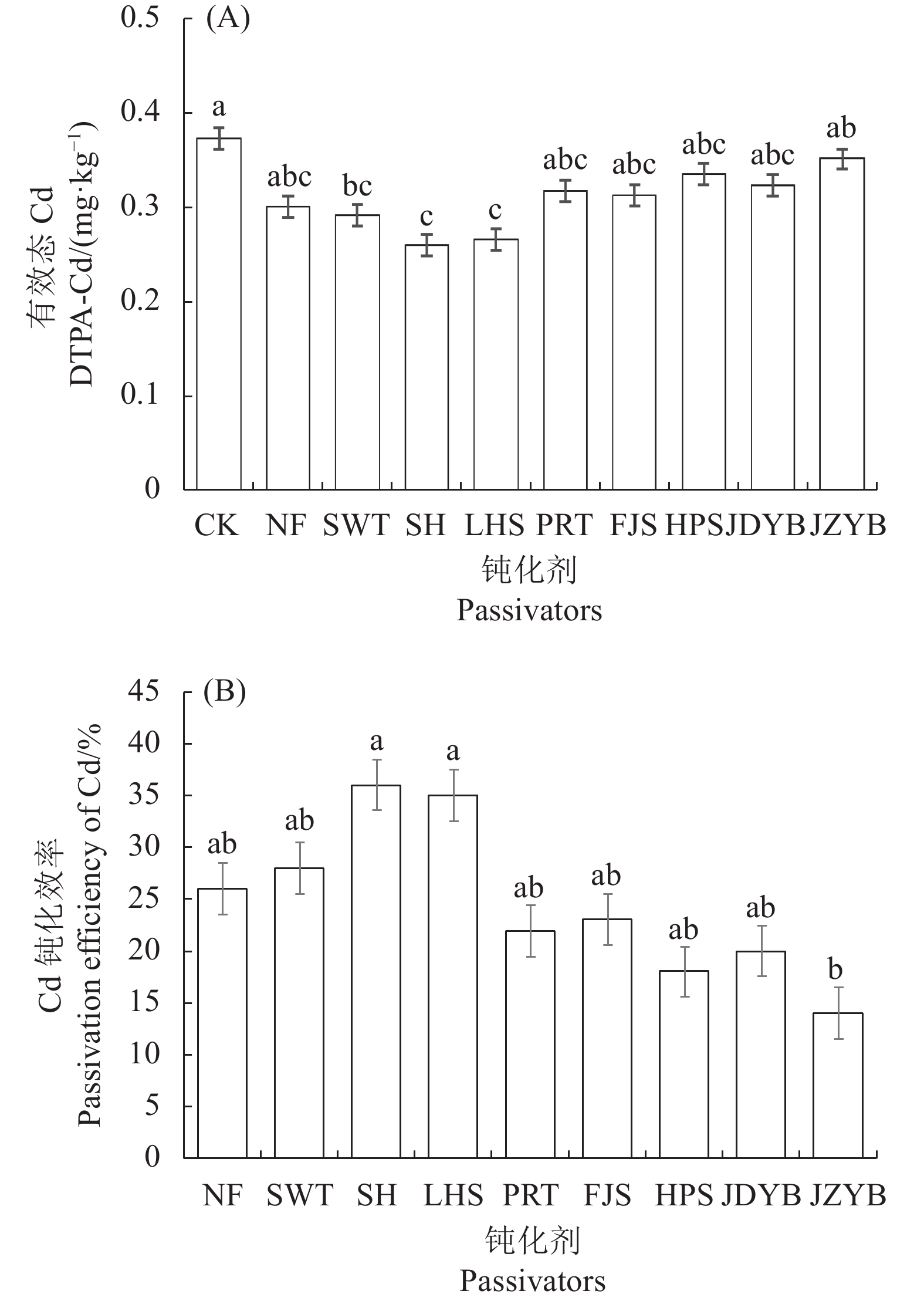
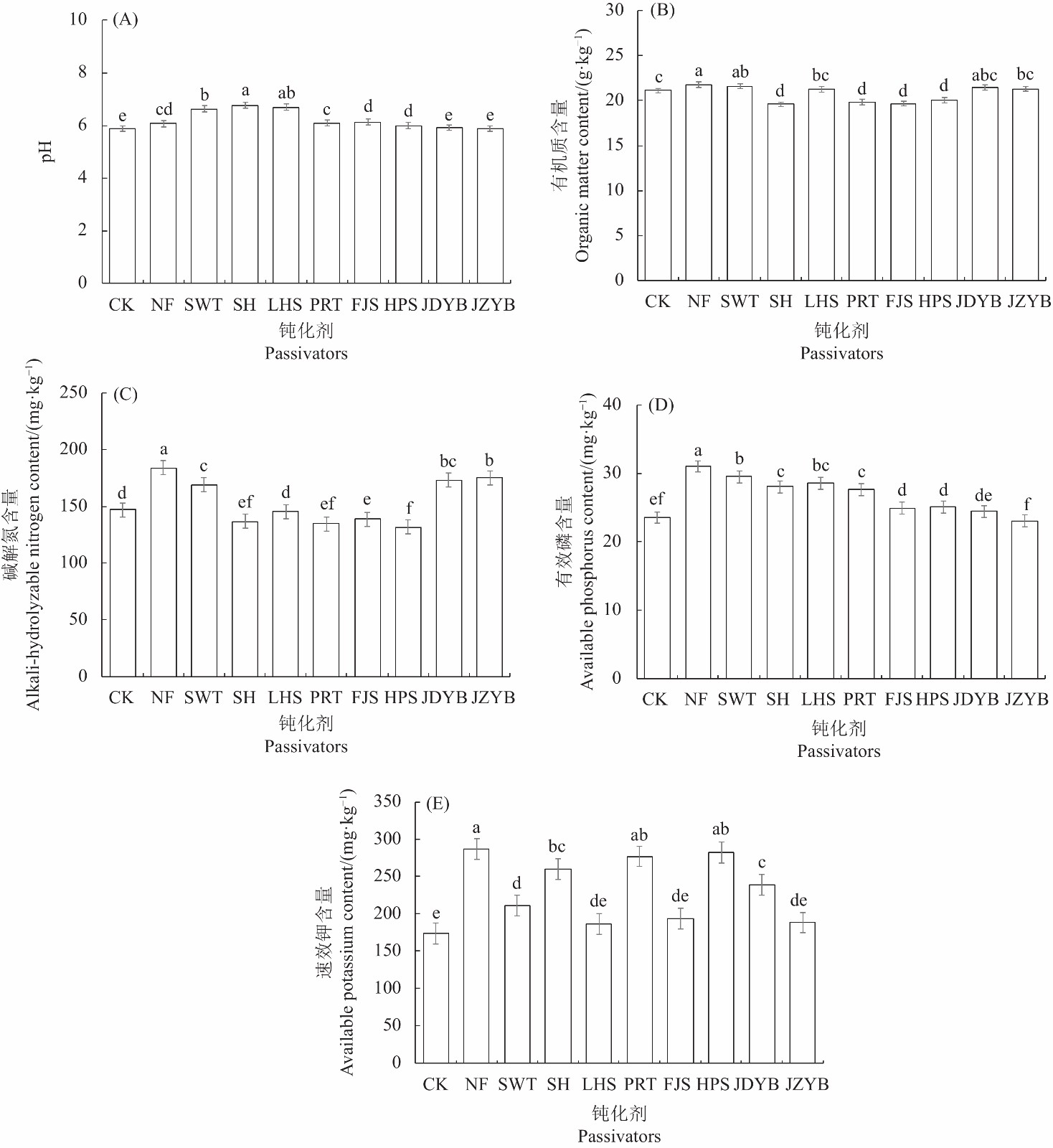
目的 研究施用不同钝化剂对黄棕壤旱地严格管控类土Cd的钝化效果,为以土壤类型划分的Cd污染土壤钝化修复提供理论参考。 方法 采用室内培养试验法,以贵州典型Cd超标黄棕壤为研究对象,将牛粪(NF)、玉米生物炭(SWT)、石灰(SH)、磷灰石(LHS)、膨润土(PRT)、方解石(FJS)、海泡石(HPS)、巨大芽孢杆菌(JDYB)和胶质芽孢杆菌(JZYB)作为钝化剂,通过室内培养70 d后,分析其土壤理化性质(pH、有机质、碱解氮、有效磷、速效钾)、Cd全量和有效态Cd含量的变化特征。 结果 (1)施用不同钝化剂均提高土壤pH 0.03~0.88,其中SH处理的土壤pH增幅最大,达14.94%。除SH、PRT、FJS和HPS会降低土壤有机质含量外,其他钝化剂均能有效增加土壤有机质含量,其中NF增加土壤有机质含量的幅度最大(31%)。相对其他钝化剂,NF对土壤速效养分(碱解氮、有效磷和速效钾)含量增加效果最好,分别增幅25.16%、31.89%和65.11%。(2)施用FJS会提高土壤Cd含量,而其他钝化剂均能降低土壤Cd含量0.1~0.26 mg·kg−1,其中LHS和HPS对土壤Cd含量的降低效果最好。(3)与对照相比,SH降低土壤有效态Cd含量的幅度最大(30.56%),而不同钝化剂对土壤Cd的钝化效果分别表现为SH(36%)>LHS(35%)>SWT(28%)>NF(26%)>FJS(23%)>PRT(22%)>JDYB(20%)>HPS(18%)>JZYB(14%)。 结论 NF对黄棕壤中的养分指标提升效果最好,而SH对黄棕壤Cd的钝化效果最为理想。 Abstract:Objective Passivator were applied on cadmium-contaminated yellow-brown dryland soil to determine the antipollution efficiency. Method In an indoor culture experiment, a typical Cd-contaminated soil collected from a strictly controlled yellow-brown dryland in Guizhou was treated with cow manure (NF), corn biochar (SWT), lime (SH), apatite (LHS), bentonite (PRT), calcite (FJS), sepiolite (HPS), Bacillus megaterium (JDYB), or B. glialis (JZYB) as the deactivation agents. After 70 d of the treatments, the soils were tested for pH, organic matters, alkaline hydrolysable nitrogen, effective variation characteristics of phosphorus and available potassium, as well as total and available Cd. Result (1) The various agents raised the soil pH by 0.03–0.88 with the greatest 14.94% increase induced by SH. And all of them, aside from SH, PRT, FJS, and HPS, significantly raised the organic matter content with the greatest increase of 31% over control by NF. NF also exerted the most increases on the available nutrients, such as 25.16% on alkaline-hydrolysable nitrogen , 31.89% on available phosphorus and 65.11% on available potassium. (2) FJS escalated the Cd in soil, but all other deactivation agents reduced the content by 0.1–0.26 mg·kg−1, with LHS and HPS rendering the largest reduction. (3) Compared to the control, SH reduced the available Cd most by 30.56%. The efficacies of the tested agents ranked SH (36%)>LHS (35%)>SWT (28%)>NF (26%)>FJS (23%)>PRT (22%)>JDYB (20%)>HPS (18%)>JZYB (14%). Conclusion Among the deactivation agents studied, NF exhibited the greatest improvement on the nutrient indices of the yellow-brown dryland soil and SH on Cd mitigation. -
Key words:
- passivator /
- yellow-brown soil /
- cadmium /
- decontamination effect /
- physiochemical properties
-
表 1 不同钝化剂基本信息
Table 1. Basic information on passivator tested
钝化剂
Passivator主要成分
Main ingredientpH值
pH value牛粪
Cow dung (NF)有机质≥13.50%
Organic matter≥13.50%7.80 生物炭
Biochar(SWT)玉米生物炭
Corn biochar7.77 石灰
Lime(SH)CaO≥56.03% 12.38 磷灰石
Apatite(LHS)P2O3≥42.06% 7.62 膨润土
Bentonite(PRT)SiO2≥66.7%;
Al2O3≥28.3%8.83 方解石
Calcite(FJS)CaO≥56.03% 8.90 海泡石
Sepiolite(HPS)SiO2≥55.65%;
MgO≥24.89%7.69 巨大芽孢杆菌
Bacillus megaterium(JDYB)有效活菌数1×1010cfu·g−1
Viable bacteria 1×1010cfu·g−16.89 胶质芽胞杆菌
Bacillus glialis(JZYB)有效活菌数1×1010cfu·g−1
Viable bacteria 1×1010cfu·g−16.79 表 2 土壤理化指标与土壤Cd活性的相关性
Table 2. Correlation between physicochemical indices and Cd activity in soil
指标
Index土壤Cd含量
Soil Cd content土壤有效态Cd
Soil available CdCd钝化率
Cd passivation ratepH −0.317 −0.650* 0.41 有机质
Organic matter−0.04 0.221 −0.068 碱解氮
Alkaline hydrolyzed Nitrogen0.005 0.105 0.120 有效磷
Available phosphorus−0.336 −0.755* 0.609 速效钾
Available potassium−0.411 −0.246 0.057 *表示显著相关。
* means significant correlation. -
[1] 田茂苑, 何腾兵, 付天岭, 等. 稻田土壤和稻米镉含量关系的研究进展 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2019, 47(8):25−28,40.TIAN M Y, HE T B, FU T L, et al. Research progress on relationship between paddy soil and cadmium content in rice grains [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(8): 25−28,40.(in Chinese) [2] 王娜, 魏样. 土壤重金属镉污染来源及其修复技术探究 [J]. 环境与发展, 2019, 31(8):55−56,58.WANG N, WEI Y. Study on sources of heavy metal cadmium pollution in soil and its remediation technology [J]. Environment and Development, 2019, 31(8): 55−56,58.(in Chinese) [3] YANG X, ZHANG W Y, QIN J H, et al. Role of passivators for Cd alleviation in rice-water spinach intercropping system [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020, 205: 111321. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111321 [4] CHEN Y H, XIE T H, LIANG Q F, et al. Effectiveness of lime and peat applications on cadmium availability in a paddy soil under various moisture regimes [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(8): 7757−7766. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5930-4 [5] 任超, 李竞天, 朱利文, 等. 不同钝化剂对碱性镉污染土壤钝化效果研究 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2021, 44(3):71−78.REN C, LI J T, ZHU L W, et al. Study on the passivation effect of different passivators on alkaline cadmium contaminated soil [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 44(3): 71−78.(in Chinese) [6] 韦小了, 牟力, 付天岭, 等. 不同钝化剂组合对土壤铬铜赋存形态及在水稻中积累的影响 [J]. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(5):349−357.WEI X L, MOU L, FU T L, et al. Effects of different passivator combinations on chromium and copper speciation in soil and accumulation in rice [J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 33(5): 349−357.(in Chinese) [7] 化党领, 朱利楠, 赵永芹, 等. 膨润土、褐煤及其混合添加对铅、镉复合污染土壤重金属形态的影响 [J]. 土壤通报, 2020, 51(1):201−206.HUA D L, ZHU L N, ZHAO Y Q, et al. Fractionation of heavy metals in Cd/Pb contaminated soil amended with bentonite and lignite [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2020, 51(1): 201−206.(in Chinese) [8] 曾秀君, 黄学平, 程坤, 等. 石灰组配有机改良剂对农田铅镉污染土壤微生物活性的影响 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2020, 33(10):2361−2369.ZENG X J, HUANG X P, CHENG K, et al. Effects of lime mixed with organic modifiers on microbial activity in lead and cadmium contaminated farmland soil [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2020, 33(10): 2361−2369.(in Chinese) [9] CHEN Z Q, FU Q Q, CAO Y G, et al. Effects of lime amendment on the organic substances changes, antibiotics removal, and heavy metals speciation transformation during swine manure composting [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 262: 128342. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128342 [10] 瞿飞, 范成五, 刘桂华, 等. 不同钝化剂对贵州典型黄壤重金属有效态的影响 [J]. 南方农业学报, 2019, 50(9):1967−1972.QU F, FAN C W, LIU G H, et al. Effects of different passivating agents on the effective state of heavy metals in typical yellow soil in Guizhou [J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2019, 50(9): 1967−1972.(in Chinese) [11] 冯乾伟, 王兵, 马先杰, 等. 黔西北典型铅锌矿区土壤重金属污染特征及其来源分析 [J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2020, 39(4):863−870.FENG Q W, WANG B, MA X J, et al. Pollution characteristics and source analysis of heavy metals in soils of typical lead-zinc mining areas in northwest Guizhou, China [J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2020, 39(4): 863−870.(in Chinese) [12] 生态环境部, 国家市场监督管理总局. 土壤环境质量 农用地土壤污染风险管控标准: GB 15618—2018[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018. [13] 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. [14] 刘娟, 张乃明, 袁启慧. 不同钝化剂对铅镉复合污染土壤钝化效果及影响因素研究 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8):1732−1741.LIU J, ZHANG N M, YUAN Q H. Passivation effect and influencing factors of different passivators on lead-cadmium compound contaminated soils [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(8): 1732−1741.(in Chinese) [15] 吴海燕, 金荣德, 范作伟, 等. 解磷巨大芽孢杆菌(Bacillus megaterium)的溶磷机理探讨 [J]. 吉林农业大学学报, 2014, 36(2):171−175.WU H Y, JIN R D, FAN Z W, et al. Mechanism of solubilizing phosphate by Bacillus megaterium [J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2014, 36(2): 171−175.(in Chinese) [16] 曾秀君, 程坤, 黄学平, 等. 石灰、腐植酸单施及复配对污染土壤铅镉生物有效性的影响 [J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2020, 36(1):121−128.ZENG X J, CHENG K, HUANG X P, et al. Effect of single and multiple application of lime and humic acid on the bioavailability of lead and cadmium in contaminated soil [J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2020, 36(1): 121−128.(in Chinese) [17] 刘勇, 刘燕, 朱光旭, 等. 石灰对Cu、Cd、Pb、Zn复合污染土壤中重金属化学形态的影响 [J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(2):158−164. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201902030LIU Y, LIU Y, ZHU G X, et al. Effects of lime on chemical forms of heavy metals under combined pollution of cu, cd, pb and zn in soils [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2019, 37(2): 158−164.(in Chinese) doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201902030 [18] 邢维芹, 张纯青, 周冬, 等. 磷酸盐、石灰和膨润土降低冶炼厂污染石灰性土壤重金属活性的研究 [J]. 土壤通报, 2019, 50(5):1245−1252.XING W Q, ZHANG C Q, ZHOU D, et al. Immobilization of heavy metals in a lead-smelting contaminated calcareous soil by phosphate, lime or bentonite [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2019, 50(5): 1245−1252.(in Chinese) [19] 刘洁, 孙可, 韩兰芳. 生物炭对土壤重金属形态及生物有效性影响的研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(6):1643−1658.LIU J, SUN K, HAN L F. Effect of biochar on soil heavy metal speciation and bioavailability: A review [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(6): 1643−1658.(in Chinese) [20] 袁兴超, 李博, 朱仁凤, 等. 不同钝化剂对铅锌矿区周边农田镉铅污染钝化修复研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(4):807−817.YUAN X C, LI B, ZHU R F, et al. Immobilization of Cd and Pb using different amendments of cultivated soils around lead-zinc mines [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(4): 807−817.(in Chinese) [21] 李可, 谢厦, 孙彤, 等. 鸡粪有机肥对设施菜地土壤重金属和微生物群落结构的影响 [J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(12):4827−4839.LI K, XIE S, SUN T, et al. Effects of organic fertilizers from chicken manure on soil heavy metals and microbial community structure in facility vegetable soil [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(12): 4827−4839.(in Chinese) [22] TIAN X, LI T, YANG K, et al. Effect of humic acids on physicochemical property and Cd(II) sorption of multiwalled carbon nanotubes [J]. Chemosphere, 2012, 89(11): 1316−1322. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.05.082 [23] 李波, 青长乐, 周正宾, 等. 肥料中氮磷和有机质对土壤重金属行为的影响及在土壤治污中的应用 [J]. 农业环境保护, 2000, 19(6):375−377.LI B, QING C L, ZHOU Z B, et al. Effects of nitrogen, phosphorus and organic matter on heavy metal behavior in soils and its application of controlling pollution [J]. Agro-Environmental Protection, 2000, 19(6): 375−377.(in Chinese) [24] 梅闯, 王衡, 蔡昆争, 等. 生物炭对土壤重金属化学形态影响的作用机制研究进展 [J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2021, 37(4):421−429.MEI C, WANG H, CAI K Z, et al. Advances on effects and mechanisms of biochar on chemical forms of heavy metals in contaminated soil [J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2021, 37(4): 421−429.(in Chinese) [25] 袁婷婷, 席雪萍, 齐超, 等. 生物炭修复土壤重金属污染的研究进展 [J]. 环境科学与管理, 2022, 47(3):123−126.YUAN T T, XI X P, QI C, et al. Research progress on biochar remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil [J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2022, 47(3): 123−126.(in Chinese) [26] 戚鑫, 陈晓明, 肖诗琦, 等. 生物炭固定化微生物对U、Cd污染土壤的原位钝化修复 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(8):1683−1689. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0233QI X, CHEN X M, XIAO S Q, et al. In situ remediation of U-and Cd-contaminated soils by immobilized microorganisms and biochar [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(8): 1683−1689.(in Chinese) doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0233 [27] 代允超, 吕家珑, 曹莹菲, 等. 石灰和有机质对不同性质镉污染土壤中镉有效性的影响 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(3):514−519. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2014.03.017DAI Y C, LV J L, CAO Y F, et al. Effects of lime and organic amendments on Cd availability in Cd-contaminated soils with different properties [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2014, 33(3): 514−519.(in Chinese) doi: 10.11654/jaes.2014.03.017 [28] 王刚, 孙育强, 杜立宇, 等. 石灰与生物炭配施对不同浓度镉污染土壤修复 [J]. 水土保持学报, 2018, 32(6):379−383.WANG G, SUN Y Q, DU L Y, et al. Study on remediation of Cd-contaminated soils with different concentrations of lime and biochar [J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 32(6): 379−383.(in Chinese) [29] 黄柏豪, 吴秦慧姿, 肖亨, 等. 连施石灰对Cd污染土壤Cd形态及稻麦吸收Cd的影响 [J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2020(3):138−143. doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.19206HUANG B H, WU Q, XIAO H, et al. Effects of continuous application of lime for three years on cadmium concentration and uptake by wheat and rice in Cd contaminated soil [J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2020(3): 138−143.(in Chinese) doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.19206 [30] 李仪, 罗绪强. 纳米羟基磷灰石对铅镉污染土壤重金属生物可给性的影响研究 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2017, 26(7):1255−1260.LI Y, LUO X Q. Effects of nano-hydroxyapatite on the bioaccessibility of heavy metals in soils polluted by Pb and Cd [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2017, 26(7): 1255−1260.(in Chinese) [31] SMICIKLAS I, ONJIA A, RAICEVIC S, et al. Factors influencing the removal of divalent cations by hydroxyapatite [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 152(2): 876−884. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.07.056 [32] 邢金峰, 仓龙, 葛礼强, 等. 纳米羟基磷灰石钝化修复重金属污染土壤的稳定性研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2016, 35(7):1271−1277.XING J F, CANG L, GE L Q, et al. Long-term stability of immobilizing remediation of a heavy metal contaminated soil with nano-hydroxyapatite [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2016, 35(7): 1271−1277.(in Chinese) [33] 姜军涛. 膨润土修复矿区污染土壤的初探[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2008.JIANG J T. A preliminary study on remediation of a mining tailings contaminated soil using natural bentonite[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2008. (in Chinese) [34] 王林, 徐应明, 孙国红, 等. 海泡石和磷酸盐对镉铅污染稻田土壤的钝化修复效应与机理研究 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2012, 21(2):314−320. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2012.02.020WANG L, XU Y M, SUN G H, et al. Effect and mechanism of immobilization of paddy soil contaminated by cadmium and lead using sepiolite and phosphate [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2012, 21(2): 314−320.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2012.02.020 [35] LIANG X F, HAN J, XU Y M, et al. In situ field-scale remediation of Cd polluted paddy soil using sepiolite and palygorskite [J]. Geoderma, 2014, 235/236: 9−18. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2014.06.029 [36] 刘五星, 徐旭士, 杨启银, 等. 胶质芽孢杆菌对土壤矿物的分解作用及机理研究 [J]. 土壤, 2004, 36(5):547−550. doi: 10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2004.05.015LIU W X, XU X S, YANG Q Y, et al. Mechanisms of bacillus mucilaginosus decomposing soil minerals [J]. Soils, 2004, 36(5): 547−550.(in Chinese) doi: 10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2004.05.015 [37] WU S C, LUO Y M, CHEUNG K C, et al. Influence of bacteria on Pb and Zn speciation, mobility and bioavailability in soil: A laboratory study [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2006, 144(3): 765−773. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2006.02.022 [38] 董立萍. 解磷菌修复土壤铅污染效应优化及机理探索[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2014.DONG L P. Effect optimization and mechanism exploration of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria in remediation of lead pollution in soil[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University, 2014. (in Chinese) [39] 王小敏, 纪宏伟, 刘文菊, 等. 巨大芽孢杆菌与印度芥菜对Cd污染土壤的联合修复效果研究 [J]. 水土保持学报, 2014, 28(4):232−236. doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2014.04.043WANG X M, JI H W, LIU W J, et al. Effect of Bacillus megaterium and Brassica juncea combination on phytoextraction of Cd from polluted soil [J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2014, 28(4): 232−236.(in Chinese) doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2014.04.043 -







 下载:
下载: