Evaluation of Sargassum horneri Liquid Fertilizer for Vegetable Seed Germination and Seedling Growth
-
摘要:
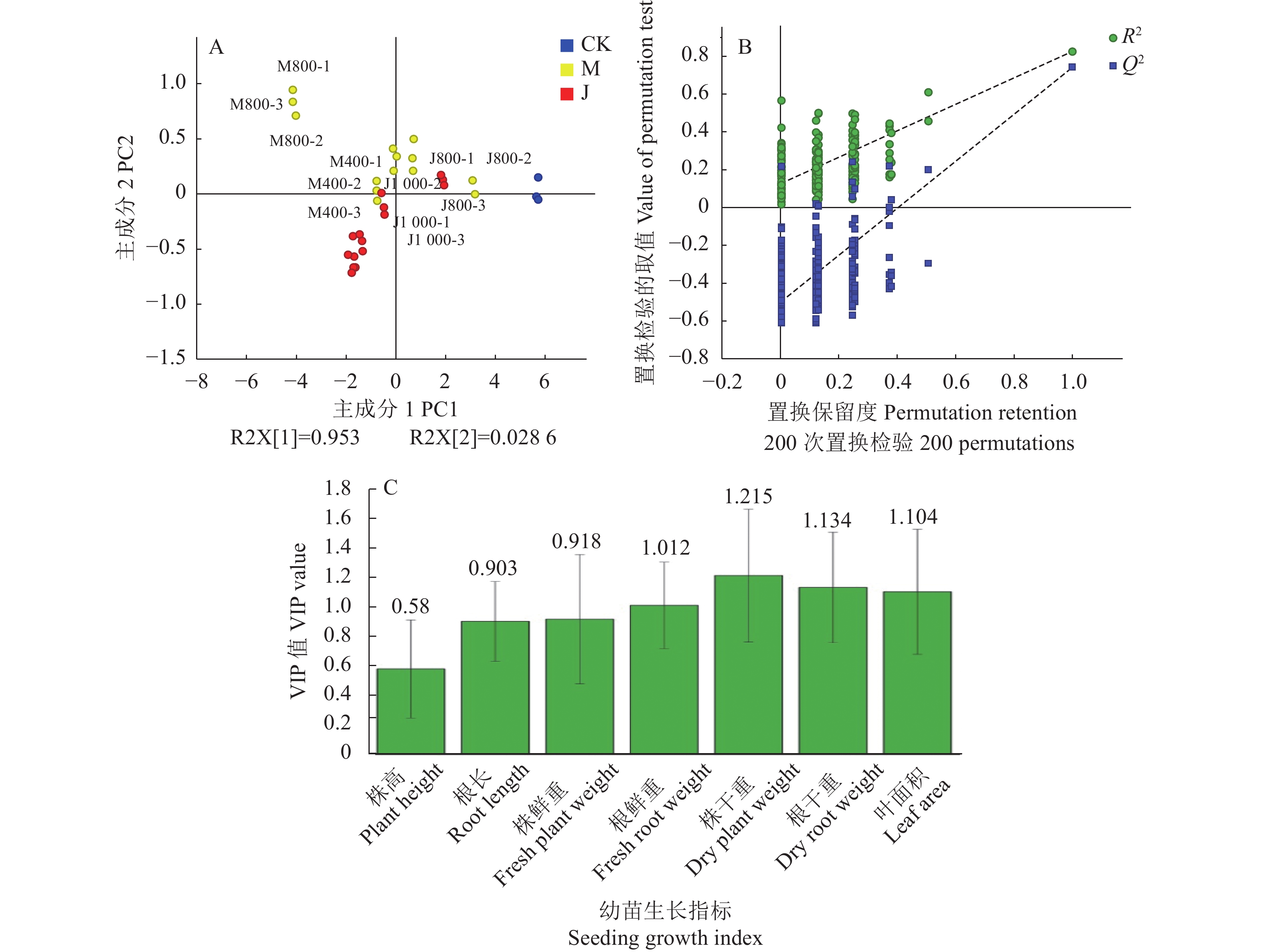
目的 铜藻为沿海常见的低质海藻,为实现铜藻高质利用,以新鲜铜藻为原料制备铜藻液体肥,研究其对上海青、黄瓜和番茄等3种蔬菜种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响,并基于偏最小二乘判别分析(Partial least squares discriminant analysis,PLS-DA)探究铜藻液体肥增肥的生物学效应。 方法 采用酶法和发酵法2种工艺制备铜藻液体肥,并各设置5组稀释倍数(200倍、400倍、600倍、800倍和1000倍)进行种子萌发试验和幼苗盆栽试验。 结果 (1)种子萌发试验中,发酵法制备铜藻液体肥的200倍液、600倍液在上海青种子萌发上效果最佳,发芽指数较空白组显著提高11.8%,较两组阳性对照分别提高1.9%和1.3%;发酵制备的200倍液对黄瓜种子萌发影响最好,发芽指数较空白和两组阳性对照均显著提高,增幅分别达33.0%、21.0%和6.7%;发酵制备的1000倍液在番茄种子萌发上成效最佳,发芽指数较空白和两组阳性对照分别显著提升13.6%、14.4%和19.3%。(2)幼苗盆栽试验中,相关性分析结果表明各生长指标间普遍存在极显著正相关性,主成分分析(Principal component analysis, PCA)结果显示铜藻液体肥对3种蔬菜的影响作用各有差异,构建实验样品的PLS-DA模型分析不同制备方法的铜藻液体肥肥效并与阳性对照对比,结果表明发酵制备的400倍液对上海青幼苗促生效果最佳,各指标均显著高于阳性对照海藻肥,其中根鲜重提高最显著,增幅为144%;酶法制备的800倍液对黄瓜幼苗生长效果最好,各指标均显著高于阳性对照海藻肥,其中根长提高最显著,增幅为28%;发酵制备的600倍液对番茄幼苗作用效果最好,各指标均显著高于阳性对照海藻肥,其中株干重提高最显著,增幅为31%。 结论 铜藻液体肥具备很好的增肥生物学效应,发酵法制备的铜藻液体肥肥效普遍优于酶法制备,施用前者能提高种子萌发率,促进幼苗地上部分和地下部分的生长,以上结果为海藻液体肥的生产与应用提供科学数据。 Abstract:Objective Effects of the liquid fertilizer made from Sargassum horneri for vegetable seed germination and seedling growth were evaluated. Methods The liquid fertilizers prepared by either enzymatic digestion or fermentation of S. horneri, a low-quality seaweed commonly found in the coastal areas, in a gradient of concentrations were applied on bok choy (Brassica chinensis), cucumber, and tomato to determine the fertilization effects on the vegetable seed germination and subsequent seedling growth in a pot experiment. Data collected were statistically analyzed by the partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLSDA). Results (1) The 200x and 600x liquid fertilizer dilutions delivered the best effects on the germination of bok choy seeds with a significantly increased germination index by 11.8% over that of blank control and by 1.9% and 1.3% over those of two positive controls. On the germination of cucumber seeds, the 200x dilution had the best effect with a significantly higher index than that of blank control by 33.0% and 21.0% and by 6.7% over those of two positive controls. For the germination of tomato seeds, the 1,000x dilution performed best with a significantly increased index over that of blank control by 13.6% and by 14.4% and 19.3% over those of the two positive controls. (2) The growth indicators of the potted seedlings were significantly correlated. The effects of the liquid fertilizer on the growth of 3 vegetable categories varied, as shown by the principal component analysis (PCA). According to the PLSDA models, the fermented liquid fertilizer at 400x dilution was superior in promoting the growth of bok choy seedlings with all indices significantly higher than those of the positive control, especially, a 144% increase on fresh root weight. And at 600x dilution, the fermented liquid fertilizer had all indices on the tomato seedlings significantly higher than those of control and the highest dry plant weight that was 31% heavier than that of the positive control. In contrast, the enzymatically digested liquid fertilizer at 800x dilution was best for the growth of cucumber seedlings with significantly higher indices on all aspects than the positive control and 28% longer roots than the positive control. Conclusion TheS. horneri liquid fertilizers prepared by either fermentation or enzymatic digestion significantly promoted the seed germination and seedling growth of bok choy, cucumber, and tomato in a pot experiment. The fermented fertilizer was more effective than the enzyme-digested counterpart. -
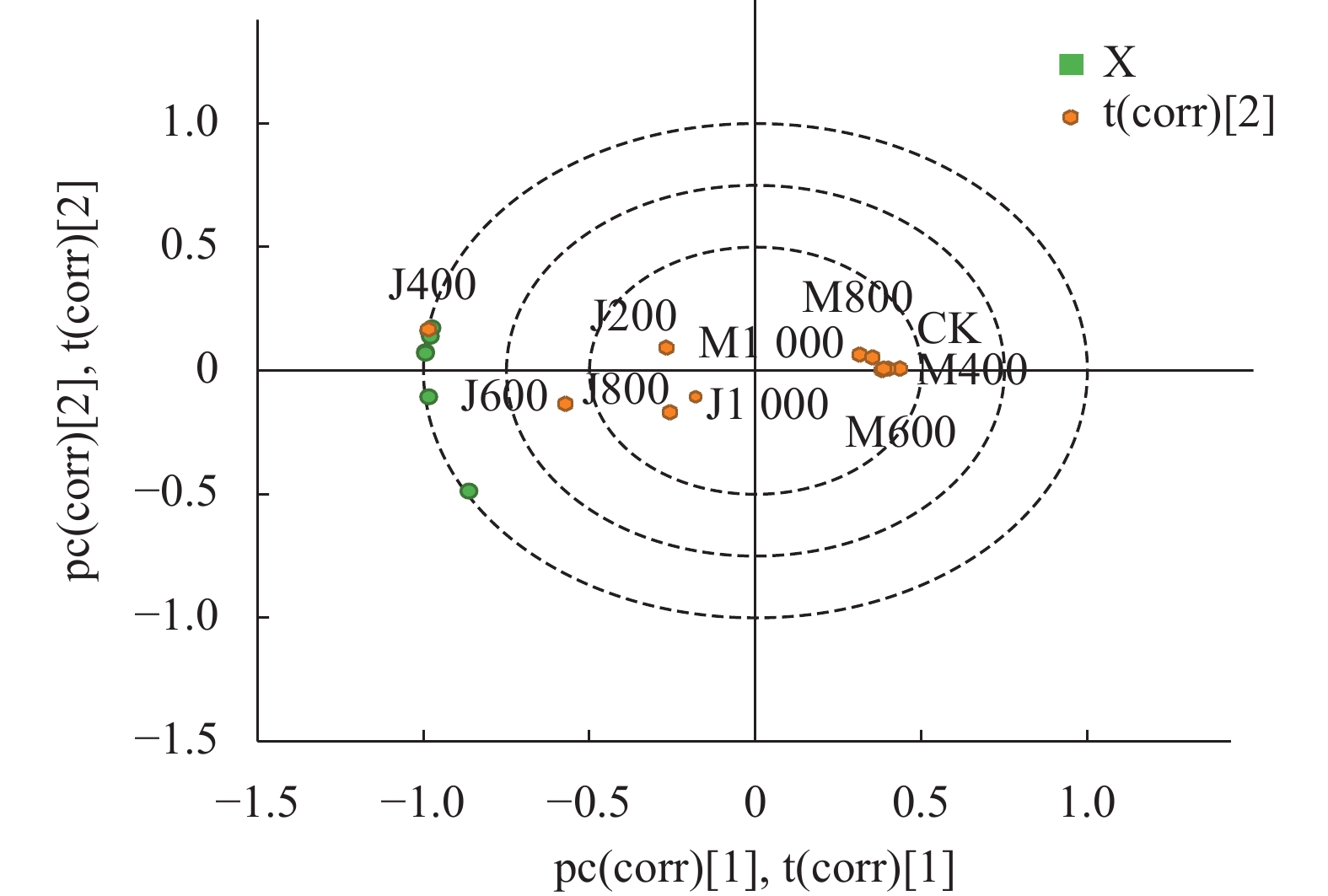
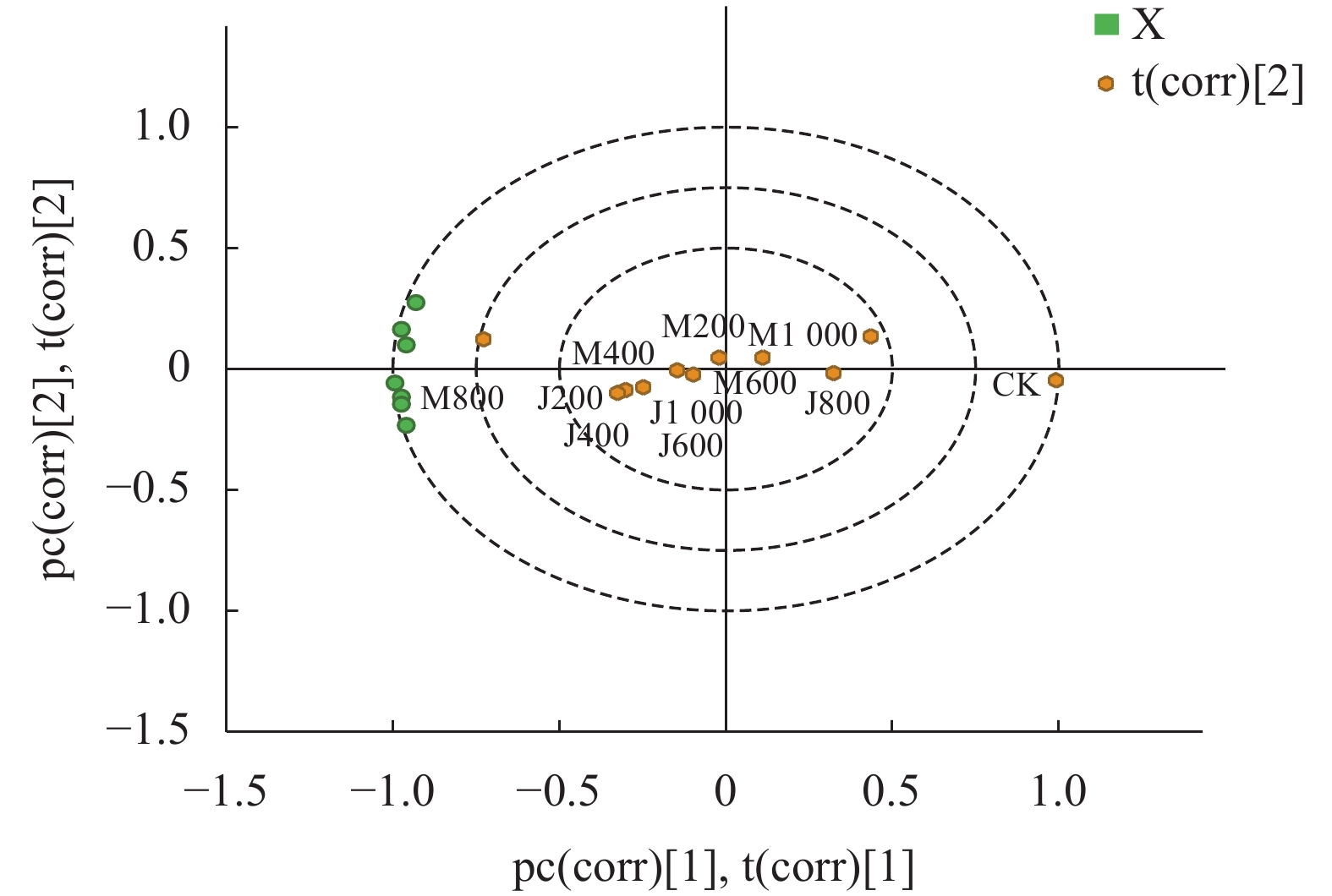
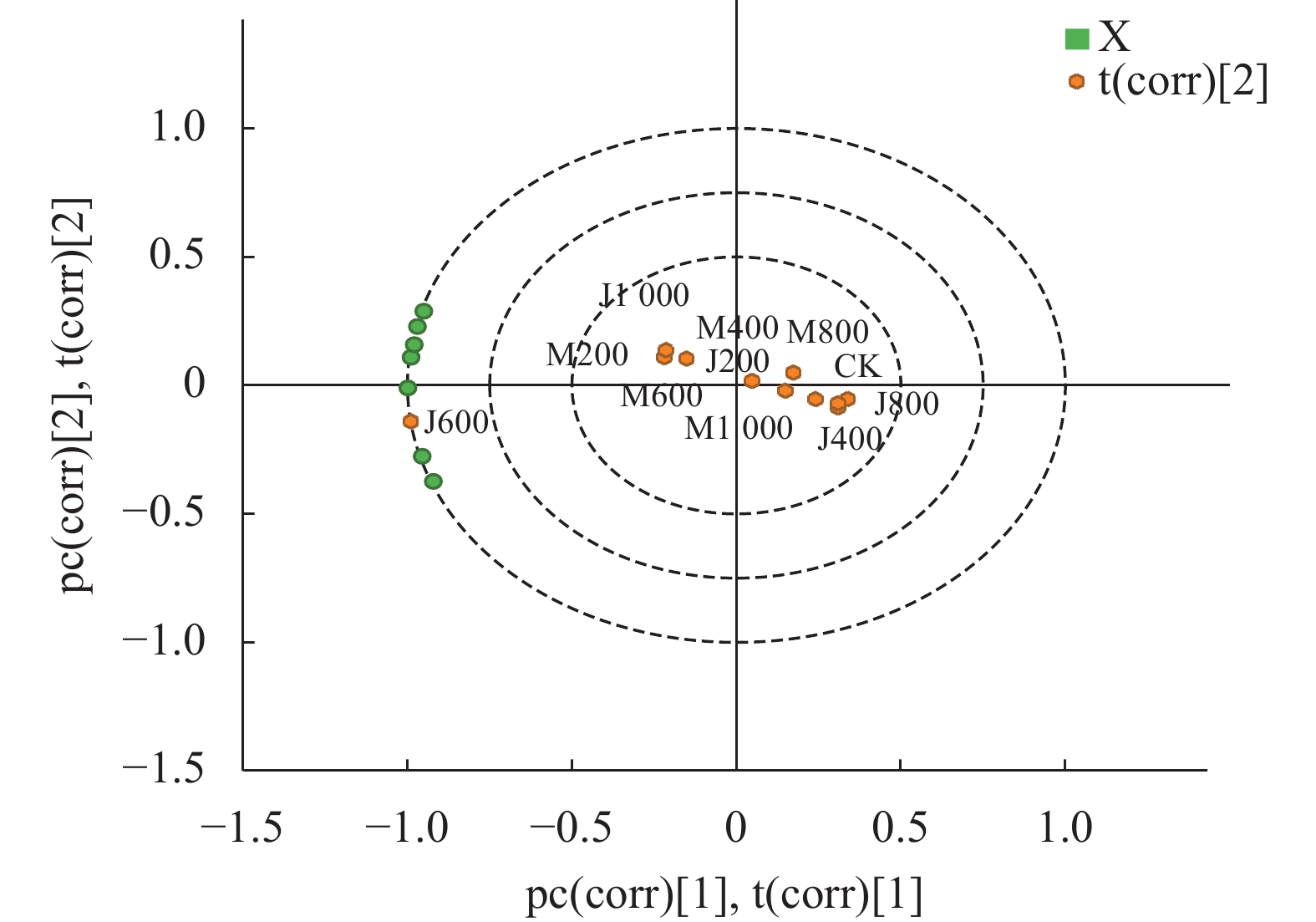
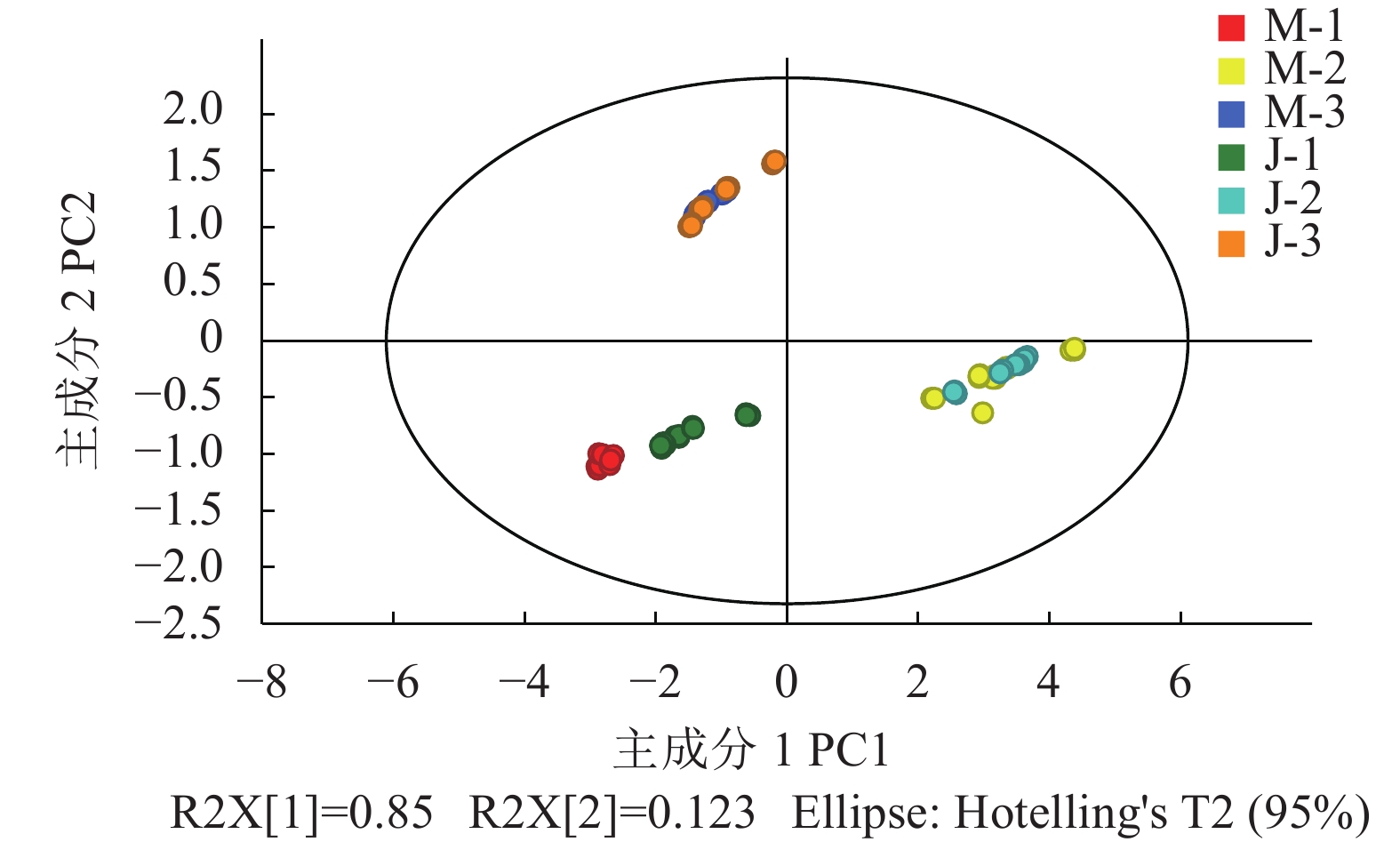
图 1 铜藻液体肥影响生长指标的主成分得分
M-1:上海青+酶解铜藻液体肥;M-2:黄瓜+酶解铜藻液体肥;M-3:番茄+酶解铜藻液体肥;J-1:上海青+酵解铜藻液体肥;J-2:黄瓜+酵解铜藻液体肥;J-3:番茄+酵解铜藻液体肥。
Figure 1. PCA plot on scores of S. horneri liquid fertilizer affecting vegetable growth indicators
M-1: B. chinensis + enzymatically digested S. horneri liquid fertilizer; M-2: cucumber + enzymatically digested S. horneri liquid fertilizer; M-3: tomato + enzymatically digested S. horneri liquid fertilizer; J-1: B. chinensis + fermented S. horneri liquid fertilizer; J-2: cucumber + fermented S. horneri liquid fertilizer; J-3: tomato + fermented enzymatically digested S. horneri liquid fertilizer.
表 1 不同铜藻液体肥对上海青种子萌发的影响
Table 1. Effects of S. horneri liquid fertilizers on bok choy seed germination
处理
Group发芽率
Germination rate/%发芽势
Germination potential/%发芽指数
Germination indexCK 100.00±0.00 a 98.67±1.15 a 89.44±1.25 d AC1 99.67±0.58 ab 99.33±0.58 a 98.11±1.4 ab AC2 100.00±0.00 a 100.00±0.00 a 98.67±1.89 a M200 100.00±0.00 a 97.33±2.52 ab 73.67±1.04 f M400 100.00±0.00 a 100.00±0.00 a 94.67±2.02 bc M600 99.67±0.58 ab 99.67±0.58 a 98.50±1.32 a M800 100.00±0.00 a 95.67±3.21 b 83.94±1.44 e M1000 100.00±0.00 a 97.67±2.31 ab 93.92±6.39 c J200 100.00±0.00 a 100.00±0.00 a 100.00±0.00 a J400 99.33±0.58 b 99.33±0.58 a 99.33±0.58 a J600 100.00±0.00 a 100.00±0.00 a 100.00±0.00 a J800 99.67±0.58 ab 99.33±1.15 a 99.44±0.96 a J1000 100.00±0.00 a 100.00±0.00 a 99.50±0.50 a 表中数据为平均值±标准偏差;同列不同小写字母表示在0.05水平差异显著。下表同。
The data in the table are mean ± standard deviation; different lowercase letters in the same column indicate significant differences at the 0.05 level. Same for following table.表 2 施用铜藻液体肥对黄瓜种子萌发的影响
Table 2. Effects of S. horneri liquid fertilizers on cucumber seed germination
处理
Group发芽率
Germination rate/%发芽势
Germination potential/%发芽指数
Germination indexCK 98.33±0.58 ab 97.67±1.53 a 69.38±3.56 e AC1 98.00±1.00 ab 97.67±1.53 a 76.28±1.09 d AC2 97.33±1.53 ab 97.00±2.00 a 86.48±2.42 bc M200 98.67±2.31 ab 98.00±1.73 a 90.18±3.35 ab M400 97.67±0.58 ab 96.67±0.58 a 88.33±3.59 abc M600 98.00±1.73 ab 97.33±1.15 a 77.72±2.45 d M800 97.00±1.00 ab 96.00±2.00 a 86.86±4.00 bc M1000 99.67±0.58 a 98.67±0.58 a 90.66±2.40 ab J200 97.00±1.00 ab 96.33±0.58 a 92.30±2.35 a J400 97.67±1.53 ab 97.00±1.00 a 83.26±2.45 c J600 98.33±2.08 ab 97.67±1.53 a 84.44±0.64 c J800 96.00±1.73 b 95.67±2.08 a 88.09±3.41 abc J1000 97.00±2.65 ab 95.67±2.31 a 75.51±1.94 d 表 3 施用铜藻液体肥对番茄种子萌发的影响
Table 3. Effects of S. horneri liquid fertilizers on tomato seed germination
处理
Group发芽率
Germination rate/%发芽势
Germination potential/%发芽指数
Germination indexCK 89.00±2.65 cd 89.00±2.65 cd 27.26±1.82 bc AC1 88.00±2.65 d 87.67±2.89 d 27.06±1.08 c AC2 89.00±2.65 cd 87.33±4.16 d 25.96±1.52 cd M200 92.33±3.21 bc 92.33±3.21 bc 31.96±0.53 a M400 93.00±1.73 bc 92.67±2.08 bc 23.16±0.70 d M600 98.00±1.73 a 98.00±1.73 a 25.25±1.46 cd M800 92.67±3.79 bc 91.67±3.06 bcd 25.09±2.56 cd M1000 91.00±0.00 bcd 91.00±0.00 bcd 25.05±2.93 cd J200 92.33±0.58 bc 92.00±0.00 bc 30.75±0.28 a J400 87.67±1.53 d 87.33±1.53 d 30.02±0.69 a J600 90.33±0.58 cd 90.00±1.00 bcd 24.67±1.41 cd J800 94.67±1.15 ab 94.00±2.00 b 29.85±1.88 ab J1000 93.00±1.00 bc 93.00±1.00 bc 30.96±0.90 a 表 4 幼苗生长指标相关性分析
Table 4. Correlation among seedling growth indicators
生长指标
growth indicators株高
Plant height根长
Root length株鲜重
Fresh plant根鲜重
Fresh root株干重
Dry plant根干重
Dry root weight叶面积
Leaf area株高 Plant height 1 根长 Root length 0.511** 1 株鲜重 Fresh plant 0.689** 0.916** 1 根鲜重 Fresh root 0.423** 0.972** 0.879** 1 株干重 Dry plant 0.695** 0.893** 0.985** 0.856** 1 根干重 Dry root weight 0.562** 0.951** 0.945** 0.938** 0.931** 1 叶面积 Leaf area −0.088 0.752** 0.574** 0.800** 0.546** 0.684** 1 *表示在0.05水平上显著相关,**表示在0.01水平上显著相关。
* and ** represented significant correlation (P<0.05) and extremely significant correlation (P<0.01) respectively.表 5 酵解400倍铜藻液体肥与阳性对照对上海青幼苗生长的影响
Table 5. Effects of 400x dilution of fermented S. horneri liquid fertilizer and positive control on growth of bok choy seedlings
处理
Group株高
Plant height/cm根长
Root length/cm株鲜重
Fresh plant weight/g根鲜重
Fresh root weight/g株干重
Dry plant weight/g根干重
Dry root weight/g叶面积
Leaf area/cm2AC1 3.342±0.007 c 4.427±0.046 b 0.406±0.002 c 0.047±0.000 c 0.019±0.000 b 0.010±0.001 b 0.503±0.007 c AC2 3.579±0.032 b 4.669±0.097 b 0.423±0.001 b 0.058±0.002 b 0.020±0.000 b 0.011±0.000 b 0.676±0.006 b J400 5.517±0.006 a 5.411±0.063 a 0.613±0.002 a 0.141±0.002 a 0.032±0.000 a 0.026±0.000 a 1.525±0.011 a 表 6 酶解800倍铜藻液体肥与阳性对照对黄瓜幼苗生长的影响
Table 6. Effects of 800x dilution of enzymatically digested S. horneri liquid fertilizer and positive control on growth of cucumber seedlings
处理
Group株高
Plant height/cm根长
Root length/cm株鲜重
Fresh plant weight/g根鲜重
Fresh root weight/g株干重
Dry plant weight/g根干重
Dry root weight/g叶面积
Leaf area/cm2AC1 7.083±0.014 c 6.718±0.031 c 2.402±0.002 c 0.557±0.003 c 0.194±0.004 c 0.027±0.000 c 1.965±0.002 c AC2 8.031±0.032 b 7.105±0.018 b 2.683±0.002 b 0.591±0.002 b 0.216±0.005 b 0.029±0.001 b 2.396±0.004 b M800 9.860±0.024 a 9.095±0.015 a 3.077±0.004 a 0.681±0.001 a 0.266±0.002 a 0.036±0.001 a 2.998±0.004 a 表 7 酵解600倍铜藻液体肥与阳性对照对番茄幼苗生长的影响
Table 7. Effects of 600x dilution of fermented S. horneri liquid fertilizer and positive control on growth of tomato seedlings
处理
Group株高
Plant height/cm根长
Root length/cm株鲜重
Fresh plant weight/g根鲜重
Fresh root weight/g株干重
Dry plant weight/g根干重
Dry root weight/g叶面积
Leaf area/cm2AC1 9.31±0.032 c 4.709±0.026 c 0.628±0.003 c 0.073±0.000 c 0.090±0.001 c 0.018±0.000 c 0.310±0.003 c AC2 9.749±0.025 b 5.536±0.028 b 0.684±0.003 b 0.087±0.000 b 0.092±0.001 b 0.019±0.000 b 0.337±0.003 b J600 10.486±0.021 a 6.367±0.030 a 0.799±0.001 a 0.112±0.001 a 0.121±0.000 a 0.024±0.000 a 0.395±0.000 a -
[1] 秦雕, 李聪, 秦宇. 中国海藻产业发展与应用现状 [J]. 科技和产业, 2021, 21(3):104−110.QIN D, LI C, QIN Y. On the development and application status of seaweed industry in China [J]. Science Technology and Industry, 2021, 21(3): 104−110.(in Chinese) [2] LIU F, LIU X F, WANG Y, et al. Insights on the Sargassum horneri golden tides in the Yellow Sea inferred from morphological and molecular data [J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2018, 63(4): 1762−1773. doi: 10.1002/lno.10806 [3] 麻坤, 刁钢. 化肥对中国粮食产量变化贡献率的研究 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2018, 24(4):1113−1120.MA K, DIAO G. Research on the contribution rate of fertilizer to grain yield in China [J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2018, 24(4): 1113−1120.(in Chinese) [4] SRIDHAR S, RENGASAMY R. Influence of Seaweed Liquid Fertilizer on Growth and Biochemical Characteristics of Arachis hypogea L. under field trial [J]. Journal of Ecobiotechnology, 2011, 3(12): 18−22. [5] 方同光, 吴秋纫, 李根深. 用于促进植物生长的海藻提取液的生产方法, 所得到的海藻提取液, 及其复合肥料: CN1269339A[P]. 2000-10-11. [6] 周丽, 高进华, 解学仕, 等. 含腐植酸型海藻生物肥的研发及肥效评价 [J]. 腐植酸, 2021(5):30−35.ZHOU L, GAO J H, XIE X S, et al. Research and development of seaweed biofertilizer containing humic acid and its fertilizer effect evaluation [J]. Humic Acid, 2021(5): 30−35.(in Chinese) [7] SIVASANKARI S, VENKATESALU V, ANANTHARAJ M, et al. Effect of seaweed extracts on the growth and biochemical constituents of Vigna sinensis [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2006, 97(14): 1745−1751. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2005.06.016 [8] WAJAHATULLAH K, USHA P.R, SOWMYALAKSHMI S, et al Seaweed extracts as biostimulants of plant growth and development [J]. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2009, 28(4): 386−399. doi: 10.1007/s00344-009-9103-x [9] ALMAROAI Y A, EISSA M A. Role of marine algae extracts in water stress resistance of onion under semiarid conditions [J]. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2020, 20(3): 1092−1101. doi: 10.1007/s42729-020-00195-0 [10] 管宇翔, 韩西红, 张琳, 等. 海藻肥对黄瓜抗旱性的影响及机理研究试验 [J]. 种子科技, 2020, 38(21):3−5.GUAN Y X, HAN X H, ZHANG L, et al. Effect of seaweed fertilizer on drought resistance of cucumber and its mechanism [J]. Seed Science & Technology, 2020, 38(21): 3−5.(in Chinese) [11] 孙晓, 尹皓婵, 张占田, 等. 海藻提取物对水稻产量及养分利用的影响 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(16):100−103.SUN X, YIN H C, ZHANG Z T, et al. Influences of seaweed extracts on rice yield and nutrient utilization [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(16): 100−103.(in Chinese) [12] 付洋. 海藻液体肥制备工艺研究及肥效初探[D]. 福州: 福建师范大学, 2018.FU Y. Studies on the preparation technology and preliminary manurial efficiency of seaweed liquid fertilizer[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Normal University, 2018. (in Chinese) [13] 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000. [14] 高紫云, 宋洪川, 郭嘉航, 等. 不同引发方式对甘遂种子萌发的影响 [J]. 云南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 41(6):44−50.GAO Z Y, SONG H C, GUO J H, et al. Effects of different initiation methods on seed germination of Euphorbia kansui [J]. Journal of Yunnan Normal University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2021, 41(6): 44−50.(in Chinese) [15] 徐本美, 顾增辉. 种子活力的研究 [J]. 种子, 1989, 8(5):53−55.XU B M, GU Z H. Study on seed vigor [J]. Seed, 1989, 8(5): 53−55.(in Chinese) [16] 袁华芳, 周刚. 雷力海藻肥在大棚番茄上的应用试验 [J]. 上海蔬菜, 2010(3):62.YUAN H F, ZHOU G. Application experiment of leili seaweed fertilizer on tomato in greenhouse [J]. Shanghai Vegetables, 2010(3): 62.(in Chinese) [17] SINGH H P, BATISH D R, KOHLI R K. Autotoxicity: Concept, organisms, and ecological significance [J]. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 1999, 18(6): 757−772. doi: 10.1080/07352689991309478 [18] 纪洪亭, 王勇, 曾燕楠, 等. 基于主成分分析评价不同类型肥料对向日葵穴盘苗素质的影响 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(29):100−106. [19] 施婷婷, 杨秀莲, 王良桂. 3个桂花品种花香组分动态特征及花被片结构解剖学观测 [J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(4):12−20.SHI T T, YANG X L, WANG L G. Dynamic characteristics of floral components and anatomical observation of petals in three cultivars of Osmanthus fragrans [J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2020, 44(4): 12−20.(in Chinese) [20] 高嘉宁, 张丹, 何海燕, 等. 基于正交偏最小二乘判别分析法分析滇重楼和华重楼品质成分差异性 [J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2019, 25(1):136−142.GAO J N, ZHANG D, HE H Y, et al. Difference in quality components of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis and P. polyphylla var. chinensis based on the orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis model [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 2019, 25(1): 136−142.(in Chinese) [21] 陈芊如, 褚德朋, Ilyas Naila, 等. 海藻提取物的农业应用研究进展 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2021, 49(20):49−56.CHEN Q R, CHU D P, NAILA I, et al. Research progress on agricultural application of seaweed extracts [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 49(20): 49−56.(in Chinese) [22] 马光恕, 廉华, 杨瑾, 等. 海藻糖对NaCl胁迫下番茄种子萌发的缓解效应 [J]. 北方园艺, 2010(1):38−40.MA G S, LIAN H, YANG J, et al. Mitigative effect of trehalose on NaCl stress of tomato seed germination [J]. Northern Horticulture, 2010(1): 38−40.(in Chinese) [23] 汤洁. 海藻植物营养剂的开发利用现状和前景 [J]. 中国农技推广, 2011, 27(6):41−43.TANG J. Present situation and prospect of development and utilization of seaweed plant nutrients [J]. China Agricultural Technology Extension, 2011, 27(6): 41−43.(in Chinese) [24] 王旭承, 王婷, 王梦娇, 等. 海藻肥对低温胁迫下铁皮石斛抗氧化能力及相关基因表达的影响 [J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2022(1):194−201.WANG X C, WANG T, WANG M J, et al. Effects of seaweed fertilizer on antioxidant capacity and related gene expression of Dendrobium officinale under low-temperature stress [J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2022(1): 194−201.(in Chinese) [25] 魏锋玉, 李赟. 海藻浸提液对小白菜种子萌发的影响 [J]. 现代农业科技, 2011(2):124−125.WEI F Y, LI Y. Effect of seaweed extract on seed germination of Chinese cabbage [J]. Modern Agricultural Sciences and Technology, 2011(2): 124−125.(in Chinese) [26] ZHENG S Y, JIANG J, HE M L, et al. Effect of kelp waste extracts on the growth and development of pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L. ) [J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 38683. doi: 10.1038/srep38683 [27] MUTALE-JOAN C, REDOUANE B, NAJIB E, et al. Screening of microalgae liquid extracts for their bio stimulant properties on plant growth, nutrient uptake and metabolite profile of Solanum lycopersicum L [J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 2820. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59840-4 [28] 颜佳雯, 朱长俊, 王浩然, 等. 不同海藻肥栽培料对平菇酶活力的影响 [J]. 生物化工, 2021, 7(3):76−78,86.YAN J W, ZHU C J, WANG H R, et al. Study on enzyme activity of pleurotusostreatus based on different seaweed fertilizers [J]. Biological Chemical Engineering, 2021, 7(3): 76−78,86.(in Chinese) [29] 何锐, 谭星, 高美芳, 等. 添加不同浓度海藻肥对水培芥蓝生长及品质的影响 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(11):2051−2059.HE R, TAN X, GAO M F, et al. Effects of different concentrations of seaweed extract on growth and quality of Chinese kale in hydroponics [J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(11): 2051−2059.(in Chinese) [30] HERNÁNDEZ-HERRERA R M, SANTACRUZ-RUVALCABA F, RUIZ-LÓPEZ M A, et al. Effect of liquid seaweed extracts on growth of tomato seedlings (Solanum lycopersicum L. ) [J]. Journal of Applied Phycology, 2014, 26(1): 619−628. doi: 10.1007/s10811-013-0078-4 [31] 杨春妹, 杨锦, 崔丹丹, 等. 海带酶解和菌解工艺优化及其降解产物对菜心抗逆性的影响 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2021, 27(8):1432−1444.YANG C M, YANG J, CUI D D, et al. Optimization of parameters for enzymatic and bacterial hydrolysis of seaweeds and the effects of two products on the stress resistance of Chinese flowering cabbage [J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2021, 27(8): 1432−1444.(in Chinese) [32] 金依静, 李蓝, 刘秋平, 等. 超声-复合酶解法提取海带中海藻酸钠的工艺优化 [J]. 食品工业科技, 2021, 42(5):132−137.JIN Y J, LI L, LIU Q P, et al. Optimization of extraction process of sodium alginate from Laminaria japonica by ultrasonic-complex enzymatic hydrolysis method [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(5): 132−137.(in Chinese) -







 下载:
下载: