Cloning and Expression under Drought of NHX6 in Hippophae rhamnoides
-
摘要:
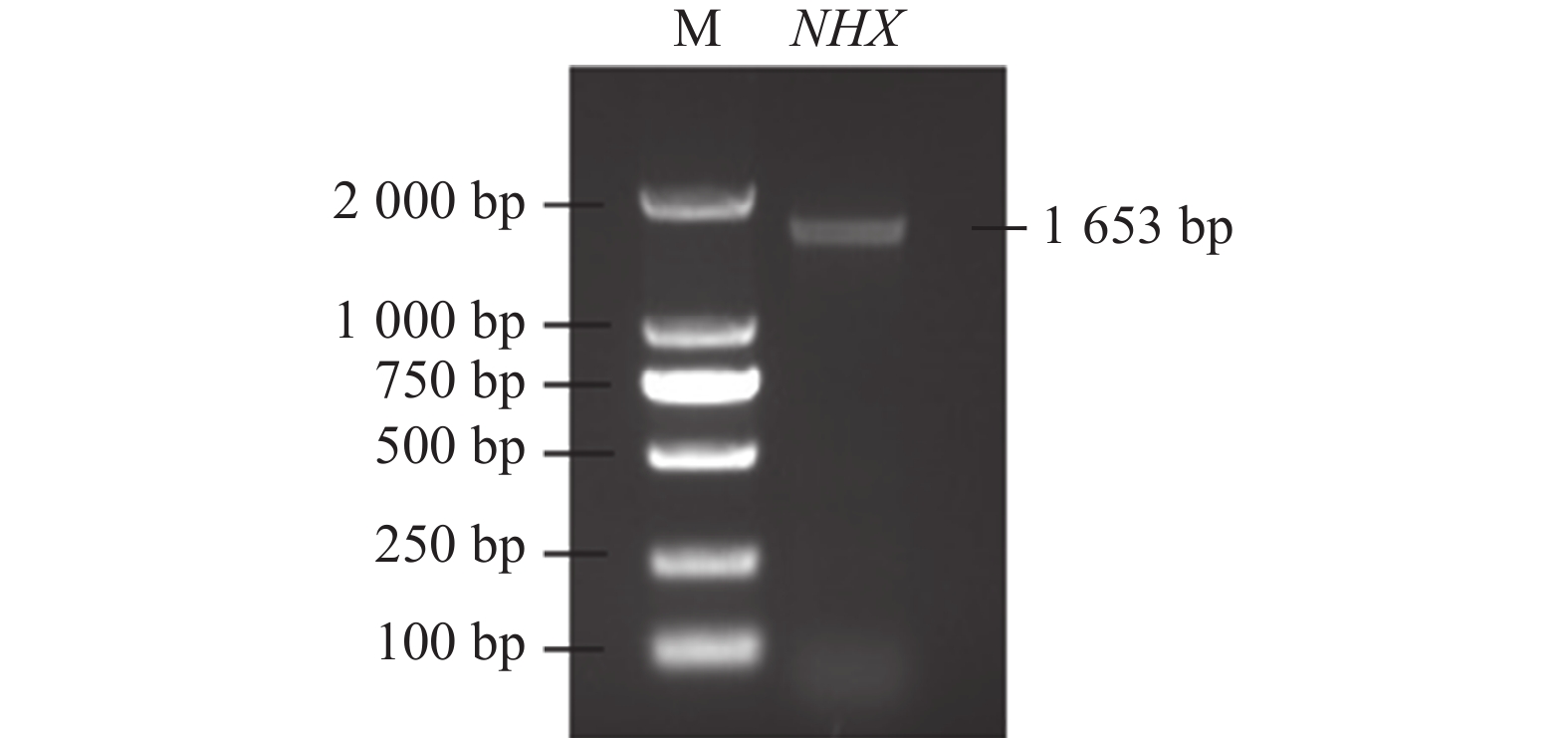
目的 克隆中国沙棘HrNHX6基因,分析其在干旱胁迫下的表达,以期为HrNHX6基因的抗旱功能研究提供参考依据。 方法 对中国沙棘HrNHX6基因进行扩增,并利用生物软件分析HrNHX6基因序列,预测其蛋白结构,在此基础上对干旱胁迫下HrNHX6基因的表达进行分析。 结果 获得的HrNHX6基因属于NHX家族NHX6基因,其编码蛋白质定位于液泡膜,无信号肽,含有13个跨膜螺旋区,具有N-糖基化位点、蛋白激酶磷酸化位点、豆蔻酰化位点、酰胺化位点、糖转运蛋白signature 位点等多种类型的修饰位点。qRT-PCR分析结果表明,干旱胁迫下不同组织之间HrNHX6基因的表达水平具显著差异,而不同干旱程度胁迫处理之间HrNHX6基因的表达水平呈极显著差异。 结论 HrNHX6蛋白的结构特性及HrNHX6基因在干旱胁迫下的表达模式表明其与中国沙棘抗旱关系密切且受干旱胁迫诱导。 Abstract:Objective NHX6 of Hippophae rhamnoides was cloned and expression under drought determined to study the stress resistance mechanism. Method HrNHX6 was cloned, amplified, and sequenced for analysis by biological software. Expression of the gene under drought stress was determined. Result Located on the tonoplast, HrNHX6 had no signal peptide and contained 13 transmembrane helical regions with numerous types of modification sites, such as N-glycosylation, protein kinase phosphorylation lation, myristoylation, amidation, and sugar transporter signature. The rusults of qRT-PCR analysis showed that the expression level of HrNHX6 gene was significantly different between different tissues under draught stress, and the expression level of HrNHX6 gene was significantly different between different drought stress treatment. Conclusion The drought resistance of H. rhamnoides was closely related to HrNHX6 as shown by the structure and expression under drought stress of the gene. The important role indicated a significant venue for improving the draught resistance of the medicinal plant. -
Key words:
- Hippophae rhamnoides /
- HrNHX6 /
- sequence analysis /
- protein structure /
- gene expression
-
图 3 HrNHX6与其他植物NHX6蛋白序列比对分析
A:氨氯吡嗪脒结合位点,B:Na+/H+交换泵。黑色背景表示相同氨基酸,红色、蓝色阴影分别表示75%、50%以上的保守性。
Figure 3. Alignment on amino acid residues of HrNHX6 and genes of other plants
A: Binding sites for ammonia chloride pyrazine microphones; B: Na+/H+ exchange pump; black background represents same amino acid; red and blue shadows, more than 75% and 50% conservatism, respectively.
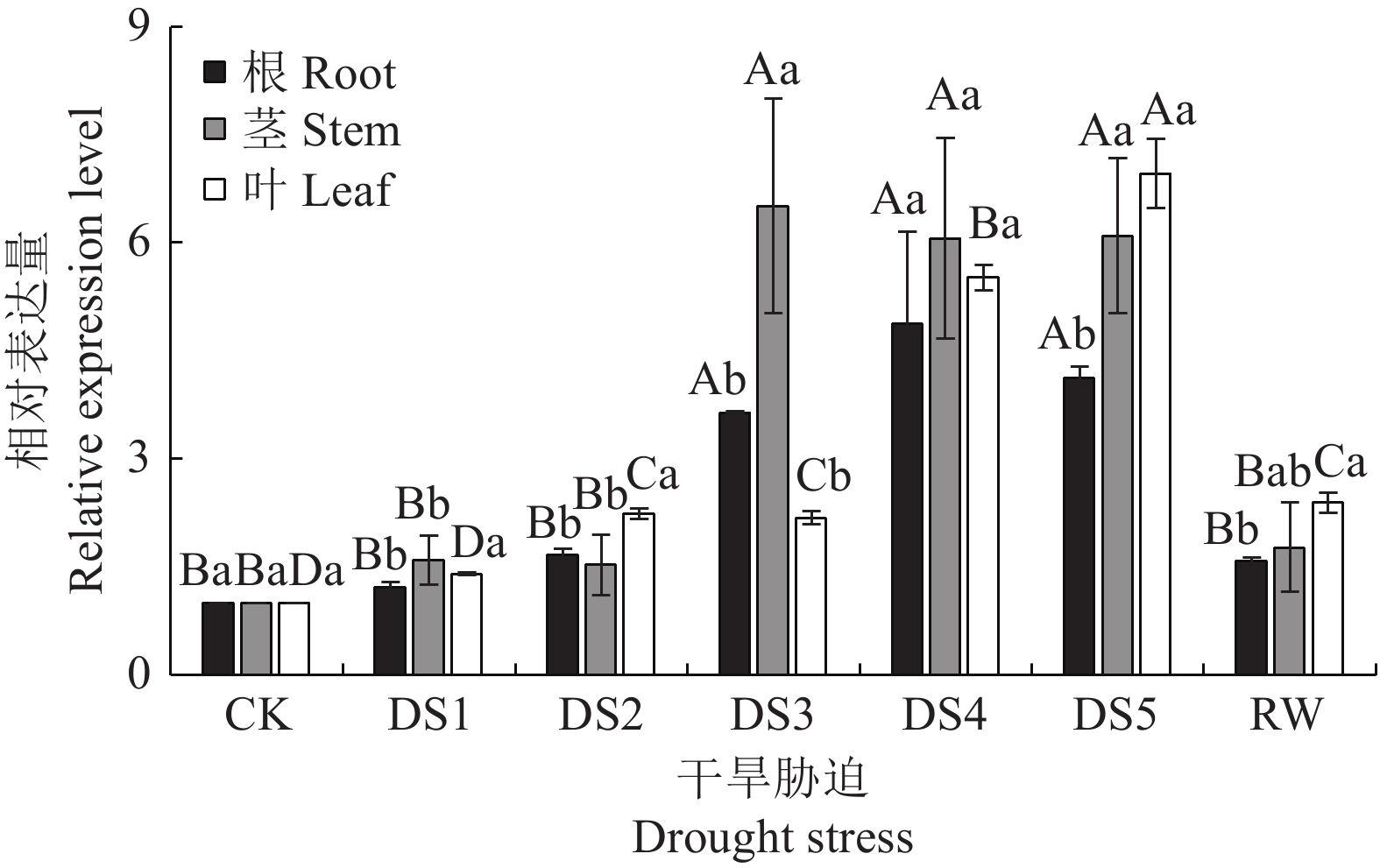
图 6 干旱胁迫下HrNHX6基因表达模式
不同大写字母表示不同胁迫处理时间下差异极显著(P<0.01),不同小写字母表示不同组织之间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 6. Expression of HrNHX6 under drought stress
Different capital letters indicate that the difference is extremely significant under different stress treatment time at P<0.01; those with different lowercase letters, significant difference between different tissues at P<0.05.
-
[1] JIA W S, XING Y, LU C M, et al. Signal transduction from water stress perception to ABA accumulation [J]. Acta Botanica Sinica, 2002(10): 1135−1141. [2] 张玉, 冷海楠, 曹宏杰, 等. 干旱胁迫对植物的影响研究 [J]. 黑龙江科学, 2022, 13(14):22−24,47.ZHANG Y, LENG H N, CAO H J, et al. Study on the influence of drought stress on botany [J]. Heilongjiang Science, 2022, 13(14): 22−24,47.(in Chinese) [3] 温琦, 赵文博, 张幽静, 等. 植物干旱胁迫响应的研究进展 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(12):11−15.WEN Q, ZHAO W B, ZHANG Y J, et al. Research progress of plant response to drought stress [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(12): 11−15.(in Chinese) [4] 孙晓东, 贾娜, 何鹏, 等. 干旱胁迫对陕北沙棘幼苗生长发育的影响 [J]. 东北农业科学, 2018, 43(2):16−20.SUN X D, JIA N, HE P, et al. Effects of drought stress on the growth and development of Hippophae rhamnoides seedlings in northern Shaanxi [J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 43(2): 16−20.(in Chinese) [5] 吴帅. 中国沙棘种源抗旱性综合评价[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2017.WU S. Comprehensive evaluation of drought resistance of Hippophae rhamnoides L. germplasm resource[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Forestry University, 2017. (in Chinese) [6] 胡建忠, 刘丽颖. 沙棘无性系对干旱胁迫的响应研究 [J]. 辽宁林业科技, 2021(4):5−8,37.HU J Z, LIU L Y. Responses of Hippophae rhamnoides clones to drought stress [J]. Liaoning Forestry Science and Technology, 2021(4): 5−8,37.(in Chinese) [7] YARRA R, HE S J, ABBAGANI S, et al. Overexpression of a wheat Na+/H+ antiporter gene (TaNHX2) enhances tolerance to salt stress in transgenic tomato plants (Solanum lycopersicum L. ) [J]. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC), 2012, 111(1): 49−57. doi: 10.1007/s11240-012-0169-y [8] APSE M P, AHARON G S, SNEDDEN W A, et al. Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiport in Arabidopsis [J]. Science, 1999, 285(5431): 1256−1258. doi: 10.1126/science.285.5431.1256 [9] FINN R D, COGGILL P, EBERHARDT R Y, et al. The Pfam protein families database: Towards a more sustainable future [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2016, 44(D1): D279−D285. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1344 [10] PADAN E, SCHULDINER S. Intracellular pH and membrane potential as regulators in the prokaryotic cell [J]. The Journal of Membrane Biology, 1987, 95(3): 189−198. doi: 10.1007/BF01869481 [11] ZHANG H X, BLUMWALD E. Transgenic salt-tolerant tomato plants accumulate salt in foliage but not in fruit [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2001, 19(8): 765−768. doi: 10.1038/90824 [12] PARDO E M, TOUM L, PÉREZ-BORROTO L S, et al. Ectopic expression of GmNHX3 and GmNHX1, encoding two Glycine max Na+/H+ vacuolar antiporters, improves water deficit tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Biologia Plantarum, 2021, 65: 157−166. doi: 10.32615/bp.2021.003 [13] 卢世雄, 许春苗, 何红红, 等. 葡萄NHX基因家族的鉴定和表达分析 [J]. 果树学报, 2019, 36(3):266−276.LU S X, XU C M, HE H H, et al. Identification and expression analysis of NHX genes family in grape [J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2019, 36(3): 266−276.(in Chinese) [14] 郭靖, 章玉香, 黄芷颐, 等. 木薯MePYL12基因克隆及采后生理性变质过程的表达分析 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2021, 36(1):17−23.GUO J, ZHANG Y X, HUANG Z Y, et al. Cloning and post-harvest physiological deterioration expression of MePYL12 of cassava [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 36(1): 17−23.(in Chinese) [15] WU G Q, XI J J, WANG Q, et al. The ZxNHX gene encoding tonoplast Na+/H+ antiporter from the xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum plays important roles in response to salt and drought [J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2011, 168(8): 758−767. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2010.10.015 [16] 赵云霞, 郭丹丽, 魏艳玲, 等. 新疆无苞芥Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白基因OpNHX1的克隆、表达分析与功能验证 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2014(7):74−80.ZHAO Y X, GUO D L, WEI Y L, et al. Cloning, expressing and functional analysis of Na+/H+ antiporter gene OpNHX1 from Olimarabidopsis pumila in Xinjiang [J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2014(7): 74−80.(in Chinese) [17] 康红霞, 伍国强, 魏明, 等. Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白在植物应答非生物逆境胁迫中的作用 [J]. 植物生理学报, 2022, 58(3):511−523.KANG H X, WU G Q, WEI M, et al. The role of Na+/H+ antiporter in response of plant to abiotic stress [J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2022, 58(3): 511−523.(in Chinese) [18] 陈鑫, 马超, 杨永娟, 等. 转碱蓬SsNHX1基因烟草的耐盐抗旱性研究 [J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2017, 25(10):1518−1526.CHEN X, MA C, YANG Y J, et al. Overexpression of Suaeda salsa SsNHX1 gene enhanced salt and drought tolerance of transgenic tobacco [J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2017, 25(10): 1518−1526.(in Chinese) [19] JIANG X Y, LEIDI E O, PARDO J M. How do vacuolar NHX exchangers function in plant salt tolerance? [J]. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2010, 5(7): 792−795. [20] 张雨良, 张智俊, 杨峰山, 等. 新疆盐生植物车前PmNHX1基因的克隆及生物信息学分析 [J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 2009, 29(1):27−33.ZHANG Y L, ZHANG Z J, YANG F S, et al. Cloning and bioinformatics analysis of PmNHX1 gene from Xinjiang halophyte Plantago maritima [J]. China Biotechnology, 2009, 29(1): 27−33.(in Chinese) [21] 张梦茹. 桑树Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白基因的表达特征及Mul-NHX5基因的耐盐功能研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2022.ZHANG M R. Expression characteristics of Na+/H+ antiporter genes in mulberry(Morus multicaulis) and salt-tolerance function of mul-NHX5 gene[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2022. (in Chinese) [22] 杨杰, 陈蓉, 胡文娟, 等. 甜橙NHX基因家族的鉴定及功能分析 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2022, 50(7):35−42.YANG J, CHEN R, HU W J, et al. Identification and functional analysis of NHX gene family in Citrus sinensis [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 50(7): 35−42.(in Chinese) [23] GAXIOLA R A, LI J, UNDURRAGA S, et al. Drought- and salt-tolerant plants result from overexpression of the AVP1 H+-pump [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2001, 98(20): 11444−11449. [24] 张业猛, 朱丽丽, 陈志国. 藜麦NHX基因家族鉴定及盐胁迫下表达分析 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2022, 38(12):184−193.ZHANG Y M, ZHU L L, CHEN Z G. Identification and expression analysis of NHX gene family in quinoa under salt stress [J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2022, 38(12): 184−193.(in Chinese) [25] 马玉花, 冶贵生, 马秀芳, 等. 柴达木盆地梭梭AQP基因克隆及结构预测 [J]. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2016, 51(2):93−97.MA Y H, YE G S, MA X F, et al. Gene clone and protein prediction of AQP gene in Haloxylon ammodendron in Qaidam Basin [J]. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2016, 51(2): 93−97.(in Chinese) [26] 王立光, 叶春雷, 陈军, 等. 植物Na+, K+/H+反向转运体: pH平衡与囊泡运输 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2020, 36(4):151−158.WANG L G, YE C L, CHEN J, et al. Na+, K+/H+ antiporter in plant: pH homeostasis and vesicle trafficking [J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2020, 36(4): 151−158.(in Chinese) -







 下载:
下载: