Preparation and Application of Polyclonal Antibodies Recognizing the Capsid Protein of Chilli Veinal Mottle Virus
-
摘要:
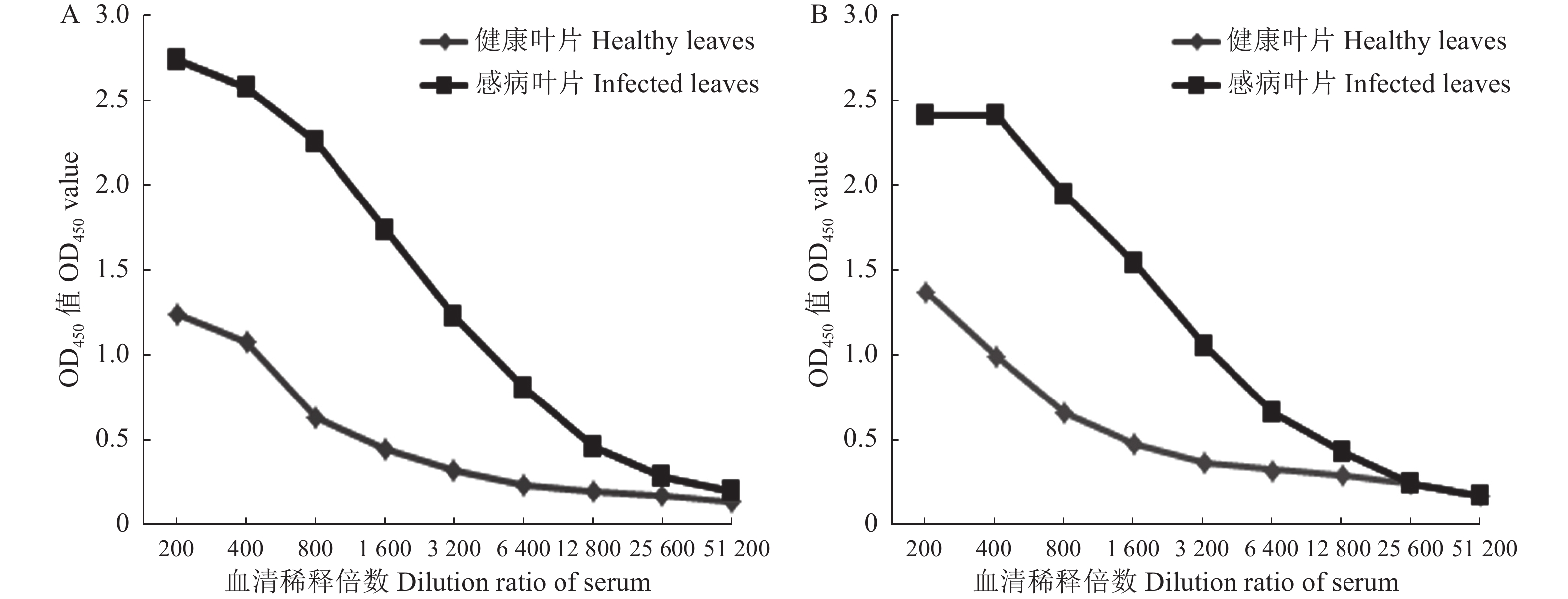
目的 辣椒脉斑驳病毒(Chilli veinal mottle virus,ChiVMV)是茄科植物生产上危害最严重的病毒之一,也是口岸检疫的对象。本研究旨在制备特异性强的ChiVMV外壳蛋白的多克隆抗体并用于田间病株的检测。 方法 通过RT-PCR方法扩增ChiVMV贵州烟草分离物外壳蛋白基因的全长(861 bp)和部分片段(396 bp),分别重组至原核表达载体pET28a中,转化Escherichia coli BL21后进行诱导表达,表达产物层析分离和透析纯化后免疫大耳兔制备多克隆抗体,最后使用酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA)、Western blot等方法检测抗体效价和特异性。 结果 成功制备了ChiVMV外壳蛋白的两种多克隆抗体antiCP1-287aa、antiCP1-132aa,抗体效价分别为1∶6400、1∶12800;两种抗体antiCP1-287aa、antiCP1-132aa均能通过Western blot方法检测到抗原;田间病株的间接ELISA检测显示,antiCP1-132aa能特异性检测ChiVMV病株,未能检测到马铃薯Y病毒(Potato virus Y, PVY)病株,而antiCP1-287aa无法区分这两种病株。 结论 多克隆抗体antiCP1-132aa的特异性较强,可用于ChiVMV田间病株的检测,也为ChiVMV外壳蛋白的功能研究奠定基础。 Abstract:Aim Chilli veinal mottle virus (ChiVMV) is one of the most harmful viruses in the production of solanaceae palnts and a subject of quarantine inspections at ports. The aim of this study is to develop polyclonal antibodies against ChiVMV coat proteins with a high level of specificity, which can then be utilized for the field detection of infected plants. Methods The full-length (861 bp) and partial fragment (396 bp) of the coat protein gene from the ChiVMV GZ-tabacco isolate were amplified using RT-PCR, recombined into the prokaryotic expression vector pET28a, and subsequently transformed into E.coil BL21 for induced expression. After chromatographic isolation and dialysis purification of the expression products, they were used to immunize Dahl rabbits for the preparation of polyclonal antibodies. The antibody potency and specificity were assessed through enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and Western blot.. Results Two polyclonal antibodies against coat proteins, namely antiCP1-287aa and antiCP1-132aa, were successfully prepared with antibody titer of 1:6400 and 1:12800, respectively. Both antibodies, antiCP1-287aa and antiCP1-132aa, effectively detected the antigen by Western blot. In indirect ELISA tests of field strains, it was observed that the ChiVMV strain was specifically detectable by antiCP1-132aa, whereas the Potato virus Y (PVY) strain was not. However, antiCP1-287aa could not differentiate between these two strains. Conclusion The polyclonal antibody, antiCP1-132aa , exhibits high specificity, making it suitable for detecting ChiVMV-infected strains in the field. Additionally, it lays the foundation for the functional study of the coat protein of ChiVMV. -
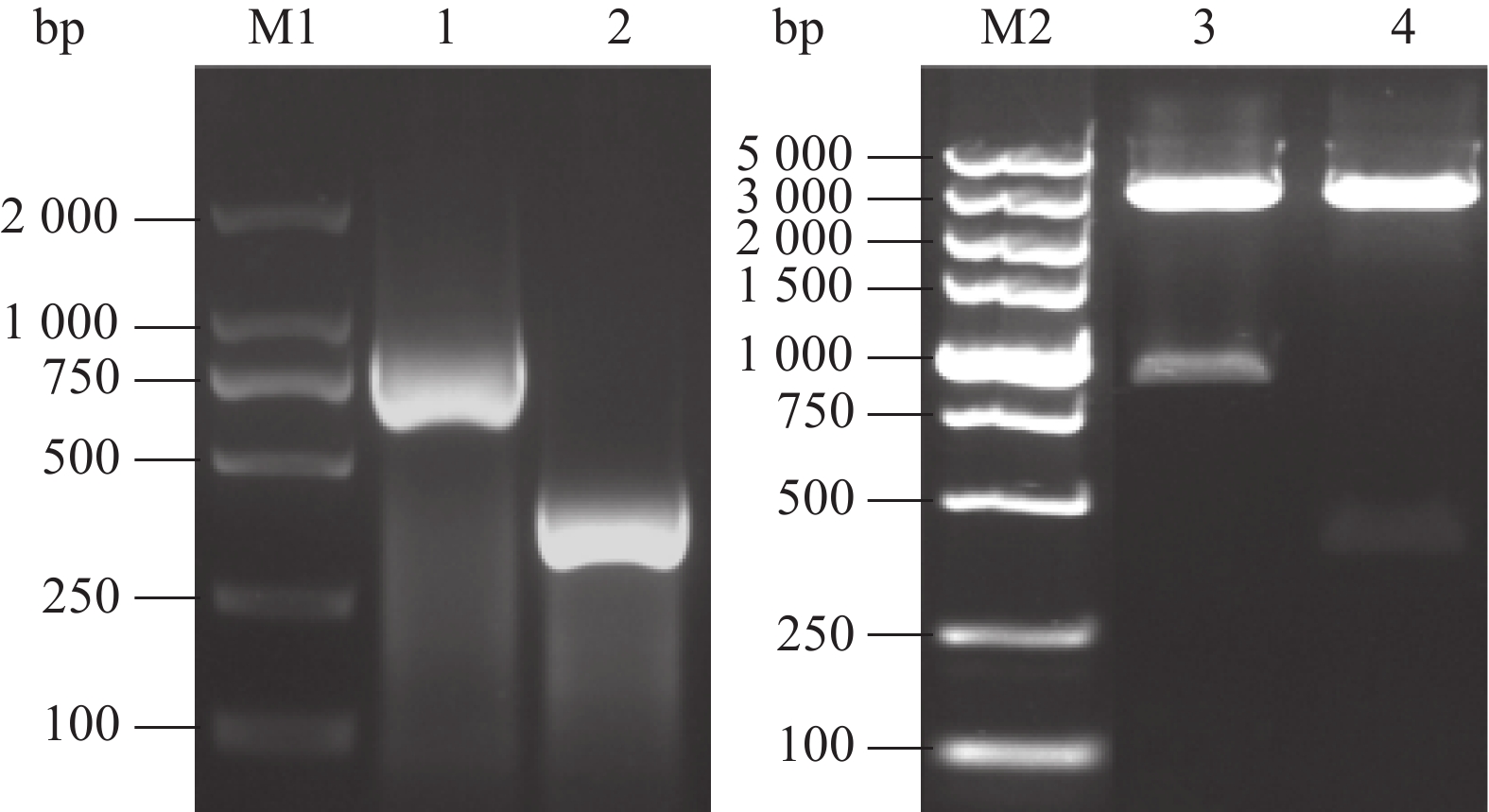
图 2 两种抗原相应基因片段的扩增及其表达载体构建
M1、M2,DL2000 DNA Marker、DL5000 DNA Marker;1、3,ChiVMV CP1-287aa序列扩增及重组质粒双酶切验证;2、4,ChiVMV CP1-132aa序列扩增及重组质粒双酶切。
Figure 2. Amplification of the corresponding gene fragments of two antigens and their expression vector construction
M1, M2, DL2000 DNA Marker, DL5000 DNA Marker; 1, 3, Amplification of ChiVMV CP1-287aa fragment and double enzyme digestion of recombinant plasmidt; 2, 4, Amplification of ChiVMV CP1-132aa fragment and double enzyme digestion of recombinant plasmid.
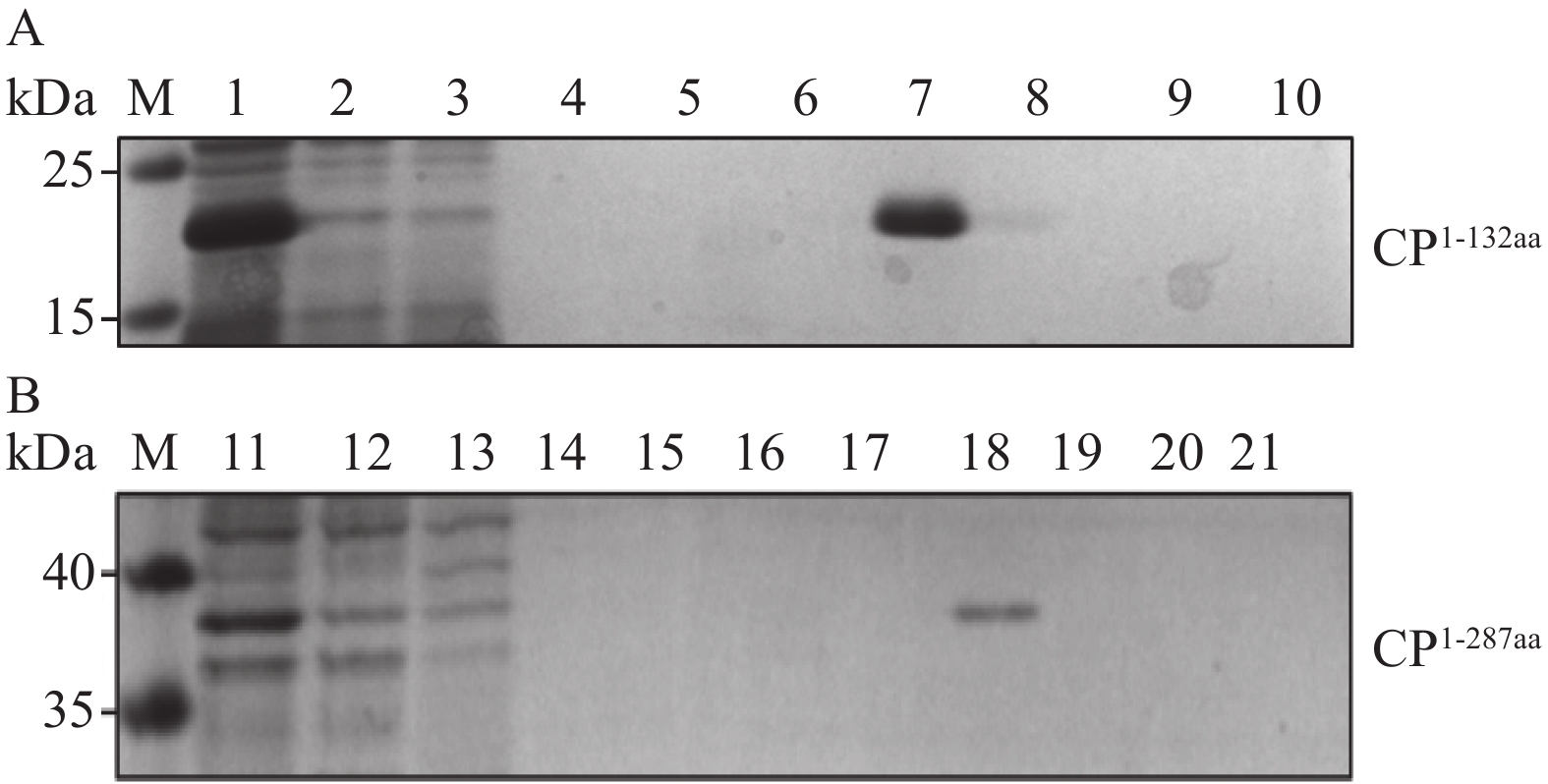
图 3 抗原蛋白的纯化
M,Prestained Protein Ladder 26616;A为CP1-132aa蛋白纯化;B为CP1-287aa蛋白纯化;1、11,未层析样品;2、12,过柱的未层析样品;3~10、13~21,不同浓度(依次为30、40、50、60、70、80、90、100、110 mmol·L−1)的咪唑洗脱液。
Figure 3. Purification of antigenic proteins
M: Prestained Protein Ladder 26616; A for CP1-132aa protein purification; B for CP1-287aa protein purification; 1, 11: unstratified samples; 2, 12: unstratified samples over the column; 3 to 10, 13 to 21: imidazole eluates of different concentrations (30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 110 mmol·L−1, in that order).
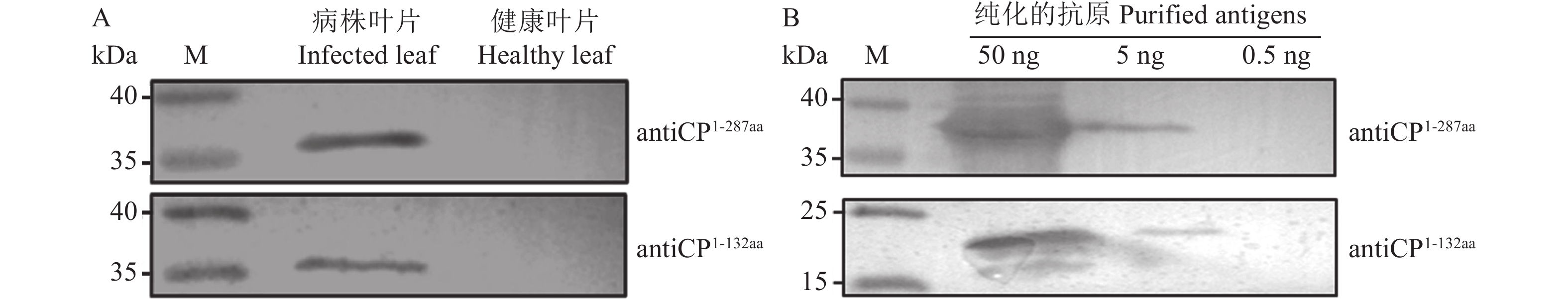
图 5 Western blot检测多克隆抗体的灵敏度
M,Prestained Protein Ladder 26616;A为使用antiCP检测感染ChiVMV叶片; B为antiCP灵敏度检测。
Figure 5. Sensitivity of polyclonal antibodies detected by Western blot
M, Prestained Protein Ladder 26616; A shows the detection of infected ChiVMV leaves using antiCP; B shows the antiCPsensitivity detection.
表 1 RT-PCR扩增引物
Table 1. The primers for PCR amplification
引物名称
Primer names序列 (5′-3′)
Primer sequences (5′-3′)扩增位置及大小
Region and length of
PCR amplificationChiVMV-CP-F CGGAATTCGCSGGAGAGAGTGTTGATGCTG 8575~8970 nt,
396 bpChiVMV-CP-R1 CCGCTCGAGAAGAATTATTTGCATCTGGTC ChiVMV-CP-F CGGAATTCGCSGGAGAGAGTGTTGATGCTG 8575~9435 nt,
861 bpChiVMV-CP-R2 CCGCTCGAGTATTCCCCGAACGCCCAGCAGATTG 划线位置为酶切位点。
The underlined position is the enzyme cleavage site.表 2 多克隆抗体检测田间烟草样品
Table 2. Detection of field tobacco samples using polyclonal antibodies
多克隆抗体
Polyclonal antibodies烟草样品总数
Total number of tobacco samples阳性株数
Number of positive samples阴性株数
Number of negative samplesantiCP1-287aa 39 13 26 antiCP1-132aa 39 2 37 -
[1] WYLIE S J, ADAMS M, CHALAM C, et al. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Potyviridae [J]. The Journal of General Virology, 2017, 98(3): 352−354. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.000740 [2] ANINDYA R, JOSEPH J, GOWRI T D S, et al. Complete genomic sequence of pepper vein banding virus (PVBV): A distinct member of the genus Potyvirus [J]. Archives of Virology, 2004, 149(3): 625−632. doi: 10.1007/s00705-003-0236-0 [3] 龚明霞, 王萌, 赵虎, 等. 辣椒脉斑驳病毒病研究进展 [J]. 园艺学报, 2020, 47(9):1741−1751.GONG M X, WANG M, ZHAO H, et al. Research progress on chilli veinal mottle virus disease [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2020, 47(9): 1741−1751. (in Chinese) [4] ONG C A, VARGHESE G, TING W P. Aetiological investigations on a vein mottle virus of chill ( Capsicum anmuum L. ) newly recorded from peninsula Malaysia [J]. Malaysian Agricultural Research and Development Institute Research Bulletin, 1979, 7(1): 78−88. [5] NG J C K, FALK B W. Virus-vector interactions mediating nonpersistent and semipersistent transmission of plant viruses [J]. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 2006, 44: 183−212. doi: 10.1146/annurev.phyto.44.070505.143325 [6] NONO-WOMDIM R, SWAI I S, CHADHA M L, et al. Occurrence of Chilli veinal mottle virus in Solanum aethiopicum in Tanzania [J]. Plant Disease, 2001, 85(7): 801. [7] 谭根堂, 史联联, 尚惠兰, 等. 陕西线辣椒病毒病病原检测简报 [J]. 辣椒杂志, 2003, 1(3):32−33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4542.2003.03.011TAN G T, SHI L L, SHANG H L, et al. Diagnosis of viruses in chili pepper in Shanxi Province [J]. Journal of China Capsicum, 2003, 1(3): 32−33. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4542.2003.03.011 [8] WANG J, LIU Z, NIU S, et al. Natural Occurrence of Chilli veinal mottle virus on Capsicum chinense in China [J]. Plant Disease, 2006, 90(3): 377. [9] 刘健, 张德咏, 张松柏, 等. 湖南和福建辣椒上辣椒脉斑驳病毒的检测及系统发育分析 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2016, 44(5):184−185.LIU J, ZHANG D Y, ZHANG S B, et al. Detection and phylogenetic analysis of pepper vein mottle virus on peppers in Hunan and Fujian [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(5): 184−185. (in Chinese) [10] 王少立, 谭玮萍, 杨园园, 等. 山东省辣椒主要病毒种类的分子检测与鉴定 [J]. 中国农业科学, 2017, 50(14):2728−2738. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2017.14.009WANG S L, TAN W P, YANG Y Y, et al. Molecular detection and identification of main viruses on pepper in Shandong Province [J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2017, 50(14): 2728−2738. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2017.14.009 [11] 王莉爽, 陈小均, 何海永, 等. 贵州辣椒脉斑驳病毒的检测及株系分化研究[J]. 南方农业学报, 2017, 48(7): 1220-1224.WANG L S, CHEN X J, HE H Y, et al. Detection of Chilli veinal mottle virus from Guizhou and its strain differentiation[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2017, 48(7): 1220-1224. (in Chinese) [12] 汤亚飞, 裴凡, 于琳, 等. 侵染广东辣椒的辣椒脉斑驳病毒的分子特征 [J]. 园艺学报, 2018, 45(11):2209−2216.TANG Y F, PEI F, YU L, et al. Molecular Characterization of Chilli veinal mottle virus Infecting Pepper in Guangdong Province [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2018, 45(11): 2209−2216. (in Chinese) [13] DING M, YANG C, ZHANG L, et al. Occurrence of Chilli veinal mottle virus in Nicotiana tabacum in Yunnan, China [J]. Plant Disease, 2011, 95(3): 357. [14] HWANG J, LI J J, LIU W Y, et al. Double mutations in eIF4E and eIFiso4E confer recessive resistance to Chilli veinal mottle virus in pepper [J]. Molecules and Cells, 2009, 27(3): 329−336. doi: 10.1007/s10059-009-0042-y [15] SHAH H, YASMIN T, FAHIM M, et al. Reaction of exotic and indigenous Capsicum genotypes against Pakistani isolates of chilli vein mottle virus [J]. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 2011, 43(3): 1707−1711. [16] 杨天生. 安徽烟区烟草蚜传病毒病的检测及病毒遗传多样性分析[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2018YANG T S. Detection of tobacco virus disease transmitted by aphids in Anhui Province and analysis of genetic diversity of the virus[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2018. (in Chinese) [17] 李嘉伦. 泸州地区烟草病毒种类鉴定及防控技术研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2019.LI J L. Identification and integrated control technigues on tobacco virus diseases in Luzhou city[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2019. (in Chinese) [18] CHEN Y, LI T T, ZHONG J, et al. First report of chilli veinal mottle virus infecting tobacco in Guizhou, China [J]. Journal of Plant Pathology, 2022, 104(3): 1159−1160. [19] 陶源, 吴兴泉. 植物病毒检测方法的研究进展 [J]. 分子植物育种, 2017, 15(7):2901−2906.TAO Y, WU X Q. Research progress on methods for the detection of plant virus [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2017, 15(7): 2901−2906. (in Chinese) [20] 迟惠荣, 毛碧增. 植物病毒检测及脱毒方法的研究进展 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2017, 33(8):26−33.CHI H R, MAO B Z. Research advances on plant virus detection and virus-elimination methods [J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2017, 33(8): 26−33. (in Chinese) [21] 吴云锋. 植物病毒学原理与方法[M]. 西安: 西安地图出版社, 1999. [22] 谢联辉, 林奇英. 植物病毒学[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2011. [23] 田绍锐, 温玉霞, 马婷, 等. 重庆地区烟叶辣椒脉斑驳病毒的检测与鉴定 [J]. 烟草科技, 2023, 56(1):33−38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0861.2023.1.yckj202301004TIAN S R, WEN Y X, MA T, et al. Detection and identification of chilli veinal mottle virus infecting tobacco in Chongqing [J]. Tobacco Science & Technology, 2023, 56(1): 33−38. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0861.2023.1.yckj202301004 [24] 龚明霞, 赵虎, 王萌, 等. 广西辣椒病毒的sRNA深度测序和RT-PCR鉴定 [J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5):1060−1072.GONG M X, ZHAO H, WANG M, et al. Identification of viruses infecting peppers in Guangxi by small RNA deep sequencing and RT-PCR [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 1060−1072. (in Chinese) -








 下载:
下载: