TrnL-F and ISSR Primer-based Molecular Identification and Genetic Diversity Determination on Camellia impressinervis and Three Closely Related Species
-
摘要:
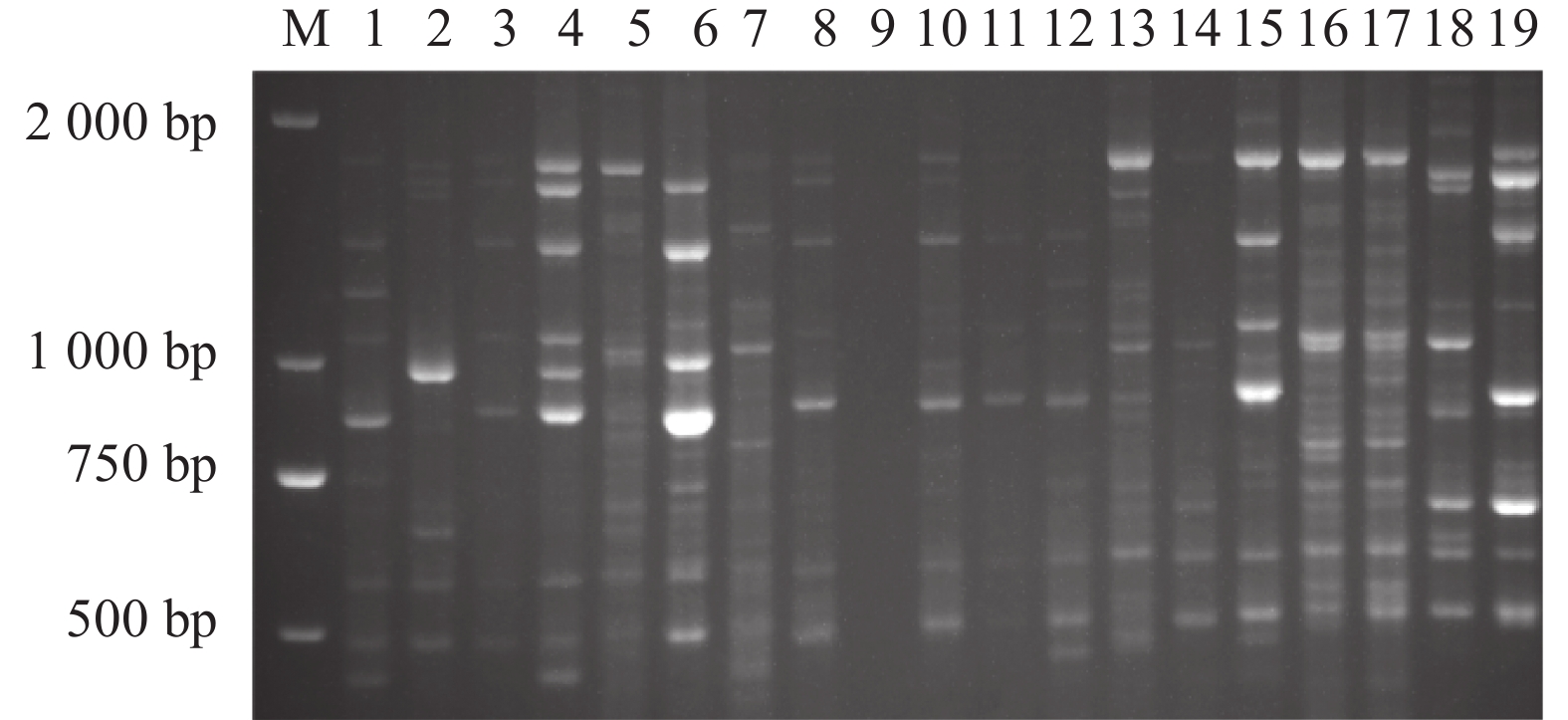
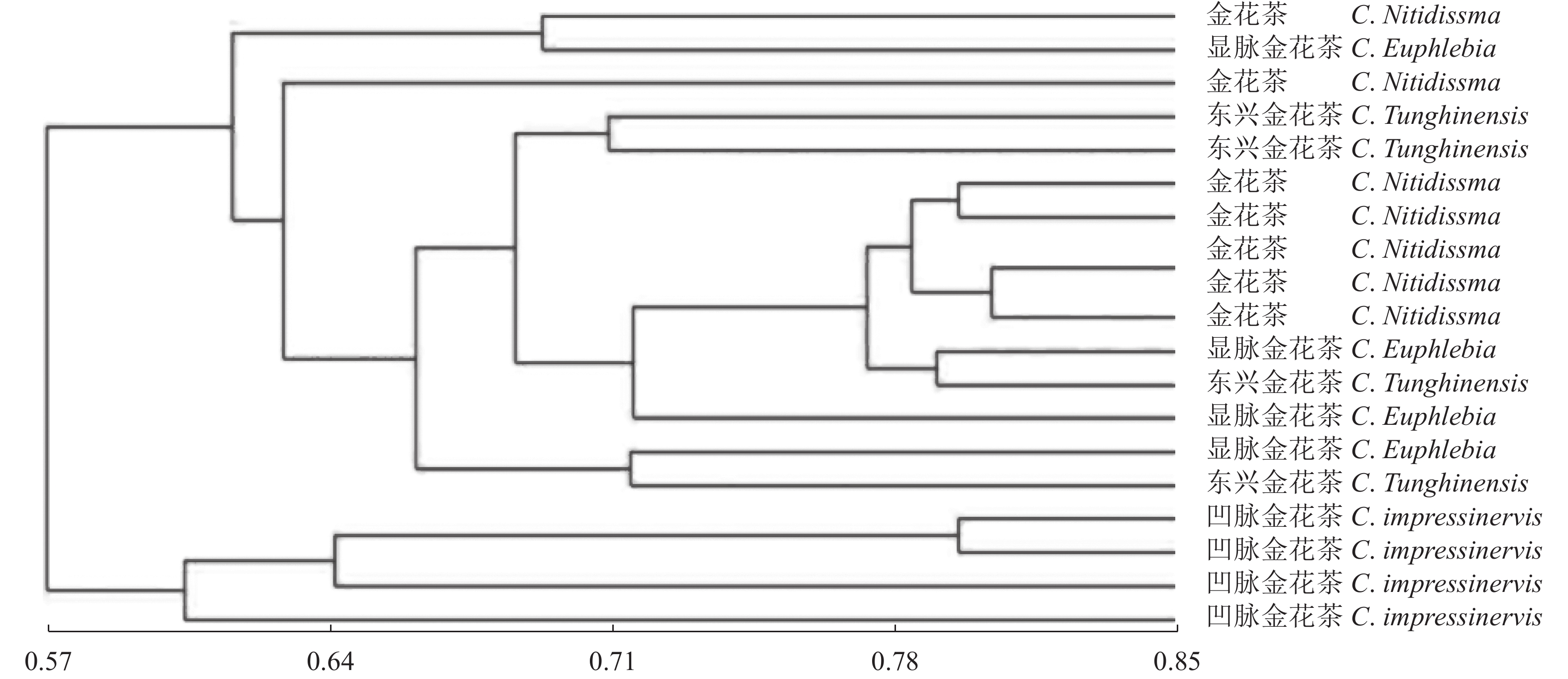
目的 凹脉金花茶是一种具有较高价值的观赏与药用两用植物,与其同属中的金花茶、显脉金花茶、东兴金花茶外形相似。通过分子指纹技术分析这4个近源种之间的遗传多样性,可为凹脉金花茶的鉴定及其种质资源保护和利用提供理论指导。 方法 利用金花茶、凹脉金花茶、显脉金花茶、东兴金花茶的19个样品评估TrnL-F条形码在这4种山茶中鉴定凹脉金花茶的潜力,并利用简单序列间重复(ISSR)引物检测4个山茶组种的遗传多样性。 结果 基于TrnL-F序列构建的进化树与检测到的单核苷酸多态性位点的差异相一致,所有凹脉金花茶样品单独聚为一类。ISSR分析显示,4个凹脉金花茶植物样本单独聚为一类,与其他3个山茶组物种的相似指数为0.57。 结论 TrnL-F可有效鉴别凹脉金花茶与3种近缘种。本研究揭示了这4个近缘种的分子亲缘关系,从分子水平证实显凹脉金花茶具有异于其他3种山茶的遗传特性。 Abstract:Objective Molecular identification and genetic diversity of Camellia impressinervis were studied to improve the preservation and utilization of the endangered species. Method A highly valuable ornamental and medicinal, but extremely endangered as classified by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature, C. impressinervis was compared with the closely related C. nitidissima, C. euphlebia, and C. tunghinensis. Using 19 specimens of the 4 species, validity of applying trnL-F barcode to confidently identify them was evaluated, and their genetic diversity examined based on the inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) primers. Result TrnL-F could accurately differentiate C. impressinervis from those closely related camellia cultivars and clustered all in a same group. The ISSR analysis grouped the 4 C. impressinervis specimens together and showed a similarity index of 0.57 with the other 3 camellia species. Conclusion The genetic fingerprint in terms of trnL-F barcode and ISSR primers successfully identified the close relationship of C. impressinervis with, but distinguishable from, C. nitidissima, C. euphlebia, and C. tunghinensis. -
Key words:
- Camellia /
- trnL-F /
- molecular identification /
- genetic diversity /
- ISSR
-
表 1 ISSR扩增引物
Table 1. Amplified ISSR primers
引物
Primer引物序列(3′-5′)
Primer sequence(3′-5′)退火温度
Annealing
temperature/℃UBC811 GAGAGAGAGAGAGAGAC 51.2 UBC815 CTCTCTCTCTCTCTCTG 50.5 UBC825 ACACACACACACACACT 50.5 UBC834 AGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGYT 49 UBC835 AGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGYC 56 UBC836 AGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGYA 52 UBC840 GAGAGAGAGAGAGAGAYT 49 UBC841 GAGAGAGAGAGAGAGAYC 52 UBC844 CTCTCTCTCTCTCTCTRC 52 UBC845 CTCTCTCTCTCTCTCTRG 50.5 UBC846 CACACACACACACACART 51.2 UBC848 CACACACACACACACARG 55 UBC851 GTGTGTGTGTGTGTGTYG 52 UBC856 ACACACACACACACACYA 52 表 2 ISSR引物扩增产物的多态性
Table 2. Polymorphisms of ISSR primers amplified products
引物
Primer扩增条带总数
Total number of amplified bands/条多态性条带数
Polymorphic strips/条多态性条带占比
Percentage of polymorphic bands/%UBC811 20 20 100.0 UBC815 12 12 100.0 UBC825 18 16 88.9 UBC834 13 13 100.0 UBC835 15 15 100.0 UBC836 16 13 81.3 UBC840 12 12 100.0 UBC841 12 10 83.3 UBC844 15 15 100.0 UBC845 12 12 100.0 UBC846 16 16 100.0 UBC848 3 3 100.0 UBC851 9 8 88.9 UBC856 9 8 88.9 总数
Total182 173 95.1 -
[1] 王欣晨, 李文兰, 阎新佳, 等. 金花茶化学成分及药理活性研究 [J]. 哈尔滨商业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 34(5):522−527,563.WANG X C, LI W L, YAN X J, et al. Research on chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of flowers from Camellia chrysantha (Hu) Tuyama [J]. Journal of Harbin University of Commerce (Natural Sciences Edition), 2018, 34(5): 522−527,563.(in Chinese) [2] 陈月圆, 黄永林, 文永新. 金花茶植物化学成分和药理作用研究进展 [J]. 广西热带农业, 2009(1):14−16.CHEN Y Y, HUANG Y L, WEN Y X. Advance in study on chemical constituents and pharmacological action of Camellia chrysantha [J]. Guangxi Tropical Agriculture, 2009(1): 14−16.(in Chinese) [3] 宁恩创, 秦小明, 杨宏. 金花茶叶水提物的降脂功能试验研究 [J]. 广西大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 29(4):350−352.NING E C, QIN X M, YANG H. The experimental study on regulating serum lipid of water soluble extractive from the leave of Camellia chrysantha (Hu) Tuyama [J]. Journal of Guangxi University (Natural Science Edition), 2004, 29(4): 350−352.(in Chinese) [4] 王永奇, 彭晓, 唐前, 等. 金花茶组植物抗IgE介导Ⅰ型过敏反应的活性筛选 [J]. 中南药学, 2009, 7(10):721−724.WANG Y Q, PENG X, TANG Q, et al. Active fraction of IgE-mediated type I allergy from section chrysamtha changon [J]. Central South Pharmacy, 2009, 7(10): 721−724.(in Chinese) [5] 马硕, 蒲志军, 张小玲, 等. 金花茶多酚对2型糖尿病大鼠胰腺的保护作用 [J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2017, 23(18):89−93.MA S, PU Z J, ZHANG X L, et al. Protective effect of Camellia nitidissima polyphenols on pancreas in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2017, 23(18): 89−93.(in Chinese) [6] 韦霄, 黄兴贤, 蒋运生, 等. 3种金花茶组植物提取物的抗氧化活性比较 [J]. 中国中药杂志, 2011, 36(5):639−641.WEI X, HUANG X X, JIANG Y S, et al. Comparison of antioxidant activities of extracts from three Camellia species [J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2011, 36(5): 639−641.(in Chinese) [7] 李翠云, 段小娴, 苏建家, 等. 金花茶对二乙基亚硝胺致大鼠肝癌前病变及肝癌细胞株作用的影响 [J]. 广西医科大学学报, 2007, 24(5):660−663. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-930X.2007.05.002LI C Y, DUAN X X, SU J J, et al. Impact of leaves and flowers of camellia chrysantha (hu) tuyama of different concentrations on diethylnitrosaminal-induced precancerous lision to liver of rat and hepatoma cells bel-7404 [J]. Journal of Guangxi Medical University, 2007, 24(5): 660−663.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-930X.2007.05.002 [8] 张宏达. 华夏植物区系的金花茶组 [J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 1979, 18(3):69−74.ZHANG H D. Chrysantha, A section of golden camellias from cathaysian flora [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni(National Science Edition), 1979, 18(3): 69−74.(in Chinese) [9] 梁盛业. 世界金花茶植物名录 [J]. 广西林业科学, 2007, 36(4):221−223.LIANG S Y. The world list of Camellia [J]. Guangxi Forestry Science, 2007, 36(4): 221−223.(in Chinese) [10] 赖彦池. 凹脉金花茶的保护遗传学研究[D]. 桂林: 广西师范大学, 2021.LAI Y C. Conservation genetic of Camellia impressinervis[D]. Guilin: Guangxi Normal University, 2021. [11] HEBERT P D N, CYWINSKA A, BALL S L, et al. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes [J]. Proceedings Biological Sciences, 2003, 270(1512): 313−321. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2002.2218 [12] CHASE M W, SALAMIN N, WILKINSON M, et al. Land plants and DNA barcodes: Short-term and long-term goals [J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B:Biological Sciences, 2005, 360(1462): 1889−1895. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2005.1720 [13] PATRICK O, JOHN M, DENNIS O, et al. Molecular footprint of Kenya's gene bank repositories based on the cp-genome signatures [J]. American Journal of Molecular Biology, 2018, 8(4): 215−244. doi: 10.4236/ajmb.2018.84019 [14] LI J S, YANG M, LI Y N, et al. Chloroplast genomes of two Pueraria DC. species: Sequencing, comparative analysis and molecular marker development [J]. FEBS Open Bio, 2022, 12(2): 349−361. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13335 [15] PARK I, SONG J H, YANG S, et al. Comparative analysis of Actaea chloroplast genomes and molecular marker development for the identification of authentic cimicifugae rhizoma [J]. Plants (Basel, Switzerland), 2020, 9(2): 157. [16] ZHANG H, TANG S, SCHNABLE J C, et al. Genome-wide DNA polymorphism analysis and molecular marker development for the Setaria italica variety SSR41 and positional cloning of the Setaria white leaf sheath gene SiWLS1 [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 743782. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.743782 [17] PEI N C, CHEN B F, KRESS W J. Advances of community-level plant DNA barcoding in China [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 225. [18] KOCYAN A, SNIJMAN D A, FOREST F, et al. Molecular phylogenetics of Hypoxidaceae - Evidence from plastid DNA data and inferences on morphology and biogeography [J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 2011, 60(1): 122−136. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2011.02.021 [19] 陈春梅, 马春雷, 马建强, 等. 茶树cpDNA测序及基于cpDNA序列的山茶属植物亲缘关系研究 [J]. 茶叶科学, 2014, 34(4):371−380. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2014.04.010CHEN C M, MA C L, MA J Q, et al. Sequencing of chloroplast genome of Camellia sinensis and genetic relationship for Camellia plants based on chloroplast DNA sequences [J]. Journal of Tea Science, 2014, 34(4): 371−380.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2014.04.010 [20] 方伟, 杨俊波, 杨世雄, 等. 基于叶绿体四个DNA片段联合分析探讨山茶属长柄山茶组、金花茶组和超长柄茶组的系统位置与亲缘关系 [J]. 云南植物研究, 2010, 32(1):1−13. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1143.2010.00001FANG W, YANG J B, YANG S X, et al. Phylogeny of Camellia sects. Longipedicellata, chrysantha and longissima(Theaceae) based on sequence data of four chloroplast DNA loci [J]. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 2010, 32(1): 1−13.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1143.2010.00001 [21] 肖政, 李纪元, 李志辉, 等. 金花茶组物种遗传关系的ISSR分析 [J]. 林业科学研究, 2014, 27(1):71−76.XIAO Z, LI J Y, LI Z H, et al. Genetic relationships among species from Camellia sect. chrysantha Chang revealed by ISSR analysis [J]. Forest Research, 2014, 27(1): 71−76.(in Chinese) [22] 张玥, 蓝增全, 吴田. 云南大围山金花茶种质资源的ISSR分析 [J]. 分子植物育种, 2018, 16(2):649−655.ZHANG Y, LAN Z Q, WU T. ISSR analysis of Camellia nitidissima germplasm resources from dawei mountain in Yunnan [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2018, 16(2): 649−655.(in Chinese) [23] 罗在柒, 陆俊, 李荣京, 等. 贵州金花茶种质资源ISSR分析及指纹图谱库构建 [J]. 乡村科技, 2020, 11(22):118−120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7909.2020.22.060LUO Z Q, LU J, LI R J, et al. ISSR analysis and fingerprint database construction of Camellia chrysantha germplasm resources in Guizhou [J]. Countryside Technology, 2020, 11(22): 118−120.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7909.2020.22.060 [24] 覃小玲, 史艳财, 李承卓, 等. 基于FTIR技术金花茶组植物物种鉴定研究 [J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2012, 32(10):2685−2689. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2012)10-2685-05QIN X L, SHI Y C, LI C Z, et al. Study on Camellia sect. chrysantha Chang species identification by FTIR technology [J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2012, 32(10): 2685−2689.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2012)10-2685-05 [25] 张晓丽, 代红军. 植物RNA提取方法的研究进展 [J]. 北方园艺, 2014(8):175−178.ZHANG X L, DAI H J. Research progress on extraction method of plant RNA [J]. Northern Horticulture, 2014(8): 175−178.(in Chinese) [26] HEINRICH M, ANAGNOSTOU S. From pharmacognosia to DNA-based medicinal plant authentication - pharmacognosy through the centuries [J]. Planta Medica, 2017, 83(14/15): 1110−1116. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-108999 [27] 刘红梅, 张存艳, 叶强, 等. 基于DNA条形码技术对喉红石斛的植物学分类研究 [J]. 中草药, 2021, 52(21):6656−6662. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2021.21.023LIU H M, ZHANG C Y, YE Q, et al. Botanical Classification of Dendrobium christyanum based on DNA barcode technology [J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2021, 52(21): 6656−6662.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2021.21.023 [28] NNEJI L M, ADEOLA A C, AYOOLA A O, et al. DNA barcoding and species delimitation of butterflies (Lepidoptera) from Nigeria [J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2020, 47(12): 9441−9457. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05984-5 [29] SARAVANAN M, MOHANAPRIYA G, LAHA R, et al. DNA barcoding detects floral origin of Indian honey samples [J]. Genome, 2019, 62(5): 341−348. doi: 10.1139/gen-2018-0058 [30] DE VERE N, RICH T C G, TRINDER S A, et al. DNA barcoding for plants [J]. Methods in Molecular Biology (Clifton, N J), 2015, 1245: 101−118. [31] TAN S L, LUO Y H, HOLLINGSWORTH P M, et al. DNA barcoding herbaceous and woody plant species at a subalpine forest dynamics plot in Southwest China [J]. Ecology and Evolution, 2018, 8(14): 7195−7205. doi: 10.1002/ece3.4254 [32] GILL B A, MUSILI P M, KURUKURA S, et al. Plant DNA-barcode library and community phylogeny for a semi-arid East African savanna [J]. Molecular Ecology Resources, 2019, 19(4): 838−846. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.13001 [33] SUCHER N J, HENNELL J R, CARLES M C. DNA fingerprinting, DNA barcoding, and next generation sequencing technology in plants[M]//Methods in Molecular Biology. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press, 2012: 13-22. [34] VIGLIANTE I, MANNINO G, MAFFEI M E. Chemical characterization and DNA fingerprinting of Griffonia simplicifolia baill [J]. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 2019, 24(6): 1032. doi: 10.3390/molecules24061032 [35] BOBAN S B, MAURYA S, JHA Z. DNA fingerprinting: An overview on genetic diversity studies in the botanical taxa of Indian Bamboo [J]. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, 2022, 69(2): 469−498. doi: 10.1007/s10722-021-01280-8 [36] ARSHAD H, SHADMA W, MOUSTAFA M. Pharmacognostic standardization and DNA fingerprinting of leaves of Datura stramonium, growing naturally in Asir region of Saudi Arabia [J]. Pakistan Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2020, 33(3): 1155−1161. [37] 姚敏. 槭叶铁线莲亚组的遗传多样性和居群动态变化研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2021.YAO M. Genetic diversity and population dynamics of Clematis subsect. acerifoliae[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2021. (in Chinese) [38] 黄蕾, 邢晓成, 张雨曲, 等. 地理因素对箭竹复合体遗传多样性与遗传分化的影响 [J]. 西北植物学报, 2021, 41(5):872−879. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2021.05.0872HUANG L, XING X C, ZHANG Y Q, et al. Effect of geographic factors on the genetic diversity and divergence of Fargesia spathacea complex [J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2021, 41(5): 872−879.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2021.05.0872 [39] 李爽, 刘上丽, 裴思玉, 等. 基于单拷贝核基因PAL研究贵州金花茶遗传多样性 [J]. 广西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 39(1):128−135.LI S, LIU S L, PEI S Y, et al. A study on genetic diversity of Camellia huana by single-copy nuclear gene PAL [J]. Journal of Guangxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 39(1): 128−135.(in Chinese) [40] 骆亮, 张文春, 李龙, 等. 不同居群朱砂根(Ardisia crenata)的荧光ISSR遗传多样性分析 [J]. 分子植物育种, 2021, 19(18):6235−6247.LUO L, ZHANG W C, LI L, et al. Genetic diversity analysis of Ardisia crenata in different populations by fluorescence ISSR [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2021, 19(18): 6235−6247.(in Chinese) [41] 杨卓, 杨晓杰, 付学鹏. 扎龙湿地10个不同居群芦苇的ITS序列分析 [J]. 种子, 2021, 40(11):122−125. doi: 10.16590/j.cnki.1001-4705.2021.11.122YANG Z, YANG X J, FU X P. ITS sequence analysis of 10 different populations of Phragmites australis in Zhalong wetland [J]. Seed, 2021, 40(11): 122−125.(in Chinese) doi: 10.16590/j.cnki.1001-4705.2021.11.122 [42] 马翠苹, 周先容, 尚进, 等. 四川花萼山不同海拔巴山榧树居群的遗传多样性 [J]. 分子植物育种, 2018, 16(19):6517−6524. doi: 10.13271/j.mpb.016.006517MA C P, ZHOU X R, SHANG J, et al. Genetic diversity of Torreya fargesii populations at different altitudes in Hua'eshan, Sichuan Province [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2018, 16(19): 6517−6524.(in Chinese) doi: 10.13271/j.mpb.016.006517 -








 下载:
下载: