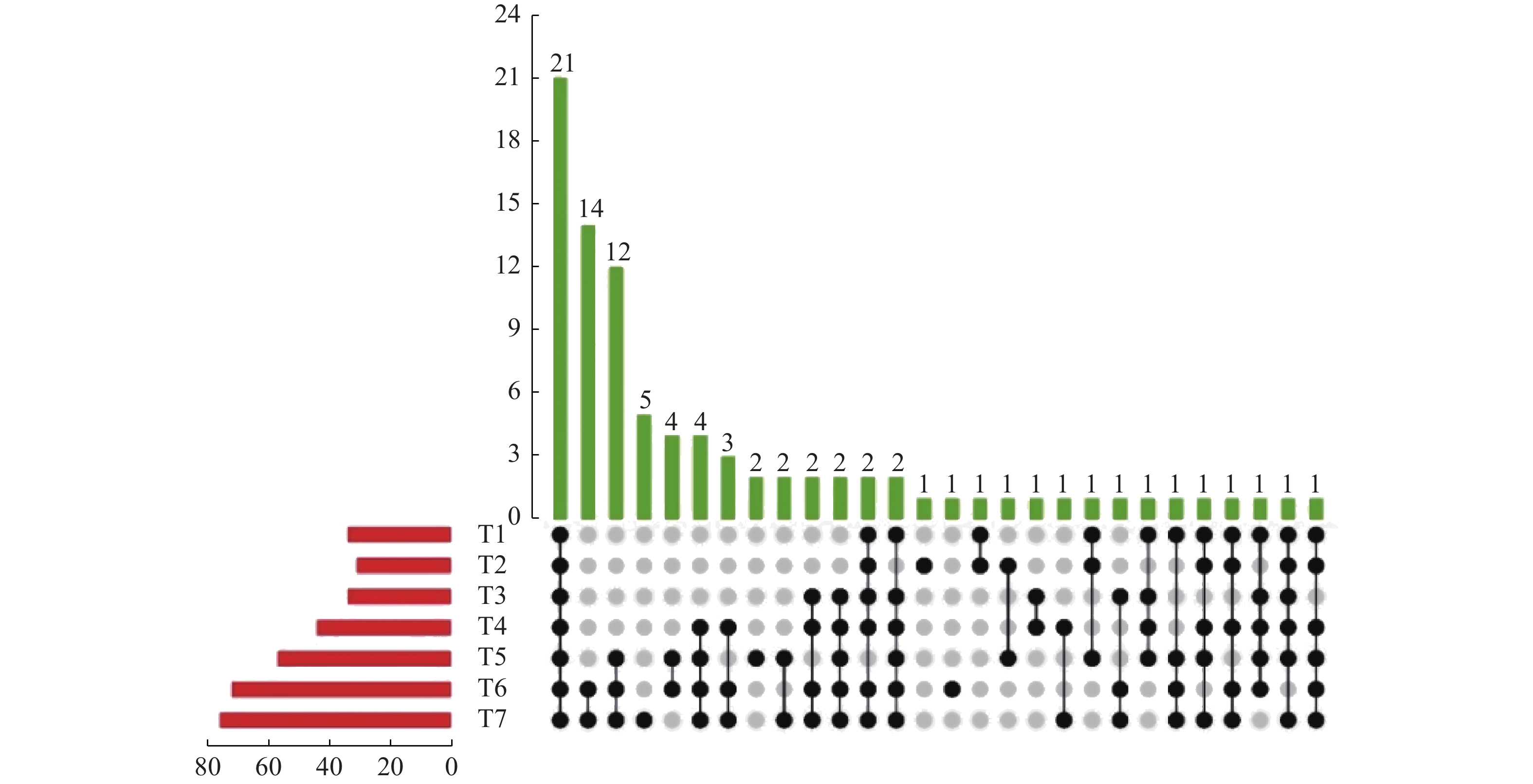
Volatiles and Amino Acids in Pericarp of Yellow Passion Fruit at Fruit Development Stages
-
摘要:
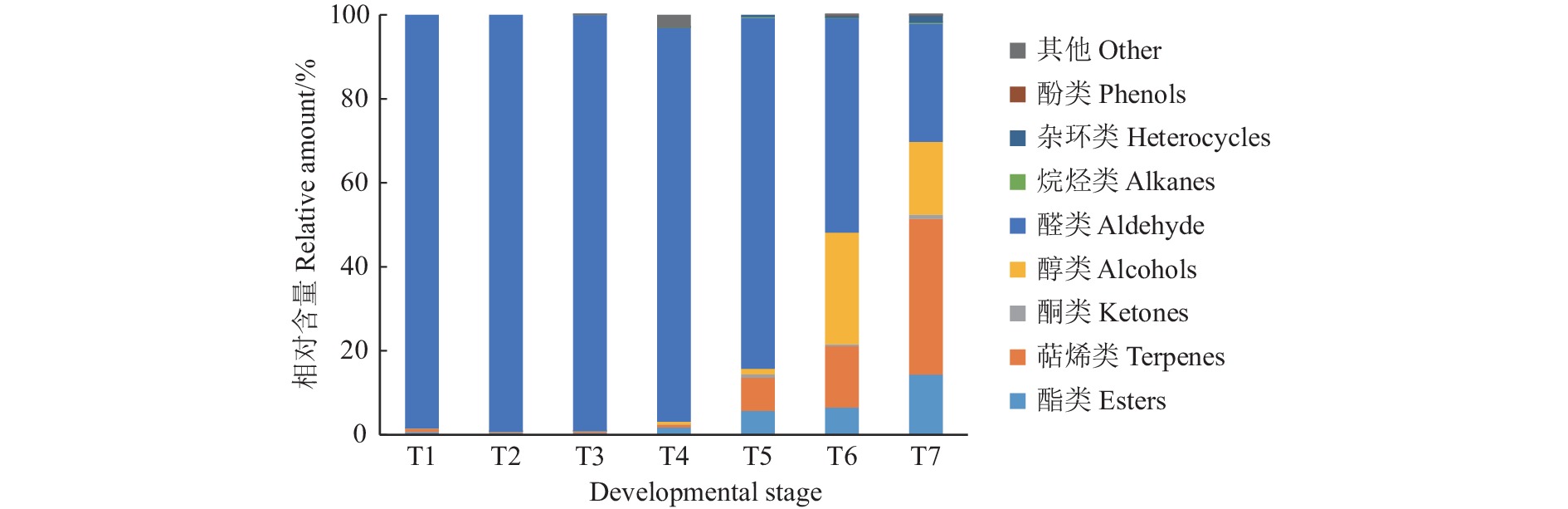
目的 研究不同发育期黄金百香果果皮挥发性成分和游离氨基酸成分的组成和动态变化规律,明确关键呈味氨基酸和特征差异挥发性成分,为黄金百香果果皮的芳香调控、产品开发及综合利用等提供参考。 方法 采用氨基酸分析仪和顶空固相微萃取气质联用仪(HS-SPME-GC-MS),检测不同发育期(T1~T7)果皮中的游离氨基酸和挥发性物质,并进行差异性分析。 结果 果皮中共检测出游离氨基酸(Free amino acid, FAA)15种。呈味氨基酸中的芳香类氨基酸含量最高,在T7时达到最大值(98.48 mg·hg−1),占比为39.03%。OPLS-DA和滋味活度值(TAV)分析表明,胱氨酸为影响香气形成的关键呈味氨基酸。果皮中共检测出90种挥发性物质,T1~T6时期以醛类为主,T7时期以萜烯类为主。OPLS-DA和ROAV分析表明,特征差异挥发性成分有9种,其中T1~T5时期以1-辛烯-3-酮为主,其次为苯甲醛(T1~T4时期)和庚醛(T5时期),T6和T7时期以(E)-β-大马烯酮的贡献作用最大。 结论 胱氨酸是影响黄金百香果果皮香气形成的关键呈味氨基酸。黄金百香果果皮挥发性物质在不同发育期存在特异性,其中果皮着色期(T1~T5)以1-辛烯-3-酮为主,完全成熟期(T6和T7)以(E)-β-大马烯酮的贡献作用最大。 Abstract:Objective Studying the composition and dynamic changes of volatile components and free amino acids (FAAs) in the pericarp of Yellow Passion Fruit during different growth stages, and clarifying the key flavor amino acids and characteristic volatile components, can provide references for the aroma regulation, product development, and comprehensive utilization of Yellow Passion Fruit pericarp. Method Using amino acid analyzer and headspace solid-phase microextraction coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (HS-SPME-GC-MS), the FAAs and volatile compounds in the pericarp of different growth stages (T1–T7) were detected and analyzed for differences. Result A total of 15 types of FAAs were detected in the pericarp. Among the flavor amino acids, aromatic amino acids had the highest content, reaching a maximum of 98.48 mg·hg−1 at T7, accounting for 39.03%. OPLS-DA and TAV analyses indicated that cystine was the key flavor amino acid that affects aroma formation. A total of 90 volatile compounds were detected in the pericarp. Aldehydes were dominant during the T1–T6 stages, while terpenes were dominant at T7. OPLS-DA and ROAV analyses showed that there were 9 types of characteristic volatile compounds with differential expression. Among them, 1-octen-3-one was the dominant compound during the T1~T5 stages, followed by benzaldehyde (T1–T4 stages) and heptanal (T5 stage). During the T6 and T7 stages, (E)-β-damascone contributed the most. Conclusion Cystine was the crucial flavoring amino acid associated with the aroma formation of the pericarp. The volatile composition varied by fruit development stages, such as 1-octene 3-one was the dominant component when the pericarp was forming color in T1-T5, while (E)- β -damalenone when the fruit was maturing in T6 and T7. -
Key words:
- Yellow Passion Fruit /
- fruit growth stages /
- pericarp /
- free amino acids /
- volatile components
-
表 1 发育期黄金百香果果皮游离氨基酸组成
Table 1. FAAs in Yellow Passion Fruit pericarp at fruit growth stages
(单位:mg·g−1) 游离氨基酸
FAAs时期 Period T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 天冬氨酸 Asp 0.1606±0.0069 ab 0.1432±0.0153 b 0.1380±0.0166 b 0.1885±0.0274 a 0.1593±0.0189 ab 0.1553±0.0215 ab 0.1771±0.0282 ab 天冬酰胺 Asn 0.9362±0.1022 b 0.7631±0.0286 c 0.7267±0.0183 c 1.6309±0.1729 a 0.3255±0.0178 de 0.4643±0.0564 d 0.2866±0.0433 e 谷氨酸 Glu 0.1557±0.0239 ab 0.1323±0.0091 bc 0.1712±0.0203 a 0.1769±0.0124 a 0.0725±0.0110 e 0.1012±0.0121 d 0.1154±0.0168 cd 甘氨酸 Gly 0.0073±0.0007 abc 0.0092±0.0011 a 0.0080±0.0009 ab 0.0086±0.0024 ab 0.0038±0.0022 d 0.0058±0.0017 bcd 0.0051±0.0003 cd 丙氨酸 Ala 0.0168±0.0018 cd 0.0228±0.0041 ab 0.0192±0.0031 bc 0.0264±0.0029 a 0.0268±0.0027 a 0.0137±0.0021 d 0.0182±0.0028 bcd 胱氨酸(Cys)2 0.4918±0.0786 c 0.5518±0.0363 c 0.5332±0.0113 c 0.4982±0.0222 c 0.5038±0.0399 c 0.8643±0.0514 b 0.9632±0.0385 a 异亮氨酸 Ile 0.0050±0.0007 c 0.0053±0.0006 c 0.0142±0.0026 a 0.0049±0.0008 c 0.0048±0.0006 c 0.0058±0.0003 c 0.0080±0.0008 b 亮氨酸 Leu 0.0168±0.0024 a 0.0170±0.0028 a 0.0153±0.0006 ab 0.0137±0.0007 ab 0.0136±0.0030 ab 0.0155±0.0014 ab 0.0128±0.0018 b 苯丙氨酸 Phe 0.0128±0.0026 cd 0.0099±0.0012 d 0.0226±0.0028 b 0.0291±0.0057 a 0.0182±0.0028 bc 0.0213±0.0029 b 0.0216±0.0029 b β-氨基异丁酸 β-AiBA 0.3621±0.0340 a 0.3072±0.0291 ab 0.2966±0.0279 b 0.2790±0.0258 b 0.2791±0.0338 b 0.2749±0.0342 b 0.2597±0.0378 b 组氨酸 His 0.2260±0.0167 a 0.1295±0.0210 d 0.1483±0.0059 cd 0.1697±0.0174 bc 0.1843±0.0070 b 0.1701±0.0194 bc 0.2189±0.0074 a 赖氨酸 Lys 0.0132±0.0033 c 0.0112±0.0015 c 0.0127±0.0014 c 0.0199±0.0013 b 0.0128±0.0018 c 0.0225±0.0028 b 0.0273±0.0028 a 氯化铵 NH4 0.0276±0.0021 b 0.0274±0.0018 b 0.0268±0.0015 b 0.0442±0.0037 a 0.0163±0.0032 d 0.0238±0.0019 bc 0.0216±0.0018 c 精氨酸 Arg 0.0236±0.0027 e 0.0218±0.0033 e 0.0237±0.0045 e 0.0578±0.0046 d 0.0989±0.0128 c 0.1240±0.0117 b 0.3583±0.0307 a 脯氨酸 Pro 0.1879±0.0302 b 0.2370±0.0114 a 0.2531±0.0101 a 0.2111±0.0042 b 0.1158±0.0123 c 0.1039±0.0069 c 0.0293±0.0034 d 总游离氨基酸 TOFAA 2.6433±0.2651 b 2.3887±0.0915 b 2.4094±0.0464 b 3.3589±0.2154 a 1.8354±0.0696 c 2.3662±0.1523 b 2.5229±0.1389 b 必需氨基酸 EAA 0.0478±0.0077 b 0.0435±0.0051 b 0.0648±0.0055 a 0.0676±0.0080 a 0.0494±0.0019 b 0.0651±0.0064 a 0.0696±0.0026 a 半必需氨基酸 SAA 0.2496±0.0146 cd 0.1512±0.0199 e 0.1719±0.0090 e 0.2276±0.0200 d 0.2832±0.0174 bc 0.2941±0.0306 b 0.5772±0.0379 a 非必需氨基酸 NEAA 1.9563±0.2181 b 1.8594±0.0470 bc 1.8494±0.0254 bc 2.7406±0.1672 a 1.2075±0.0191 e 1.7084±0.1114 cd 1.5949±0.0997 d 同行数据后不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Data with different lowercase letters on same row indicate significant difference at P<0.05.表 2 发育期黄金百香果果皮呈味氨基酸含量
Table 2. The pericarp of Yellow Passion Fruit exhibits flavor amino acid content during the growth period (单位:mg·g−1)
呈味氨基酸
Flavor amino acid发育期 Developmental stage T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 鲜味氨基酸 DAA 0.329 4±0.028 4 ab 0.286 7±0.021 4 bc 0.322 0±0.029 0 b 0.385 3±0.026 1 a 0.244 5±0.027 8 c 0.279 0±0.029 9 bc 0.319 7±0.032 9 b 甜味氨基酸 SAA 0.438 0±0.031 3 a 0.398 4±0.036 1 a 0.428 5±0.008 5 a 0.415 8±0.020 9 a 0.330 7±0.019 5 b 0.293 4±0.023 5 bc 0.271 5±0.005 4 c 苦味氨基酸 BAA 0.045 5±0.004 5 e 0.044 1±0.002 6 e 0.053 1±0.005 9 de 0.076 4±0.004 0 d 0.117 3±0.013 5 c 0.145 3±0.011 5 b 0.379 1±0.030 4 a 芳香类氨基酸 AAA 0.504 6±0.081 1 c 0.561 7±0.037 4 c 0.555 8±0.013 3 c 0.527 2±0.022 6 c 0.522 0±0.037 1 c 0.885 6±0.048 7 b 0.984 8±0.041 3 a 同行数据后不同小写字母表示不同时期间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Different lowercase letters after peer data indicate significant differences during different time periods (P<0.05).表 3 发育期黄金百香果果皮中呈味氨基酸及TAV
Table 3. Flavor amino acids and TAVs in Yellow Passion Fruit pericarp at fruit growth stages
种类
Species氨基酸
Amino acid味觉阈值[20]
Taste threshold/ (mg·g−1)滋味活度值 TAV T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 鲜味氨基酸 DAA Asp 1.00 0.161 0.143 0.152 0.188 0.159 0.155 0.177 Glu 0.30 0.52 0.44 0.48 0.59 0.24 0.34 0.38 Lys 0.50 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.04 0.03 0.04 0.05 甜味氨基酸 SAA Gly 1.30 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 Ala 0.60 0.03 0.04 0.03 0.04 0.04 0.02 0.03 His 0.20 1.13 0.65 0.89 0.85 0.92 0.85 1.09 Pro 3.00 0.06 0.08 0.07 0.07 0.04 0.03 0.01 苦味氨基酸 BAA Ile 0.90 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 Leu 1.90 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 Arg 0.50 0.05 0.04 0.05 0.12 0.20 0.25 0.72 芳香类氨基酸 AAA (Cys)2 0.02 24.59 27.59 26.09 24.91 25.19 43.21 48.16 Phe 0.90 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.02 表 4 发育期黄金百香果果皮挥发性物质的气味描述、香气阈值及相对香气活度值
Table 4. Description, threshold, and ROAV of volatiles in Yellow Passion Fruit pericarp at fruit growth stages
挥发性物质
Volatile substances香气阈值
Odor thresholds /(μg·kg−1)相对气味活度值 ROAV 香气描述
Odor descriptionT1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 异戊醛
3-Methyl butanal1.10[21] 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 3.84 0.05 0.02 巧克力味、麦芽味[22] 庚醛
Heptanal3.00[23-25] 5.40 4.21 4.18 4.62 57.09 0.62 0.28 油味、草味[22] (E)-2-己烯醛
(E)-2-Hexenal17.00[25-29] 15.77 15.31 10.52 10.19 30.97 0.57 0.20 草味、脂肪味[22] 1-辛烯-3-酮
1-Octen-3-one0.05[23] 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 1.45 0.86 蘑菇味[22,23] 正辛醛
Octanal0.70[25,29] 16.76 22.09 33.84 24.96 30.14 1.03 0.17 脂肪味、蜂蜜、柑橘、柠檬、果味[22,23,25] 苯甲醛
Benzaldehyde350.00[29,30] 43.70 52.19 52.63 48.49 5.41 0.09 0.00 樱桃、杏仁味,烤肉,焦糖,苦味[31-33] 苯乙醛
Phenylacetaldehyde4.00[23,25,29,34] 0.00 0.00 0.00 1.71 4.10 0.10 0.03 刺鼻的绿色气味、风信子、花香、玫瑰味[23,25] (E)-β-大马烯酮
(E)-β-Damascenone0.00075[24] 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 100.00 100.00 玫瑰、花香,蜂蜜味、甜香,果香、烤苹果味[24,25] γ-癸内酯
γ-Decalactone1.00[23] 4.27 2.41 6.51 9.40 31.99 0.28 0.08 桃味、杏、椰子、果香,甜味[22,23,26,35] -
[1] RINALDI M M, COSTA A M, FALEIRO F G, et al. Conservação pós-colheita de frutos de Passiflora setacea DC. submetidos a diferentes sanitizantes e temperaturas de armazenamento[J]. Brazilian Journal of Food Technology, 2017, 20: ■-■(页码?请补充).RINALDI M M, COSTA A M, FALEIRO F G, et al. Conservação pós-colheita de frutos de Passiflora setacea DC. submetidos a diferentes sanitizantes e temperaturas de armazenamento [J]. Brazilian Journal of Food Technology, 2017, 20−e2016046. [2] 冯颖, 张萍萍, 赵存朝, 等. 响应面优化百香果果皮果脯制备工艺 [J]. 食品工业科技, 2022, 43(17):275−282.FENG Y, ZHANG P P, ZHAO C C, et al. Optimization of preparation technology of passion fruit peel and preserved fruit by response surface methodology [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(17): 275−282.(in Chinese) [3] 刘文静, 潘葳, 吴建鸿. 5种百香果品系间氨基酸组成比较及评价分析 [J]. 食品工业科技, 2019, 40(24):237−241.LIU W J, PAN W, WU J H. Comparative analysis and evaluation of amino acids composition among five passion fruit varieties [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2019, 40(24): 237−241.(in Chinese) [4] 邝瑞彬, 孔凡利, 杨护, 等. 百香果果汁营养特性分析与评价 [J]. 食品工业科技, 2021, 42(9):347−357.KUANG R B, KONG F L, YANG H, et al. Analysis and assessment of nutritional components of passion fruits juice [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(9): 347−357.(in Chinese) [5] 董经崇, 胡文效, 邱磊, 等. ‘玫瑰香’葡萄皮游离态和结合态香气成分分析 [J]. 中外葡萄与葡萄酒, 2022(4):14−22.DONG J C, HU W X, QIU L, et al. Analysis of free and combined aroma components in’Muscat hamburg’ grape skin [J]. Sino-Overseas Grapevine & Wine, 2022(4): 14−22.(in Chinese) [6] 李春秀, 李勋兰, 梁国鲁, 等. 不同成熟阶段柠檬果皮挥发物和酚类成分分析 [J]. 食品科学, 2022, 43(4):215−224.LI C X, LI X L, LIANG G L, et al. Analysis of volatile components and phenols from peels of two lemon cultivars during fruit ripening [J]. Food Science, 2022, 43(4): 215−224.(in Chinese) [7] 张赫宇, 徐瑞, 李勇. 不同萃取头对橘子皮挥发性化合物的研究 [J]. 现代食品, 2022, 28(6):140−145.ZHANG H Y, XU R, LI Y. Research of volatile substances in orange peels by different extraction fibers [J]. Modern Food, 2022, 28(6): 140−145.(in Chinese) [8] 赵明, 邹瑜, 何海旺, 等. 基于GC-MS的不同香蕉品种果实香气品质分析 [J]. 西南农业学报, 2021, 34(5):964−970.ZHAO M, ZOU Y, HE H W, et al. Analysis of aromatic components from six banana varieties by GC-MS [J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 34(5): 964−970.(in Chinese) [9] ZHANG X M, JIA H J. Changes in aroma volatile compounds and ethylene production during Hujingmilu peach (Prunus persica L. ) fruit development [J]. Journal of Plant Physiology and Molecular Biology, 2005, 31(1): 41−46. [10] 刘士健. 腊肉加工过程中主体风味物质变化研究[D]. 重庆: 西南农业大学, 2005.LIU S J. Study on change of main flavour composition in preserved ham during processing[D]. Chongqing: Agricultural University Of Southwest, 2005. (in Chinese) [11] 朱奕凡, 王妍, 汪国云, 等. 不同杨梅品种果实游离氨基酸组成分析 [J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2021, 47(6):736−742.ZHU Y F, WANG Y, WANG G Y, et al. Analysis of free amino acid composition in fruits of different bayberry(Morella rubra) varieties [J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture and Life Sciences), 2021, 47(6): 736−742.(in Chinese) [12] KIEFFER D A, PICCOLO B D, VAZIRI N D, et al. Resistant starch alters gut microbiome and metabolomic profiles concurrent with amelioration of chronic kidney disease in rats [J]. American Journal of Physiology Renal Physiology, 2016, 310(9): F857−F871. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00513.2015 [13] 郭艳峰, 吴惠婵, 夏雨, 等. 百香果不同发育阶段果汁挥发性成分研究 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2017, 32(3):299−304.GUO Y F, WU H C, XIA Y, et al. Volatiles in juice of passion fruitsat different developmental stages [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 32(3): 299−304.(in Chinese) [14] 陈庆, 贾强, 董浩, 等. 紫红百香果果汁挥发性香气分析及仿香研究 [J]. 现代食品科技, 2018, 34(12):258−263.CHEN Q, JIA Q, DONG H, et al. Studies on volatile aroma compounds of the juice of purple Passiflora edulis and aroma simulation experiments [J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2018, 34(12): 258−263.(in Chinese) [15] 潘葳, 刘文静, 韦航, 等. 不同品种百香果果汁营养与香气成分的比较 [J]. 食品科学, 2019, 40(22):277−286. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181218-201PAN W, LIU W J, WEI H, et al. Comparative analysis of nutritional and aroma components in passion fruit juices from five cultivars [J]. Food Science, 2019, 40(22): 277−286.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181218-201 [16] 何洁, 莫仁甫, 廖洁, 等. 紫果西番莲中游离氨基酸主成分分析 [J]. 轻工科技, 2018, 34(11):5−7.HE J, MO R F, LIAO J, et al. Principal component analysis of free amino acids in Passiflora edulis [J]. Light Industry Science and Technology, 2018, 34(11): 5−7.(in Chinese) [17] 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. 植物中游离氨基酸的测定: GB/T 30987—2020[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2020. [18] 谷镇, 杨焱. 食用菌呈香呈味物质研究进展 [J]. 食品工业科技, 2013, 34(5):363−367.GU Z, YANG Y. Research progress in flavor components of edible fungus [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2013, 34(5): 363−367.(in Chinese) [19] PRIPIS-NICOLAU L, DE REVEL G, BERTRAND A, et al. Formation of flavor components by the reaction of amino acid and carbonyl compounds in mild conditions [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2000, 48(9): 3761−3766. doi: 10.1021/jf991024w [20] 林媚, 张伟清, 王天玉, 等. 15个杂交柑橘品种的果实游离氨基酸组成及其对风味品质的影响 [J]. 果树学报, 2022, 39(3):352−365.LIN M, ZHANG W Q, WANG T Y, et al. Study on the composition of free amino acid and the effects on fruit flavor quality in 15 hybrid citrus varieties [J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2022, 39(3): 352−365.(in Chinese) [21] VAN GEMERT L J. Odour thresholds: Compilations of odour threshold values in air, water and other media [M]. Publisher: Oliemans Punter & Partners BV, Zeist, The Netherlands, 2011. [22] LIU X S, LIU J B, YANG Z M, et al. Aroma-active compounds in Jinhua ham produced with different fermentation periods [J]. Molecules, 2014, 19(11): 19097−19113. doi: 10.3390/molecules191119097 [23] BURDOCK, GEORGE A. Fenaroli's handbook of flavor ingredients(6th ed. ) [M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2010. [24] 王超. 新疆引种红枣风味特征研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2021.WANG C. Study on the flavor characteristics of introduced jujube from Xinjiang[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2021. (in Chinese) [25] 张文文. 鲜食葡萄香气特征与感官品评的研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2018.ZHANG W W. Study on the characteristics of aroma and sensory evaluation of table grapes[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2018. (in Chinese) [26] GENOVESE A, LAMORTE S A, GAMBUTI A, et al. Aroma of Aglianico and Uva di Troia grapes by aromatic series [J]. Food Research International, 2013, 53(1): 15−23. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2013.03.051 [27] 谢永恒. 甜瓜中关键香气物质鉴定及其相互作用研究[D]. 上海: 上海应用技术大学, 2021XIE Y H. Identification and perceptual interaction of key aroma compounds in muskmelon[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Institute of Technology, 2021. (in Chinese) [28] 李维妮, 郭春锋, 张宇翔, 等. 气相色谱-质谱法分析乳酸菌发酵苹果汁香气成分 [J]. 食品科学, 2017, 38(4):146−154.LI W N, GUO C F, ZHANG Y X, et al. GC-MS analysis of aroma components of apple juice fermented with lactic acid bacteria [J]. Food Science, 2017, 38(4): 146−154.(in Chinese) [29] PINO J A, MESA J. Contribution of volatile compounds to mango (Mangifera indica L. ) aroma [J]. Flavour and Fragrance Journal, 2006, 21(2): 207−213. doi: 10.1002/ffj.1703 [30] WANG L B, BAI J H, YU Z F. Responses of volatile compounds in inner tissues on refrigeration in full ripe tomatoes [J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 2017, 41(6): e13272. doi: 10.1111/jfpp.13272 [31] 李晓颍, 武军凯, 王海静, 等. 欧李果实发育期内挥发性成分变化特征 [J]. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(9):1964−1980.LI X Y, WU J K, WANG H J, et al. Characterization of volatiles changes in Chinese dwarf cherry fruit during its development [J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2021, 54(9): 1964−1980.(in Chinese) [32] NOGUEROL-PATO R, GONZÁLEZ-BARREIRO C, CANCHO-GRANDE B, et al. Quantitative determination and characterisation of the main odourants of Mencía monovarietal red wines [J]. Food Chemistry, 2009, 117(3): 473−484. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.04.014 [33] KIM Y, LEE K G, KIM M K. Volatile and non-volatile compounds in green tea affected in harvesting time and their correlation to consumer preference [J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 2016, 53(10): 3735−3743. doi: 10.1007/s13197-016-2349-y [34] 孙宝国, 陈海涛. 食用调香术[M]. 3版. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2017. [35] DU X F, PLOTTO A, BALDWIN E, et al. Evaluation of volatiles from two subtropical strawberry cultivars using GC-olfactometry, GC-MS odor activity values, and sensory analysis [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2011, 59(23): 12569−12577. doi: 10.1021/jf2030924 [36] QIN G H, TAO S T, ZHANG H P, et al. Evolution of the aroma volatiles of pear fruits supplemented with fatty acid metabolic precursors [J]. Molecules, 2014, 19(12): 20183−20196. doi: 10.3390/molecules191220183 [37] 王博, 李霁昕, 李经纬, 等. 采后苯并噻重氮处理对‘玉金香’甜瓜氨基酸代谢酯类香气物质及其代谢机理的影响 [J]. 食品科学, 2018, 39(17):212−220.WANG B, LI J X, LI J W, et al. Effect of postharvest benzothiadiazole treatment on aroma esters derived from amino acid metabolism and metabolic mechanism in ‘Yujinxiang’ melon [J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(17): 212−220.(in Chinese) [38] 程远, 万红建, 姚祝平, 等. 不同品种樱桃番茄氨基酸组成及风味分析 [J]. 核农学报, 2019, 33(11):2177−2185.CHENG Y, WAN H J, YAO Z P, et al. Comparative analysis of the amino acid constitution and flavor quality in different cherry tomato varieties [J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 33(11): 2177−2185.(in Chinese) [39] 侯娜, 赵莉莉, 魏安智, 等. 不同种质花椒氨基酸组成及营养价值评价 [J]. 食品科学, 2017, 38(18):113−118. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201718018HOU N, ZHAO L L, WEI A Z, et al. Amino acid composition and nutritional quality evaluation of different germplasms of Chinese prickly ash(Zanthoxylum bungeanum maxim) [J]. Food Science, 2017, 38(18): 113−118.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201718018 [40] 方灵, 孔宝玉, 韦航, 等. 不同发育阶段黄金百香果挥发性成分差异性研究 [J]. 果树学报, 2022, 39(12):2376−2389.FANG L, KONG B Y, WEI H, et al. Study on variation of volatile components in Golden Passion Fruit at different development stages [J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2022, 39(12): 2376−2389.(in Chinese) [41] POLLIEN P, FAY L B, BAUMGARTNER M, et al. First attempt of odorant quantitation using gas chromatography-olfactometry [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1999, 71(23): 5391−5397. doi: 10.1021/ac990367q [42] BUETTNER A, SCHIEBERLE P. Evaluation of aroma differences between hand-squeezed juices from Valencia late and Navel oranges by quantitation of key odorants and flavor reconstitution experiments [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2001, 49(5): 2387−2394. doi: 10.1021/jf001363l [43] SEROT T, PROST C, VISAN L, et al. Identification of the main odor-active compounds in musts from French and Romanian hybrids by three olfactometric methods [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2001, 49(4): 1909−1914. doi: 10.1021/jf0012291 [44] XIONG C, LI Q, LI S H, et al. In vitro antimicrobial activities and mechanism of 1-octen-3-ol against food-related bacteria and pathogenic fungi [J]. Journal of Oleo Science, 2017, 66(9): 1041−1049. doi: 10.5650/jos.ess16196 -







 下载:
下载: