Identification and Growth-promoting Effects of Endophytic Pseudomonas sp. from Hippophae thibetana Root Nodules
-
摘要:
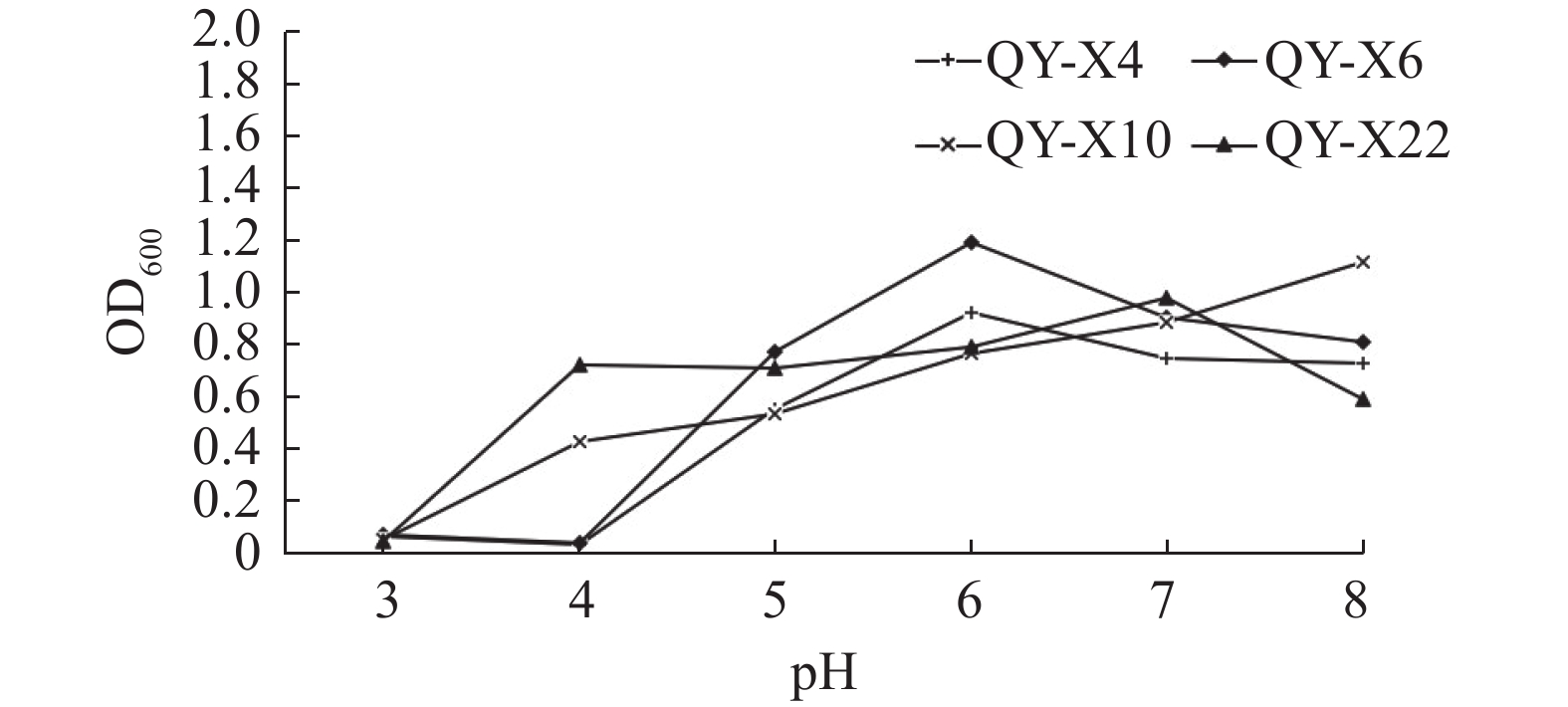
目的 获取西藏沙棘根瘤内生菌中具有多重生物学活性的假单胞菌属菌株,探究筛选所得菌株的促生作用,为研发高效生物菌肥提供基础材料。 方法 利用纯培养方法,从西藏沙棘根瘤中分离假单胞菌,通过形态、生理生化及16S rDNA序列比对鉴定菌株,测定菌株溶磷、产IAA、产铁载体及产降解纤维素酶的能力,接种宿主植物验证其促生效果。 结果 4株根瘤内生菌与参考假单胞菌属同源性为99%以上,鉴定为假单胞菌属。溶磷和产IAA的定性及定量结果表明,4株菌均具有溶解无机磷和产IAA的能力,其中溶解无机磷能力较强的菌株是QY-X10和QY-X22,均达到400 mg·L−1;菌株QY-X4产IAA能力较其他菌株强,达1.9 mg·L−1;4株菌株具有产铁载体的能力,除QY-X10以外,均具产降解纤维素酶的能力;促生试验结果表明,QY-X6可有效促进种子的萌发;QY-X6、QY-X10处理组叶片数显著高于对照;QY-X6、QY-X10处理组苗长显著高于对照;QY-X10、QY-X22处理组最大叶片长显著高于对照。 结论 分离筛选出4株假单胞菌,均可溶解无机磷和产IAA,兼具产铁载体;3株兼具产降解纤维素的能力;接种试验发现,4株菌株处理组可有效促进植株的生长发育,分离菌株可为研发生物菌肥提供基础材料。 Abstract:Objective EndogenousPseudomonas sp. in the root nodules of Hippophae thibetana that displayed a biological activity were isolated for toxicological identification and growth-promoting effect determination for the development of a biological agent for crop fertilization. Methods Strains of Pseudomonas sp. were isolated from the root nodules of H. thibetana by pure culture method. They were identified by morphology, physiological biochemistry, and 16S rDNA sequence, as well as examined for the growth-promoting effect on the host plant by artificial inoculation for evidence of phosphorus-dissolving and IAA-, iron- and cellulase-producing capacities. Results Out of the isolated endophytic strains, 4 showed greater than 99% 16S rDNA alignment with the reference Pseudomonas. Among them, QY-X10 and QY-X22 produced 400 mg·L−1 of solubilized phosphorus; QY-X4 yielded the highest IAA at 1.9 mg·L−1; all 4 strains contained iron-generating carriers; except QY-X10, all could degrade cellulose; QY-X6 promoted seed germination; and QY-X6 and QY-X10 helped the host plant to grow significantly more leaves and longer seedlings, while QY-X10 and QY-X22 did significantly to make the maximum-length leaves longer than did control. Conclusion There were 4 Pseudomonas sp. identified in this study that exhibited significant abilities to dissolve inorganic phosphorus and produce IAA and iron. Three of them could also degrade cellulose. By inoculating these strains on the host plants, the seed germination and seedling growth were effectively promoted. It appeared that they could be applied for crop fertilization. -
Key words:
- Pseudomonas sp. /
- Hippophae thibetana /
- strain identification /
- growth-promoting effect
-
表 1 分离菌株生化测定结果
Table 1. Biochemical identification of isolated Pseudomonas sp.
指标
IndexQY-X4 QY-X6 QY-X10 QY-X22 恶臭假单胞菌A3菌株Pseudomonas putida A3 strain 半乳糖
Galactose- + + + + 麦芽糖
Maltose+ + + + - 蔗糖生化管
Sucrose biochemical tube- - + + - 葡萄糖
Glucose utilization- - + + + 果糖
Fructose+ + + + + 明胶生化
Gelatin hydrolysis- - - - N 硫化氢
H2S- - - - N L-鼠李糖
L-Rhamnose- + + + N 甲基红试验
Methyl red test- - - - - V-P反应
V-P Test- - - - - 运动性
Motility运动 运动 不运动 不运动 N 革兰氏染色
Gram stain- - - - - +表示阳性,-表示阴性。N表示不确定。
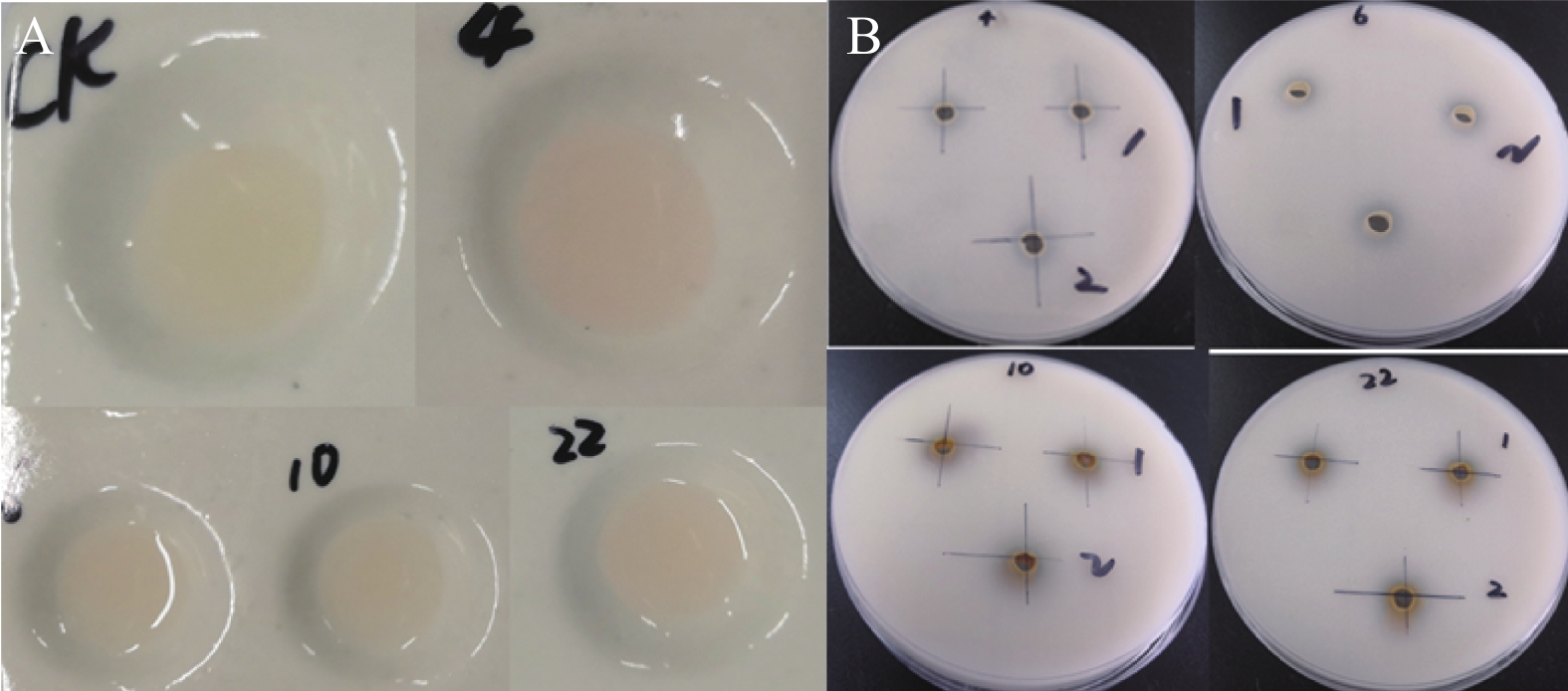
+indicates positive; -indicates negative; N indicates undetermined.表 2 菌株溶解磷、产IAA的定性测定
Table 2. Qualitative determination of phosphorus-dissolving and IAA-producing abilities of isolated Pseudomonas sp.
菌株
Strain溶解无机磷能力SI
Phosphate solubilization (inorganic) SI/mm产IAA能力
IAA productionQY-X4 1.781±0.066 a ++ QY-X6 1.778±0.079 a + QY-X10 1.456±0.108 b + QY-X22 1.605±0.118 ab ++ 同列不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05),下同。/表示无效果。+表示浅红色,++表示粉红。
Datas with different lowercase letters on the same column indicate significant difference at 0.05 level. Same for below. /indicates no effect; + indicates light red; and ++ indicates pink.表 3 菌株溶解磷、产IAA的定量测定
Table 3. Quantitative determination of phosphorus-dissolving and IAA-producing abilities of isolated Pseudomonas sp.
菌株
Strain溶解无机磷量
Phosphate solubilization (inorganic)/
(mg·L−1)IAA含量
IAA production/
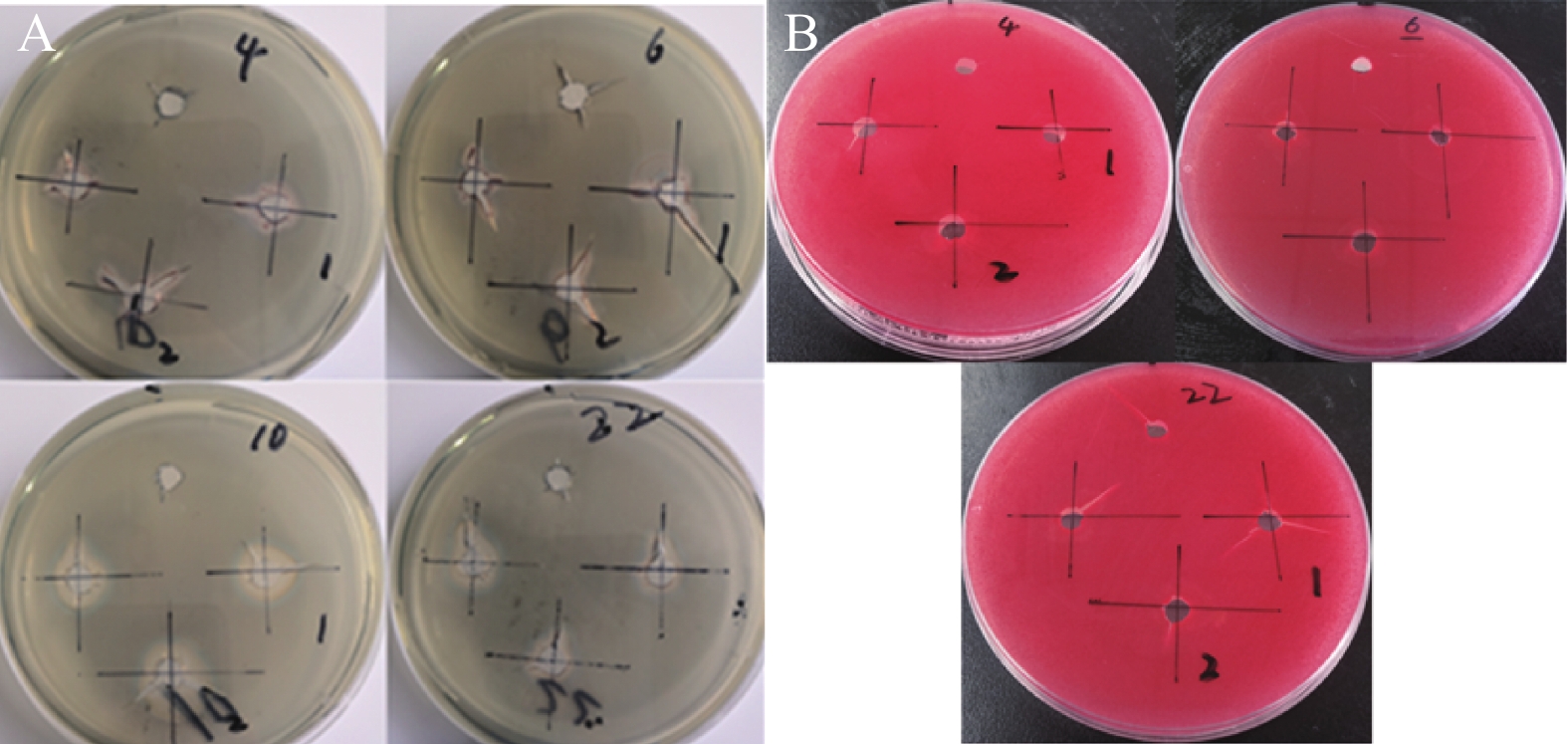
(mg·L−1)QY-X4 230.232±3.482 b 1.919±0.243 a QY-X6 207.335±26.067 b 1.019±0.141 bc QY-X10 418.131±9.898 a 0.627±0.135 c QY-X22 417.266±4.765 a 1.063±0.268 b 表 4 菌株产铁载体及降解纤维素酶测定
Table 4. Determination of iron-producing and cellulose-degrading abilities of isolated Pseudomonas sp.
菌株
strain产铁载体能力SI
iron-producing siderophore SI/mm产降解纤维素酶能力SI
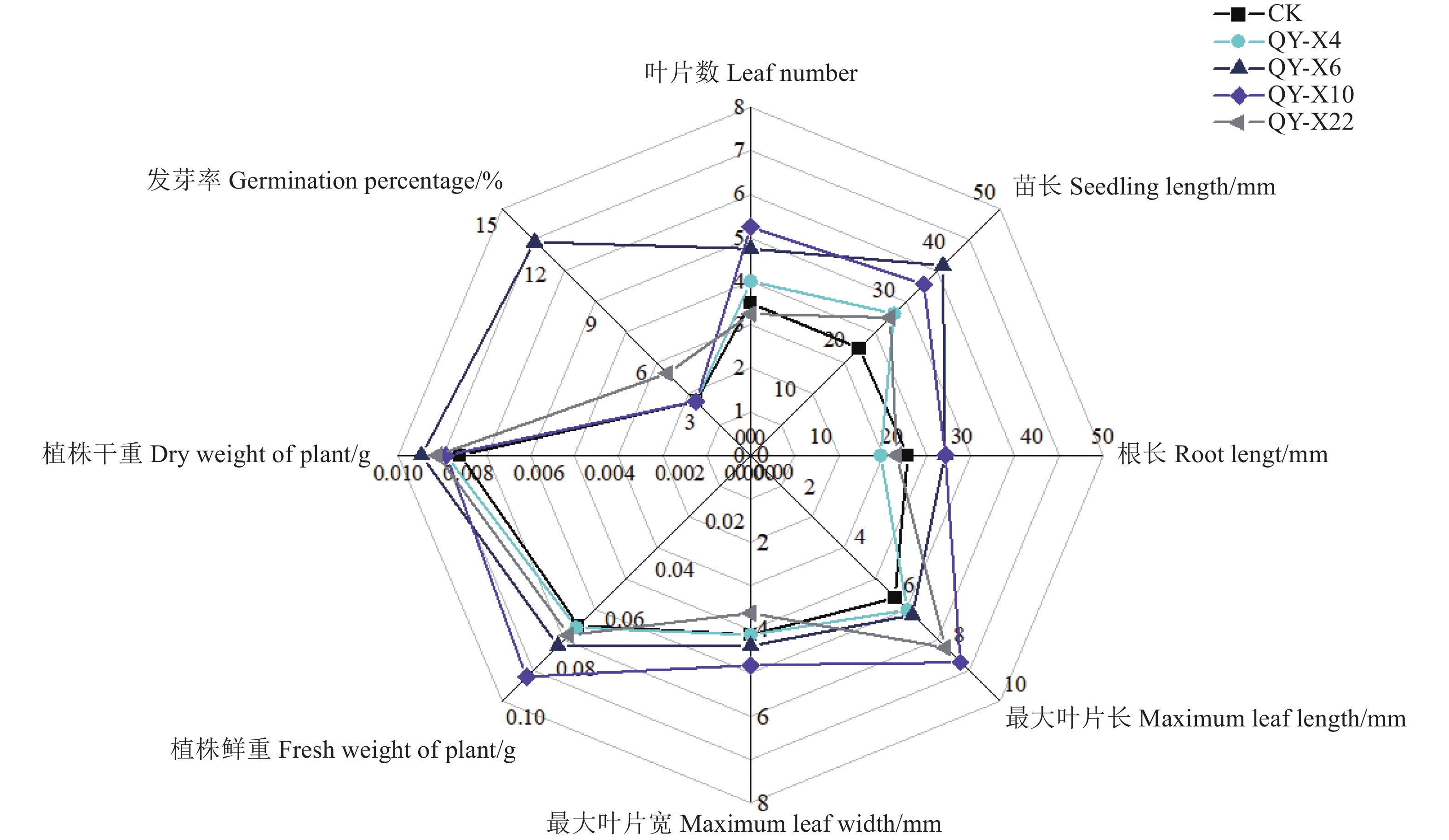
Degrading cellulase SI/mmQY-X4 1.742±0.3232 a 1.671±0.3225 a QY-X6 1.727±0.3556 a 2.177±0.2710 a QY-X10 1.986±0.1822 a / QY-X22 1.830±0.1663 a 1.797±0.1597 a 表 5 菌株对西藏沙棘幼苗的促生效果
Table 5. Growth promoting effects of Pseudomonas sp. on Hippophae thibetana seedlings
菌株
Strain叶片数
Leaf number苗长
Seedling length/mm根长
Root length/mm最大叶片长
Maximum leaf length/mm最大叶片宽
Maximum leaf width/mm植株鲜重
fresh weight of plant/g植株干重
Dry weight of plant/g发芽率
germination percentage/%CK 3.500±1.000 c 21.763±21.763 b 22.300±5.324 ab 5.803±0.616 c 4.125±0.530 ab 0.069±0.006 a 0.008±0.0004 a 3.3 b QY-X4 4.000±0.816 bc 28.775±28.775 ab 18.460±2.761 b 6.290±1.521 bc 4.130±0.241ab 0.070±0.017 a 0.009±0.0032 a 3.3 b QY-X6 4.750±0.500 ab 38.603±38.603 a 27.585±3.578 a 6.500±0.887 bc 4.380±1.076 ab 0.077±0.019 a 0.009±0.0006 a 13.0 a QY-X10 5.250±0.500 a 34.778±34.778 a 27.635±6.579 a 8.418±0.910 a 4.823±0.597 a 0.090±0.009 a 0.009±0.0009 a 3.3 b QY-X22 3.250±0.500 c 27.988±27.988 ab 20.708±3.412 ab 7.820±1.235 ab 3.628±0.364 b 0.073±0.014 a 0.009±0.0015 a 5.0 b -
[1] 林美珍, 张吉科, 张国伟, 等. 论沙棘根系与功能Ⅲ: 共生固氮机理、条件与初级氮代谢 [J]. 沙棘, 2006, 19(3):7−14.LIN M Z, ZHANG J K, ZHANG G W, et al. Root systems of seabuckthorn and their functions: Ⅲ. Mechanism of symbiotic nitrogen fixation, conditions, and primary nitrogen metabolism [J]. Hippophae, 2006, 19(3): 7−14.(in Chinese) [2] 邱并生. 根瘤内生细菌 [J]. 微生物学通报, 2013, 40(3):544.QIU B S. Nodule endophytic bacteria [J]. Microbiology China, 2013, 40(3): 544.(in Chinese) [3] LUGTENBERG B, KAMILOVA F. Plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria [J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 2009, 63: 541−556. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.62.081307.162918 [4] COOMBS J T, FRANCO C M M. Visualization of an endophytic Streptomyces species in wheat seed [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2003, 69(7): 4260−4262. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.7.4260-4262.2003 [5] 张爱梅, 韩雪英, 王嘉, 等. 马衔山中国沙棘根瘤内共生细菌多样性研究 [J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(1):294−301.ZHANG A M, HAN X Y, WANG J, et al. Diversity of endophytic bacteria in root nodules of Hippophae rhamnoides in the Maxian Mountains [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(1): 294−301.(in Chinese) [6] 郭振华, 陈立红. 阿尔山不同时期落叶松根际土壤固氮菌的多样性研究 [J]. 西北植物学报, 2019, 39(4):729−739. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2019.04.0729GUO Z H, CHEN L H. Community structure and diversity of culturable nitrogen fixing bacteria from Larix gmelinii rhizosphere soil at different stages in Arxan [J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2019, 39(4): 729−739.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2019.04.0729 [7] 池景良, 郝敏, 王志学, 等. 解磷微生物研究及应用进展 [J]. 微生物学杂志, 2021, 41(1):1−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7021.2021.01.001CHI J L, HAO M, WANG Z X, et al. Advances in research and application of phosphorus-solubilizing microorganism [J]. Journal of Microbiology, 2021, 41(1): 1−7.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7021.2021.01.001 [8] 雷海英, 赵青松, 杨潇, 等. 苦参根际高效固氮菌的分离及复合菌肥对幼苗的促生效应 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2020, 36(9):157−166.LEI H Y, ZHAO Q S, YANG X, et al. Isolation of efficient nitrogen-fixing bacteria from the rhizosphere of Sophora flavescens and the growth-promoting effect of compound microbial fertilizer on seedlings [J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2020, 36(9): 157−166.(in Chinese) [9] 闫双堆, 刘利军, 曹燕篆, 等. 3株多环芳烃高效降解菌株的分离鉴定及降解特性 [J]. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(12):4439−4446.YAN S D, LIU L J, CAO Y Z, et al. Isolation, identification, and degradation characteristics of three effective PAHs degradation strains [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(12): 4439−4446.(in Chinese) [10] 杨顺, 杨婷, 林斌, 等. 两株溶磷真菌的筛选、鉴定及溶磷效果的评价 [J]. 微生物学报, 2018, 58(2):264−273.YANG S, YANG T, LIN B, et al. Isolation and evaluation of two phosphate-dissolving fungi [J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2018, 58(2): 264−273.(in Chinese) [11] 罗兴, 邹兰, 吴清山, 等. 乌头产吲哚乙酸内生细菌遗传多样性、抗逆性及其对水稻幼苗生长的影响 [J]. 微生物学报, 2022, 62(4):1485−1500.LUO X, ZOU L, WU Q S, et al. Genetic diversity, stress resistance, and effect on rice seedling growth of indoleacetic acid-producing endophytic bacteria isolated from Aconitum carmichaelii Debeaux [J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2022, 62(4): 1485−1500.(in Chinese) [12] 东秀珠, 蔡妙英. 常见细菌系统鉴定手册[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001. [13] 刘艳萍, 滕松山, 赵蕾. 高产嗜铁素恶臭假单胞菌A3菌株的鉴定及其对黄瓜的促生作用 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(6):1507−1514.LIU Y P, TENG S S, ZHAO L. Identification of a siderophore-producing bacterium Pseudomonas putida A3 and its growth-promoting effects on cucumber seedlings [J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2011, 17(6): 1507−1514.(in Chinese) [14] GLICKMANN E, DESSAUX Y. A critical examination of the specificity of the salkowski reagent for indolic compounds produced by phytopathogenic bacteria [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1995, 61(2): 793−796. doi: 10.1128/aem.61.2.793-796.1995 [15] 樊梦颖, 张明明, 张情, 等. 不同月份沙棘根瘤细菌群落结构特征的分析对比 [J]. 西北林学院学报, 2020, 35(6):160−167.FAN M Y, ZHANG M M, ZHANG Q, et al. Comparison of the characteristics of bacterial community in root nodules of Hippophae rhamnoides in different months [J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2020, 35(6): 160−167.(in Chinese) [16] 田国杰, 王晗, 陈立红. 内蒙古赤峰地区主要树种根际固氮菌的分离和鉴定 [J]. 内蒙古林业科技, 2016, 42(1):21−26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4066.2016.01.006TIAN G J, WANG H, CHEN L H. Isolation and determination of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in rhizosphere of main tree species in Chifeng, Inner Mongolia [J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia Forestry Science and Technology, 2016, 42(1): 21−26.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4066.2016.01.006 [17] 朱培淼, 杨兴明, 徐阳春, 等. 高效解磷细菌的筛选及其对玉米苗期生长的促进作用 [J]. 应用生态学报, 2007, 18(1):107−112. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2007.01.018ZHU P M, YANG X M, XU Y C, et al. High effective phosphate-solubilizing bacteria: Their isolation and promoting effect on corn seedling growth [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2007, 18(1): 107−112.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2007.01.018 [18] 雷平, 黄军, 黄彬彬, 等. 1株产铁载体辣椒内生细菌的分离鉴定及其促生长作用 [J]. 激光生物学报, 2020, 29(4):379−384. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7146.2020.04.012LEI P, HUANG J, HUANG B B, et al. Isolation, identification and growth promoting effect of a siderophore-producing endophytic bacterium from capscium [J]. Acta Laser Biology Sinica, 2020, 29(4): 379−384.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7146.2020.04.012 [19] 苑博华, 廖祥儒, 郑晓洁, 等. 吲哚乙酸在植物细胞中的代谢及其作用 [J]. 生物学通报, 2005, 40(4):21−23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0006-3193.2005.04.010YUAN B H, LIAO X R, ZHENG X J, et al. Metabolism and function of 1AA in plant cell [J]. Bulletin of Biology, 2005, 40(4): 21−23.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0006-3193.2005.04.010 [20] 吴婧, 聂彩娥, 朱媛媛, 等. 一株兼具产IAA能力纤维素降解菌的筛选、鉴定及条件优化 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2020, 36(12):54−63.WU J, NIE C E, ZHU Y Y, et al. Isolation, identification of a cellulose-degrading bacterium with IAA-producing ability and optimization of its culture conditions [J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2020, 36(12): 54−63.(in Chinese) [21] 刘丹丹, 李敏, 刘润进. 我国植物根围促生细菌研究进展 [J]. 生态学杂志, 2016, 35(3):815−824. doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.201603.033LIU D D, LI M, LIU R J. Recent advances in the study of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2016, 35(3): 815−824.(in Chinese) doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.201603.033 [22] SARWAR M, FRANKENBERGER W T Jr. Influence of L-tryptophan and auxins applied to the rhizosphere on the vegetative growth of Zea mays L [J]. Plant and Soil, 1994, 160(1): 97−104. doi: 10.1007/BF00150350 [23] 刘梦洁, 尹清强, 常娟, 等. 植物乳杆菌和纤维素酶对玉米秸秆降解及糖化效果的影响 [J]. 中国饲料, 2020(23):34−39.LIU M J, YIN Q Q, CHANG J, et al. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and cellulase on the degradation and saccharification of corn straw [J]. China Feed, 2020(23): 34−39.(in Chinese) [24] 张爱梅, 殷一然, 齐汝楠. 产纤维素酶沙棘根瘤内生放线菌的筛选、鉴定及其酶活性测定 [J]. 西北师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(5):71−76. doi: 10.16783/j.cnki.nwnuz.2019.05.013ZHANG A M, YIN Y R, QI R N. Screening, identification and enzyme activity of endophytic actinomycetes producing cellulase from root nodules of Hippophae rhamnoides [J]. Journal of Northwest Normal University (Natural Science), 2019, 55(5): 71−76.(in Chinese) doi: 10.16783/j.cnki.nwnuz.2019.05.013 [25] 朱凤, 陈夕军, 童蕴慧, 等. 水稻内生细菌的分离及其拮抗性与潜在致病性测定 [J]. 中国生物防治, 2007, 23(1):68−72.ZHU F, CHEN X J, TONG Y H, et al. Isolation of rice endophytic bacteria and their antagonism and potential pathogenicity [J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2007, 23(1): 68−72.(in Chinese) [26] 金玲, 巴峰, 计平生, 等. 小麦内生有害细菌的发现和作用研究 [J]. 植物病理学报, 1996, 26(2):123−126.JIN L, BA F, JI P S, et al. Discovery of deleterious endobacteria and their effects on growth of wheat [J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 1996, 26(2): 123−126.(in Chinese) -







 下载:
下载: