Characteristics of SSRs in Zicaitai Mitochondrial Genome
-
摘要:
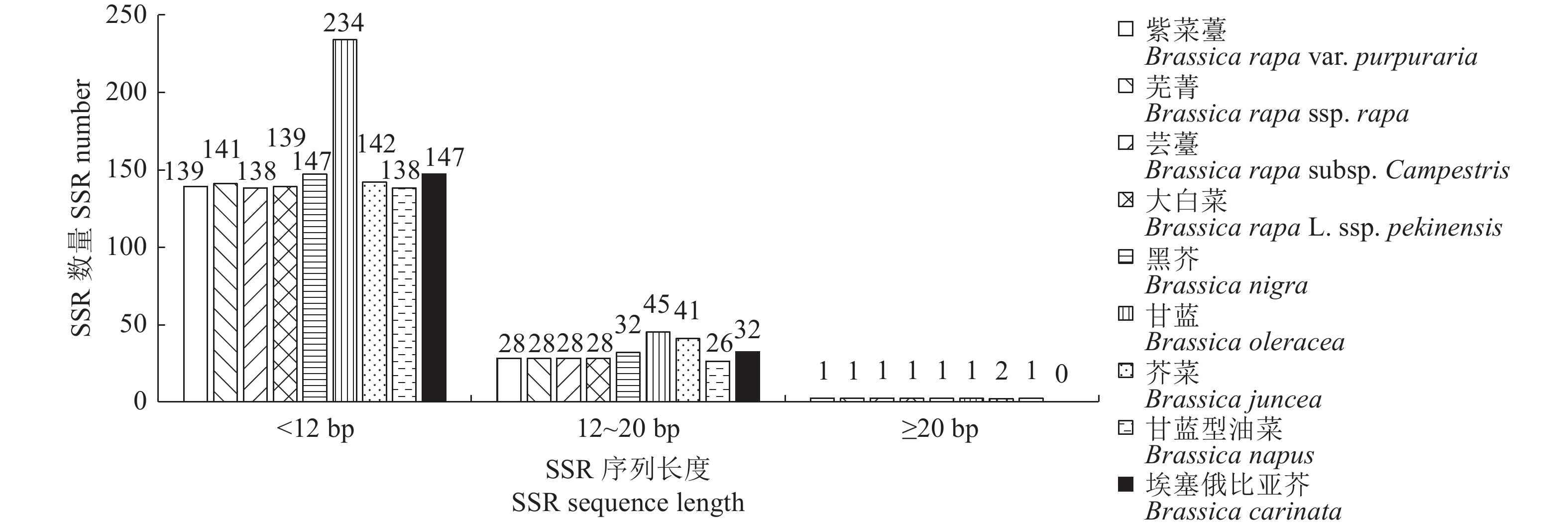
目的 分析紫菜薹(Brassica rapa var. purpuraria)线粒体基因组SSR序列的分布特征,并与芸薹属主要物种进行比较,为紫菜薹SSR分子标记的开发及遗传进化研究提供参考。 方法 利用MISA软件对紫菜薹及芸薹属6个基本种(包括白菜3个变种)的线粒体基因组进行搜索,并对搜索到的SSR序列分布特征进行比较分析。 结果 在紫菜薹及芸薹属6个基本种(包括白菜3个变种)的线粒体基因组中,分别筛选到168、170、167、168、180、280、185、165、179个完整的SSR序列,相对密度分别为764 、774 、760 、764 、775 、777、721 、744 、771 个·Mb−1,SSR序列的总长度分别为1562、1577、1547、1562、1664、2564、1722、1524、1646 bp,占各自线粒体基因组序列总长度的比例分别为0.71%、0.72%、0.70%、0.71%、0.72%、0.71%、0.67%、0.69%和0.71%。在1~6个不同核苷酸重复单元中,紫菜薹及芸薹属6个基本种的SSR序列均是单核苷酸重复单元最多,然后依次是二核苷酸、四核苷酸、三核苷酸、五核苷酸,均未发现六核苷酸重复单元。其中,A/T、AG/CT、AT/AT和C/G是芸薹属线粒体基因组共有的常见重复单元类型。 结论 紫菜薹线粒体基因组大小为219 779 bp,共筛选出168个SSR分子标记,相对密度为764 个·Mb−1,平均长度为9 bp,以单核苷酸重复单元的数量最多,其次为二、四核苷酸重复单元类型,具有较大的多态性标记开发潜力。 Abstract:Objective The simple sequence repeats (SSRs) in the mitochondrial genome of zicaitai (Brassica rapa var. Purpuraria) were compared with those of other species in the genus. Method MISA software was used to search the mitochondrial genomes of zicaitai as well as 5 other major species and 3 mutants of Brassica rapa. The SSR sequence distributions of the specimens were compared and analyzed. Result In the mitochondrial genomes, 168, 170, 167, 168, 180, 280, 185, 165, and 179 complete SSRs were screened. The sequences showed relative densities of 764, 774, 760, 764, 775, 777, 721, 744, and 771 per Mb with total lengths of 1562, 1577, 1547, 1562, 1664, 2564, 1722, 1524, and 1646 bp that accounted for 0.71%, 0.72%, 0.70%, 0.71%, 0.72%, 0.71%, 0.67%, 0.69%, and 0.71% of the total sequence length of each specimen, respectively. Among the 1-6 different nucleotide repeat units in zicaitai and the other major Brassica species, most SSRs were mononucleotide, which was followed by dinucleotide, tetranucleotide, trinucleotide, and pentanucleotide, but no hexonucleotide. A/T, AG/CT, AT/AT, and C/G were the common repeat unit types in them. Conclusion The mitochondrial genome of zicaitai was 219779 bp with 168 SSRs at the relative density of 764 markers/Mb and 9 bp in length. Mono-, di-, and tetra-nucleotides were the most abundant repeat units, which could potentially be developed as highly polymorphic markers for species differentiation. -
Key words:
- Zicaitai /
- Brassica /
- mitochondrion /
- SSR
-
表 1 紫菜薹及芸薹属线粒体基因组信息
Table 1. Mitochondrial genome sequences of zicaitai and other Brassica species
物种
Species染色体数
Number of chromosomesGenBank
登录号
GenBank accession线粒体
基因组大小
Genome size/bp紫菜薹
Brassica rapa var. purpurariaAA, 2n = 2x = 20 OP729396.1 219779 芜菁
Brassica rapa ssp. rapaAA, 2n = 2x = 20 NC_049892.1 219736 芸薹
Brassica rapa subsp. CampestrisAA, 2n = 2x = 20 NC_016125.1 219747 大白菜
Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensisAA, 2n = 2x = 20 MN910310 219778 黑芥
Brassica nigraBB, 2n = 2x = 16 NC_029182.1 232407 甘蓝
Brassica oleraceaCC, 2n = 2x = 18 NC_016118.1 360271 芥菜
Brassica junceaAABB, 2n = 4x = 36 MG872829.1 256592 甘蓝型油菜
Brassica napusAACC, 2n = 4x = 38 NC_008285.1 221853 埃塞俄比亚芥
Brassica carinataBBCC, 2n = 4x = 34 NC_016120.1 232241 表 2 紫菜薹及芸薹属线粒体基因组中SSR的分布概况
Table 2. Distribution of SSRs in mitochondrial genomes of zicaitai and other Brassica species
物种
SpeciesSSR总长度
Total length of SSR/bpSSR数量
SSR numberSSR分布密度
SSR density/(个·Mb−1)SSR平均长度
Average length of SSR/bpSSR长度占比
Length ratio of SSR/%紫菜薹
Brassica rapa var. purpuraria1562 168 764 9 0.71 芜菁
Brassica rapa ssp. rapa1577 170 774 9 0.72 芸薹
Brassica rapa subsp. Campestris1547 167 760 9 0.70 大白菜
Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis1562 168 764 9 0.71 黑芥
Brassica nigra1664 180 775 9 0.72 甘蓝
Brassica oleracea2564 280 777 9 0.71 芥菜
Brassica juncea1722 185 721 9 0.67 甘蓝型油菜
Brassica napus1524 165 744 9 0.69 埃塞俄比亚芥
Brassica carinata1646 179 771 9 0.71 表 3 紫菜薹及芸薹属线粒体基因组SSR重复单元的数目和占比
Table 3. Number and proportion of SSR repeat types in mitochondrial genomes of zicaitai and other Brassica species
物种
Species单核苷酸
Mononucleotide二核苷酸
Dinucleotide三核苷酸
Trinucleotide四核苷酸
Tetranucleotide五核苷酸
Pentanucleotide紫菜薹
Brassica rapa var. purpuraria83
(49.40%)61
(36.31%)5
(2.98%)18
(10.71%)1
(0.60%)芜菁
Brassica rapa ssp. rapa84
(49.41%)61
(35.88%)5
(2.94%)19
(11.18%)1
(0.59%)芸薹
Brassica rapa subsp. Campestris82
(49.10%)61
(36.53%)5
(2.99%)18
(10.78%)1
(0.60%)大白菜
Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis82
(48.81%)62
(36.90%)5
(2.98%)18
(10.71%)1
(0.60%)黑芥
Brassica nigra85
(47.22%)69
(38.33%)6
(3.33%)19
(10.56%)1
(0.56%)甘蓝
Brassica oleracea137
(48.93%)106
(37.86%)6
(2.14%)29
(10.36%)2
(0.71%)芥菜
Brassica juncea78
(42.16%)71
(38.38%)7
(3.78%)28
(15.14%)1
(0.54%)甘蓝型油菜
Brassica napus84
(50.91%)58
(35.15%)4
(2.42%)18
(10.91%)1
(0.61%)埃塞俄比亚芥
Brassica carinata85
(47.49%)68
(37.99%)6
(3.35%)19
(10.61%)1
(0.56%)表 4 紫菜薹及芸薹属线粒体基因组SSR的重复基元类型及数量
Table 4. Number of SSRs of mitochondrial genomes in zicaitai and other Brassica species
重复基元类型
Motif types紫菜薹
Brassica rapa var.
purpuraria芜菁
Brassica rapa ssp.
rapa芸薹
Brassica rapa subsp.
Campestris大白菜
Brassica rapa L. ssp.
pekinensis黑芥
Brassica
nigra甘蓝
Brassica
oleracea芥菜
Brassica
juncea甘蓝型油菜
Brassica
napus埃塞俄比亚芥
Brassica
carinataA/T 67 68 66 67 71 112 65 68 70 AG/CT 36 36 36 37 41 62 45 34 41 AT/AT 19 19 19 19 19 34 19 18 18 C/G 16 16 16 15 14 25 13 16 15 AATG/ATTC 5 5 5 5 5 8 5 5 5 AC/GT 4 4 4 4 7 7 5 4 7 AAG/CTT 4 4 4 4 4 5 5 3 4 AAAG/CTTT 4 4 4 4 3 6 10 5 3 AAAC/GTTT 3 4 3 3 4 5 4 3 4 AAAT/ATTT 3 3 3 3 3 4 3 3 3 CG/CG 2 2 2 2 2 3 2 2 2 AAC/GTT 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 AACG/CGTT 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 1 2 ACTC/AGTG 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 — 1 CCGG/CCGG 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 ACTAG/AGTCT 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 AGC/CTG — — — — 1 — 1 — 1 ACTG/AGTC — — — — — — 1 — — -
[1] 聂启军, 李金泉, 董斌峰, 等. 紫菜薹名优品种: 洪山菜薹 [J]. 湖北农业科学, 2020, 59(22):133−135.NIE Q J, LI J Q, DONG B F, et al. A famous variety of purple Caitai—Hongshan Caitai [J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences , 2020, 59(22): 133−135. (in Chinese) [2] 邝敏杰, 齐敏玉, 何静仁, 等. 紫菜薹花色苷组分鉴定及其稳定性和抗氧化性 [J]. 中国农业科学, 2014, 47(20):4067−4077.KUANG M J, QI M Y, HE J R, et al. Identification of anthocyanins in Brassica campestris L. and their stability and antioxidant activity [J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica , 2014, 47(20): 4067−4077. (in Chinese) [3] ZHANG X, ZHANG K, WU J, et al. QTL-seq and sequence assembly rapidly mapped the gene BrMYBL2.1 for the purple trait in Brassica rapa [J]. Scientific Reports , 2020, 10: 2328. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58916-5 [4] LI G H, CHEN H C, LIU J L, et al. A high-density genetic map developed by specific-locus amplified fragment (SLAF) sequencing and identification of a locus controlling anthocyanin pigmentation in stalk of Zicaitai ( Brassica rapa L. ssp. chinensis var. purpurea) [J]. BMC Genomics , 2019, 20(1): 343. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5693-2 [5] 吴朝林, 陈文超. 中国紫菜薹地方品种初步研究 [J]. 作物品种资源, 1997, (3):8−10.WU (C /Z)L, CHEN W C. Preliminary study on local varieties of Chinese purple flowering Chinese cabbage [J]. China Seed Industry , 1997(3): 8−10. (in Chinese) [6] 唐向民, 杨守臻, 陈怀珠, 等. 栽培大豆和野生大豆线粒体基因组密码子使用偏性的比较分析 [J]. 广西植物, 2020, 40(7):926−934.TANG X M, YANG S Z, CHEN H Z, et al. Comparative analysis on codon usage bias in mitogenome of two species in genus Glycine [J]. Guihaia , 2020, 40(7): 926−934. (in Chinese) [7] 王建军, 徐园园, 刘同坤, 等. 紫菜薹BrbHLH49基因克隆与功能分析 [J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2021, 44(3):421−427.WANG J J, XU Y Y, LIU T K, et al. Cloning and function analysis of BrbHLH49 gene in purple tsai-Tai [J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University , 2021, 44(3): 421−427. (in Chinese) [8] 郭宁, 郑姝宁, 武剑, 等. 紫菜薹、紫色芜菁和紫色白菜花青苷分析 [J]. 园艺学报, 2014, 41(8):1707−1715.GUO N, ZHENG S N, WU J, et al. The anthocyanin metabolic profiling analysis of three purple Brassica rapa vegetables [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica , 2014, 41(8): 1707−1715. (in Chinese) [9] 姚满昌. 紫菜薹: 小青菜: 水稻高效栽培模式 [J]. 长江蔬菜, 2017, (23):32−33.YAO M C. Efficient cultivation model of purple flowering cabbage-small vegetables-rice [J]. Journal of Changjiang Vegetables , 2017(23): 32−33. (in Chinese) [10] 郑海涛, 吴平安, 邓正春, 等. 富硒紫菜薹高产栽培关键技术 [J]. 湖南农业科学, 2012, (24):29−30.ZHENG H T, WU P A, DENG Z C, et al. Key techniques for high-yield cultivation of selenium-enriched purple flowering cabbage [J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences , 2012(24): 29−30. (in Chinese) [11] 朱红芳, 李晓锋, 奚丹丹, 等. 优质紫菜薹新品系“申薹紫仙” 的选育 [J]. 上海农业学报, 2021, 37(5):35−38.ZHU H F, LI X F, XI D D, et al. Breeding of a new high quality purple-Caitai “Shentaizixian” [J]. Acta Agriculturae Shanghai , 2021, 37(5): 35−38. (in Chinese) [12] 曹艳会. 紫菜薹雄性不育杂交制种技术 [J]. 种子科技, 2011, 29(10):30−31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2690.2011.10.019CAO Y H. Hybrid seed production techniques of male sterility in purple flowering Chinese flowering Chinese cabbage [J]. Seed Science & Technology , 2011, 29(10): 30−31. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2690.2011.10.019 [13] 白占兵, 丁茁荑, 李雪峰, 等. 紫菜薹总DNA的快速提取与SSR分子标记鉴定 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2009, 25(14):63−66.BAI Z B, DING Z Y, LI X F, et al. Rapid extraction total DNA from purple tsai-Tai and characterization with SSR molecular marker [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin , 2009, 25(14): 63−66. (in Chinese) [14] DING Z Y, BAI Z B, WU Y F, et al. Study on genetic relationship of purple tsai-Tai germplasms with SSR markers [J]. Agricultural Science & Technology , 2012, 13(8): 1664−1669. [15] 周晓波, 白占兵, 丁茁荑, 等. 利用SSR分析红菜苔的遗传多样性 [J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2012, 13(6):1088−1092.ZHOU X B, BAI Z B, DING Z Y, et al. Genetic diversity of tsai-Tai germplasm revealed by SSR markers [J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources , 2012, 13(6): 1088−1092. (in Chinese) [16] 戴希刚, 郭瑞, 陶敏, 等. 红菜薹种质资源遗传多样性ISSR分析 [J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2019, 41(1):154−162.DAI X G, GUO R, TAO M, et al. ISSR analysis of genetic diversity of germplasm resources in purple flowering stalk [J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis , 2019, 41(1): 154−162. (in Chinese) [17] 张婉, 崔继哲, 于拴仓, 等. 白菜品种的SSR指纹图谱数据库的构建 [J]. 分子植物育种, 2013, 11(6):843−857.ZHANG W, CUI J Z, YU S C, et al. Construction o f SSR fingerprint database of Chinese cabbage varieties( Brassica campestris L. ssp. pekinensis) [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding , 2013, 11(6): 843−857. (in Chinese) [18] 李光光, 黄红弟, 张华, 等. 利用SSR分子标记研究白菜类亚种资源的遗传多样性 [J]. 热带作物学报, 2017, 38(7):1316−1322.LI G G, HUANG H D, ZHANG H, et al. Genetic diversity analysis in Chinese cabbage[ssp. chinensis(L. ) makino]resources based on SSR molecular markers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops , 2017, 38(7): 1316−1322. (in Chinese) [19] 王晶, 闫国华, 张晓明, 等. 甜樱桃高密度连锁图谱的构建 [J]. 果树学报, 2014, 31(S1):29−35.WANG J, YAN G H, ZHANG X M, et al. Construction of high density linkage map of sweet cherry [J]. Journal of Fruit Science , 2014, 31(S1): 29−35. (in Chinese) [20] 马猛, 闫会, 高闰飞, 等. 紫甘薯SSR标记遗传图谱构建与重要农艺性状QTL定位 [J]. 作物学报, 2021, 47(11):2147−2162. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2021.04271MA M, YAN H, GAO R F, et al. Construction linkage maps and identification of quantitative trait loci associated with important agronomic traits in purple-fleshed sweetpotato [J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica , 2021, 47(11): 2147−2162. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2021.04271 [21] REN Y J. The complete mitochondrial genome of turnip ( Brassica rapa ssp. rapa) [J]. Mitochondrial DNA Part B , 2021, 6(4): 1566−1567. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2021.1917314 [22] CHANG S X, YANG T T, DU T Q, et al. Mitochondrial genome sequencing helps show the evolutionary mechanism of mitochondrial genome formation in Brassica [J]. BMC Genomics , 2011, 12: 497. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-497 [23] LI P R, ZHANG D S, SU T B, et al. Genome-wide analysis of mRNA and lncRNA expression and mitochondrial genome sequencing provide insights into the mechanisms underlying a novel cytoplasmic male sterility system, BVRC-CMS96, in Brassicarapa [J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics , 2020, 133(7): 2157−2170. doi: 10.1007/s00122-020-03587-z [24] HANDA H. The complete nucleotide sequence and RNA editing content of the mitochondrial genome of rapeseed ( Brassica napus L. ): Comparative analysis of the mitochondrial genomes of rapeseed and Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Nucleic Acids Research , 2003, 31(20): 5907−5916. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg795 [25] BEIER S, THIEL T, MÜNCH T, et al. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction [J]. Bioinformatics, 2017, 33(16): 2583−2585. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx198 [26] 邱炳发, 梁馨元, 王建忠, 等. 大花序桉基因组SSR的分布特征及序列分析 [J]. 南方农业学报, 2021, 52(10):2744−2750. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2021.10.014QIU B F, LIANG X Y, WANG J Z, et al. Characteristics and analysis of simple sequence repeats(SSR) in Eucalyptus cloeziana genome [J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture , 2021, 52(10): 2744−2750. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2021.10.014 [27] 李新玉, 王希胤. 重复序列对植物基因组大小进化的影响 [J]. 华北理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 43(4):98−107.LI X Y, WANG X Y. Effects of repetitive sequences to evolution of plant genome size [J]. Journal of North China University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition) , 2021, 43(4): 98−107. (in Chinese) [28] ZHAO C X, ZHU R L, LIU Y. Simple sequence repeats in bryophyte mitochondrial genomes [J]. Mitochondrial DNA Part A, DNA Mapping, Sequencing, and Analysis , 2016, 27(1): 191−197. [29] SHEN J S, LI X Q, LI M Z, et al. Characterization, comparative phylogenetic, and gene transfer analyses of organelle genomes of Rhododendron × pulchrum [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science , 2022, 13: 969765. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.969765 [30] VARSHNEY R K, GRANER A, SORRELLS M E. Genic microsatellite markers in plants: Features and applications [J]. Trends in Biotechnology , 2005, 23(1): 48−55. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2004.11.005 [31] BIET E, SUN J, DUTREIX M. Conserved sequence preference in DNA binding among recombination proteins: An effect of ssDNA secondary structure [J]. Nucleic Acids Research , 1999, 27(2): 596−600. doi: 10.1093/nar/27.2.596 [32] 周勃, 任海龙, 张龑, 等. 金花菜与苜蓿属主要物种基因组SSR分布特征的比较分析 [J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(9):2217−2223.ZHOU B, REN H L, ZHANG Y, et al. Characteristics and analysis of simple sequence repeats(SSR) in Medicago polymorpha and main medicagospecies genome [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences , 2022, 59(9): 2217−2223. (in Chinese) [33] LIU G , XIE Y J, ZHANG D Q, et al. Analysis of SSR loci and development of SSR primers in Eucalyptus [J]. Journal of Forestry Research, 2018, 29(2): 273−282. [34] 严佳文, 解璞, 袁启凤, 等. 紫果西番莲基因组调查及SSR特征分析 [J]. 分子植物育种, 2020, 18(24):8171−8177.YAN J W, XIE P, YUAN Q F, et al. Genome survey and characteristic analysis of SSR in Passiflora edulis Sims [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding , 2020, 18(24): 8171−8177. (in Chinese) [35] 奚丹丹, 高璐, 李晓锋, 等. 基于转录组测序的菜薹SSR分子标记开发及初步验证[J/OL]. 分子植物育种, 1-8[2024-01-16] http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20220916.1333.050.html.XI D D, GAO L, LI X F, et al. Development and Identification of SSR Molecular Markers Based on Transcriptome Sequencing of Caitai[J/OL]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 1-8[2024-01-16] http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20220916.1333.050.html.(in Chinese) -







 下载:
下载:

