Cloning and Expression of Mannose-1-phosphate Guanyltransferase Gene in Anoectochilus roxburghii
-
摘要:
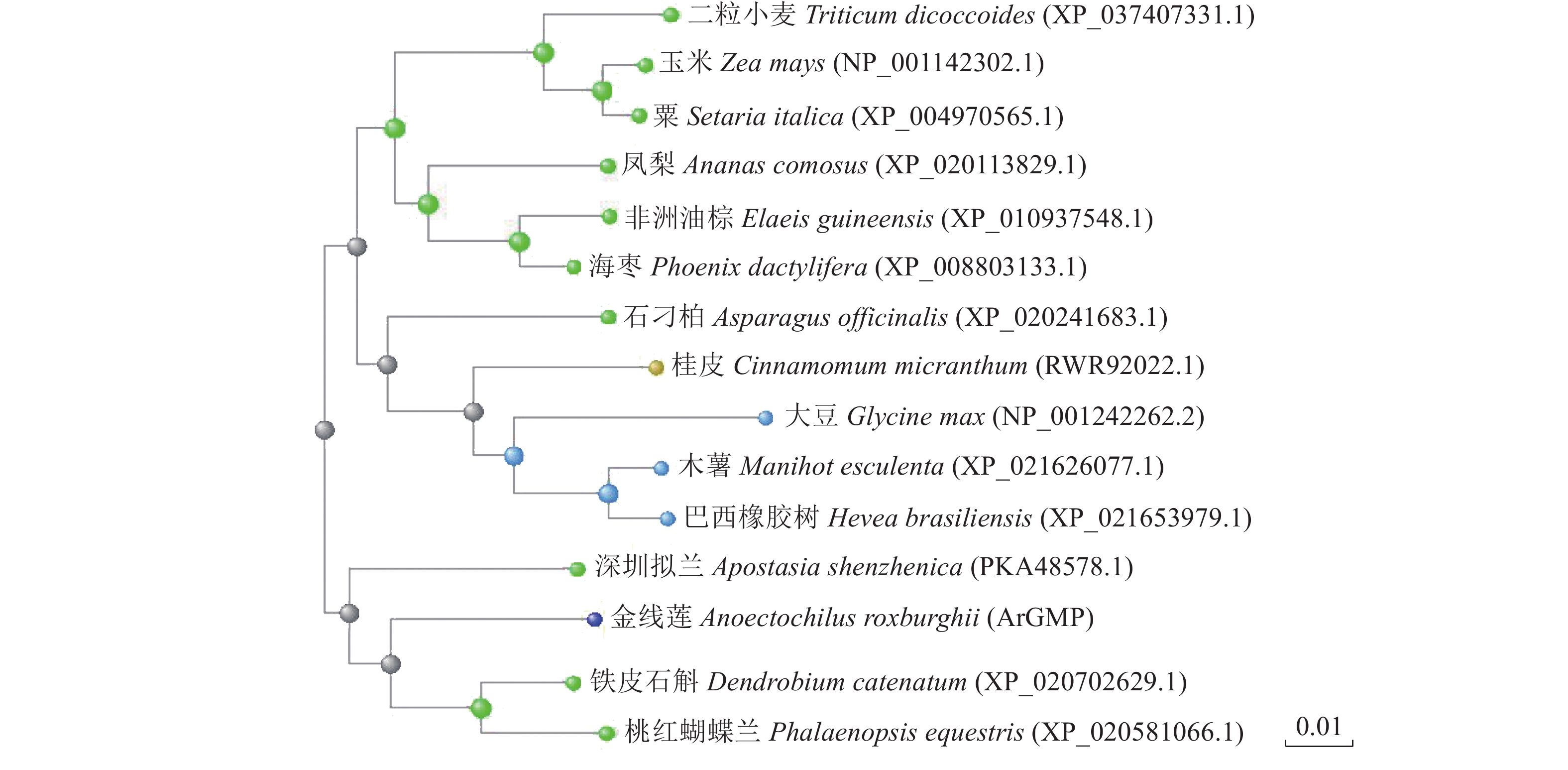
目的 甘露糖是金线莲多糖重要组成成分,对甘露糖-1-磷酸尿苷转移酶(GMP)基因进行克隆和基因表达调控分析,为进一步研究金线莲多糖的生物合成奠定基础。 方法 以梅花山金线莲植株为材料,克隆ArGMP基因的cDNA序列和基因组序列,利用在线软件进行生物信息学分析,并对其基因表达调控模式进行qRT-PCR分析。 结果 金线莲ArGMP基因ORF区序列长1086 bp,共编码361个氨基酸;基因组序列长度为1760 bp,含有3个内含子,GenBank登录号OQ030271。生物信息学分析表明:ArGMP蛋白是一种较稳定的、无跨膜结构的亲水蛋白,该蛋白与铁皮石斛、深圳拟兰、蝴蝶兰等兰科植物的亲缘关系较近。qRT-PCR结果显示:ArGMP基因在金线莲不同组织中的表达量差异显著,在花中的表达量最高;在不同种植温度处理条件下,25 ℃时表达量最高,高温严重抑制其表达;35 ℃高温处理不同时间显示,处理3 h后ArGMP基因表达量显著下降;而不同浓度NaCl胁迫处理对ArGMP基因表达基本无影响。 结论 克隆了甘露糖-1-磷酸尿苷转移酶基因的cDNA序列和基因组序列,发现该基因具有组织特异性表达的特点,且该基因受温度调控,而不受盐胁迫调控,这为进一步研究金线莲多糖生物合成调控机制奠定理论基础。 -
关键词:
- 金线莲 /
- 甘露糖-1-磷酸尿苷转移酶 /
- 多糖 /
- 基因表达
Abstract:Objective Cloning and expression of mannose-1-phosphate guanyltransferase (GMP) gene that regulates the polysaccharide synthesis in Anoectochilus roxburghii were studied. Method ArGMP cDNA and genome sequences were cloned, and bioinformatics analyzed using online software. Gene expression pattern was then determined by qRT-PCR. Result The ORF of ArGMP was 1 086 bp encoded 361 amino acids with a length of 1 760 bp that contained 3 introns. It has an accession number of OQ030271 in GenBank. A stable hydrophilic protein free of a transmembrane structure, it was closely related to those of Dendrobium officinale, Apostasia shenzhenica, and Phalaenopsis equestris. Expressed differently in different tissues, the highest level was found in the flowers. The expression varied under different temperatures that peaked at 25 ℃, decreased significantly after 3 h at 35 ℃, and was severely inhibited beyond that. However, it was not affected by the stress exerted by NaCl in different concentrations. Conclusion The cDNA and sequence of GMP gene from A. roburghii were successfully cloned to display a tissue-specific expression pattern that could be significantly affected by temperature but not salt stress. -
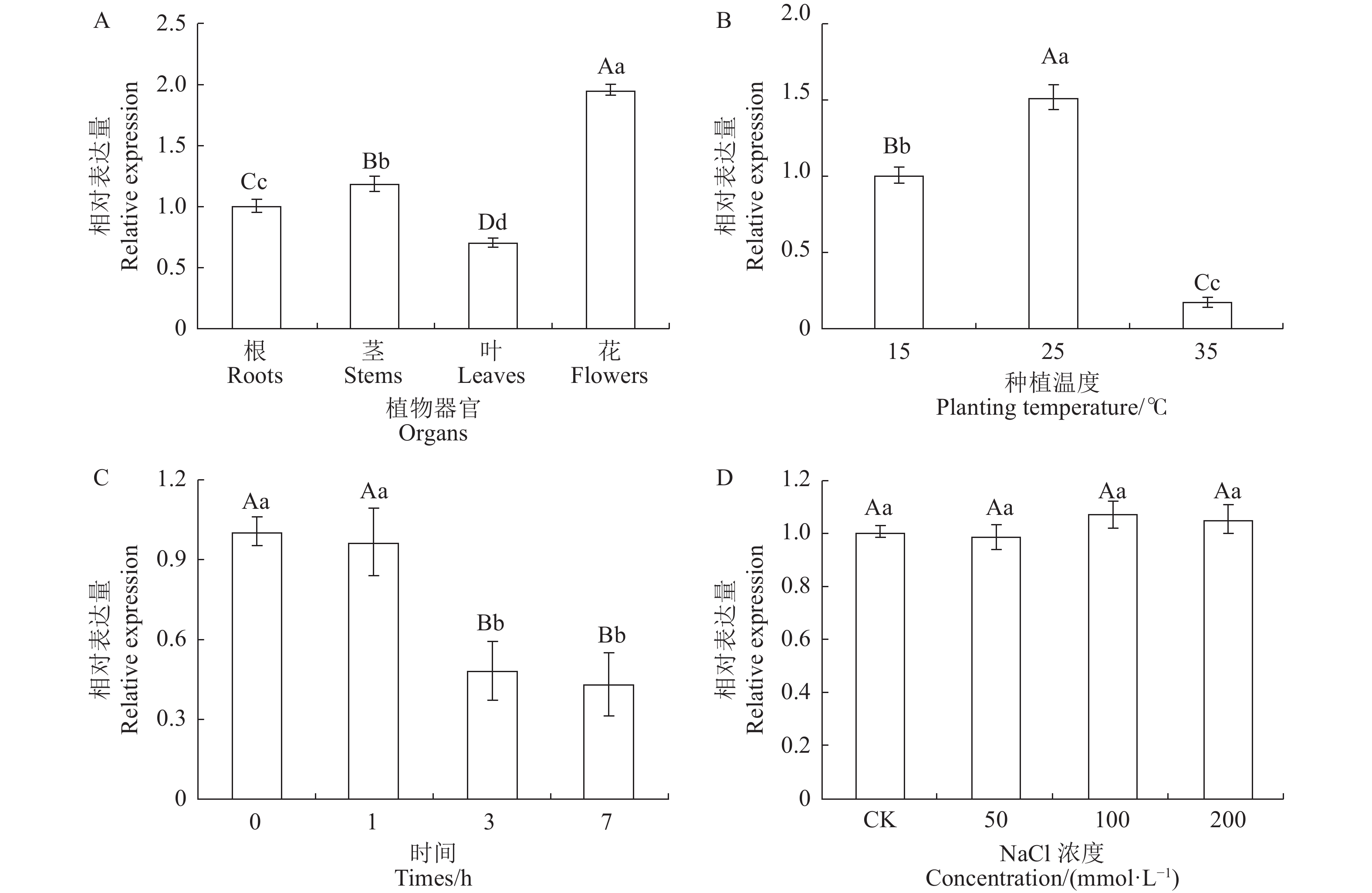
图 5 ArGMP基因在不同处理的表达情况
A:不同组织样品;B:不同种植温度处理;C:高温处理不同时间;D:盐胁迫处理。不同大、小写字母表示处理间差异极显著(P<0.01)或显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 5. Expressions of ArGMP under different treatments
A: Different tissues; B: different temperatures; C: high temperature treatment; D: salt stress. Data with different capital letters indicate extremely significant differences atP<0.01; those with different lowercase letters, significant differences at P<0.05.
表 1 基因克隆和RT-qPCR引物序列
Table 1. Sequences of cloned gene and RT-qPCR primer
引物名称
Primer正向引物(5′-3′)
Forward primer(5′-3′)反向引物(5′-3′)
Reverse primer(5′-3′)作用
FunctiongGMP ACCATGAAAGCCCTAATTCTTG TCACATAACAATCTCAGGCT 基因克隆 Gene clone GMP-RT CCTTCTAAGCTGGCTTTCGG CAACTCTTGCCCACTGTCCC qRT-PCR Actin AGATGAGGCACAGTCCAAGA GCTGGAACATTGAAGGTCTC 内参基因 Reference gene 表 2 ArGMP蛋白的基元和结构域分析
Table 2. Motifs and domains of ArGMP
结构域
Motifs or Domains结构域功能中文描述
Function of domain结构域在ArGMP中的位置
Domain position in ArGMPASN_GLYCOSYLATION N-糖基化 aa323~326 CAMP_PHOSPHO_SITE 依赖cAMP和cGMP蛋白激酶磷酸化 aa238~242 CK2_PHOSPHO_SITE 酪蛋白激酶II磷酸化 aa137~140,aa182~185,aa192~195,aa262~265 MYRISTYL N-蛋白质豆蔻酰化 aa8~13,aa72~77,aa129~134,aa169~174,aa278~283,aa284~289 PKC_PHOSPHO_SITE 蛋白激酶 C 磷酸化 aa154~156,aa236~238 TYR_PHOSPHO_SITE 酪氨酸激酶磷酸化 aa138~145,aa201~209 -
[1] 中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会. 中国植物志-第六卷, 第一分册-蕨类植物门[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1999: 204-227. [2] YANG Z G, ZHANG X H, YANG L W, et al. Protective effect of Anoectochilus roxburghii polysaccharide against CCl4-induced oxidative liver damage in mice [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2017, 96: 442−450. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.12.039 [3] 马玉芳, 郑小香, 郑乃珍, 等. 金线莲多糖协同ConA对小鼠脾淋巴细胞分泌Th1、Th2型细胞因子及其mRNA表达量的影响 [J]. 中国食品学报, 2018, 18(4):72−78. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2018.04.011MA Y F, ZHENG X X, ZHENG N Z, et al. Regulatory effects of Anoectochilus roxburghii polysaccharide(ARP) on ConA-induced cytokines secretion and mRNA expression by murine splenocytes [J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2018, 18(4): 72−78.(in Chinese) doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2018.04.011 [4] GUO Y L, YE Q, YANG S L, et al. Therapeutic effects of polysaccharides from Anoectochilus roxburghii on type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2019, 122: 882−892. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.015 [5] YU X L, LIN S E, ZHANG J Q, et al. Purification of polysaccharide from artificially cultivated Anoectochilus roxburghii (wall. ) Lindl. by high-speed counter current chromatography and its antitumor activity [J]. Journal of Separation Science, 2017, 40(22): 4338−4346. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201700340 [6] TANG T T, DUAN X Y, KE Y, et al. Antidiabetic activities of polysaccharides from Anoectochilus roxburghii and Anoectochilus formosanus in STZ-induced diabetic mice [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2018, 112: 882−888. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.02.042 [7] 王常青, 严成其, 王勇, 等. 台湾金线莲多糖的分离纯化及其体外抑瘤活性研究 [J]. 中国生化药物杂志, 2008, 28(2):93−96.WANG C Q, YAN C Q, WANG Y, et al. Isolaiton, purification and in vitro anti-tumor activities of Anoectochilus formosanus polysaccharide [J]. Chinese Journal of Biochemical Pharmaceutics, 2008, 28(2): 93−96.(in Chinese) [8] 林守二, 黄丽英, 俞晓玲. 柱前衍生化HPLC法分析人工栽培金线莲中多糖的单糖组成 [J]. 福建医科大学学报, 2016, 50(3):148−154. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4194.2016.03.002LIN S E, HUANG L Y, YU X L. Analyze monosaccharide composition of polysaccharide in artificial cultivated Anoectochilus roxburghii by pre-column derivatization HPLC [J]. Journal of Fujian Medical University, 2016, 50(3): 148−154.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4194.2016.03.002 [9] NARASAKI C T, MERTENS K, SAMUEL J E. Characterization of the GDP-D-mannose biosynthesis pathway in Coxiella burnetii: The initial steps for GDP-β-D-virenose biosynthesis [J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(10): e25514. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025514 [10] PENG L, LI J, LIU Y, et al. Effects of mixed carbon sources on galactose and mannose content of exopolysaccharides and related enzyme activities in Ganoderma lucidum [J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(45): 39284−39291. doi: 10.1039/C6RA04798J [11] 赵丽娜, 徐军伟. 过表达GDP-D-甘露糖焦磷酸化酶(GMP)基因提高灵芝多糖的生产 [J]. 菌物学报, 2021, 40(5):1099−1109.ZHAO L N, XU J W. Overexpression of GDP-D-mannose pyrophosphorylase (GMP) gene improves the production of polysaccharides in Ganoderma lingzhi [J]. Mycosystema, 2021, 40(5): 1099−1109.(in Chinese) [12] ZHOU J S, BAI Y, DAI R J, et al. Improved polysaccharide production by homologous co-overexpression of phosphoglucomutase and UDP glucose pyrophosphorylase genes in the mushroom Coprinopsis cinerea [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2018, 66(18): 4702−4709. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b01343 [13] HOWLETT R, READ N, VARGHESE A, et al. Streptomyces coelicolor strains lacking polyprenol phosphate mannose synthase and protein O-mannosyl transferase are hyper-susceptible to multiple antibiotics [J]. Microbiology, 2018, 164(3): 369−382. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000605 [14] 李鹏佳, 焦茂娟, 王启军, 等. 魔芋GDP-甘露糖焦磷酸化酶基因及其启动子的克隆与分析 [J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 41(3):14−22. doi: 10.13718/j.cnki.xdzk.2019.03.003LI P J, JIAO M J, WANG Q J, et al. Cloning and characterization of GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase gene in konjac and its promoter [J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 41(3): 14−22.(in Chinese) doi: 10.13718/j.cnki.xdzk.2019.03.003 [15] 郑云柯, 胡翔宇, 宋希强, 等. 石斛属植物基因组DNA提取方法的对比 [J]. 热带生物学报, 2015, 6(2):168−172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7054.2015.02.011ZHENG Y K, HU X Y, SONG X Q, et al. Optimized extraction method for genomic DNA from Dendrobium Species (Orchidaceae) [J]. Journal of Tropical Biology, 2015, 6(2): 168−172.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7054.2015.02.011 [16] 林江波, 王伟英, 邹晖, 等. 金线莲3个持家基因表达稳定性分析 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2018, 33(11):1125−1129. doi: 10.19303/j.issn.1008-0384.2018.11.001LIN J B, WANG W Y, ZOU H, et al. Expression stabilities of three housekeeping genes of Anoectochilus roxburghii [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 33(11): 1125−1129.(in Chinese) doi: 10.19303/j.issn.1008-0384.2018.11.001 [17] LIVAK K J, SCHMITTGEN T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−△△Ct Method. Methods,2001, 25(4), 402-408. [18] CRONJE C, GEORGE G M, FERNIE A R, et al. Manipulation of l-ascorbic acid biosynthesis pathways in Solanum lycopersicum: Elevated GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase activity enhances l-ascorbate levels in red fruit [J]. Planta, 2012, 235(3): 553−564. doi: 10.1007/s00425-011-1525-6 [19] 申艳红, 陈晓静, 卢秉国, 等. 番木瓜GDP-D-甘露糖焦磷酸化酶基因的克隆及分析 [J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 40(2):172−177. doi: 10.13323/j.cnki.j.fafu(nat.sci.).2011.02.017SHEN Y H, CHEN X J, LU B G, et al. Cloning and analysis of GDP-D-mannose pyrophosphorylase gene from papaya [J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 40(2): 172−177.(in Chinese) doi: 10.13323/j.cnki.j.fafu(nat.sci.).2011.02.017 [20] 范林洪, 李锐, 童永鳌, 等. 金发草GDP-D-甘露糖焦磷酸化酶基因的克隆及功能分析 [J]. 四川大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 52(3):682−688.FAN L H, LI R, TONG Y A, et al. Cloning and analysis of GDP-D-mannose pyrophosphorylase gene from Pogonatherum paniceum [J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 52(3): 682−688.(in Chinese) [21] WANG C K, PENG D Y, ZHU J H, et al. Transcriptome analysis of Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua: Identification of genes involved in polysaccharide biosynthesis [J]. Plant Methods, 2019, 15(1): 1−14. doi: 10.1186/s13007-018-0385-5 [22] SAWAKE S, TAJIMA N, MORTIMER J C, et al. KONJAC1 and 2 are key factors for GDP-mannose generation and affect l-ascorbic acid and glucomannan biosynthesis in Arabidopsis [J]. The Plant Cell, 2015, 27(12): 3397−3409. doi: 10.1105/tpc.15.00379 [23] 肖瑶, 周天山, 李佼, 等. 茶树GDP-D-甘露糖焦磷酸化酶基因cDNA全长的克隆与表达分析 [J]. 茶叶科学, 2015, 35(1):55−63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2015.01.010XIAO Y, ZHOU T S, LI J, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of GDP-D-mannose pyrophosphorylase c DNA in Camellia sinensis [J]. Journal of Tea Science, 2015, 35(1): 55−63.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2015.01.010 [24] 李超汉, 李青竹, 史庆华, 等. 超表达番茄GDP-D-甘露糖焦磷酸化酶基因马铃薯对温度胁迫的响应 [J]. 中国农业科学, 2011, 44(23):4952−4961. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2011.23.024LI C H, LI Q Z, SHI Q H, et al. Effect of tomato GMPase overexpression on tolerance of potato plants to temperature stress [J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2011, 44(23): 4952−4961.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2011.23.024 [25] 程智慧, 关志华, 薛琳, 等. 叶面喷施NaCl对加工番茄果实耐挤压性和品质的影响 [J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 35(2):97−100, 105. doi: 10.13207/j.cnki.jnwafu.2007.02.021CHENG Z H, GUAN Z H, XUE L, et al. Effects of foliage application of sodium chloride on fruit compression tolerance and quality in processing tomato [J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2007, 35(2): 97−100, 105.(in Chinese) doi: 10.13207/j.cnki.jnwafu.2007.02.021 [26] 鲁少尉, 齐飞, 李天来. NaCl胁迫对番茄叶片光合特性及蔗糖代谢的影响 [J]. 北方园艺, 2012(9):14−18.LU S W, QI F, LI T L. Effect of NaCl stress on photosynthetic characteristics and sucrose metabolizing in tomato leaf [J]. Northern Horticulture, 2012(9): 14−18.(in Chinese) -








 下载:
下载: