Net Electric Charges of Dual Targeted Proteins in Mitochondria and Plastid of Plants
-
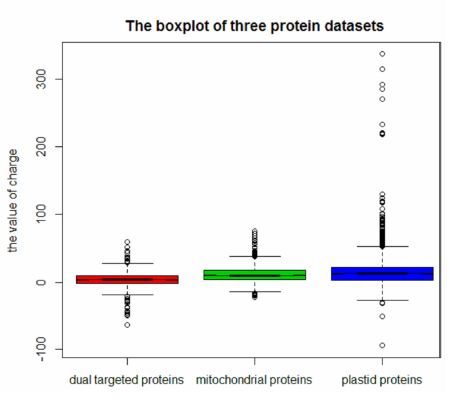
摘要: 蛋白质亚细胞定位分析是揭示蛋白质功能的关键步骤。1个蛋白质分子能被定位到2个亚细胞位置,这一现象被称为蛋白质的“双定位”。本研究首先从Uniprot、MitoP2、MGI、TAIR、DBMLoc等蛋白质数据库及已发表文献中收集双定位于线粒体与质体的植物蛋白质数据,共获得703个双定位蛋白质,组成测试数据集。再从Uniprot数据库中选取唯一定位于线粒体的829个和唯一定位于质体的6 376个植物蛋白质,组成参照数据集,分析双定位于线粒体与质体的植物蛋白质的带电特征。结果表明,与单定位于线粒体或质体的植物蛋白质相比,双定位线粒体与质体的植物蛋白质具有更低的净电荷量;此外,双定位蛋白质电荷分布较为集中对称,线粒体蛋白质次之,质体蛋白质最为分散。本文研究结果将为揭示植物蛋白质双定位的分子机制奠定理论基础。Abstract: Protein targeting is an important tool to determine the functionality of a protein. Adual targeted protein isa protein that located in two subcellular locations. It was estimated that more than 400 proteins were putatively targeted to mitochondria as well as plastid based on the ambiguous N-terminal pre-sequences in land plant genomes. In this study, the dual targeted proteins were searched against the protein databases of Uniprot, Mito P2, MGI, TAIR, and DBMLoc as well as the existing publications. A total of 703 proteins localized in both mitochondria and plastid in plants were collected. Whilst, 829 exclusive mitochondrial and 6 376 exclusive plastid proteins were downloaded from Uniprotfor comparison. The net electric charges of the dual targeted proteins were analyzed based on these 3 data sets. The results indicated the net charge of the plant dual targeted proteins was significantly lower than that of the proteins exclusively existed in mitochondrial or plastid. The charge differentiation provideda critical clue for the study of the molecular mechanism of dual targeted proteins in plants.
-
Key words:
- dual targeted protein /
- plant /
- mitochondria /
- plastid /
- net electric charge
-
表 1 双定位于质体和线粒体、单定位于质体或线粒体的植物蛋白质及其转运肽数量
Table 1. Quantities of dual targeted,mitochondrion,and plastid proteins in plants
数据集 蛋白质数量/个 转运肽数量/个 双定位蛋白质 703 17 单定位于线粒体蛋白质 829 376 单定位于质体蛋白质 6376 686 表 2 不同物种中鉴定的植物双定位蛋白质
Table 2. Numbers of identified dual targeted proteins in mitochondrion and plastid in differentplant species
物种 蛋白质数量/个 比例/% 拟南芥Arabidopsis thaliana 669 95.16 水稻Oryza sativa 11 1.56 玉米Zea mays 4 0.57 烟草Nicotiana tabacum 3 0.43 橡胶树Hevea brasiliensis 3 0.43 美花烟草Nicotiana sylvestris 2 0.28 小立碗藓Physcomitrella patens 2 0.28 本氏烟Nicotiana benthamiana 2 0.28 陆地棉Gossypium hirsutum 2 0.28 草莓Fragaria ananassa 1 0.14 表 3 3个蛋白质数据集净电荷的基本统计数值
Table 3. Basic statistics of electric charges of 3 protein datasets
N Median Mean Sd dual targeted proteins 703 4 4.32055 11.80667 mitochondria proteins 829 10.5 11.93426 12.45905 plastid proteins 6376 13 14.59857 18.07391 注:*N代表数据集包含的总数,Median代表数据集的中位数,Mean代表数据集的平均值,Sd代表数据集的标准差。 表 4 连续修正的左边Mann-Whitney秩和检验
Table 4. Left sided Mann-Whitney rank sum test with continuity correction
线粒体蛋白质 质体蛋白质 双定位蛋白质 W=184273.5,p-value,<2.2e-16 W=1336275,p-value<2.2e-16 线粒体蛋白质 - W = 2405490,p-value=9.898e-06 质体蛋白质 - - 注:W是Wilcoxon-MannWhitne统计量。 -
[1] YOGEV O,PINES O.Dual targeting of mitochondrial proteins:mechanism,regulation and function[J].Biochim Biophys Acta,2011,1808(3):1012-1020. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2010.07.004 [2] MITSCHKE J,FUSS J,BLUM T,et al.Prediction of dual protein targeting to plant organelles[J].New Phytol,2009,183(1):224-235. doi: 10.1111/nph.2009.183.issue-1 [3] CARRIE C,SMALL I.A reevaluation of dual-targeting of proteins to mitochondria and chloroplasts[J].Biochim Biophys Acta,2013,1833(2):253-259. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.05.029 [4] SILVAFILHO M C.One ticket for multiple destinations:dual targeting of proteins to distinct subcellular locations[J].Curr Opin Plant Biol,2003,6(6):589-595. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2003.09.008 [5] KARNIELY S,PINES O.Single translation-dual destination:mechanisms of dual protein targeting in eukaryotes[J].EMBO reports,2005,6(5):420-425. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400394 [6] CONSORTIUM U P.The Universal Protein Resource (UniProt) in 2010[J].Nucleic Acids Res,2010,38(Database issue):D142-148. [7] ELSTNER M,ANDREOLI C,KLOPSTOCK T,et al.The mitochondrial proteome database:MitoP2[J].Methods Enzymol,2009,457:3-20. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(09)05001-0 [8] DRABKIN H J, BLAKE J A.Manual Gene Ontology annotation workflow at the Mouse Genome Informatics Database[J].Database,2012,2012:bas045. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2147984368&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [9] LAMESCH P,BERARDINI T Z,LI D.The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR):improved gene annotation and new tools[J].Nucleic Acids Res,2012,40(Database issue):D1202-D1210. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1090 [10] ZHANG S,XIA X,SHEN J,et al.DBMLoc:a Database of proteins with multiple subcellular localizations[J].BMC Bioinformatics,2008,9:127. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-127 [11] EMANUELSSON O,NIELSEN H,BRUNAK S,et al.Predicting subcellular localization of proteins based on their N-terminal amino acid sequence[J].J Mol Biol,2000,300(4):1005-1016. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.3903 [12] HORTON P,PARK K J,OBAYASHI T,et al.WoLF PSORT:protein localization predictor[J].Nucleic Acids Res,2007,35(Web Server issue):W585-587. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm259 [13] BLUM T,BRIESEMEISTER S,KOHLBACHER O.MultiLoc2:integrating phylogeny and Gene Ontology terms improves subcellular protein localization prediction[J].BMC Bioinformatics,2009,(10):274. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1982228765&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [14] SMALL I,PEETERS N,LEGEAI F,et al.Predotar:A tool for rapidly screening proteomes for N-terminal targeting sequences[J].Proteomics,2004,4(6):1581-1590. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1615-9861 [15] YU C,CHEN Y,LU C,et al.Prediction of protein subcellular localization[J].Proteins,2006,64(3):643-651. doi: 10.1002/prot.21018 [16] CHOU K,SHEN H.Plant-mPLoc:a top-down strategy to augment the power for predicting plant protein subcellular localization[J].PLoS One,2010,5(6):e11335. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011335 [17] MORGANTE C V,RODRIGUES R A,MARBACH P A,et al.Conservation of dual-targeted proteins in Arabidopsis and rice points to a similar pattern of gene-family evolution[J].Mol Genet Genomics,2009,281(5):525-538. doi: 10.1007/s00438-009-0429-7 [18] SCHWACKE R,FISCHER K,KETELSEN B,et al.Comparative survey of plastid and mitochondrial targeting properties of transcription factors in Arabidopsis and rice[J].Mol Genet Genomics,2007,277(6):631-646. doi: 10.1007/s00438-007-0214-4 [19] CARRIE C,GIRAUD E,WHELAN J.Protein transport in organelles:Dual targeting of proteins to mitochondria and chloroplasts[J].FEBS J,2009,276(5):1187-1195. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.06876.x [20] CAMON E,MAGRANE M,BARRELL D,et al.The Gene Ontology Annotation (GOA) Database:sharing knowledge in Uniprot with Gene Ontology[J].Nucleic Acids Res,2004,32(Database issue):D262-D266. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh021 [21] BERGLUND A K,SPANNING E,BIVERSTAHL H,et al.Dual targeting to mitochondria and chloroplasts:characterization of Thr-tRNA synthetase targeting peptide[J].Mol Plant,2009,2(6):1298-1309. doi: 10.1093/mp/ssp048 [22] PUJOL C,MARECHAL-DROUARD L,DUCHENE A M.How can organellar protein N-terminal sequences be dual targeting signals in silico analysis and mutagenesis approach[J].J Mol Biol,2007,369(2) 356-367. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.03.015 [23] DINURMILLS M,TAL M,PINES O.Dual targeted mitochondrial proteins are characterized by lower MTS parameters and total net charge[J].PLoS One,2008,3(5):e2161. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002161 -








 下载:
下载: