Isolation, identification, biological characteristics, and indoor drug screening of the pathogenic bacteria of Atractylodes macrocephala root rot disease
-
摘要:
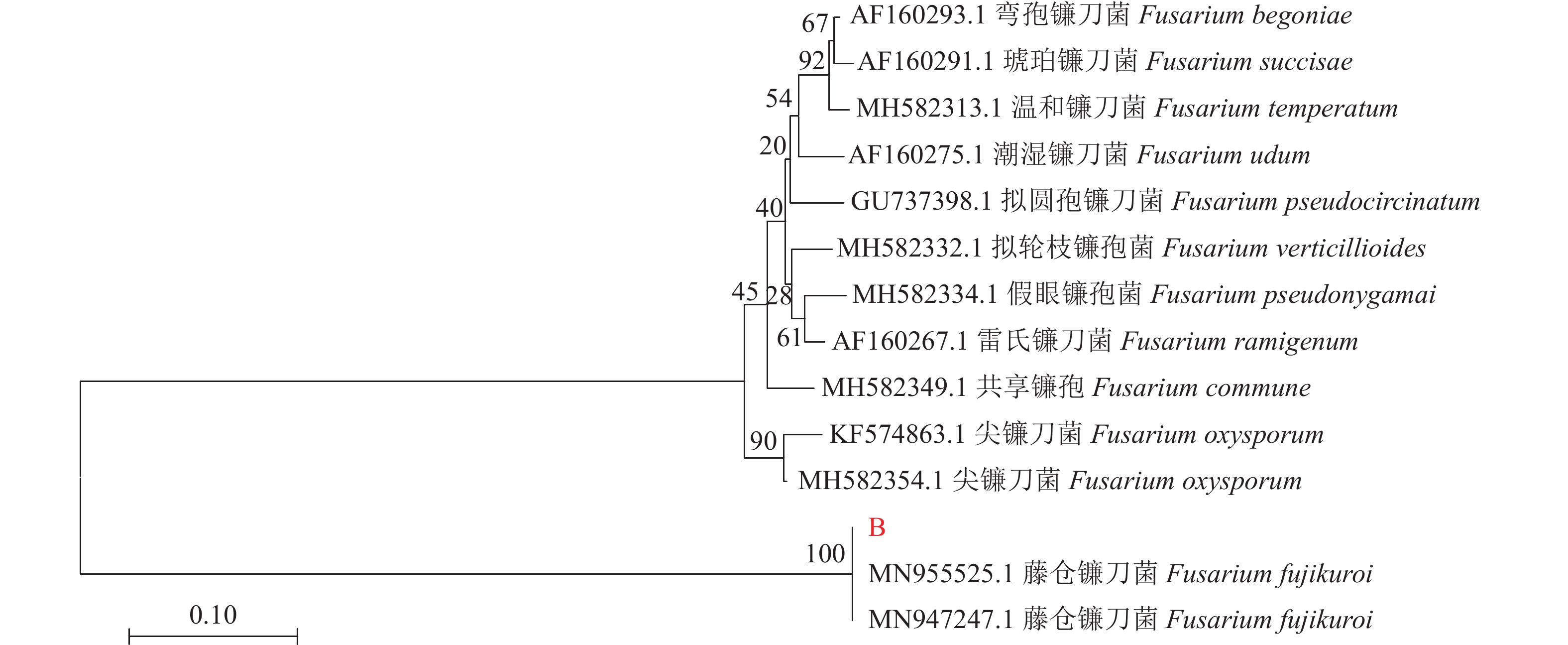
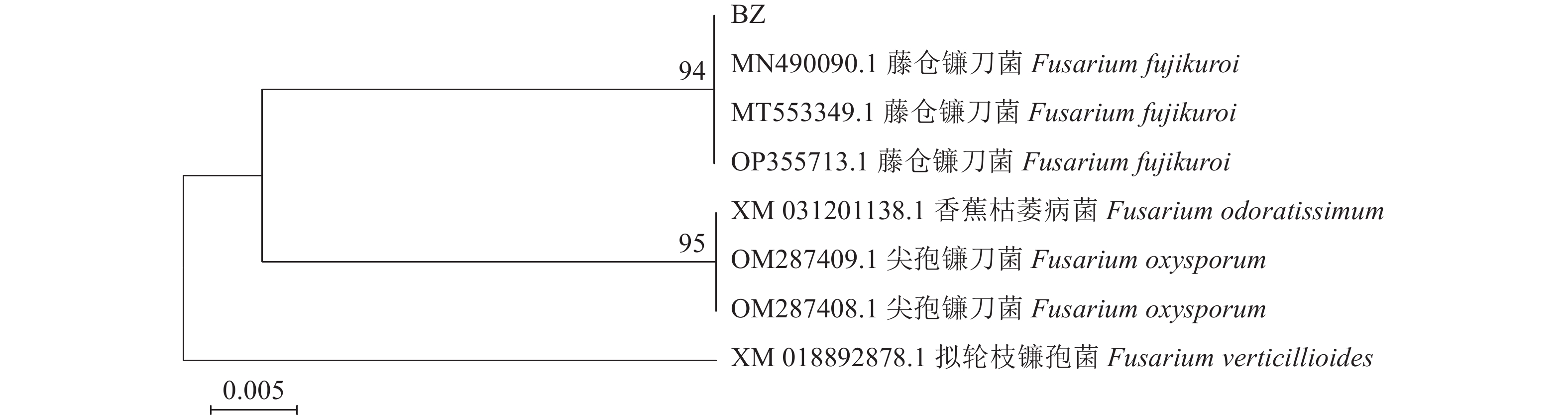
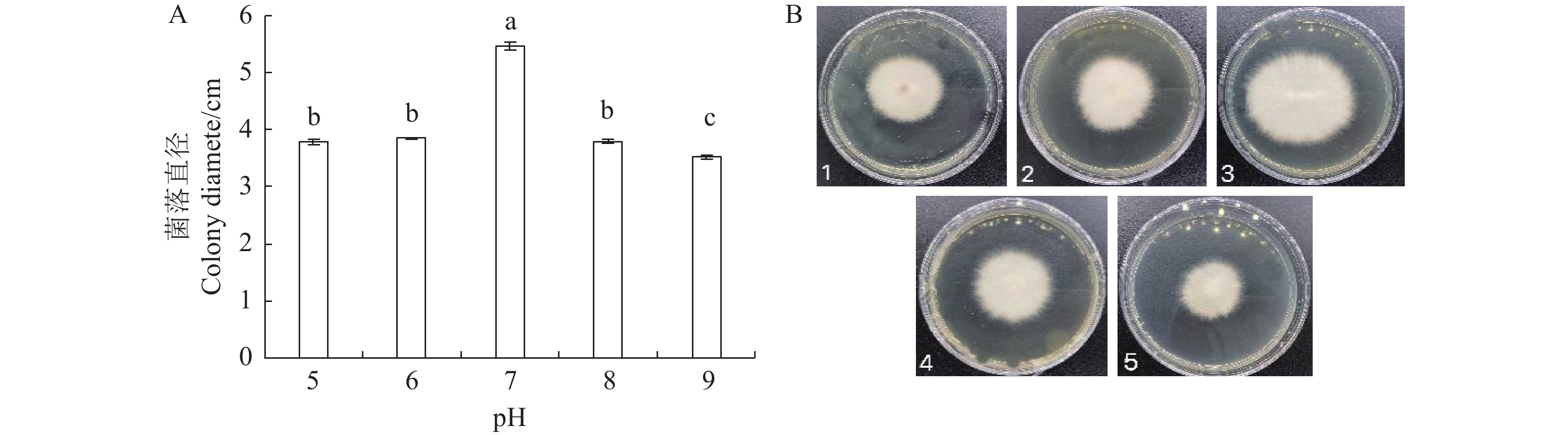
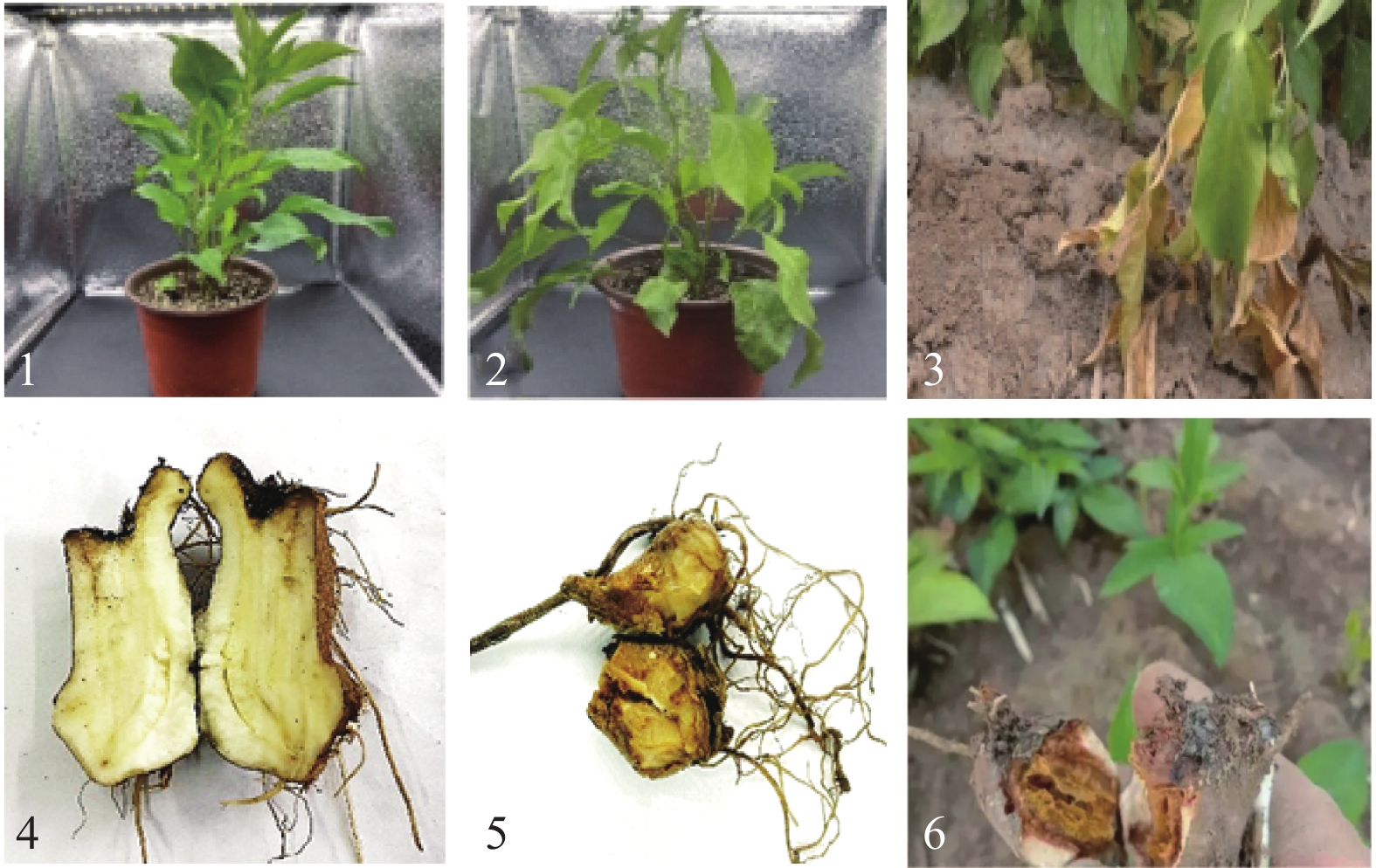
目的 明确河南信阳地区白术根腐病病原菌种属,研究其生物学特性并筛选可用于防控其病原菌的植物源农药。 方法 从种植区采集病株,室内分离病原菌并纯化,利用形态学和多基因联合分析对病原菌进行鉴定,并对病原菌的生物学特性进行研究,利用菌丝生长速率法评价3种植物源杀菌剂对其菌落的抑制作用。 结果 该病原菌菌丝白色,孢子呈卵圆形,两端稍尖,大型分生孢子3~5隔,大小为(7~10) μm×(3~4) μm,小型分生孢子2隔或无格,大小为(3~5) μm×(1~2) μm,多基因联合分析表明该病原菌与藤仓镰刀菌(Fusarium fujikuroi)同源性高,结合形态学特征与分子生物学分析将信阳白术根腐病病原菌鉴定为藤仓镰刀菌(Fusarium fujikuroi),这是藤仓镰刀菌引起白术根腐病的首次报道。生物学特性研究显示,该病原菌最适培养条件为温度28 ℃、pH为7,最适生长碳源为蔗糖,最适生长氮源为硝酸钾。3种植物源杀菌剂中,0.3%丁子香酚可溶液剂的EC50为6.906 mg·L−1,高于其他供试药剂,对病原菌的毒力最强。 结论 河南信阳地区白术根腐病病原菌为藤仓镰刀菌,最适培养条件为温度28 ℃、pH为7,最适生长碳源为蔗糖,最适生长氮源为硝酸钾。该研究结果为信阳地区白术根腐病科学防控提供了依据。 Abstract: :Objective In order to identify the pathogenic genera of Atractylodes macrocephala root rot disease in Xinyang, Henan Province, study their biological characteristics, and screen for Botanical fungicides that can be used for prevention and control. Method Morphological and multi gene analysis were used to identify the pathogens, and the biological characteristics of the pathogens were studied. Result The pathogen has white hyphae, oval shaped spores with slightly pointed ends, and large conidia with 3-5 septa and sizes of 7-10μm×3-4μm. Small conidia with 2 compartments or no compartments, size 3-5μm × 1-2μm. Multi gene joint analysis showed that the pathogen had high homology with Fusarium Fujikuroi. Combining morphological characteristics and molecular biology analysis, the pathogen of Atractylodes macrocephala root rot in Xinyang was identified as Fusarium Fujikuroi. This is the first report of Fusarium Fujikuroi causing Atractylodes macrocephala root rot. Research on biological characteristics shows that the optimal cultivation conditions for this pathogen are temperature 28 ℃, pH 7, sucrose as the optimal carbon source for growth, and potassium nitrate as the optimal nitrogen source for growth. Among the three botanical fungicides, the EC50 of 0.3% eugenol soluble agent is 6.906 mg/L, which is higher than other tested agents and has the strongest toxicity to pathogens.. Conclusion The pathogen of Atractylodes macrocephala root rot in Xinyang, Henan Province is Fusarium fuciformis. The optimal cultivation conditions are temperature 28 ℃, pH 7, sucrose as the carbon source for growth, and potassium nitrate as the nitrogen source for growth. The research results provide a basis for the scientific prevention and control of root rot disease of Atractylodes macrocephala in Xinyang area. -
Key words:
- Atractylodes macrocephala /
- root rot /
- Fusarium Fujikura /
- Botanical fungicides
-
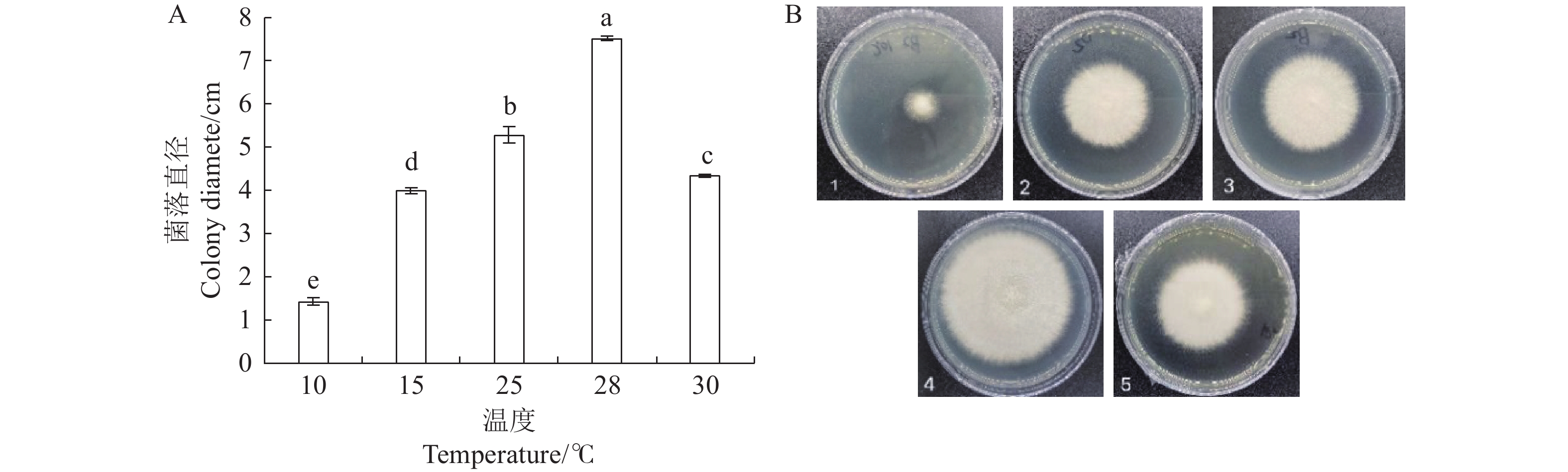
图 7 不同温度对病原菌生长的影响
注: 图A:10、15、25、28、30 ℃条件下培养5 d的菌丝长度;不同字母表示处理间差异达显著水平(P<0.05),图8~10同。图B: 数字1-5分别为10、15、25、28、30 ℃条件下培养5 d的菌落大小。
Figure 7. Effect of Different Temperatures on the Growth of Pathogens
Note: Fig.A:the mycelial length cultured at 10 °C, 15 °C, 25 °C, 28 °C and 30 °C for 5 d. Different letters indicated that the difference between treatments was significant ( P < 0.05 ), Same for Figs 8-10.Fig.B:Num.1-5 show colonies cultured at 10 ℃, 15 ℃, 25 ℃, 28 ℃, and 30 ℃ for 5 d, respectively.
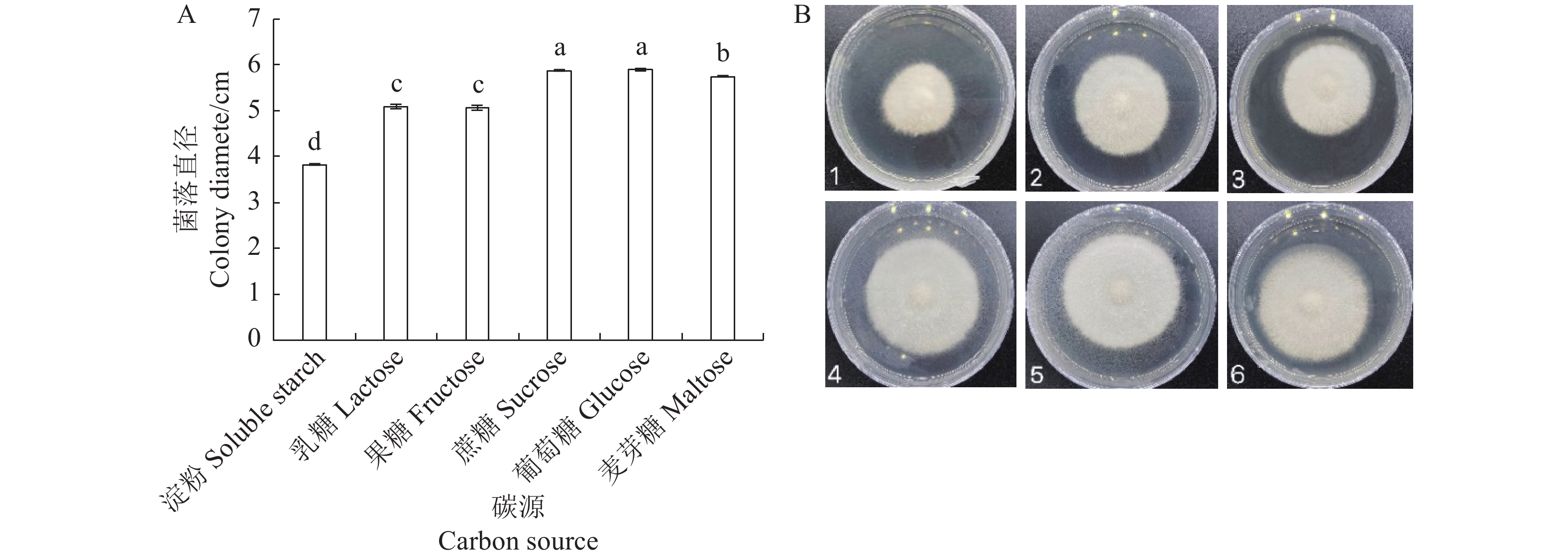
图 9 不同碳源对病原菌生长的影响
注: 图A:淀粉、乳糖、果糖、蔗糖、葡萄糖、麦芽糖条件下培养5 d的菌丝长度;图B: 数字1-5分别为淀粉、乳糖、果糖、蔗糖、葡萄糖、麦芽糖条件下培养5 d的菌落大小。
Figure 9. Effect of Different Carbon Sources on the Growth of Pathogens
Note: Fig.A:the mycelial length cultured at Soluble starch, Lactose, Fructose, Sucrose, Glucose, Maltose for 5 d. Fig.B:Num.1-5 show colonies cultured at Soluble starch, Lactose, Fructose, Sucrose, Glucose, Maltose for 5 d.
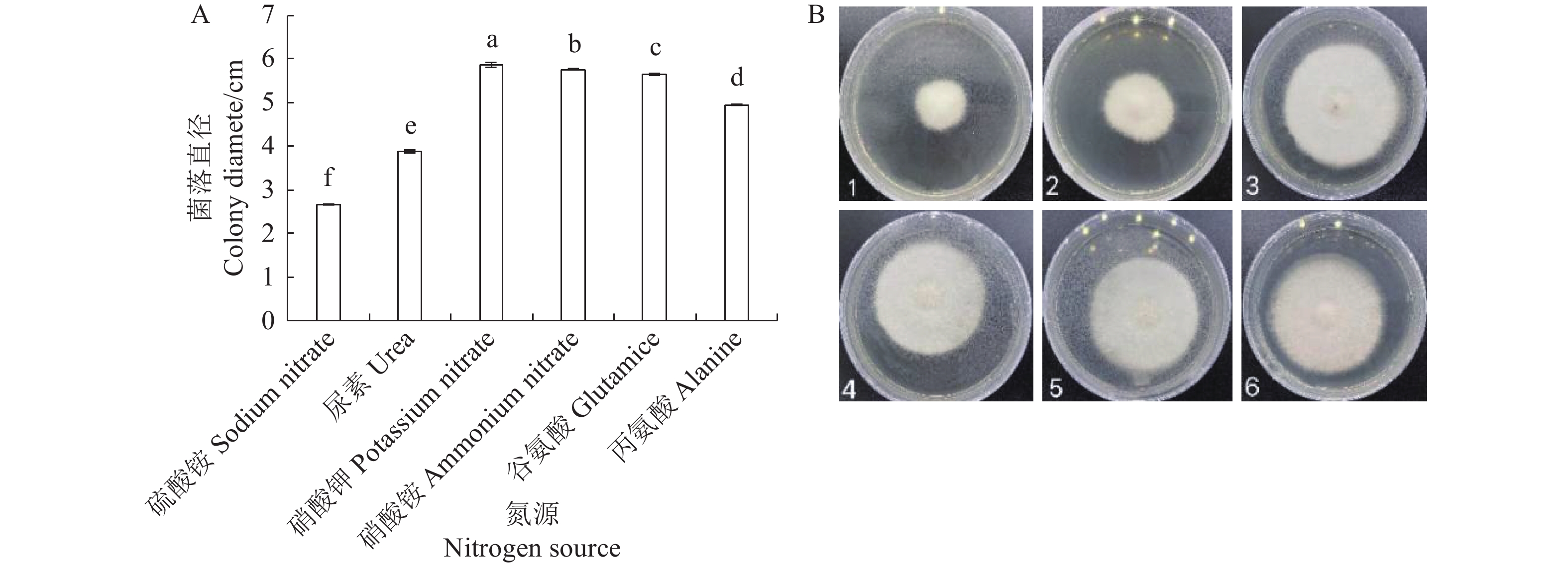
图 10 不同氮源对病原菌生长的影响
注: 图A:硫酸铵、尿素、硝酸钾、硝酸铵、谷氨酸、丙氨酸条件下培养5 d的菌丝长度;图B: 数字1-5分别为硫酸铵、尿素、硝酸钾、硝酸铵、谷氨酸、丙氨酸条件下培养5 d的菌落大小。
Figure 10. Effect of different nitrogen sources on the growth of pathogenic bacteria
Note: Fig.A:the mycelial length cultured at Sodium nitrate, Urea, Potassium nitrate, Ammonium nitrate, Glutamice, Alanine for 5 d. Fig.B:Num.1-5 show colonies cultured at Sodium nitrate, Urea, Potassium nitrate, Ammonium nitrate, Glutamice, Alanine for 5 d.
表 1 引物信息
Table 1. Primer information
基因
Gene引物
Primer序列
SequenceITS ITS1 5'-TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG-3′ ITS4 5′-TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC-3′ ACT ACT-512F 5′-ATGTGCAAGGCCGGTTTCGC-3′ ACT-783R 5′-TACGAGTCCTTCTGGCCCAT-3′ TUB-2 T1 5′-GCCGTCAACGACCCCTTCATTGA-3′ Bt2 5′-ACCCTCAGTGTAGTGACCCTTGGC-3′ GAPDH GDF1 5′-GCCGTCAACGACCCCTTCATTGA-3′ GDR1 5′-GGGTGGAGTCGTACTTGAGCATGT-3′ 表 2 3种植物源农药室内毒力测定浓度设置
Table 2. Concentration settings for indoor toxicity determination of three plant-based pesticides
供试药剂
Pesticide药剂浓度
Pesticide concentration/(μg·mL−1)1%蛇床子素EW
1% osthole EW200、 100、 50、 25、 12.5 0.5%小檗碱AS
0.5% berberine AS250、 125、 62.5、 31.25、15.625 0.3%丁子香酚SL
0.3% eugenol SL60、 30、 15、 7.5、 3.75 CK — 表 3 3种植物源杀菌剂对白术根腐病病原菌的室内毒力测定
Table 3. Indoor toxicity test results of plant-based fungicides on Fusarium fujikuroi
药剂名称
Pesticide毒力回归方程
Toxicity regression equationR2 EC50 值
EC50 value/(mg·L−1)0.3% 丁子香酚SL
0.3% eugenol SLy=1.2062x+3.9877 0.9919 6.906 0.5% 小檗碱AS
0.5% berberine ASy=1.0629x+2.7199 0.9907 139.637 1% 蛇床子素EW
1% osthole EWy=1.2181x+3.5096 0.9909 16.749 -
[1] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典-一部: 2020年版[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020: 107. [2] 纪莉景, 肖颖, 李耀发, 等. 引起河北省保定市白术根腐病的病原镰刀菌种类鉴定 [J]. 植物病理学报, 2021, 51(2):282−286.JI L J, XIAO Y, LI Y F, et al. Identification of pathogenic Fusarium species causing Atractylodes macrocephala root rot in Baoding, Hebei Province [J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 2021, 51(2): 282−286. (in Chinese) [3] 杨成前, 宋廷杰, 吴中宝, 等. 白术根腐病发生危害与防治调查 [J]. 中药材, 2007, 30(5):517−519. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4454.2007.05.005YANG C Q, SONG T J, WU Z B, et al. Investigation on the occurrence, harm and control of Atractylodes macrocephala root rot [J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2007, 30(5): 517−519. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4454.2007.05.005 [4] 张礼维. 贵州白术根腐病病原鉴定及防治研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2015.ZHANG L W. Identification of pathogen and control of root rot of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. in Guizhou[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2015. (in Chinese) [5] 刘凡. 白术根腐病病原鉴定、生物学特性和防治研究[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2012.LIU F. Identification, biological characteristics and control of root rot on Atractylodes macrocephala[D]. Yaan: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2012. (in Chinese) [6] 刘英慧, 赵来顺. 白术根腐病研究初报 [J]. 植物病理学报, 1991, 21(1):38.LIU Y H, ZHAO L S. A preliminary report on the study of root rot on largehead atractylodes [J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 1991, 21(1): 38. (in Chinese) [7] 臧少先, 安信伯, 石丽军, 等. 白术根腐病症状类型及病原鉴定 [J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2005, 28(3):73−76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1573.2005.03.019ZANG S X, AN X B, SHI L J, et al. Symptom and pathogen identification of root rot on largehead atractylodes rhizome [J]. Journal of Agricultural University of Hebei, 2005, 28(3): 73−76. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1573.2005.03.019 [8] 王飞, 李雪梦, 高素霞, 等. 河南白术茎基腐病病原的鉴定及药剂筛选 [J]. 植物病理学报, 2023, 53(5):779−788.WANG F, LI X M, GAO S X, et al. Pathogen identification of stem-base rot disease of Atractylodes macrocephala in Henan Province and screening of fungicides [J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 2023, 53(5): 779−788. (in Chinese) [9] 游景茂, 郭杰, 李哲, 等. 湖北省白术主要病害类型及绿色防控技术 [J]. 湖北农业科学, 2019, 58(21):54−56.YOU J M, GUO J, LI Z, et al. The green prevention and control technology of the main diseases of Atractylodes macrocephala in Hubei Province [J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 58(21): 54−56. (in Chinese) [10] 周佳, 王铁霖, 苗玉焕, 等. 乌头黑斑病病原菌的鉴定、生物学特性及其有效杀菌剂研究 [J]. 中国中药杂志, 2022, 47(5):1215−1221.ZHOU J, WANG T L, MIAO Y H, et al. Identification, biological characteristics, and fungicide screening of pathogen of black spot in Aconitum carmichaelii [J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2022, 47(5): 1215−1221. (in Chinese) [11] 李程锦, 尚怀国, 苏霞, 等. 丹参根腐病病原菌的分离、鉴定及防控药剂筛选 [J]. 山东农业科学, 2022, 54(9):119−125.LI C J, SHANG H G, SU X, et al. Isolation and identification of root rot pathogens of Salvia miltiorrhiza and fungicide screening [J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 54(9): 119−125. (in Chinese) [12] 韦鑫. 白术根腐病生防菌的筛选及控病研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2016.WEI X. Screening biocontrol strains and researching the control of the Atractylodes macrocephala koidz[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2016. (in Chinese) [13] 李勇, 王蓉, 陈卉青, 等. 一株地黄根腐病新病原的分离与鉴定 [J]. 中国中药杂志, 2021, 46(11):2783−2787.LI Y, WANG R, CHEN H Q, et al. Isolation and identification of a new phytopathogen causing root rot of Rehmannia glutinosa [J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2021, 46(11): 2783−2787. (in Chinese) [14] 迟阳, 李升, 魏书琴. 不同碳源和氮源对紫菀根腐病菌菌丝生长的影响 [J]. 湖北农业科学, 2015, 54(20):5025−5027.CHI Y, LI S, WEI S Q. The influence on the growth of hyphae of root rot disease of Aster tataricus l. f. in different carbon and nitrogen sources [J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 54(20): 5025−5027. (in Chinese) [15] 杨成前, 吴中宝, 余中莲, 等. 重庆市白术根腐病发生危害及其病原菌生物学特性 [J]. 南方农业学报, 2018, 49(8):1561−1567. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2018.08.14YANG C Q, WU Z B, YU Z L, et al. Occurence and damage of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. root rot and biological characteristics of its pathogen [J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2018, 49(8): 1561−1567. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2018.08.14 [16] JOHN F. Leslie and Brett A. Summerell The Fusarium Laboratory Manual[M]. USA: Blackwell publishing, 2006: 200. [17] 白容霖, 潘丽梅, 刘伟成. 吉林省人参细菌性软腐病病原 [J]. 植物保护学报, 2000, 27(1):63−68. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-7518.2000.01.013BAI R L, PAN L M, LIU W C. Studies on the pathogen of ginseng bacterial soft rot in Jilin Province [J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2000, 27(1): 63−68. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-7518.2000.01.013 [18] 罗文富, 喻盛甫, 贺承福, 等. 三七根腐病病原及复合侵染的研究 [J]. 植物病理学报, 1997, 27(1):85−91. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-0914.1997.01.023LUO W F, YU S F, HE C F, et al. Study on pathogen and compound infection of root rot of panax notoginseng [J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 1997, 27(1): 85−91. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-0914.1997.01.023 [19] 张玉方, 闫光凡, 刘先齐. 白芷根腐病的病程及组织病理学研究 [J]. 中国中药杂志, 1998, 23(10):596−597. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-5302.1998.10.008ZHANG Y F, YAN G F, LIU X Q. Study on the course and histopathology of root rot of Angelica dahurica [J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 1998, 23(10): 596−597. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-5302.1998.10.008 [20] 赵庆芳, 周紫鹃, 王树红, 等. 7种植物对黄芪根腐病病原菌的抑制作用研究 [J]. 西北师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 45(5):92−95.ZHAO Q F, ZHOU Z J, WANG S H, et al. Study on the inhibition effects of 7 kinds of plant to the growth of Astragalus membranaceus root rot fungi [J]. Journal of Northwest Normal University (Natural Science), 2009, 45(5): 92−95. (in Chinese) [21] 冯茜, 何苗, 黄云, 等. 川芎根腐病的症状及病原鉴定 [J]. 植物保护学报, 2008, 35(4):377−378. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-7518.2008.04.018FENG Q, HE M, HUANG Y, et al. Symptoms of root rot on Ligusticum chuanxiong and identification of its pathogen [J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2008, 35(4): 377−378. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-7518.2008.04.018 [22] 曹敏, 余米, 唐祥友, 等. 茅苍术根腐病主要病原菌的分离鉴定及室内药剂筛选 [J]. 中药材, 2022, 45(8):1789−1795.CAO M, YU M, TANG X Y, et al. Isolation and identification of pathogens of Atractylodes lancea root rot disease and fungicide screening in laboratory [J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2022, 45(8): 1789−1795. (in Chinese) [23] 王树桐, 王亚南, 胡同乐, 等. 板蓝根根腐病病原鉴定 [J]. 植物保护学报, 2011, 38(5):473−474.WANG S T, WANG Y N, HUTONG L, et al. Identification of the root rot pathogens of Isatis indigotica [J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2011, 38(5): 473−474. (in Chinese) [24] 黄亚萍. 当归根腐病病原物研究[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2011.HUANG Y P. Studies on the pathogens causing Angelica sinensis root rot[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2011. (in Chinese) [25] 刘静华. 水稻恶苗病拮抗细菌的筛选及生防机制初探[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳师范大学, 2023.LIU J H. Screening of antagonistic bacteria against Fusarium fujikuroi in rice and preliminary study on its biocontrol mechanism[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Normal University, 2023. (in Chinese) [26] 梁嘉俊, 凌君, 楚渠, 等. 安康市桑树褐斑病致病菌分离鉴定 [J]. 北方蚕业, 2022, 43(1):6−9,27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9922.2022.01.002LIANG J J, LING J, CHU Q, et al. Isolation and identification of mulberry brown spot disease in Ankang city [J]. North Sericulture, 2022, 43(1): 6−9,27. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9922.2022.01.002 [27] 舒然, 龙海江, 龙友华, 等. 李果斑病病原菌生物学特性及室内毒力测定 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2021, 36(9):1075−1080. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2021.9.fjnyxb202109012SHU R, LONG H J, LONG Y H, et al. Biological characteristics and lab toxicity test results of plum fruit spot pathogen [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 36(9): 1075−1080. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2021.9.fjnyxb202109012 [28] 冯岩, 谢梓烁, 欧枝凯, 等. 镰刀菌引致的百香果病害研究 [J]. 仲恺农业工程学院学报, 2019, 32(4):13−18.FENG Y, XIE Z S, OU Z K, et al. Study on diseases of Passiflora edulia caused by Fusarium [J]. Journal of Zhongkai University of Agriculture and Engineering, 2019, 32(4): 13−18. (in Chinese) [29] 刘彤珂, 宋水林, 熊桂红, 等. 百合根腐病病原分离与鉴定 [J]. 生物灾害科学, 2023, 46(1):1−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-3704.2023.01.01LIU T K, SONG S L, XIONG G H, et al. Isolation and identification of lily root rot pathogen [J]. Biological Disaster Science, 2023, 46(1): 1−7. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-3704.2023.01.01 [30] 沈会芳, 邓海滨, 杨祁云, 等. 广东韶关烟区烟草镰刀菌根腐病病原鉴定及致病性分析 [J]. 中国烟草科学, 2023, 44(4):49−57.SHEN H F, DENG H B, YANG Q Y, et al. Identification and pathogenicity analysis of tobacco Fusarium root rot pathogens in Shaoguan, Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Tobacco Science, 2023, 44(4): 49−57. (in Chinese) [31] 董晓菲, 叶祖云, 刘雨虹, 等. 槟榔芋软腐病生防真菌的筛选 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2020, 35(5):538−544.DONG X F, YE Z Y, LIU Y H, et al. Fungi for controlling soft-rot disease on taro [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 35(5): 538−544. (in Chinese) [32] 侯恩庆. 水稻穗腐病镰刀菌及相关毒素研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2013.HOU E Q. Studies on biological characteristics and toxin of rice spikelet rot disease (RSRD) pathogens Fusarium spp[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2013. (in Chinese) [33] 王燕, 王春伟, 王琳, 等. 甜瓜镰刀菌果腐病新病原菌 Fusarium incarnatum的鉴定及生物学特性 [J]. 园艺学报, 2019, 46(3):529−539.WANG Y, WANG C W, WANG L, et al. Identification and biological characteristics of a novel pathogen Fusarium incarnatum causing muskmelon fruit Fusarium rot [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2019, 46(3): 529−539. (in Chinese) [34] 孙华, 李敏, 栗梅芳, 等. 4种杀菌剂对麻山药褐腐病菌室内毒力测定 [J]. 中国植保导刊, 2022, 42(6):73−76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6820.2022.06.018SUN H, LI M, LI M F, et al. Indoor toxicity test of four fungicides to brown rot of yam [J]. China Plant Protection, 2022, 42(6): 73−76. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6820.2022.06.018 [35] 陈美航, 漆江, 鲁道旺, 等. 德江天麻腐烂病病原菌分离鉴定及活性测试 [J]. 农药, 2023, 62(11):833−837.CHEN M H, QI J, LU D W, et al. Pathogen isolation and identification and fungicide screening of gastrodia tuber rot in Dejiang [J]. Agrochemicals, 2023, 62(11): 833−837. (in Chinese) [36] 王涛, 李志涛, 王兴宁, 等. 12种杀菌剂对三线镰刀菌的室内毒力测定 [J]. 云南化工, 2021, 48(6):52−54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-275X.2021.06.18WANG T, LI Z T, WANG X N, et al. Indoor toxicity determination of 12 fungicides to Fusarium triline [J]. Yunnan Chemical Technology, 2021, 48(6): 52−54. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-275X.2021.06.18 -








 下载:
下载: