Effect of biochar on the stability of soil aggregates and nitrogen distribution of fertilizer in woodland soil
-
摘要:
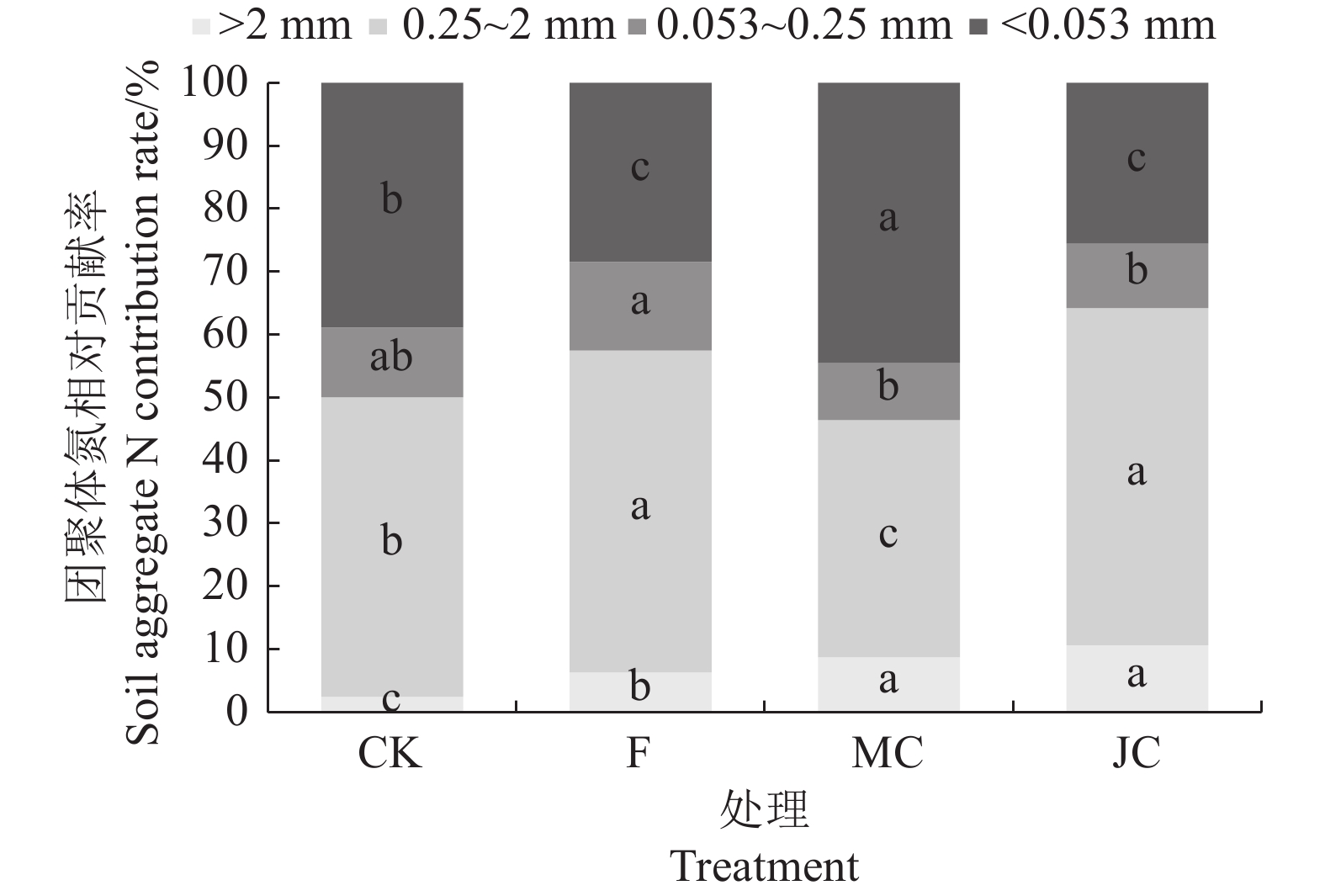
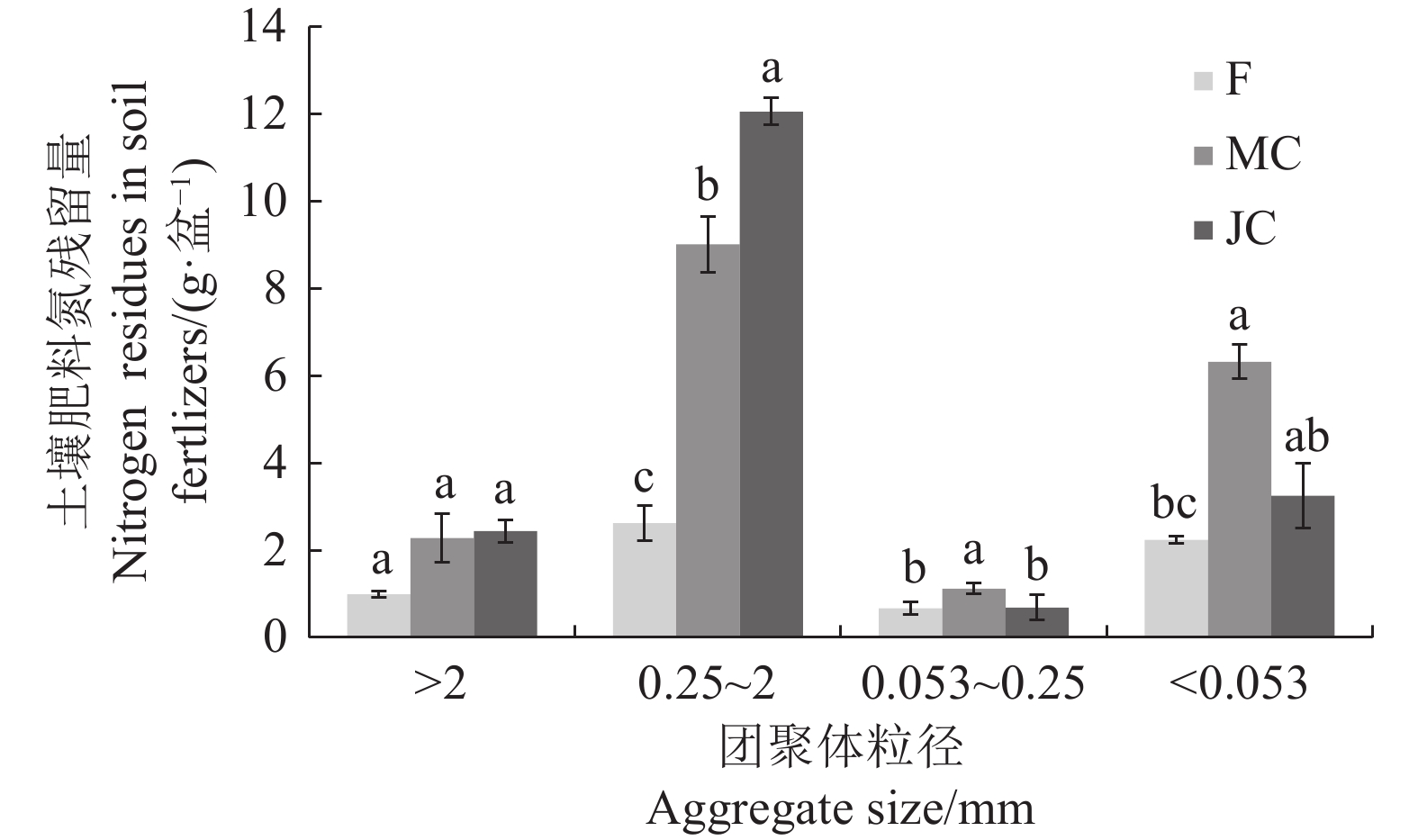
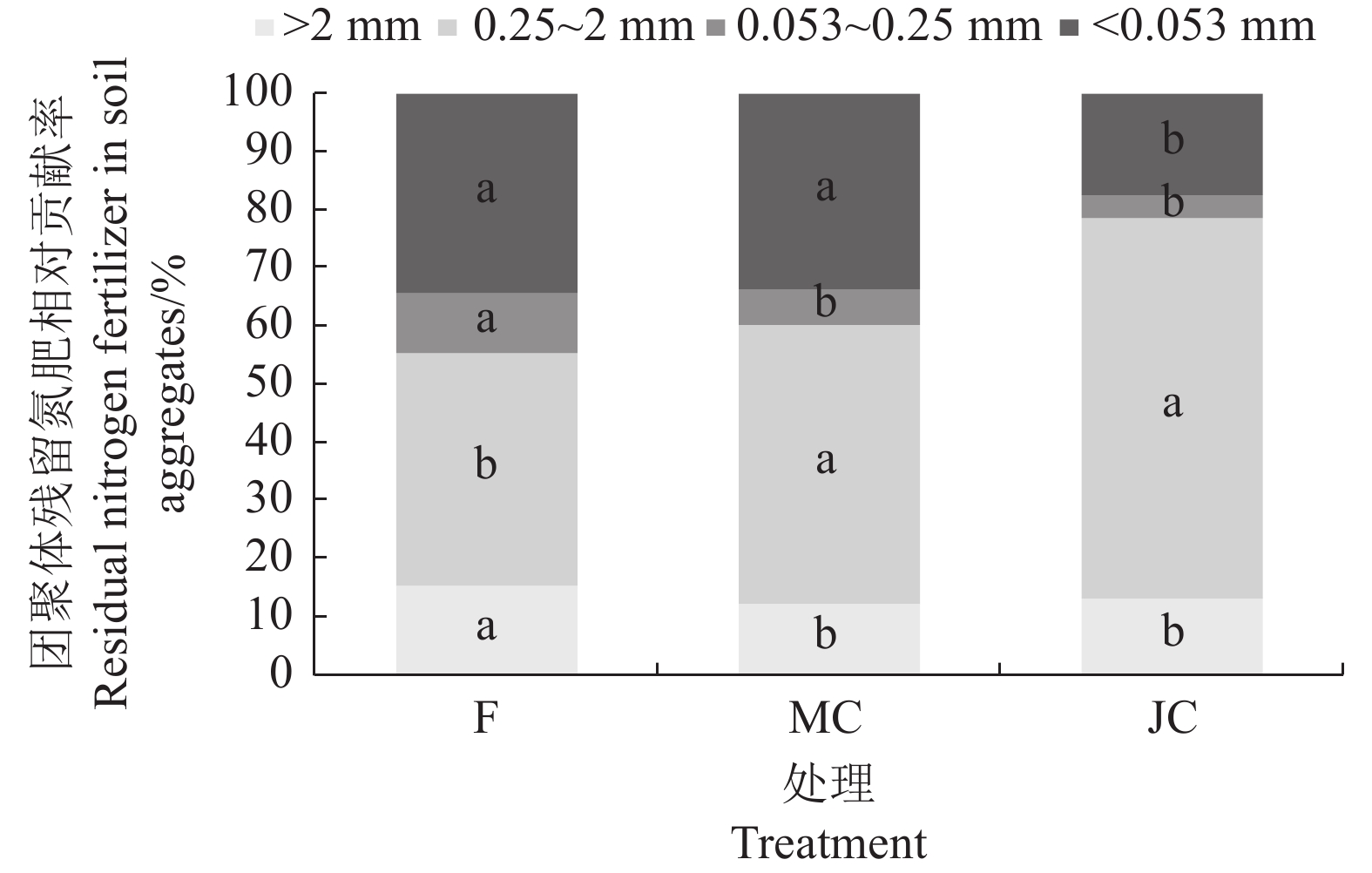
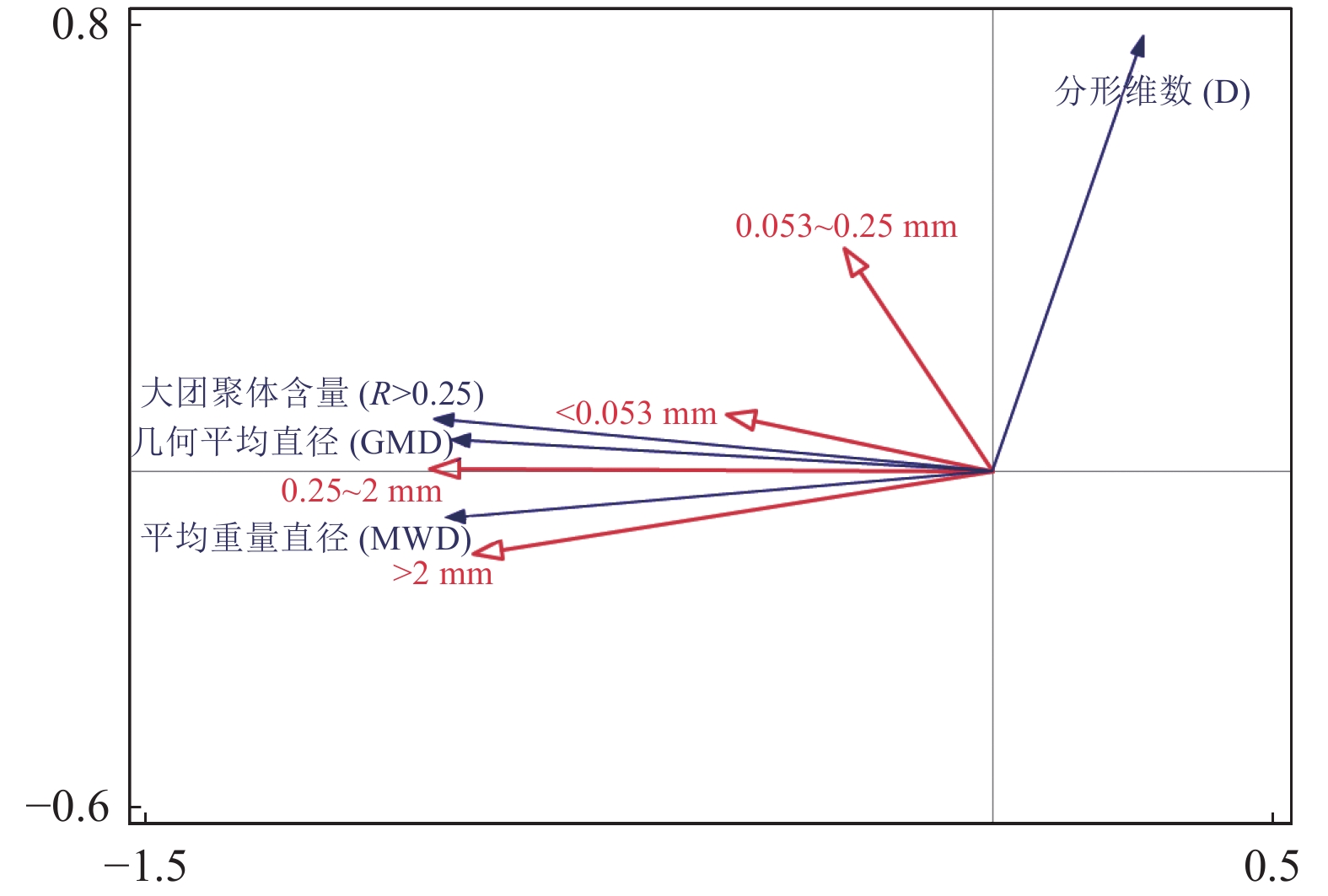
目的 林地土壤抗侵蚀能力渗透性及保水性与土壤团聚体结构稳定性紧密相关,氮素的固持与分布直接影响林下植被生长与林地土壤团聚体形成。研究生物炭添加对林地土壤结构稳定性与残留氮素分配的影响,可以为增强林地土壤团聚体稳定性、提高土壤氮素固持水平提供参考。 方法 基于福建省林地土壤进行盆栽试验(1 年),设置4 个处理:对照(CK)、化肥(F)、木炭+化肥(MC)、秸秆炭+化肥(JC),除CK外,化肥及生物炭处理均每盆施用尿素、过磷酸钙、氯化钾1 g、2.19 g、0.44 g,追肥15N-尿素,共追施5 g,生物炭施用量为每盆140 g。测定不同处理土壤团聚体组成、团聚体稳定性指标、团聚体氮素含量与分布,结合15N示踪技术分析肥料氮在土壤团聚体内的残留特点,揭示生物炭对林地土壤团聚体稳定性与氮素分配的影响。 结果 (1)与F处理相比,MC与JC处理显著提高了土壤大团聚体含量,其中>2 mm土壤团聚体增幅最大,分别增长了108.92%与119.11%;(2)施用生物炭增强了土壤团聚体稳定性,MC与JC处理平均重量直径(MWD)、几何平均直径(GMD)及>0.25 mm大团聚体含量(R>0.25 mm)团聚体稳定性指标较F处理均显著提升,分形维数值(D)显著下降,JC处理土壤团聚体稳定性优于MC处理;(3)施用生物炭提高了不同粒径土壤团聚体中全氮含量,MC处理土壤全氮总量高于JC处理,二者的>2 mm团聚体氮素贡献率较F处理分别显著增加了38.09%与69.10%;(4)施用生物炭使0.25~2 mm粒级团聚体δ15N富集,MC与JC处理土壤肥料氮残留量以>0.25 mm粒级最多,较F处理显著增加了2.25 倍与3.89 倍,土壤大团聚体中氮肥残留量与团聚体稳定性显著正相关。 结论 施用生物炭有利于增强林地土壤团聚体稳定性,减少土壤氮素与肥料淋失,肥料氮在大团聚体中的固持高于微团聚体,秸秆炭对土壤团聚体稳定性提升效果更显著,木炭施用更有利于土壤氮素含量增加。 Abstract:Objective Soil erosion resistance, permeability, and water retention of woodland soils are closely related to the structural stability of soil aggregates. The study on the effects of biochar addition on soil structure stability and residual nitrogen distribution can provide reference for enhancing the stability of soil aggregates and improving the level of soil nitrogen retention. Method In this study a pot experiment (1 year) was conducted based on the woodland soil in Fujian Province and four treatments were set up: control (CK), chemical fertilizer (F), wood biochar + chemical fertilizer (MC), and straw biochar + chemical fertilizer (JC). In addition to CK, the application amounts of urea, superphosphate and potassium chloride in each basin were 1g, 2.19g and 0.44g, respectively. 15N-urea was used for topdressing, a total of 5g was applied, and the application amount of biochar was 140g per basin. The effects of biochar on soil aggregate stability and nitrogen distribution were analyzed by measuring soil aggregate content, aggregate stability index, aggregate nitrogen content and distribution, combined with 15N tracer technology to analyze the residual characteristics of fertilizer nitrogen in soil aggregates. Results (1) Compared with F treatment, MC and JC treatment significantly increased the content of soil macroaggregates, and the content of soil macroaggregates >2 mm increased the most, by 108.92% and 119.11%, respectively. (2)The application of biochar enhanced the stability of soil aggregates. Compared with F treatment, the stability indexes of MWD, GMD and aggregates with R>0.25mm under MC and JC treatment were significantly increased, while D was significantly decreased. The stability of soil aggregates under JC treatment was better than that under MC treatment.(3) The application of biochar increased the total nitrogen content of soil aggregates of different particle sizes, and the total nitrogen content of MC treatment was higher than that of JC, and the nitrogen contribution rate of aggregates >2 mm was significantly increased by 38.09% and 69.10%, respectively, compared with F treatment. (4) The application of biochar enriched δ15N in 0.25~2 mm aggregates, and the residue nitrogen of soil fertilizer under MC and JC treatment was the highest in >0.25 mm aggregates, which significantly increased by 2.25 times and 3.89 times compared with F treatment. The residual nitrogen fertilizer in soil large aggregates was significantly positively correlated with the stability of aggregates. Conclusion The application of biochar can enhance the stability of soil aggregates and reduce the loss of soil nitrogen and fertilizer. The retention of fertilizer nitrogen in large aggregates is higher than that in micro-aggregates. Straw biochar has a more significant effect on the stability of soil aggregates, and wood biochar application is more conducive to the increase of soil nitrogen content. -
Key words:
- Biochar /
- Aggregate stability /
- Nitrogen fertilizer utilization /
- The 15N mark /
- Woodland soil structure
-
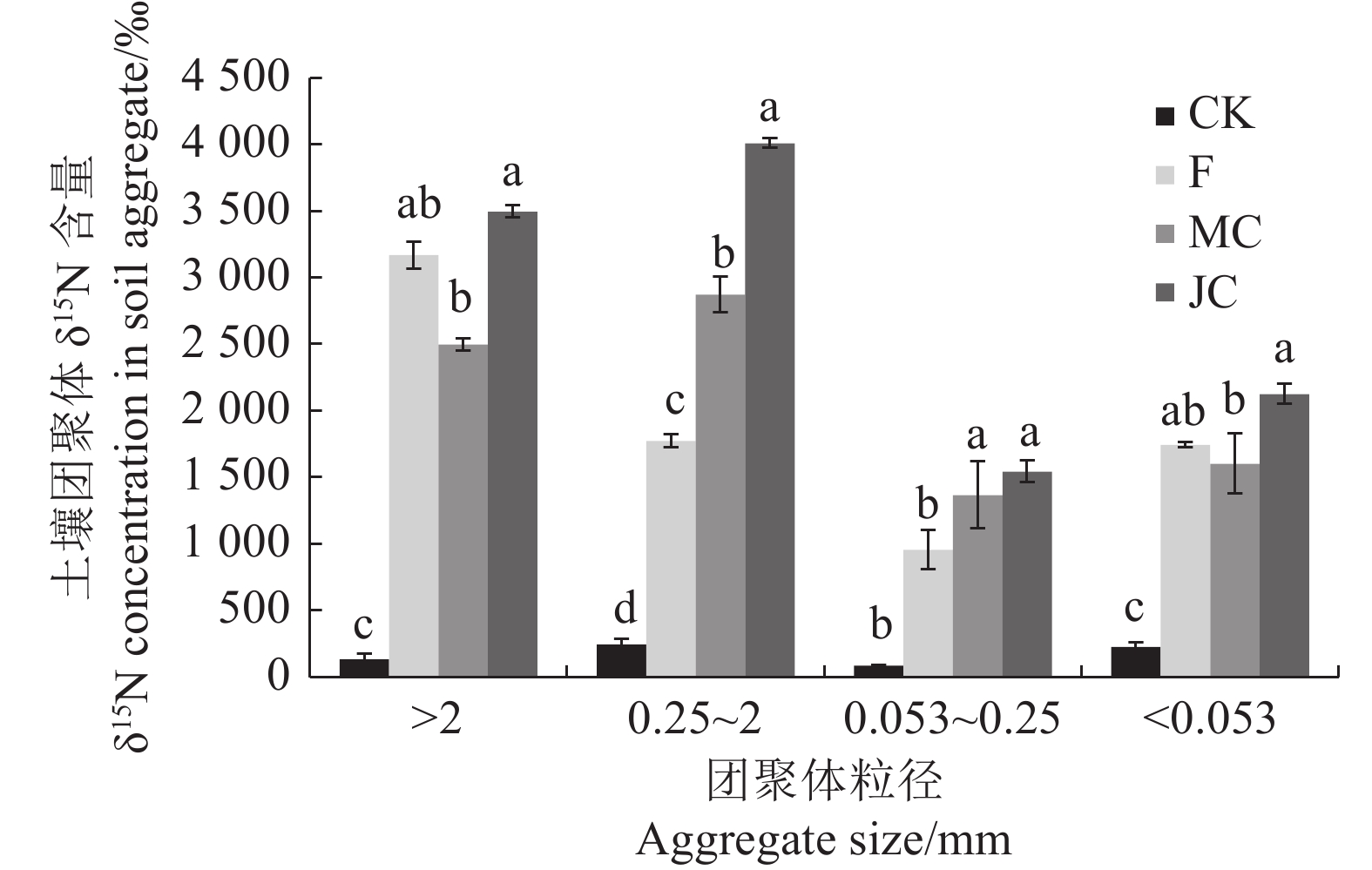
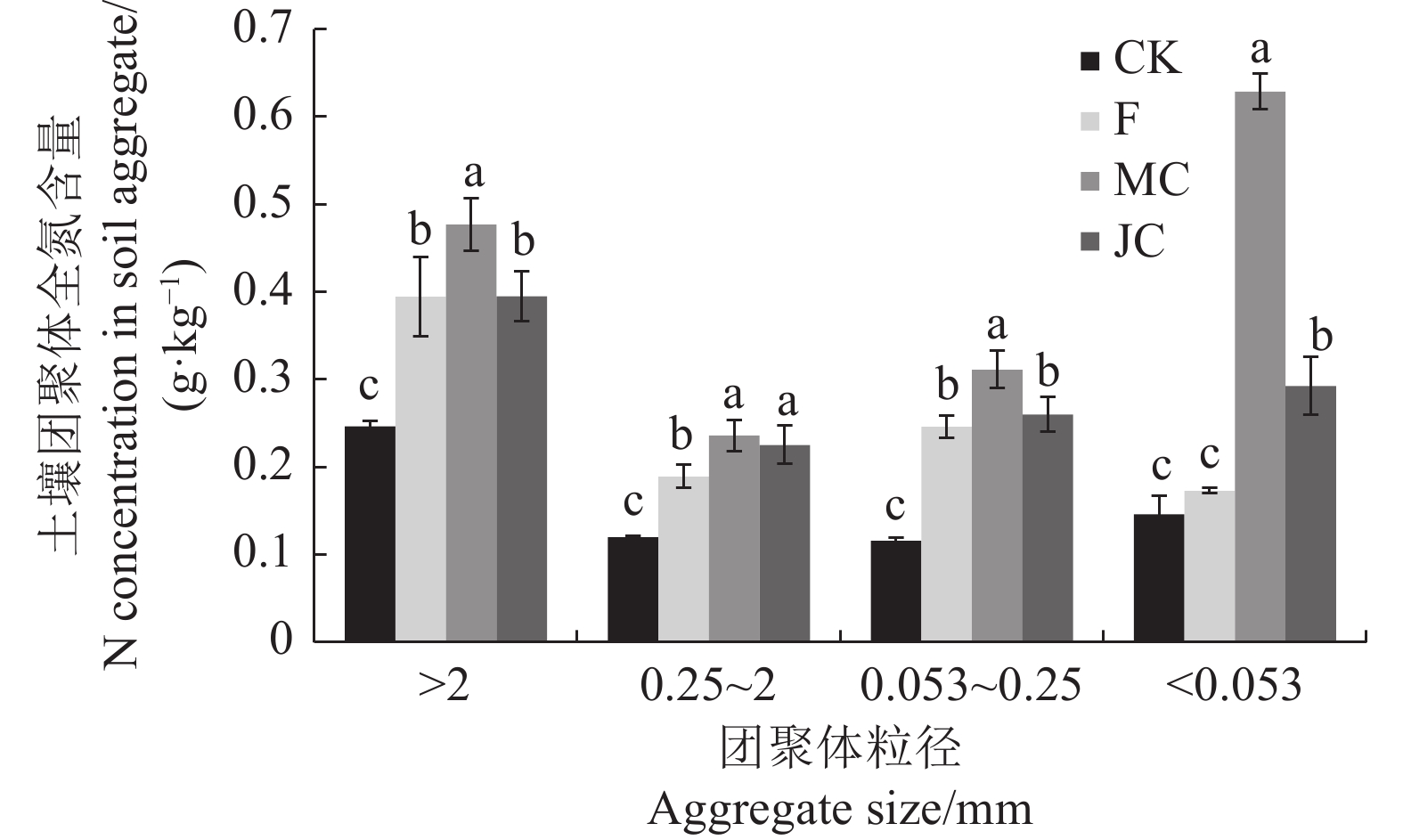
图 1 生物炭对土壤团聚体全氮含量的影响
同一粒径土壤团聚体不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。图中误差线选用SD值表示各处理重复间标准差。下同。
Figure 1. Effect of biochar on the total nitrogen content of soil aggregates
Different lowercase letters of soil aggregates of the same particle size indicate significant differences between treatments (P<0.05). The SD is used for the error line to represent the standard deviation between each treatment replicate. the same below
表 1 不同处理肥料施用量
Table 1. Fertilizer application amount of different treatments
处理
Treatment每盆土壤肥料投入量 Fertilizer input per pot of soil/(g·盆−1) 追肥
After manuring基肥
Base fertilizer15N-尿素
15N(10.10%)尿素
N(46%)过磷酸钙
P2O5 (12%)氯化钾
K2O(60%)木炭
Wood Biochar秸秆炭
Straw BiocharCK 0 0 0 0 0 0 F 5 1 2.19 0.44 0 0 MC 5 1 2.19 0.44 140 0 JC 5 1 2.19 0.44 0 140 表 2 生物炭对土壤各粒级团聚体分布的影响
Table 2. Effects of biochar on the distribution of aggregates in soil
处理
Treatment不同粒级土壤团聚体含量
Soil aggregate content/%>2 mm 0.25~2 mm 0.053~0.25 mm <0.053 mm CK 1.30±0.47c 51.64±0.91c 12.45±0.68a 34.61±1.15a F 3.14±0.73b 53.22±0.51c 11.25±0.27ab 32.39±0.75a MC 6.56±0.66a 57.49±0.48b 10.46±0.75b 25.49±0.66b JC 6.88±0.39a 60.77±0.33a 10.11±1.27b 22.24±1.22c 表中数值为平均值±标准差。同列数据后不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。
Data is mean±SD. Different letters in the same column indicate significant differences between treatments (P<0.05). The same below.表 3 生物炭对土壤团聚体稳定性的影响
Table 3. Effect of biochar on the stability of soil aggregates
处理
Treatment平均重量
直径
MWD/mm几何平均
直径
GMD/mm>0.25 mm大团聚
体含量
R>0.25 mm/%分形维数
DCK 0.69±0.04c 0.24±0.01c 52.94±0.45d 2.78±0.03a F 0.81±0.05b 0.28±0.04c 56.36±0.22c 2.77±0.05a MC 1.06±0.05a 0.39±0.01b 64.05±1.14b 2.72±0.16b JC 1.12±0.03a 0.45±0.02a 67.65±0.72a 2.69±0.23b -
[1] 刘亚龙, 王萍, 汪景宽. 土壤团聚体的形成和稳定机制: 研究进展与展望 [J]. 土壤学报, 2023, 60(3):627−643.LIU Y L, WANG P, WANG J K. Formation and stability mechanism of soil aggregates: Progress and prospect [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2023, 60(3): 627−643. (in Chinese) [2] 张玉琪, 吴玉鑫, 李强, 等. 东祁连山不同退化程度高寒草甸土壤氮素与团聚体特征及关系研究 [J]. 草地学报, 2021, 29(10):2286−2293.ZHANG Y Q, WU Y X, LI Q, et al. Characteristics and relationship between soil nitrogen and aggregates in alpine meadows with different degradation in eastern Qilian Mountains [J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(10): 2286−2293. (in Chinese) [3] KHAN Z, YANG X J, FU Y Q, et al. Engineered biochar improves nitrogen use efficiency via stabilizing soil water-stable macroaggregates and enhancing nitrogen transformation [J]. Biochar, 2023, 5: 52. doi: 10.1007/s42773-023-00252-8 [4] 武玉, 徐刚, 吕迎春, 等. 生物炭对土壤理化性质影响的研究进展 [J]. 地球科学进展, 2014, 29(1):68−79. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2014.01-0068WU Y, XU G, LÜ Y C, et al. Effects of biochar amendment on soil physical and chemical properties: Current status and knowledge gaps [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2014, 29(1): 68−79. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2014.01-0068 [5] 杨宇, 李成蓉, 彭银, 等. 生物炭与有机肥施用对红壤理化性质及氮素径流损失的影响 [J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2023, (4):16−24. doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.22176YANG Y, LI C R, PENG Y, et al. Effects of biochar and organic fertilizer application on physical and chemical properties of red soil and nitrogen losses by runoff [J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2023(4): 16−24. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.22176 [6] 刘慧屿, 娄春荣, 韩英祚, 等. 秸秆生物炭与减量氮肥配施对玉米氮素利用率及土壤结构的影响 [J]. 土壤通报, 2020, 51(5):1180−1188.LIU H Y, LOU C R, HAN Y Z, et al. Impact of biochar addition combined with reduced nitrogen fertilizer on nitrogen use efficiency and soil structure in brown earth [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2020, 51(5): 1180−1188. (in Chinese) [7] 陈洪鹏, 于春晓, 王光美, 等. 生物炭和双氰胺对滨海盐碱土氮素转化及大豆氮素吸收利用的影响[J/OL]. 生态学杂志, 2023: 1-11. (2023-11-21). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1148.Q.20231120.1138.004.html.CHEN H P, YU C X, WANG G M, et al. Effects of biochar and dicyandiamide on nitrogen transformation and soybean nitrogen absorption and utilization in coastal saline-alkali soil[J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2023: 1-11. (2023-11-21). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1148.Q.20231120.1138.004.html.(in Chinese) [8] 李晨, 陈明婉, 金鑫, 等. 施入生物炭对热带农田土壤团聚体组成及碳氮含量的影响 [J]. 土壤通报, 2023, 54(5):1071−1079.LI C, CHEN M W, JIN X, et al. Effects of biochar application on soil aggregate composition and carbon and nitrogen contents in tropical farmland [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2023, 54(5): 1071−1079. (in Chinese) [9] 王凯, 刘勇, 赵蕊蕊, 等. 生物炭和有机肥对毛白杨人工林土壤氮矿化的影响 [J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2022, 50(10):61−68.WANG K, LIU Y, ZHAO R R, et al. Effects of biochar and organic fertilizer on soil nitrogen mineralization in Populus tomentosa plantation [J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2022, 50(10): 61−68. (in Chinese) [10] ZHOU H, FANG H, ZHANG Q, et al. Biochar enhances soil hydraulic function but not soil aggregation in a sandy loam [J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 2019, 70(2): 291−300. doi: 10.1111/ejss.12732 [11] 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000: 272-288. [12] 杨培岭, 罗远培, 石元春. 用粒径的重量分布表征的土壤分形特征 [J]. 科学通报, 1993, 38(20):1896−1899. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1993.20.010YANG P L, LUO Y P, SHI Y C. Fractal characteristics of soil characterized by weight distribution of particle size [J]. Cinese Science Bulletin, 1993, 38(20): 1896−1899. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1993.20.010 [13] SHENG M H, AI X Y, HUANG B C, et al. Effects of biochar additions on the mechanical stability of soil aggregates and their role in the dynamic renewal of aggregates in slope ecological restoration [J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 898: 165478. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.165478 [14] HAN L F, SUN K, JIN J, et al. Some concepts of soil organic carbon characteristics and mineral interaction from a review of literature [J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2016, 94: 107−121. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.11.023 [15] NICHOLS K A, HALVORSON J J. Roles of biology, chemistry, and physics in soil macroaggregate formation and stabilization [J]. The Open Agriculture Journal, 2013, 7(1): 107−117. doi: 10.2174/1874331520131011003 [16] LEHMANN J, KINYANGI J, SOLOMON D. Organic matter stabilization in soil microaggregates: Implications from spatial heterogeneity of organic carbon contents and carbon forms [J]. Biogeochemistry, 2007, 85(1): 45−57. doi: 10.1007/s10533-007-9105-3 [17] SPOKAS K, NOVAK J, VENTEREA R. Biochar’s role as an alternative N-fertilizer: Ammonia capture [J]. Plant and Soil, 2011, 350: 35−42. [18] 王静, 唐刚, 刘磊, 等. 土壤有机质含量对红壤性稻田残留氮在团聚体内分布的影响 [J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2022, (12):10−16. doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.21620WANG J, TANG G, LIU L, et al. Effects of soil organic matter content on the distribution of residual nitrogen in aggregates in a red paddy soil [J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2022(12): 10−16. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.21620 [19] 邵兴芳, 申小冉, 张建峰, 等. 外源氮在中、低肥力红壤中的转化与去向研究 [J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2014, (2):6−11. doi: 10.11838/sfsc.20140202SHAO X F, SHEN X R, ZHANG J F, et al. Exogenous nitrogen transformation and fate characteristics under different fertility red soils [J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2014(2): 6−11. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11838/sfsc.20140202 [20] 王清奎, 汪思龙. 土壤团聚体形成与稳定机制及影响因素 [J]. 土壤通报, 2005, 36(3):415−421. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2005.03.031WANG Q K, WANG S L. Forming and stable mechanism of soil aggregate and influencing factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2005, 36(3): 415−421. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2005.03.031 [21] 张彬, 赵天启, 贺启珅, 等. 放牧对短花针茅荒漠草原土壤团聚体组成及稳定性的影响 [J]. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(12):3263−3270.ZHANG B, ZHAO T Q, HE Q S, et al. Effects of grazing on soil aggregate composition and stability in Stipa breviflora desert steppe [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2022, 33(12): 3263−3270. (in Chinese) [22] 陈晓芬, 李忠佩, 刘明, 等. 不同施肥处理对红壤水稻土团聚体有机碳、氮分布和微生物生物量的影响 [J]. 中国农业科学, 2013, 46(5):950−960. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2013.05.010CHEN X F, LI Z P, LIU M, et al. Effects of different fertilizations on organic carbon and nitrogen contents in water-stable aggregates and microbial biomass content in paddy soil of subtropical China [J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2013, 46(5): 950−960. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2013.05.010 [23] 李天豪. 生物炭对煤矿复垦土壤团聚体稳定性、碳氮分布和微生物群落的影响[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2021.LI T H. Effects of biochar on soil aggregate stability, carbon and nitrogen distribution and microbial community in coal mine reclamation[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2021. (in Chinese) [24] 谭文峰, 许运, 史志华, 等. 胶结物质驱动的土壤团聚体形成过程与稳定机制 [J]. 土壤学报, 2023, 60(5):1297−1308. doi: 10.11766/trxb202308060312TAN W F, XU Y, SHI Z H, et al. The formation process and stabilization mechanism of soil aggregates driven by binding materials [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2023, 60(5): 1297−1308. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11766/trxb202308060312 [25] 李伟, 代镇, 张光鑫, 等. 生物炭和氮肥配施提高 土团聚体稳定性及作物产量 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2019, 25(5):782−791. doi: 10.11674/zwyf.18191LI W, DAI Z, ZHANG G X, et al. Combination of biochar and nitrogen fertilizer to improve soil aggregate stability and crop yield in Lou soil [J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2019, 25(5): 782−791. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11674/zwyf.18191 [26] 樊慧琳, 张佳敏, 李欢, 等. 典型稻田红壤发生层团聚体稳定性及有机碳的含量变化 [J]. 土壤通报, 2023, 54(5):1060−1070.FAN H L, ZHANG J M, LI H, et al. Soil aggregate stability and the variation in organic carbon content of pedogenic horizons in typical paddy red earth [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2023, 54(5): 1060−1070. (in Chinese) -







 下载:
下载: