Isolation and identification of a novel duck adenovirus B2 strain with insertion and deletion mutation characteristics
-
摘要:
目的 对一份疑似鸭腺病毒B2(Duck adenovirus B2, DAdV B2)感染的番鸭白肝病的病例进行确诊,并对分离株进行测序,为福建省DAdV B2流行病学研究提供参考。 方法 开展病料PCR检测,并进行病毒的分离鉴定、全基因二代测序,利用 MegAlign和SnapGene软件对测序结果进行同源性及遗传进化分析,再进行动物回归试验,确定对雏番鸭的致病性。 结果 病料样本检测为DAdV B2阳性,并成功分离到一株DAdV B2毒株,命名为DAdV B2/BG48。该分离株感染鸡肝癌细胞(LMH)细胞后细胞变大变圆、最后死亡崩解,形成特征性细胞病变;感染MDEF后细胞由长梭形变为圆形并聚集,细胞间出现空隙。测序结果表明,BG48基因组在pX基因区域中有3 bp的插入,在ORF19B基因区域有33 bp的插入,在ORF64和ORF67基因区域的交界处有42 bp的缺失,ORF67基因起始密码子往后第133位碱基为G,没有突变为终止密码子,其他编码基因与 CH-GD-12-2014、实验室之前鉴定的BG27和BG18无特征性差异。动物回归试验显示,2日龄的番鸭对DAdV B2分离株BG48易感,致病率为50%,死亡率为0%,发病鸭可见与自然感染病鸭相似的临床症状和病理变化。 结论 成功从番鸭白肝病病例中分离鉴定1 株DAdV B2突变株BG48,BG48具有多位点插入和缺失特征,提示DAdV B2毒株容易突变,临床流行毒株复杂。本结果为DAdV B2的分子流行病学调查和遗传进化研究提供了参考。 Abstract: :Objective In order to isolate duck adenovirus B2 (DAdV B2) strain from "Pale liver disease" and provide a reference for the DAdV B2 epidemiological study in Fujian Province. Methods The samples were detected by PCR, and the virus isolation was carried out and identified by the whole genome sequencing and ducklings challenge. Result A DAdV B2 strain, named DAdV B2/BG48, was successfully isolated from duckling pale liver disease. DAdV B2/BG48 infected LMH cells became large and round, and finally died and disintegrated. MDEF cells with with DAdV B2/BG48 inoculation became round and clustered together with intercellular space appeared. The results of next generation sequencing showed that BG48 genome had a 3 bp insertion in the pX gene region, a 33 bp insertion in the ORF19B gene domain, and 42 bp deletion at the junction of ORF64 and ORF67. There was no truncated mutation in the ORF67 gene. Other coding genes had no characteristic differences as compared to previously identified strains such as CH-GD-12-2014, BG27 and BG18. Duckling challenge experiments showed that the morbidity and mortality of BG48 to 2-day-old Muscovy ducks were 50% and 0%, respectively, and the clinical symptoms and pathological changes of diseased ducklings were similar to those of naturally infected ducks. Conclusion A novel DAdV B2 strain named BG48 was successfully isolated and identified from a case of "Pale liver disease" in Muscovy duck. BG48 has the characteristics of multi-site insertion and deletion, suggesting that DAdV B2 strain was prone to mutation with a complex clinical epidemic. These results provide a reference for the molecular epidemiological investigation and the genetic evolution of DAdV B2. -
Key words:
- White liver disease /
- Duck adenovirus B2 /
- Isolation and identification /
- Insertion and deletion /
- ORF67
-
图 2 BG48感染MDEF和LMH细胞的细胞病变
A:正常MDEF细胞(200×);B:BG48接种MDEF细胞4 d后的CPE(200×);C:正常LMH细胞(100×);D:BG48接种LMH细胞4 d后的CPE(100×)。
Figure 2. Cytopathic effect of BG 48 infected MDEF and LMH cells
A: normal MDEF cells (200×); B: CPE 4 days after MDEF cells (200×); C: normal LMH cells (100×); and D: BG 48 CPE 4 days after LMH cells (100×).
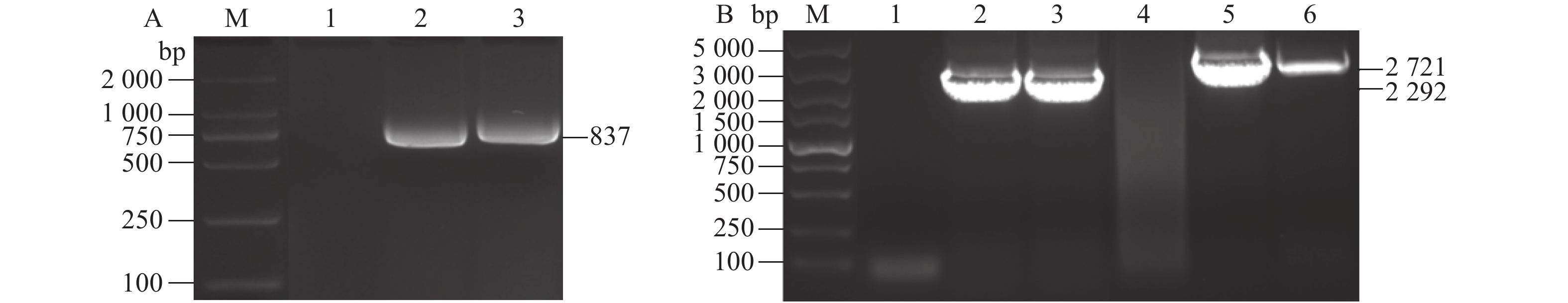
图 4 基因插入或缺失的PCR扩增验证
A:pX扩增产物琼脂糖凝胶电泳;M为DNA DL 2000 相对分子质量标准,1为阴性对照,2为阳性对照,3为BG48。B:ORF19B和ORF64/67扩增产物琼脂糖凝胶电泳;M为DNA DL 5000 相对分子质量标准,1~3为ORF19B引物扩增,1为阴性对照,2为阳性对照,3为BG48 ,4~6为ORF64/67引物扩增,4为阴性对照,5为阳性对照,6为BG48。
Figure 4. PCR amplification verification of gene insertion or deletion by PCR amplifications
A: pX amplification; M: DNA DL 2000 marker; 1: Negative control; 2: Positive control; 3: BG 48. B: ORF19B and ORF64/67 amplification; 1–3 is the PCR amplification results of ORF19B primer. M: DNA DL 5000 marker 1: Negative Control; 2: Positive Control; 3: BG48; 4–6 is the PCR amplification results of ORF64/67 primer 4: Negative Control; 5: Positive Control; 6: BG 48.
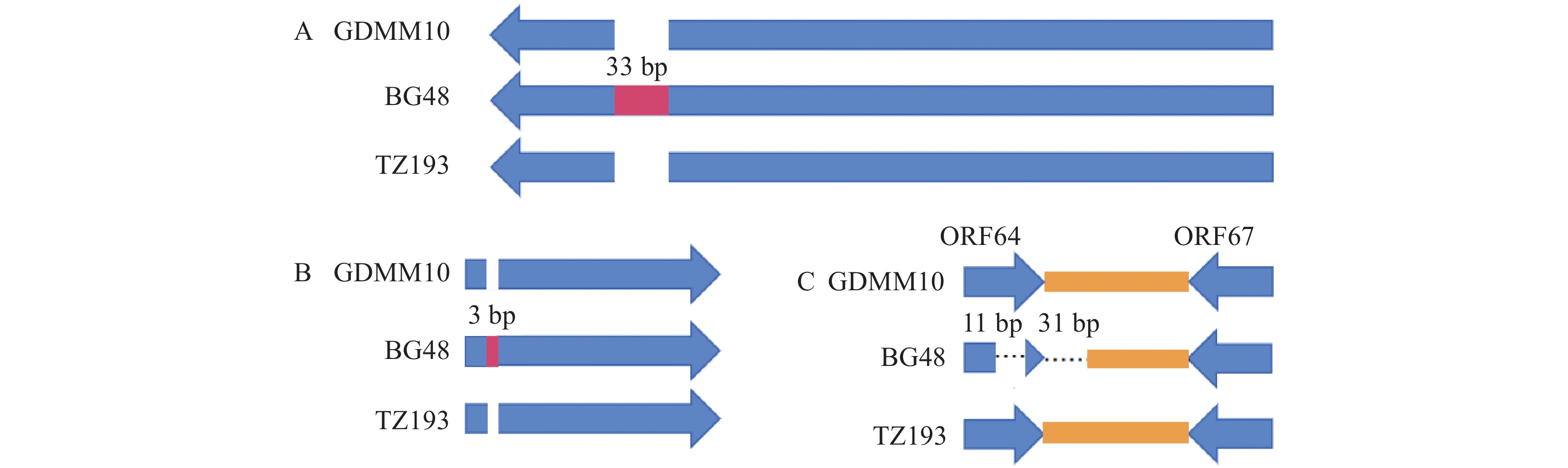
图 5 BG48基因组基因插入与缺失
A:ORF19B; B:pX; C:ORF64和ORF67及其之间非编码区(蓝色箭头代表ORFs;橙色四边形代表非编码区;虚线代表缺失区域;红色代表插入区域)。
Figure 5. Map of gene insertions and deletions in the BG48 genome
A: ORF19B; B: pX;C: Coding and non-coding regions between ORF 64 and ORF 67 (Blue arrows representing ORFs; orange quadrangle representing non-coding regions; dashed lines representing the delected region; red representing the inserted region).
表 1 引物序列
Table 1. Primer sequences
引物名称
Primer names引物序列(5′- 3')
Primer sequences(5′-3')退火温度
Annealing temperature/℃扩增长度
Product length/bpDAdV B2 fiber 1-F TATCCCTACTGGTGGCCCTC 59.9 581 DAdV B2 fiber 1-R TCAGTGGCTGCGTACACTTT ORF67-F ATGTACGCAATTCCATTCTCA 49.8 174 ORF67-R GTTACAAATTAACTTTTGAA pX-F ACATCCTCATCACCAACCAT 52.3 837 pX-R TCCAGCTGCAAGATCTATGT ORF64/67-F CTTAGGACTCCAAACCCAAATAGAT 56.8 2721 ORF64/67-R TGCCATGCGCTACGCTAAG ORF19B-F ACAGGCTCCATGAGCTCTCAC 58.5 2292 ORF19B-R TTGAGCCAGAGTCCGTAAAGC -
[1] 陈仕龙, 俞博, 肖世峰, 等. 鸭2型腺病毒感染导致番鸭“肝白化病” 的研究 [J]. 福建农业科技, 2017, (8):1−3.CHEN S L, YU B, XIAO S F, et al. Primary study on duck adenovirus 2 infection resulted in Muscovy ducklings' pale liver disease [J]. Fujian Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017(8): 1−3. (in Chinese) [2] SHI X J, ZHANG X Y, SUN H W, et al. Isolation and pathogenic characterization of duck adenovirus 3 mutant circulating in China [J]. Poultry Science, 2022, 101(1): 101564. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2021.101564 [3] BOUQUET J F, MOREAU Y, MCFERRAN J B, et al. Isolation and characterisation of an adenovirus isolated from Muscovy ducks [J]. Avian Pathology:Journal of the W V P A, 1982, 11(2): 301−307. doi: 10.1080/03079458208436102 [4] MAREK A, KAJÁN G L, KOSIOL C, et al. Complete genome sequences of pigeon adenovirus 1 and duck adenovirus 2 extend the number of species within the genus Aviadenovirus [J]. Virology, 2014, 462/463: 107−114. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2014.04.033 [5] ZHANG X H, ZHONG Y J, ZHOU Z H, et al. Molecular characterization, phylogeny analysis and pathogenicity of a Muscovy duck adenovirus strain isolated in China in 2014 [J]. Virology, 2016, 493: 12−21. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2016.03.004 [6] CHEN S L, LIN F Q, JIANG B, et al. Isolation and characterization of a novel strain of duck aviadenovirus B from Muscovy ducklings with acute hepatitis in China [J]. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases, 2022, 69(5): 2769−2778. doi: 10.1111/tbed.14428 [7] YIN L J, ZHOU Q, MAI K J, et al. Epidemiological investigation of duck adenovirus 3 in Southern China, during 2018-2020 [J]. Avian Pathology:Journal of the W V P A, 2022, 51(2): 171−180. doi: 10.1080/03079457.2022.2034737 [8] CHU L L, YE S Q, WANG J Y, et al. An insertion and deletion mutant of adenovirus in Muscovy ducks [J]. Archives of Virology, 2022, 167(9): 1879−1883. doi: 10.1007/s00705-022-05474-y [9] 徐彬. 鸭腺病毒3型(DAdV-3)对鸡致病特性的鉴定[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2023.XU B. Identification of pathogenic properties of duck adenovirus type 3(DAdV-3)in chickens[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2023. (in Chinese) [10] 江丹丹, 林昶, 黄志坚, 等. 鸭腺病毒B血清1型和血清2型双重PCR检测方法的建立及应用 [J]. 中国预防兽医学报, 2022, 44(8):855−860.JIANG D D, LIN C, HUANG Z J, et al. Establishment and application of duplex PCR assay for detection of duck adenovirus B serotype 1 and serotype 2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 2022, 44(8): 855−860. (in Chinese) [11] ROWE W P, HUEBNER R J, GILMORE L K, et al. Isolation of a cytopathogenic agent from human adenoids undergoing spontaneous degeneration in tissue culture [J]. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine, 1953, 84(3): 570−573. doi: 10.3181/00379727-84-20714 [12] 赵蕾, 史爱华, 李林, 等. Ⅰ群4型禽腺病毒DC株在LMH细胞的增殖工艺研究 [J]. 中国家禽, 2018, 40(20):18−22.ZHAO L, SHI A H, LI L, et al. Proliferation of group Ⅰ fowl adenovirus serotype 4 DC strain in LMH cells [J]. China Poultry, 2018, 40(20): 18−22. (in Chinese) [13] ANDERSON C W, YOUNG M E, FLINT S J. Characterization of the adenovirus 2 virion protein, mu [J]. Virology, 1989, 172(2): 506−512. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90193-1 [14] LEE T W R, LAWRENCE F J, DAUKSAITE V, et al. Precursor of human adenovirus core polypeptide Mu targets the nucleolus and modulates the expression of E2 proteins[J]. The Journal of General Virology, 2004, 85(Pt 1): 185-196. [15] ZHAO M L, DUAN X Y, WANG Y Q, et al. A novel role for PX, a structural protein of fowl adenovirus serotype 4 (FAdV4), as an apoptosis-inducer in leghorn male hepatocellular cell [J]. Viruses, 2020, 12(2): 228. doi: 10.3390/v12020228 [16] 李小凤, 韦悠, 罗思思, 等. X蛋白(pX)在血清4型禽腺病毒感染LMH细胞后对Toll样受体的影响 [J]. 西南农业学报, 2023, 36(12):2814−2821.LI X F, WEI Y, LUO S S, et al. Effect of X protein (pX) on Toll-like receptors after LMH cell infection with fowl adenovirus serotype 4 [J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 36(12): 2814−2821. (in Chinese) [17] PEI Y L, CORREDOR J C, KRELL P J, et al. Fowl adenovirus 9 ORF19, a lipase homolog, is nonessential for virus replication and is suitable for foreign gene expression [J]. Virus Research, 2019, 260: 129−134. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2018.12.001 -







 下载:
下载: